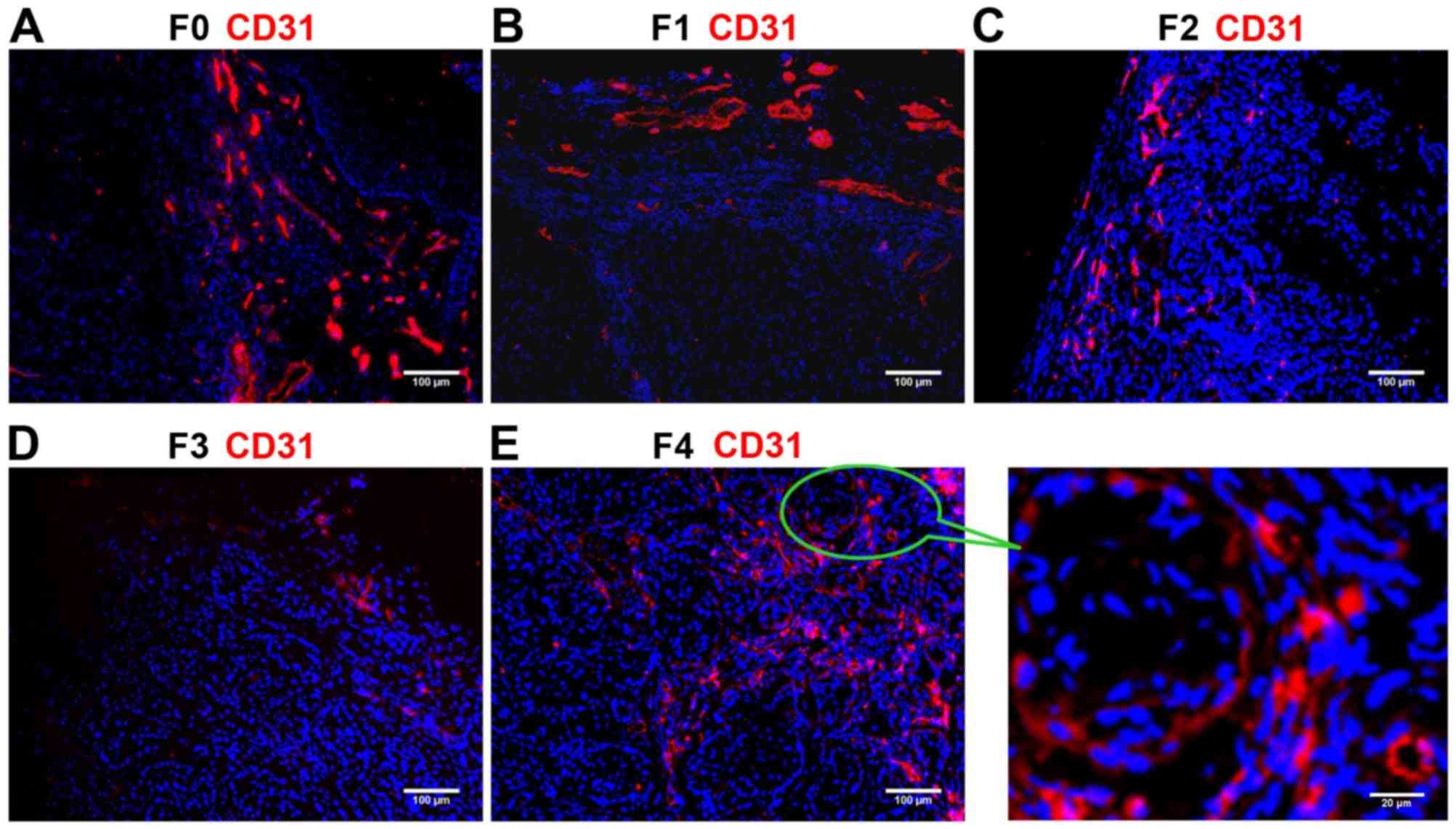
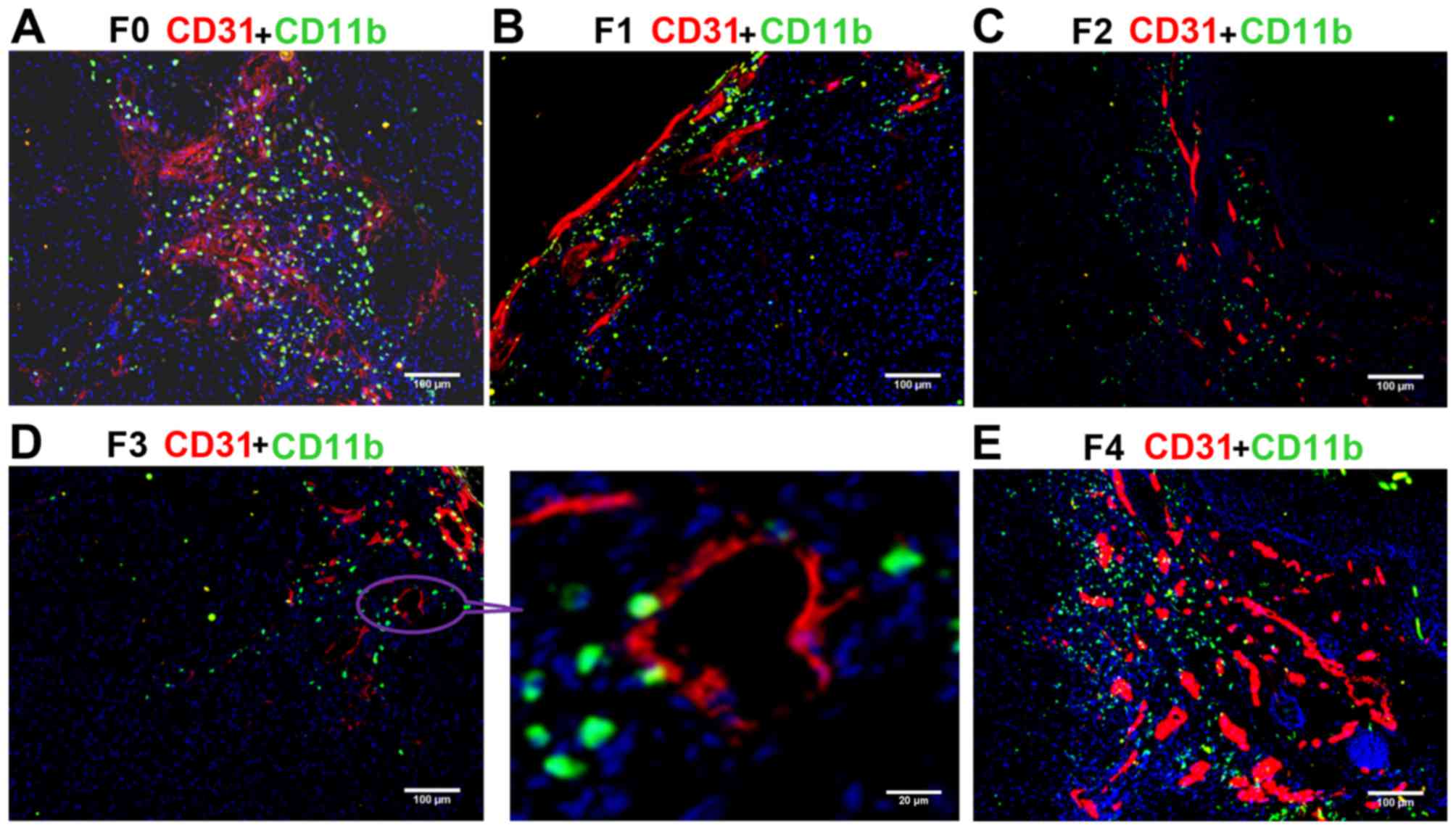
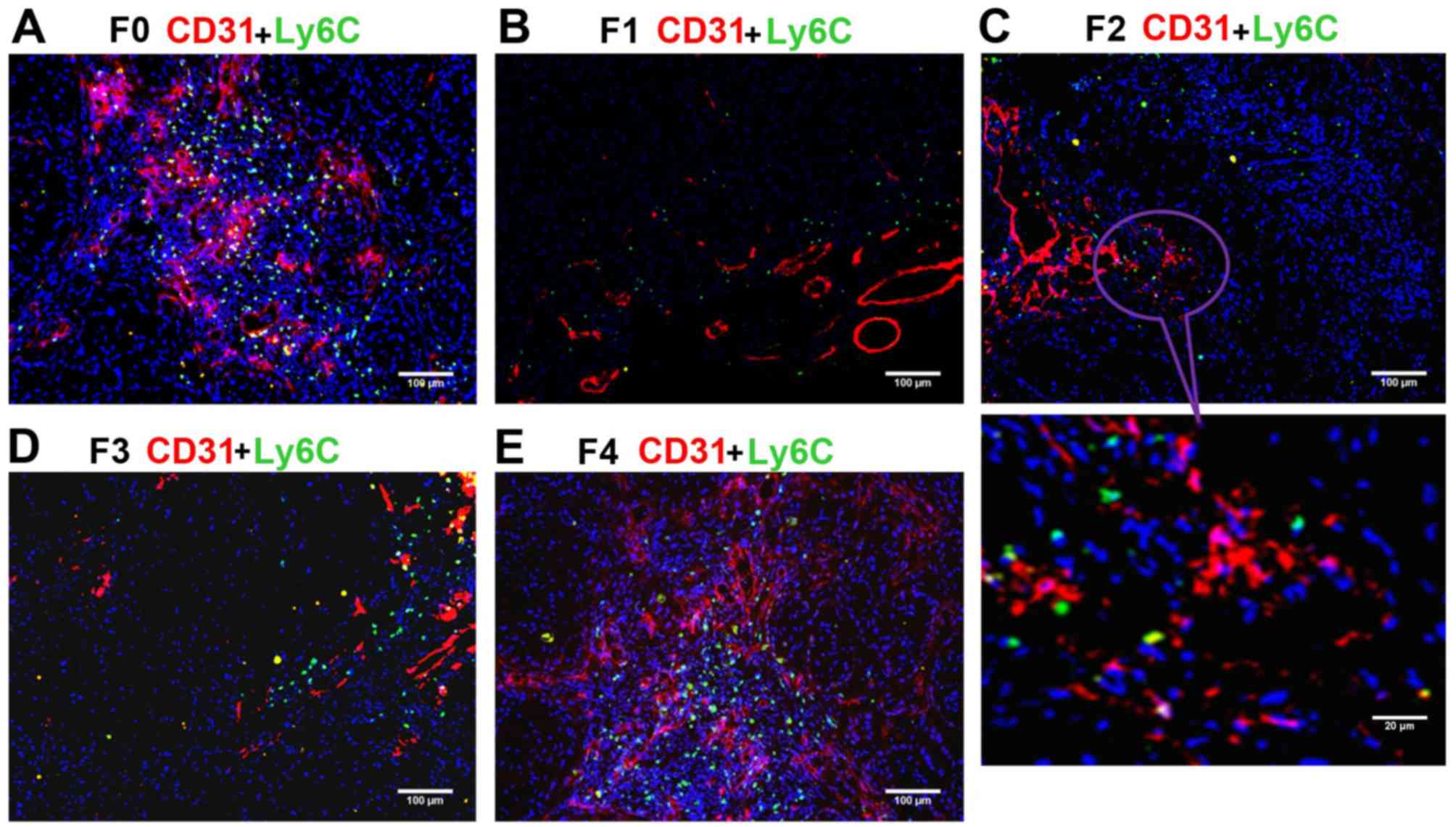
|
1
|
Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, Harewood
R, Spika D, Wang XS, Bannon F, Ahn JV, Johnson CJ, Bonaventure A,
et al: Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis
of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279
population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet.
385:977–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stinchcombe TE and Socinski MA: Current
treatments for advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am
Thorac Soc. 6:pp. 233–241. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morgensztern D, Waqar S, Subramanian J,
Gao F and Govindan R: Improving survival for stage IV non-small
cell lung cancer: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results
survey from 1990 to 2005. J Thorac Oncol. 4:1524–1529. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zetter BR: Angiogenesis and tumor
metastasis. Annu Rev Med. 49:407–424. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weidner N: Intratumor microvessel density
as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol. 147:9–19.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dvorak HF, Sioussat TM, Brown LF, Berse B,
Nagy JA, Sotrel A, Manseau EJ, Van de Water L and Senger DR:
Distribution of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial
growth factor) in tumors: Concentration in tumor blood vessels. J
Exp Med. 174:1275–1278. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett
N, Phillips HS and Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in
vivo. Nature. 362:841–844. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Toi M, Matsumoto T and Bando H: Vascular
endothelial growth factor: Its prognostic, predictive, and
therapeutic implications. Lancet Oncol. 2:667–673. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor as a target for anticancer therapy. Oncologist. 9 Suppl
1:S2–S10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hu P, Liu W, Wang L, Yang M and Du J: High
circulating VEGF level predicts poor overall survival in lung
cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:1157–1167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen P, Zhu J, Liu DY, Li HY, Xu N and Hou
M: Over-expression of survivin and VEGF in small-cell lung cancer
may predict the poorer prognosis. Med Oncol. 31:7752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J, Tang D, Wang S, Li QG, Zhang JR,
Li P, Lu Q, Niu G, Gao J, Ye NY and Wang DR: High expressions of
galectin-1 and VEGF are associated with poor prognosis in gastric
cancer patients. Tumor Biol. 35:2513–2519. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piperdi B, Merla A and Perez-Soler R:
Targeting angiogenesis in squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
Drugs. 74:403–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pallis AG and Syrigos KN: Targeting tumor
neovasculature in non-small-cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 86:130–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Liu X, Zhu Y, Lu S,
Feng J, He J, Han B, Wang J, et al: BEYOND: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, phase III study of
first-line carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or placebo in
Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent nonsquamous
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:2197–2204. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tejpar S, Prenen H and Mazzone M:
Overcoming resistance to antiangiogenic therapies. Oncologist.
17:1039–1050. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sica A and Bronte V: Altered macrophage
differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. J Clin
Invest. 117:1155–1166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kusmartsev S and Gabrilovich DI: Role of
immature myeloid cells in mechanisms of immune evasion in cancer.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 55:237–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D and Sotomayor
EM: Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 25:267–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Talmadge JE: Pathways mediating the
expansion and immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and their relevance to cancer therapy. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:5243–5248. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen
J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP and Gabrilovich DI: Increased
production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: A
mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol. 166:678–689.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Young MR and Lathers DM: Myeloid
progenitor cells mediate immune suppression in patients with head
and neck cancers. Int J Immunopharmacol. 21:241–252. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ebos JM, Lee CR and Kerbel RS: Tumor and
host-mediated pathways of resistance and disease progression in
response to antiangiogenic therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5020–5025.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kioi M, Vogel H, Schultz G, Hoffman RM,
Harsh GR and Brown JM: Inhibition of vasculogenesis, but not
angiogenesis, prevents the recurrence of glioblastoma after
irradiation in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:694–705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil
A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC and Moses
HL: Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits
Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell.
13:23–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan DA, Kawahara TL, Sutphin PD, Chang
HY, Chi JT and Giaccia AJ: Tumor vasculature is regulated by
PHD2-mediated angiogenesis and bone marrow-derived cell
recruitment. Cancer Cell. 15:527–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C,
Baldwin ME, Schanz S, Fuh G, Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Tumor
refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+
myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol. 25:911–920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang L, DeBusk LM, Fukuda K, Fingleton B,
Green-Jarvis B, Shyr Y, Matrisian LM, Carbone DP and Lin PC:
Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr+CD11b+ cells in
tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer
Cell. 6:409–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Zhong C, Yu L, Liang XH,
Yao J, Blanchard D, Bais C, Peale FV, van Bruggen N, et al: Bv8
regulates myeloid-cell-dependent tumour angiogenesis. Nature.
450:825–831. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Youn JI, Nagaraj S, Collazo M and
Gabrilovich DI: Subsets of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 181:5791–5802. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sawanobori Y, Ueha S, Kurachi M, Shimaoka
T, Talmadge JE, Abe J, Shono Y, Kitabatake M, Kakimi K, Mukaida N
and Matsushima K: Chemokine-mediated rapid turnover of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Blood.
111:5457–5466. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dietlin TA, Hofman FM, Lund BT, Gilmore W,
Stohlman SA and van der Veen RC: Mycobacteria-induced Gr-1+ subsets
from distinct myeloid lineages have opposite effects on T cell
expansion. J Leukoc Biol. 81:1205–1212. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Movahedi K, Guilliams M, Van den Bossche
J, Van den Bergh R, Gysemans C, Beschin A, De Baetselier P and Van
Ginderachter JA: Identification of discrete tumor-induced
myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T
cell-suppressive activity. Blood. 111:4233–4244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Avraham-Davidi I, Yona S, Grunewald M,
Landsman L, Cochain C, Silvestre JS, Mizrahi H, Faroja M,
Strauss-Ayali D, Mack M, et al: On-site education of VEGF-recruited
monocytes improves their performance as angiogenic and arteriogenic
accessory cells. J Exp Med. 210:2611–2625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gordon S and Taylor PR: Monocyte and
macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:953–964. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB and Lewis
CE: The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour
angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:618–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Comito G, Giannoni E, Segura CP,
Barcellos-de-Souza P, Raspollini MR, Baroni G, Lanciotti M, Serni S
and Chiarugi P: Cancer-associated fibroblasts and M2-polarized
macrophages synergize during prostate carcinoma progression.
Oncogene. 33:2423–2431. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Denney L, Kok WL, Cole SL, Sanderson S,
McMichael AJ and Ho LP: Activation of invariant NKT cells in early
phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis results in
differentiation of Ly6Chi inflammatory monocyte to M2 macrophages
and improved outcome. J Immunol. 189:551–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chu HX, Broughton BR, Kim HA, Lee S,
Drummond GR and Sobey CG: Evidence that Ly6C(hi) monocytes are
protective in acute ischemic stroke by promoting M2 macrophage
polarization. Stroke. 46:1929–1937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jalali S, Chung C, Foltz W, Burrell K,
Singh S, Hill R and Zadeh G: MRI biomarkers identify the
differential response of glioblastoma multiforme to anti-angiogenic
therapy. Neuro Oncol. 16:868–879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ahn GO, Tseng D, Liao CH, Dorie MJ,
Czechowicz A and Brown JM: Inhibition of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18)
enhances tumor response to radiation by reducing myeloid cell
recruitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 8363–8368. 2010;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hong S, Tan M, Wang S, Luo S, Chen Y and
Zhang L: Efficacy and safety of angiogenesis inhibitors in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:909–921. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Blakely C and Jahan T: Emerging
antiangiogenic therapies for non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 11:1607–1618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Giuliano S and Pagès G: Mechanisms of
resistance to anti-angiogenesis therapies. Biochimie. 95:1110–1119.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sitohy B, Nagy JA and Dvorak HF:
Anti-VEGF/VEGFR therapy for cancer: Reassessing the target. Cancer
Res. 72:1909–1914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wood SL, Pernemalm M, Crosbie PA and
Whetton AD: The role of the tumor-microenvironment in lung
cancer-metastasis and its relationship to potential therapeutic
targets. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:558–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saintigny P and Burger JA: Recent advances
in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management.
Discov Med. 13:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gyanchandani R, Alves MV Ortega, Myers JN
and Kim S: A proangiogenic signature is revealed in FGF-mediated
bevacizumab-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol
Cancer Res. 11:1585–1596. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Curtarello M, Zulato E, Nardo G, Valtorta
S, Guzzo G, Rossi E, Esposito G, Msaki A, Pastò A, Rasola A, et al:
VEGF-targeted therapy stably modulates the glycolytic phenotype of
tumor cells. Cancer Res. 75:120–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mira E, Carmona-Rodríguez L, Tardáguila M,
Azcoitia I, González-Martín A, Almonacid L, Casas J, Fabriás G and
Mañes S: A lovastatin-elicited genetic program inhibits M2
macrophage polarization and enhances T cell infiltration into
spontaneous mouse mammary tumors. Oncotarget. 4:2288–2301. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK, Aikawa E,
Stangenberg L, Wurdinger T, Figueiredo JL, Libby P, Weissleder R
and Pittet MJ: The healing myocardium sequentially mobilizes two
monocyte subsets with divergent and complementary functions. J Exp
Med. 204:3037–3047. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Arnold L, Henry A, Poron F, Baba-Amer Y,
van Rooijen N, Plonquet A, Gherardi RK and Chazaud B: Inflammatory
monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into
antiinflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis. J Exp Med.
204:1057–1069. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G,
Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G and
Geissmann F: Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a
population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science.
317:666–670. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Anzai A, Anzai T, Nagai S, Maekawa Y,
Naito K, Kaneko H, Sugano Y, Takahashi T, Abe H, Mochizuki S, et
al: Regulatory role of dendritic cells in postinfarction healing
and left ventricular remodeling. Circulation. 125:1234–1245. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Varol C, Landsman L, Fogg DK, Greenshtein
L, Gildor B, Margalit R, Kalchenko V, Geissmann F and Jung S:
Monocytes give rise to mucosal, but not splenic, conventional
dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 204:171–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ancuta P, Liu KY, Misra V, Wacleche VS,
Gosselin A, Zhou X and Gabuzda D: Transcriptional profiling reveals
developmental relationship and distinct biological functions of
CD16+ and CD16- monocyte subsets. BMC Genomics. 10:4032009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hettinger J, Richards DM, Hansson J, Barra
MM, Joschko AC, Krijgsveld J and Feuerer M: Origin of monocytes and
macrophages in a committed progenitor. Nat Immunol. 14:821–830.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
McDonnell CO, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Toomey D,
Foley D, Kay EW, Leen E and Walsh TN: Effect of neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy on angiogenesis in oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg.
90:1373–1378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ahn GO and Brown JM: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 is required for tumor vasculogenesis but not
for angiogenesis: Role of bone marrow-derived myelomonocytic cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:193–205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|