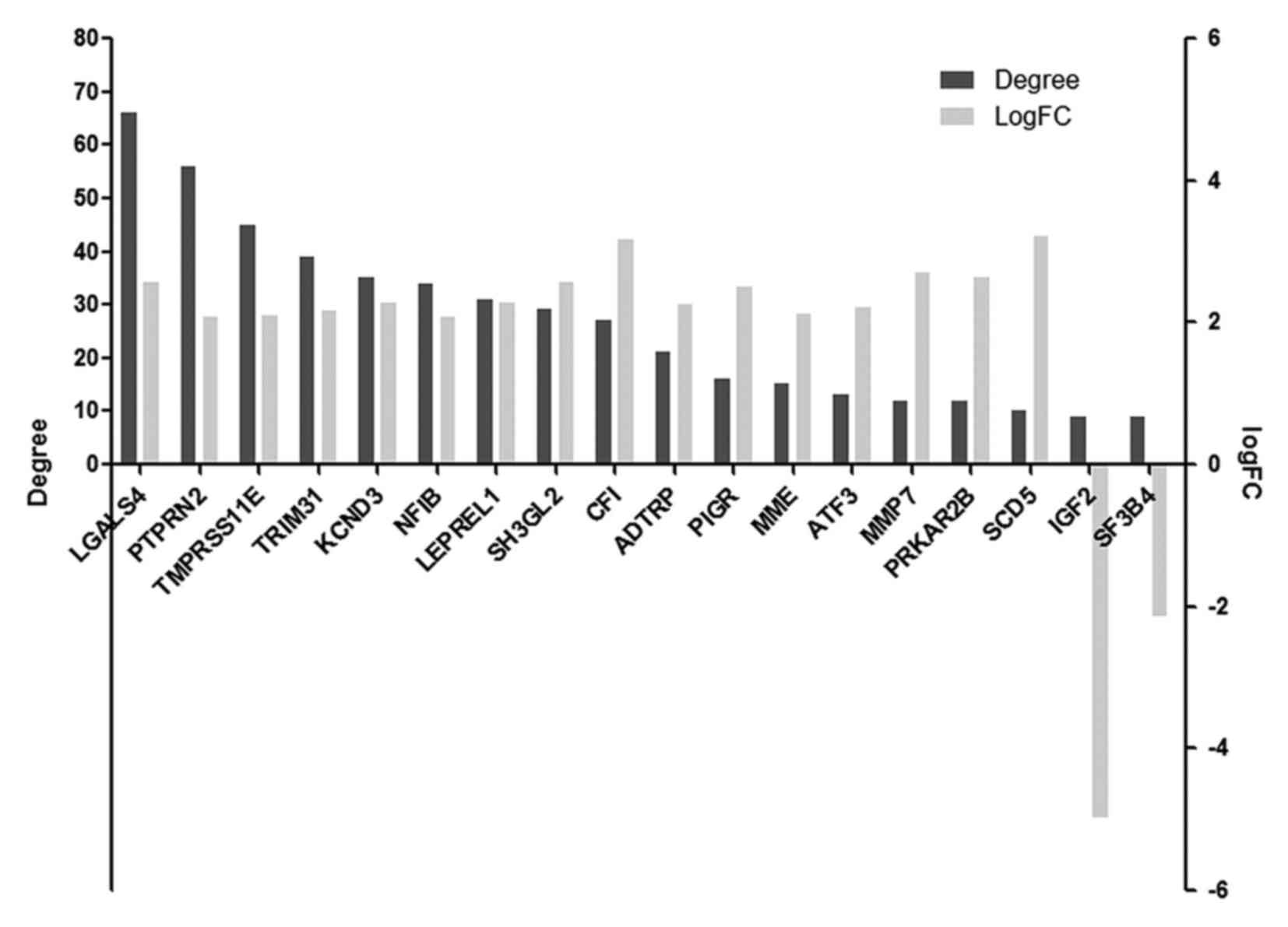
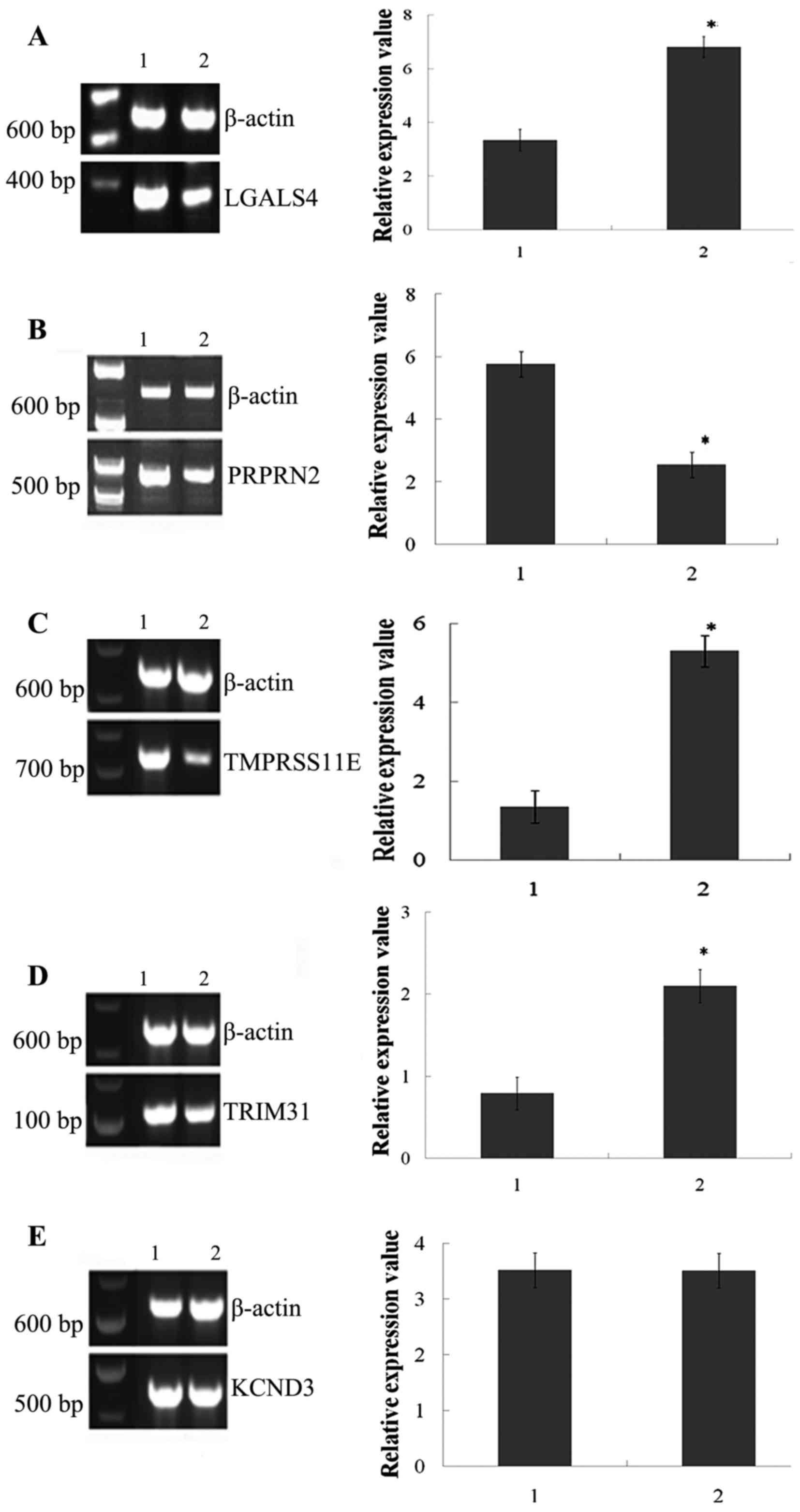
|
1
|
Rubio G, García-Mora B, Santamaria C and
Pontones JL: A flowgraph model for bladder carcinoma. Theor Biol
Med Model. 11 Suppl 1:S32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen WQ, Zeng HM, Zheng RS, Zhang SW and
He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2007. Chin J Cancer
Res. 24:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharma S, Ksheersagar P and Sharma P:
Diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. Am Fam Physician.
80:717–723. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman
HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, Kassouf W, Kiemeney LA, La Vecchia C,
Shariat S and Lotan Y: Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 63:234–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wyszynski A, Tanyos SA, Rees JR, Marsit
CJ, Kelsey KT, Schned AR, Pendleton EM, Celaya MO, Zens MS, Karagas
MR and Andrew AS: Body mass and smoking are modifiable risk factors
for recurrent bladder cancer. Cancer. 120:408–414. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Letašiová S, Medve'ová A, Šovčíková A,
Dušinská M, Volkovová K, Mosoiu C and Bartonová A: Bladder cancer,
a review of the environmental risk factors. Environ Health. 11
Suppl 1:S112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xue Y, Wu G, Wang X, Zou X, Zhang G, Xiao
R, Yuan Y, Long D, Yang J, Wu Y, et al: CIP2A is a predictor of
survival and a novel therapeutic target in bladder urothelial cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:4062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tabata K, Matsumoto K, Minami S, Ishii D,
Nishi M, Fujita T, Saegusa M, Sato Y and Iwamura M: Nestin is an
independent predictor of cancer-specific survival after radical
cystectomy in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder.
PLoS One. 9:e915482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan Y, Yang FQ, Zhang HM, Li J, Li W, Wang
GC, Che JP, Zheng JH and Liu M: Bromodomain 4 protein is a
predictor of survival for urothelial carcinoma of bladder. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4231–4238. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dyrskjøt L, Kruhøffer M, Thykjaer T,
Marcussen N, Jensen JL, Møller K and Ørntoft TF: Gene expression in
the urinary bladder: A common carcinoma in situ gene expression
signature exists disregarding histopathological classification.
Cancer Res. 64:4040–4048. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Biton A, Bernard-Pierrot I, Lou Y, Krucker
C, Chapeaublanc E, Rubio-Pérez C, López-Bigas N, Kamoun A,
Neuzillet Y, Gestraud P, et al: Independent component analysis
uncovers the landscape of the bladder tumor transcriptome and
reveals insights into luminal and basal subtypes. Cell Rep.
9:1235–1245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nayak RR, Kearns M, Spielman RS and Cheung
VG: Coexpression network based on natural variation in human gene
expression reveals gene interactions and functions. Genome Res.
19:1953–1962. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Voineagu I, Wang X, Johnston P, Lowe JK,
Tian Y, Horvath S, Mill J, Cantor RM, Blencowe BJ and Geschwind DH:
Transcriptomic analysis of autistic brain reveals convergent
molecular pathology. Nature. 474:380–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kristensen VN, Lingjærde OC, Russnes HG,
Vollan HK, Frigessi A and Børresen-Dale AL: Principles and methods
of integrative genomic analyses in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
14:299–313. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma L, Robinson LN and Towle HC: ChREBP*Mlx
is the principal mediator of glucose-induced gene expression in the
liver. J Biol Chem. 281:28721–28730. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rifai N and Ridker PM: Proposed
cardiovascular risk assessment algorithm using high-sensitivity
C-reactive protein and lipid screening. Clin Chem. 47:28–30.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pepper SD, Saunders EK, Edwards LE, Wilson
CL and Miller CJ: The utility of MAS5 expression summary and
detection call algorithms. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:2732007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sims AH, Smethurst GJ, Hey Y, Okoniewski
MJ, Pepper SD, Howell A, Miller CJ and Clarke RB: The removal of
multiplicative, systematic bias allows integration of breast cancer
gene expression datasets - improving meta-analysis and prediction
of prognosis. BMC Med Genomics. 1:422008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taminau J, Taminau MJ, Meganck S and
BiocGenerics S: Package ‘inSilicoMerging’. 2013.https://bioc.ism.ac.jp/packages/3.1/bioc/html/inSilicoMerging.htmlFeb
06–2015
|
|
21
|
Smyth G, Thorne N and Wettenhall J: LIMMA:
Linear Models for Microarray Data User's Guide. 2003.http://www.
bioconductor.org2005Feb 08–2015
|
|
22
|
Datta S, Satten GA, Benos DJ, Xia J,
Heslin MJ and Datta S: An empirical bayes adjustment to increase
the sensitivity of detecting differentially expressed genes in
microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 20:235–242. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reiner A, Yekutieli D and Benjamini Y:
Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery
rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics. 19:368–375. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang J, Yu H, Liu BH, Zhao Z, Liu L, Ma
LX, Li YX and Li YY: DCGL v2. 0: An R package for unveiling
differential regulation from differential co-expression. PLoS One.
8:e797292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu H, Liu BH, Ye ZQ, Li C, Li YX and Li
YY: Link-based quantitative methods to identify differentially
coexpressed genes and gene pairs. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:3152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu BH, Yu H, Tu K, Li C, Li YX and Li YY:
DCGL: An R package for identifying differentially coexpressed genes
and links from gene expression microarray data. Bioinformatics.
26:2637–2638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scardoni G and Laudanna C: Centralities
based analysis of complex networksNew Frontiers in Graph Theory.
ISBN, 978-953-51-0115-4. INTECH Open Access Publisher; 2012,
http://www.intechopen.com/books/new-frontiers-in-graph-theory/centralities-based-analysis-of-networks
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zotenko E, Mestre J, O'Leary DP and
Przytycka TM: Why do hubs in the yeast protein interaction network
tend to be essential: Reexamining the connection between the
network topology and essentiality. PLoS Comput Biol.
4:e10001402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koschützki D and Schreiber F: Centrality
analysis methods for biological networks and their application to
gene regulatory networks. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2:193–201.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hosack DA, Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Lane
HC and Lempicki RA: Identifying biological themes within lists of
genes with EASE. Genome Biol. 4:R702003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoon H and Liu RH: Effect of 2
alpha-hydroxyursolic acid on NF-kappaB activation induced by
TNF-alpha in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Agric Food Chem.
56:8412–8417. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC, De Santis
M, Gakis G, Lebret T, Ribal MJ, Van der Heijden AG and Sherif A:
European Association of Urology: EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive
and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur
Urol. 65:778–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tripodi D, Quéméner S, Renaudin K, Ferron
C, Malard O, Guisle-Marsollier I, Sébille-Rivain V, Verger C,
Géraut C and Gratas-Rabbia-Ré C: Gene expression profiling in
sinonasal adenocarcinoma. BMC Med Genomics. 2:652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Selamat SA, Chung BS, Girard L, Zhang W,
Zhang Y, Campan M, Siegmund KD, Koss MN, Hagen JA, Lam WL, et al:
Genome-scale analysis of DNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma and
integration with mRNA expression. Genome Res. 22:1197–1211. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miwa HE, Koba WR, Fine EJ, Giricz O, Kenny
PA and Stanley P: Bisected, complex N-glycans and galectins in
mouse mammary tumor progression and human breast cancer.
Glycobiology. 23:1477–1490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu Y, Liu P, Wen W, Grubbs CJ, Townsend
RR, Malone JP, Lubet RA and You M: Cross-species comparison of
orthologous gene expression in human bladder cancer and
carcinogen-induced rodent models. Am J Transl Res. 3:8–27.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM proteins and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:792–804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dokmanovic M, Chang BD, Fang J and
Roninson IB: Retinoid-induced growth arrest of breast carcinoma
cells involves co-activation of multiple growth-inhibitory genes.
Cancer Biol Ther. 1:24–27. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sugiura T and Miyamoto K: Characterization
of TRIM31, upregulated in gastric adenocarcinoma, as a novel RBCC
protein. J Cell Biochem. 105:1081–1091. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Bai X, Peng Y and
He P: TRIM31 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and
serves as a potential tumor suppressor. Tumour Biol. 35:5747–5752.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nurse P: A long twentieth century of the
cell cycle and beyond. Cell. 100:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Peng ZG, Yao YB, Yang J, Tang YL and Huang
X: Mangiferin induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase through
ATR-Chk1 pathway in HL-60 leukemia cells. Genet Mol Res.
14:4989–5002. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Andries V, Vandepoele K, Staes K, Berx G,
Bogaert P, van Isterdael G, Ginneberge D, Parthoens E,
Vandenbussche J, Gevaert K and van Roy F: NBPF1, a tumor suppressor
candidate in neuroblastoma, exerts growth inhibitory effects by
inducing a G1 cell cycle arrest. BMC Cancer. 15:3912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li N, Sun M, Wang Y, Lv Y, Hu Z, Cao W,
Zheng J and Jiao X: Effect of cell cycle phase on the sensitivity
of SAS cells to sonodynamic therapy using low-intensity ultrasound
combined with 5-aminolevulinic acid in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
12:3177–3183. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
de Stanchina E, McCurrach ME, Zindy F,
Shieh SY, Ferbeyre G, Samuelson AV, Prives C, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ
and Lowe SW: E1A signaling to p53 involves the p19ARFtumor
suppressor. Genes Dev. 12:2434–2442. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chakraborty A, Uechi T and Kenmochi N:
Guarding the ‘translation apparatus’: Defective ribosome biogenesis
and the p53 signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
2:507–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Stegh AH: Targeting the p53 signaling
pathway in cancer therapy - the promises, challenges and perils.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:67–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|