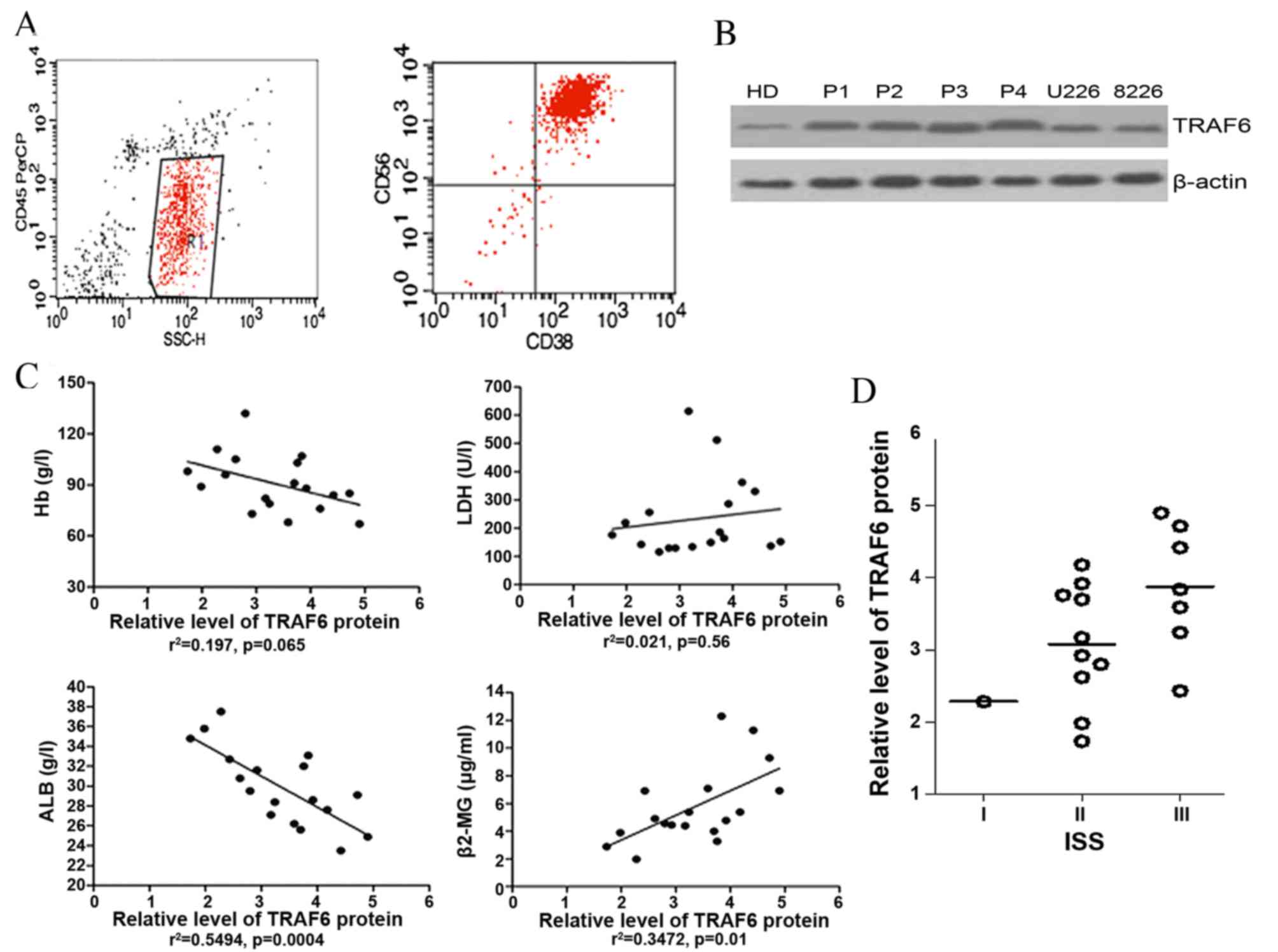
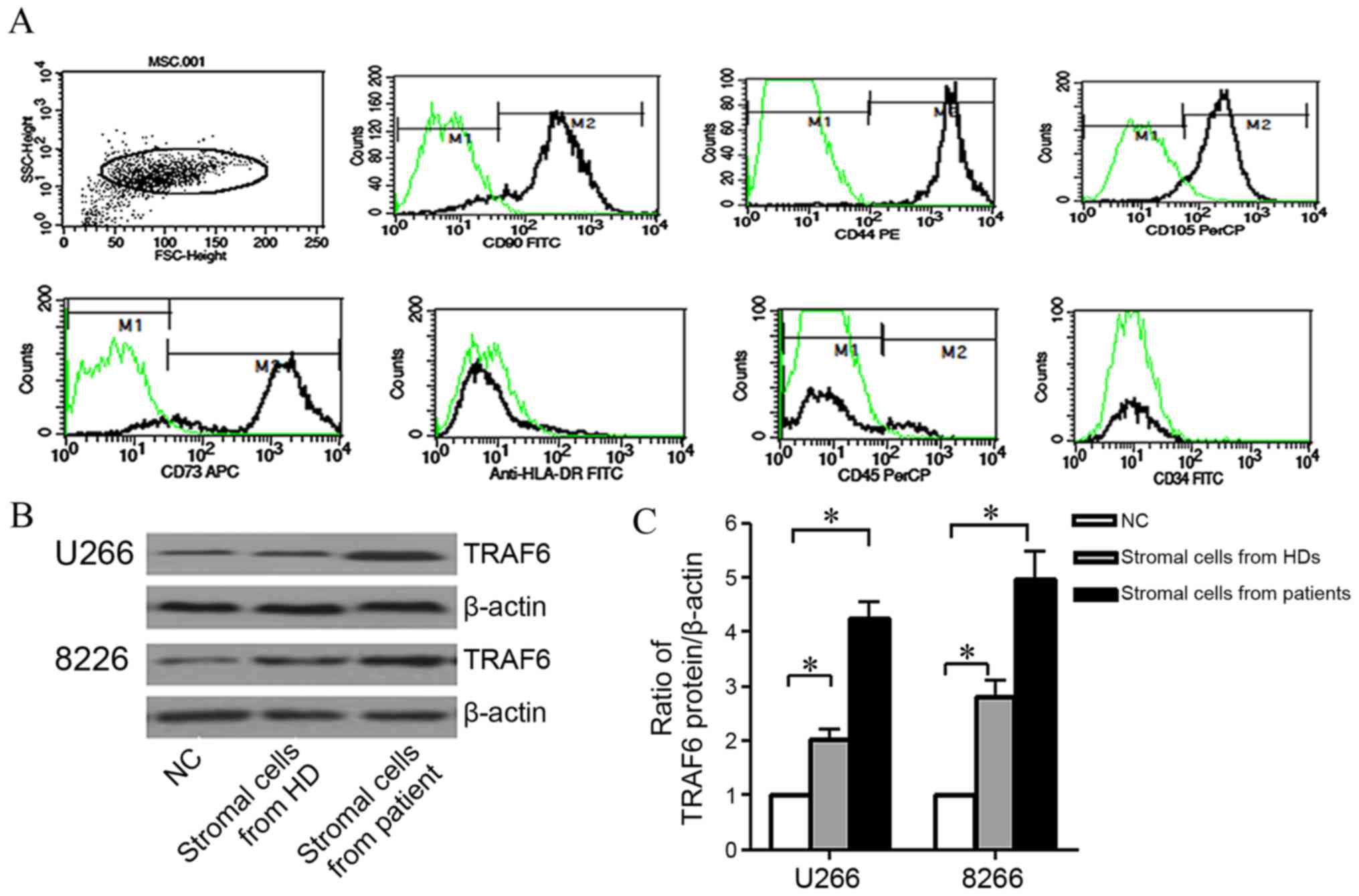
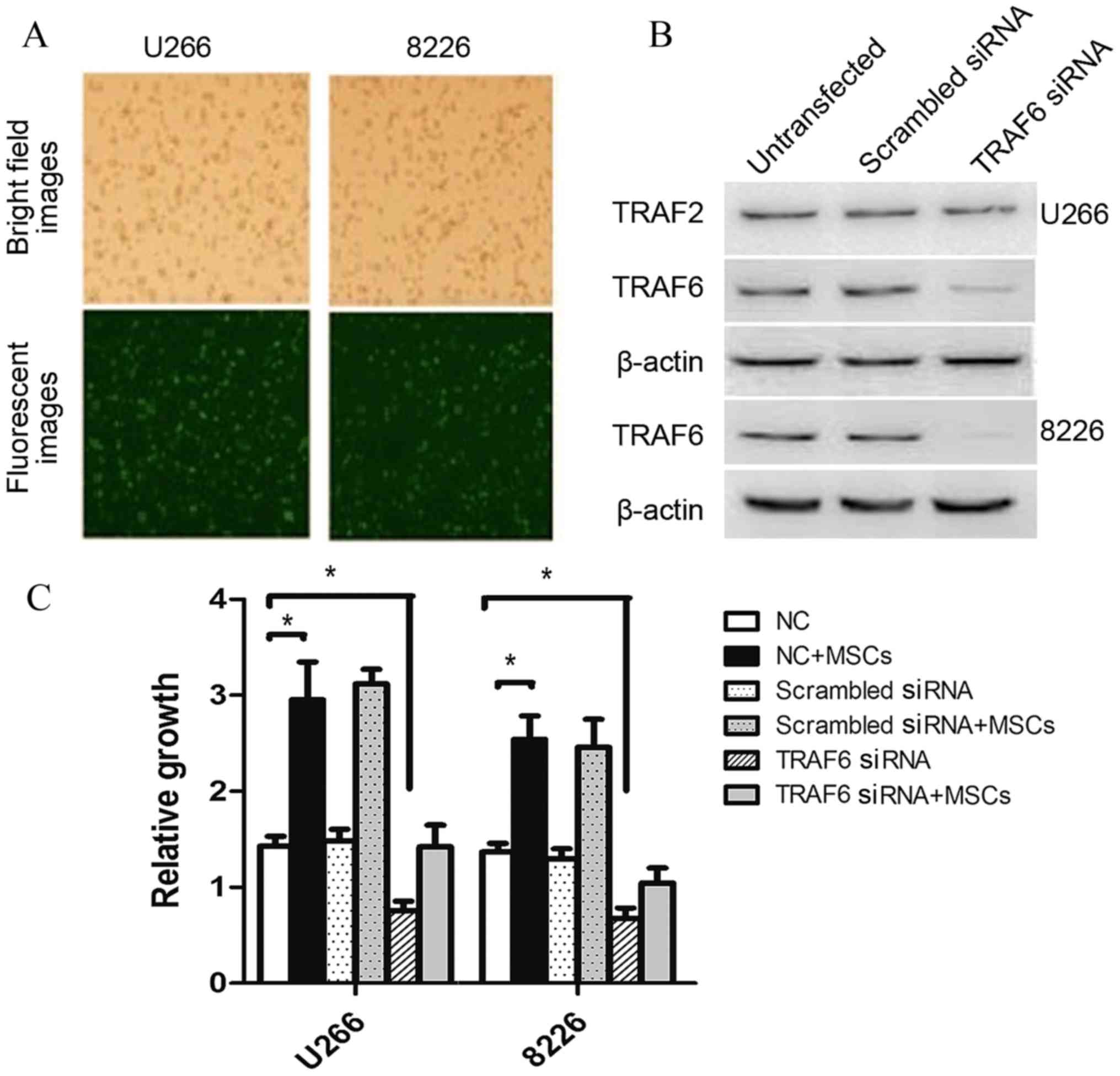
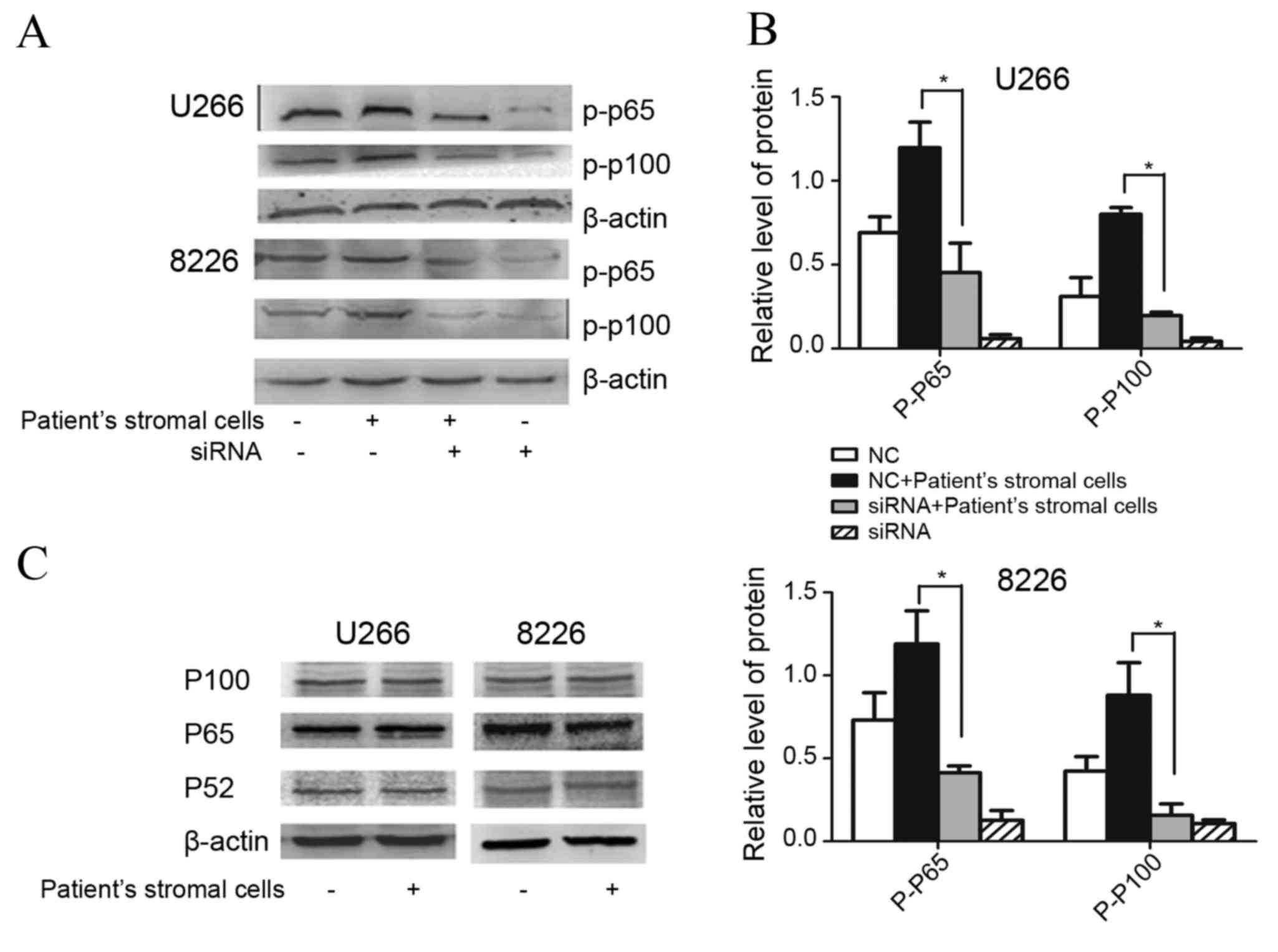
|
1
|
Wu H and Arron JR: TRAF6, a molecular
bridge spanning adaptive immunity, innate immunity and
osteoimmunology. Bioessays. 25:1096–1105. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhong L, Cao F and You Q: Effect of TRAF6
on the biological behavior of human lung adenocarcinoma cell.
Tumour Biol. 34:231–239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chaudhry SI, Hooper S, Nye E, Williamson
P, Harrington K and Sahai E: Autocrine IL-1β-TRAF6 signalling
promotes squamous cell carcinoma invasion through paracrine TNFα
signalling to carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene.
32:747–758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun YS, Ye ZY, Qian ZY, Xu XD and Hu JF:
Expression of TRAF6 and ubiquitin mRNA in skeletal muscle of
gastric cancer patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:812012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fang J, Rhyasen G, Bolanos L, Rasch C,
Varney M, Wunderlich M, Goyama S, Jansen G, Cloos J, Rigolino C, et
al: Cytotoxic effects of bortezomib in myelodysplastic
syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia depend on autophagy-mediated
lysosomal degradation of TRAF6 and repression of PSMA1. Blood.
120:858–867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang G, Gao Y, Li L, Jin G, Cai Z, Chao JI
and Lin HK: K63-linked ubiquitination in kinase activation and
cancer. Front Oncol. 2:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abe M: Targeting the interplay between
myeloma cells and the bone marrow microenvironment in myeloma. Int
J Hematol. 94:334–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Armstrong AP, Tometsko ME, Glaccum M,
Sutherland CL, Cosman D and Dougall WC: A RANK/TRAF6-dependent
signal transduction pathway is essential for osteoclast
cytoskeletal organization and resorptive function. J Biol Chem.
277:44347–44356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sezer O, Heider U, Zavrski I, Kühne CA and
Hofbauer LC: RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin in myeloma bone
disease. Blood. 101:2094–2098. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hongming H and Jian H: Bortezomib inhibits
maturation and function of osteoclasts from PBMCs of patients with
multiple myeloma by downregulating TRAF6. Leuk Res. 33:115–122.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng Y, Cai Z, Wang S, Zhang X, Qian J,
Hong S, Li H, Wang M, Yang J and Yi Q: Macrophages are an abundant
component of myeloma microenvironment and protect myeloma cells
from chemotherapy drug-induced apoptosis. Blood. 114:3625–3628.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tucci M, Stucci S, Strippoli S, Dammacco F
and Silvestris F: Dendritic cells and malignant plasma cells: An
alliance in multiple myeloma tumor progression? Oncologist.
16:1040–1048. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Zhu X, Li N, Chen T, Yang M, Yao M,
Liu X, Jin B, Wang X and Cao X: CMRF-35-like molecule 3
preferentially promotes TLR9-triggered proinflammatory cytokine
production in macrophages by enhancing TNF receptor-associated
factor 6 ubiquitination. J Immunol. 187:4881–4889. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobayashi T, Walsh PT, Walsh MC, Speirs
KM, Chiffoleau E, King CG, Hancock WW, Caamano JH, Hunter CA, Scott
P, et al: TRAF6 is a critical factor for dendritic cell maturation
and development. Immunity. 19:353–363. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen H, Li M, Campbell RA, Burkhardt K,
Zhu D, Li SG, Lee HJ, Wang C, Zeng Z, Gordon MS, et al:
Interference with nuclear factor kappa B and c-Jun NH2-terminal
kinase signaling by TRAF6C small interfering RNA inhibits myeloma
cell proliferation and enhances apoptosis. Oncogene. 25:6520–6527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng MM, Zhang Z, Bemis K, Belch AR,
Pilarski LM, Shively JE and Kirshner J: The systemic cytokine
environment is permanently altered in multiple myeloma. PLoS One.
8:e585042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Greipp PR, San Miguel J, Dune BG, Crowley
JJ, Barlogie B, Bladé J, Boccadoro M, Child JA, Avet-Loiseau H,
Kyle RA, et al: International staging system for multiple myeloma.
J Clin Oncol. 23:3412–3420. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hao M, Xie ZQ, Han YJ, An G, Meng HX,
Huang J, Li CH, Zou DH and Qiu LG: Effect of mesenchymal stem cells
on multiple myeloma cells growth and inhibition of bortezomib
induced cell apoptosis. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 31:680–683.
2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang HM, Wang XF, Liu XX, Xu RR, Shi W,
Ding RS and Jiang SH: Effects of down-regulated TRAF6 gene
expression on the proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma
cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 34:941–945. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu H, Tamashiro S, Baritaki S, Penichet
M, Yu Y, Chen H, Berenson J and Bonavida B: TRAF6 activation in
multiple myeloma: A potential therapeutic target. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 12:155–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaneko M, Kanda Y, Oshima K, Nannya Y,
Suguro M, Yamamoto R, Chizuka A, Hamaki T, Matsuyama T, Takezako N,
et al: Simple prognostic model for patients with multiple myeloma:
A single-cencer study in Japan. Ann Hematol. 81:33–36. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dimopoulos MA, Barlogie B, Smith TL and
Alexanian R: High serum lactate dehydrogenase level as a marker for
drug resistance and short survival in multiple myeloma. Ann Intern
Med. 115:931–935. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nagura E: Prognositic factors in multiple
myeloma. Nihon Rinsho. 65:2351–2356. 2007.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rajkumar SV and Kyle RA: Multiple myeloma:
Diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 80:pp. 1371–1382. 2005;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gunn WG, Conley A, Deininger L, Olson SD,
Prockop DJ and Gregory CA: A crosstalk between myeloma cells and
marrow stromal cells stimulates production of DKK1 and
interleukin-6: A potential role in the development of lytic bone
disease and tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Stem Cells.
24:986–991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu G, Liu K, Anderson J, Patrene K,
Lentzsch S, Roodman GD and Ouyang H: Expression of XBP1s in bone
marrow stromal cells is critical for myeloma cell growth and
osteocast formation. Blood. 119:4205–4214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Annunziata CM, Davis RE, Demchenko Y,
Bellamy W, Gabrea A, Zhan F, Lenz G, Hanamura I, Wright G, Xiao W,
et al: Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative
NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple
myeloma. Cancer Cell. 12:115–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rong Z, Cheng L, Ren Y, Li Z, Li Y, Li X,
Li H, Fu XY and Chang Z: Interleukin-17F signaling requires
ubiquitination of interleukin-17 receptor via TRAF6. Cell Signal.
19:1514–1520. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Theoleyre S, Wittrant Y, Tat SK, Fortun Y,
Redini F and Heymann D: The molecular triad OPG/RANK/RANKL:
Involvement in the orchestration of pathophysiological bone
remodeling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:457–475. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu H, Tamashiro S, Baritaki S, Penichet
M, Yu Y, Chen H, Berenson J and Bonavida B: TRAF6 activation in
multiple myeloma: A potential therapeutic target. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 12:155–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|