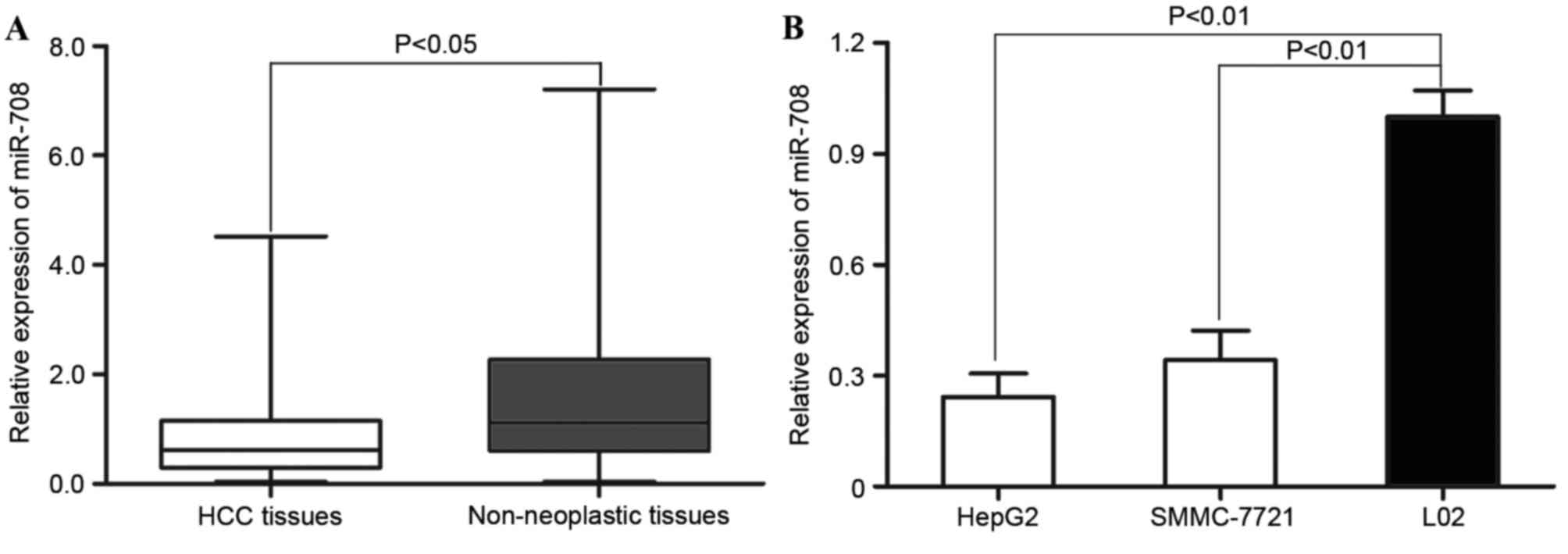
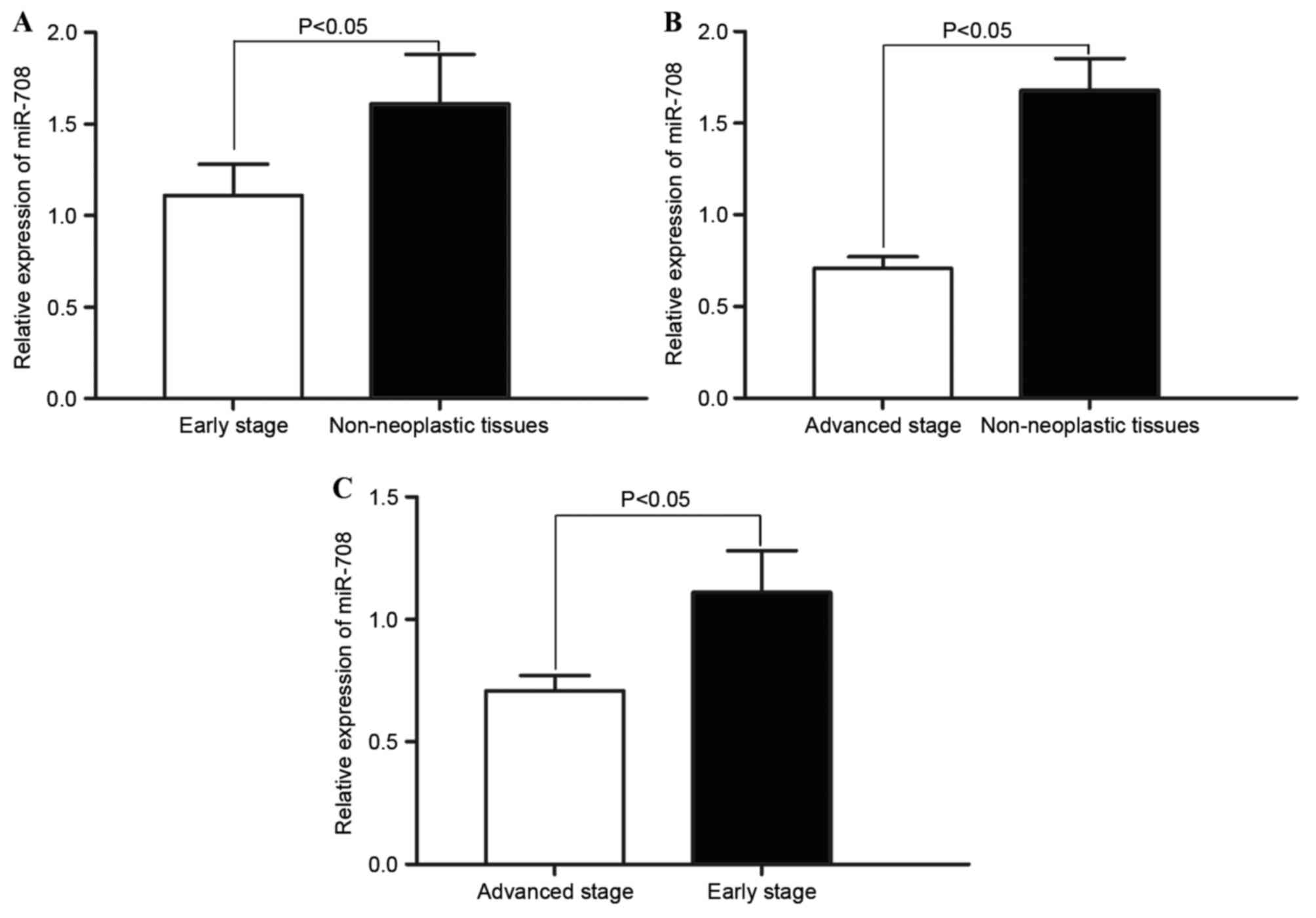
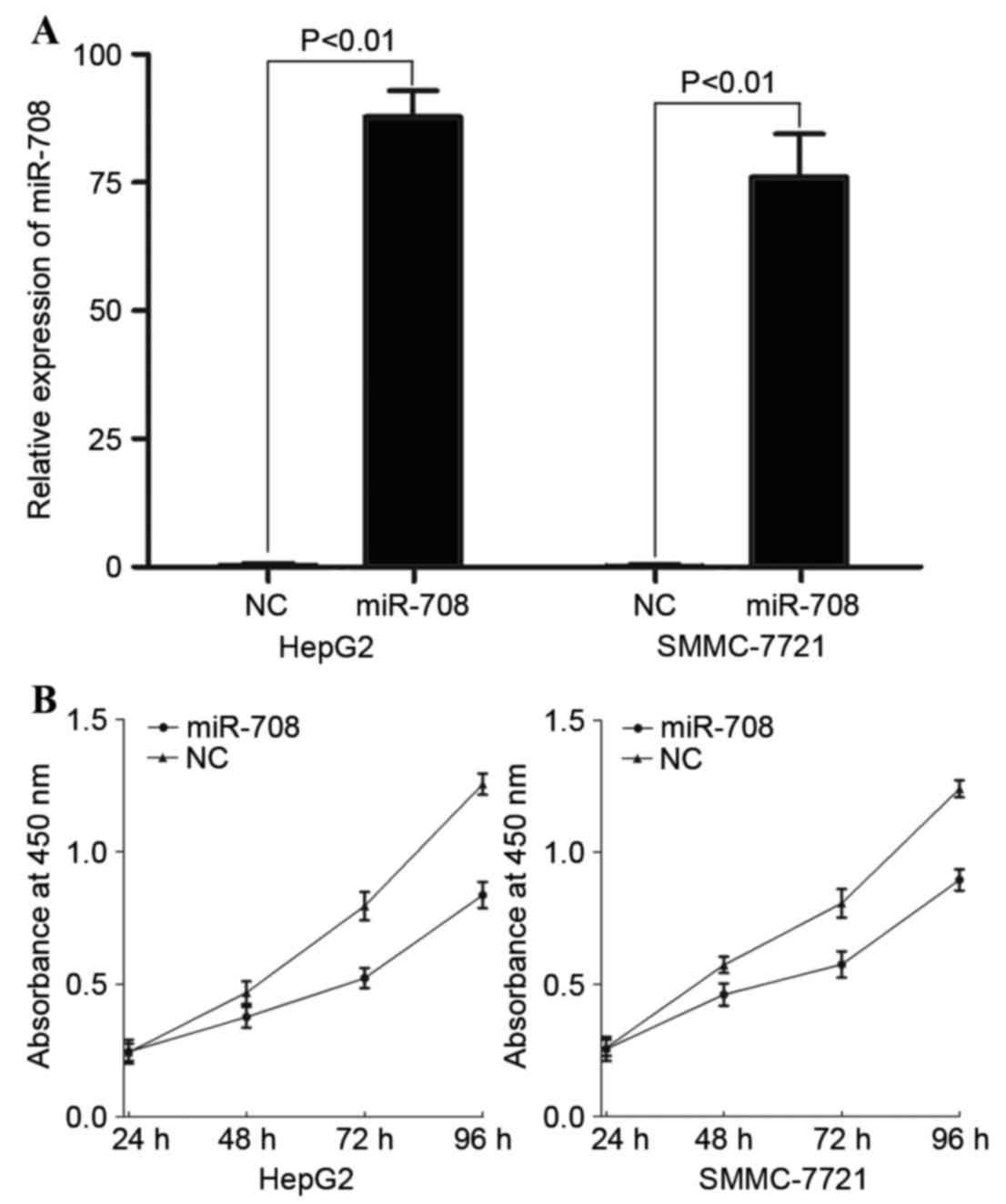
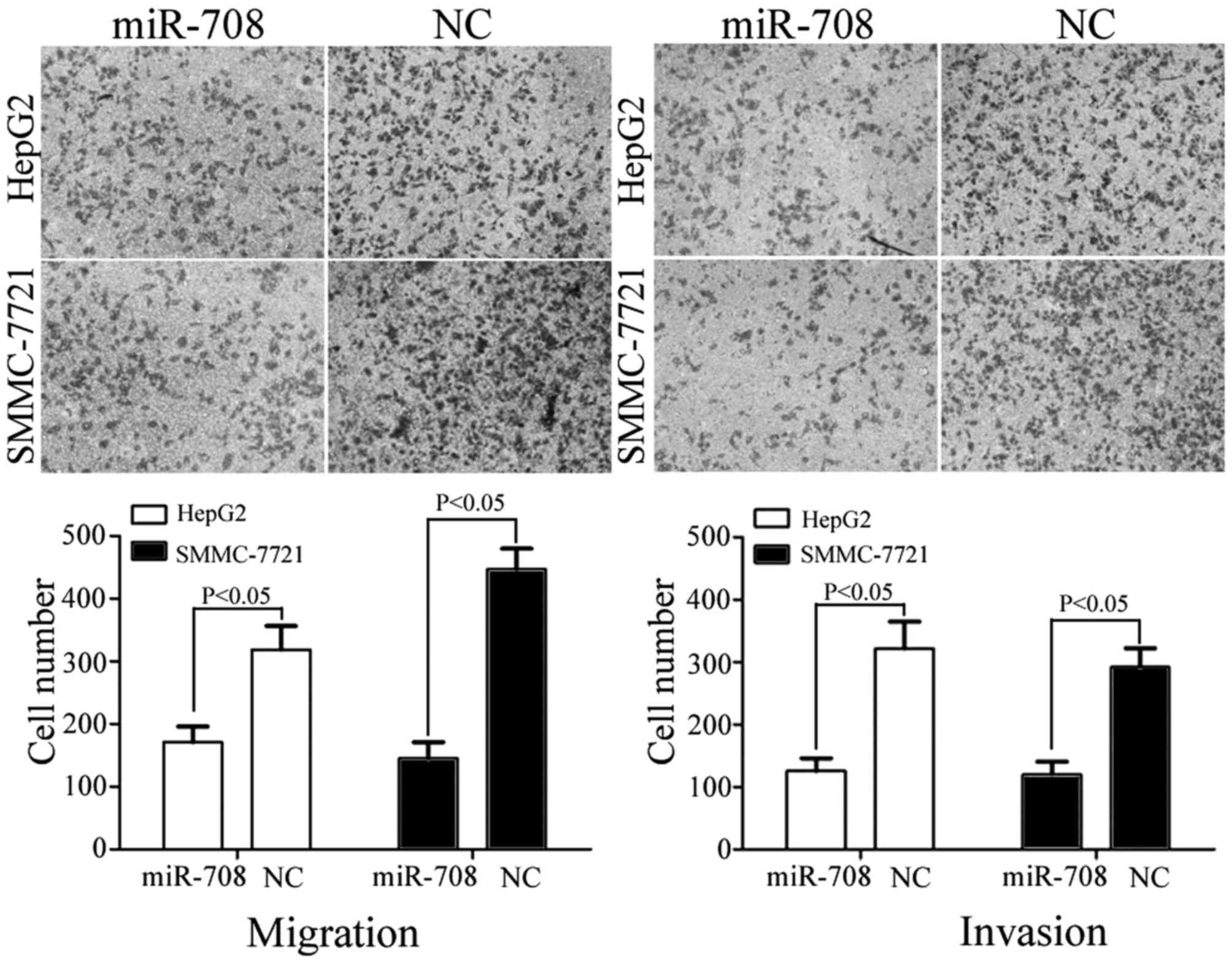
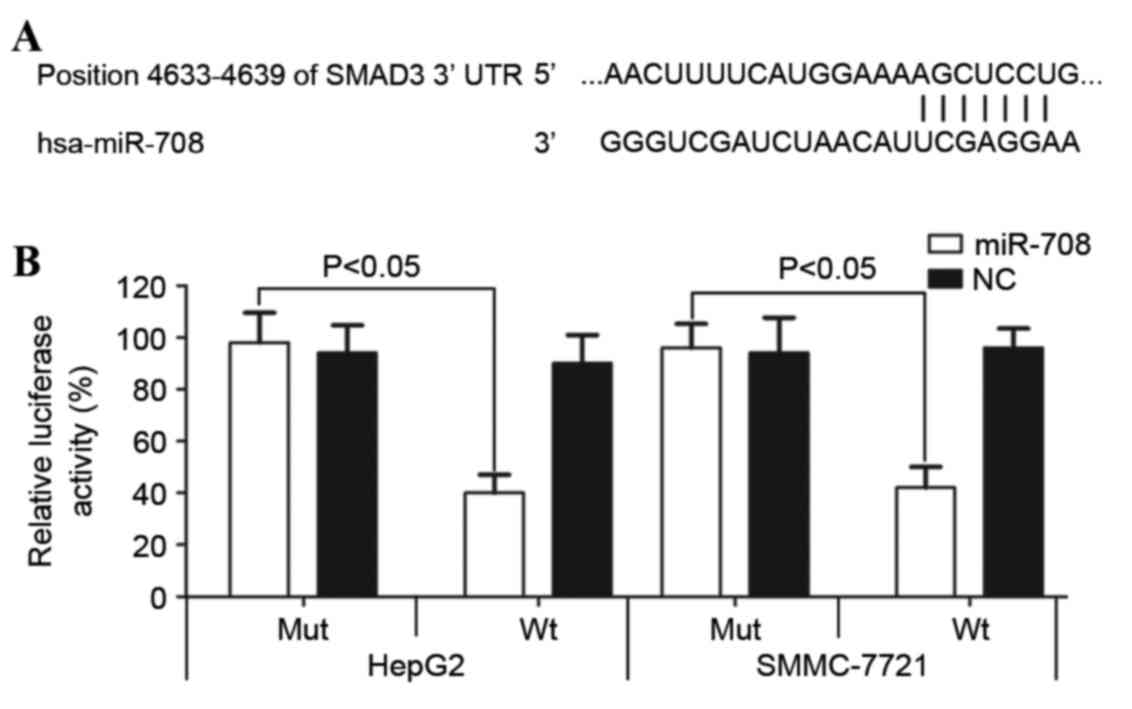
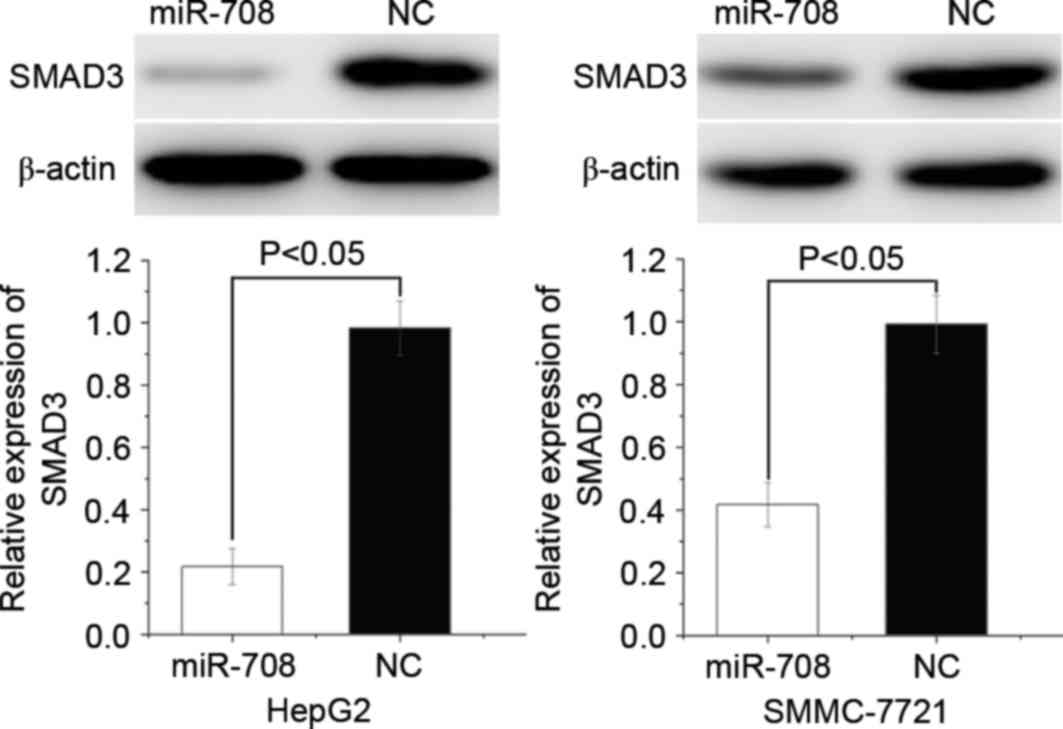
|
1
|
Liu H, Li W, Chen C, Pei Y and Long X:
MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via
downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 36:6313–6319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huitzil-Melendez FD, Capanu M, O'Reilly
EM, Duffy A, Gansukh B, Saltz LL and Abou-Alfa GK: Advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: Which staging systems best predict
prognosis? J Clin Oncol. 28:2889–2895. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vertemati M, Moscheni C, Petrella D,
Lamperti L, Cossa M, Gambacorta M, Goffredi M and Vizzotto L:
Morphometric analysis of hepatocellular nodular lesions in HCV
cirrhosis. Pathol Res Pract. 208:240–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang T, Chen EQ and Tang H: Hepatitis B
virus gene mutations and hepatocarcinogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:4509–4513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao J, Xie L, Yang WS, Zhang W, Gao S,
Wang J and Xiang YB: Risk factors of hepatocellular
carcinoma-current status and perspectives. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:743–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang LY, Fang F, Ou DP, Wu W, Zeng ZJ and
Wu F: Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: A specific subtype
of hepatocellular carcinoma with good outcome after hepatic
resection. Ann Surg. 249:118–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iwakawa HO and Tomari Y: Molecular
insights into microRNA-mediated translational repression in plants.
Mol Cell. 52:591–601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Engels BM and Hutvagner G: Principles and
effects of microRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene regulation.
Oncogene. 25:6163–6169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niyazi M, Zehentmayr F, Niemöller OM,
Eigenbrod S, Kretzschmar H, Schulze-Osthoff K, Tonn JC, Atkinson M,
Mörtl S and Belka C: MiRNA expression patterns predict survival in
glioblastoma. Radiat Oncol. 6:1532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen G, Lu L, Liu C, Shan L and Yuan D:
MicroRNA-377 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
inhibiting TIAM1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01177142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tahara H, Kay MA, Yasui W and Tahara E:
MicroRNAs in Cancer: The 22nd Hiroshima Cancer Seminar/the 4th
Japanese Association for RNA Interference Joint International
Symposium, 30 August 2012, Grand Prince Hotel Hiroshima. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 43:579–582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Liu K, Liu S, Ji B, Wang Y and
Liu Y: MicroRNA-133a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting
IGF-1R in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:9779–9788.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Bo L, Zhao X and Chen Q:
MicroRNA-133a inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation
ability, migration and invasion by targeting matrix
metallopeptidase 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
11:3900–3907. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li D, Liu X, Lin L, Hou J, Li N, Wang C,
Wang P, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Zhou W, et al: MicroRNA-99a inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma growth and correlates with prognosis of
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol Chem.
286:36677–36685. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morishita A and Masaki T: miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:128–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y and Zucman-Rossi J:
Identification of novel oncogenes and tumor suppressors in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 30:75–86. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saini S, Yamamura S, Majid S, Shahryari V,
Hirata H, Tanaka Y and Dahiya R: MicroRNA-708 induces apoptosis and
suppresses tumorigenicity in renal cancer cells. Cancer Res.
71:6208–6219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jang JS, Jeon HS, Sun Z, Aubry MC, Tang H,
Park CH, Rakhshan F, Schultz DA, Kolbert CP and Lupu R: Increased
miR-708 expression in NSCLC and its association with poor survival
in lung adenocarcinoma from never smokers. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3658–3667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian F, Byfield S DaCosta, Parks WT, Yoo
S, Felici A, Tang B, Piek E, Wakefield LM and Roberts AB: Reduction
in Smad2/3 signaling enhances tumorigenesis but suppresses
metastasis of breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 63:8284–8292.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGF-beta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 24:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:pp. 2999–3004. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Lu Z, Li Y, Ji D, Zhang P, Liu Q
and Yao Y: miR-143 inhibits proliferation and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via down-regulation of TLR2
expression. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 30:1076–1079.
2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang XW, Zhang LJ, Huang XH, Chen LZ, Su
Q, Zeng WT, Li W and Wang Q: miR-145 suppresses cell invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: miR-145 targets ADAM17. Hepatol
Res. 44:551–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J, Nie Q, Mao Q and Qiu
Y: miR-708 acts as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 30:870–876. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song T, Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong J, Cai W,
Gao J and Hong B: miR-708 promotes the development of bladder
carcinoma via direct repression of Caspase-2. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 139:1189–1198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Li D, Zhuang Y, Shi Q, Wei W and Ju
X: Overexpression of miR-708 and its targets in the childhood
common precursor B-cell ALL. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 60:2060–2067.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saini S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Arora S,
Yamamura S, Chang I, Zaman MS, Deng G, Tanaka Y and Dahiya R:
miRNA-708 control of CD44(+) prostate cancer-initiating cells.
Cancer Res. 72:3618–3630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li G, Yang F, Xu H, Yue Z, Fang X and Liu
J: MicroRNA-708 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and
suppresses tumor invasion and migration. Biomed Pharmacother.
73:154–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kaminska B, Wesolowska A and Danilkiewicz
M: TGF beta signalling and its role in tumour pathogenesis. Acta
Biochim Pol. 52:329–337. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Massagué J: TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang YA, Zhang GM, Feigenbaum L and Zhang
YE: Smad3 reduces susceptibility to hepatocarcinoma by sensitizing
hepatocytes to apoptosis through downregulation of Bcl-2. Cancer
Cell. 9:445–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim SH, Ahn S and Park CK: Smad3 and its
phosphoisoforms are prognostic predictors of hepatocellular
carcinoma after curative hepatectomy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 11:51–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao W, Zou J, Wang B, Fan P, Mao J, Li J,
Liu H, Xiao J, Ma W, Wang M, et al: microRNA-140 suppresses the
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through targeting
Smad3. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 36:739–745. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu C, Cheng H, Shi S, Cui X, Yang J, Chen
L, Cen P, Cai X, Lu Y, Wu C, et al: MicroRNA-34b inhibits
pancreatic cancer metastasis through repressing Smad3. Curr Mol
Med. 13:467–478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang Y, Liu L, Cai J, Wu J, Guan H, Zhu X,
Yuan J, Chen S and Li M: Targeting Smad2 and Smad3 by miR-136
suppresses metastasis-associated traits of lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Oncol Res. 21:345–352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang H, Sun P, Lei Z, Li M, Wang Y, Zhang
HT and Liu J: miR-145 inhibits invasion and metastasis by directly
targeting Smad3 in nasopharyngeal cancer. Tumour Biol.
36:4123–4131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|