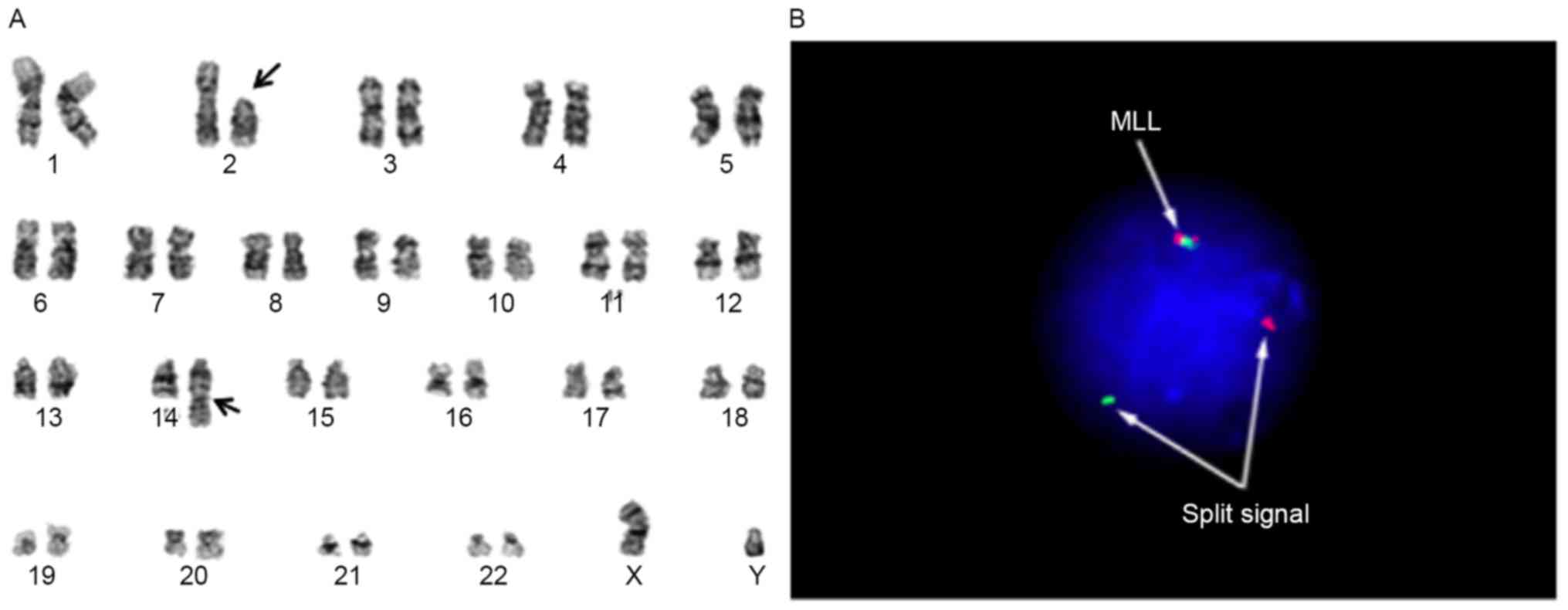
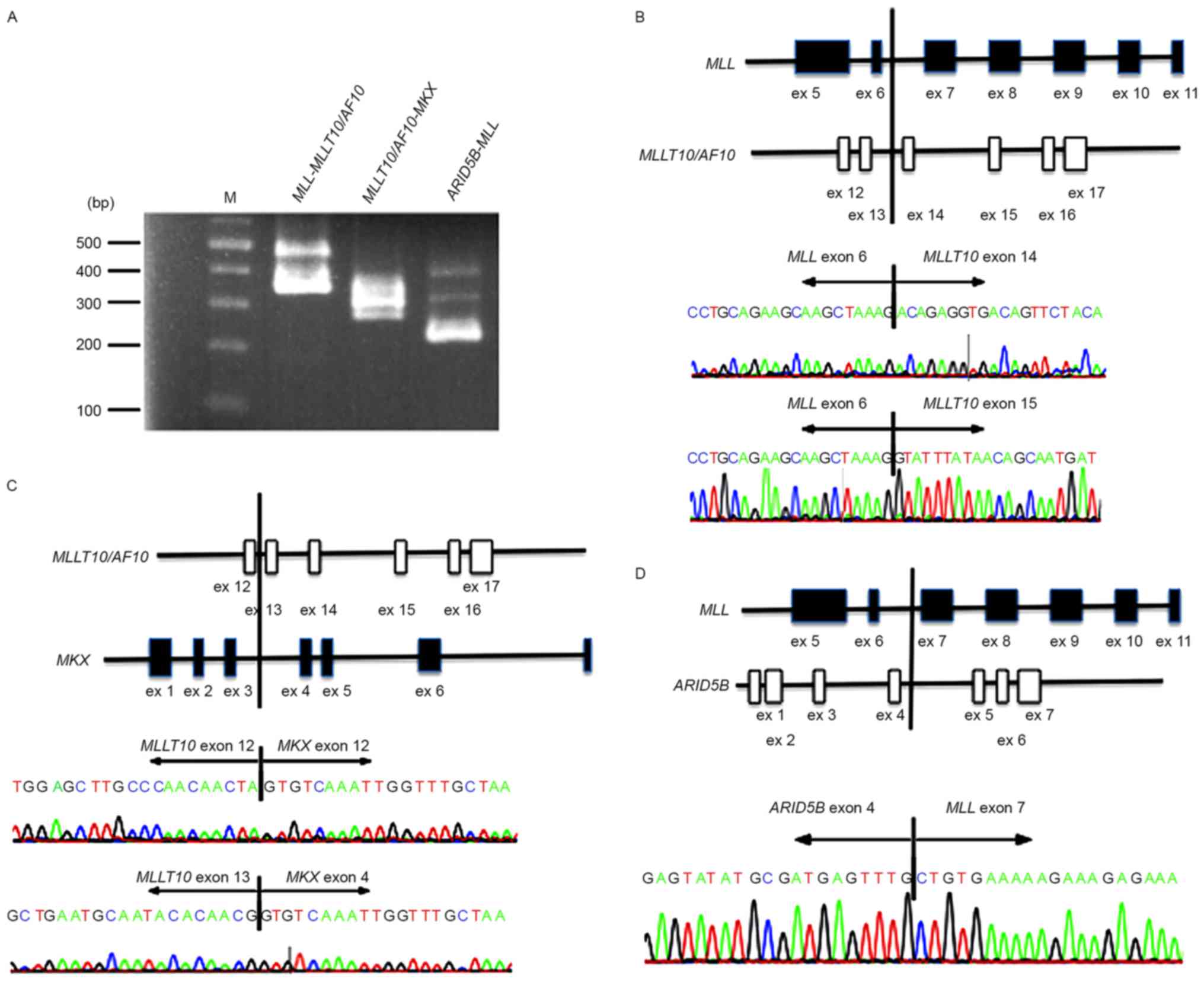
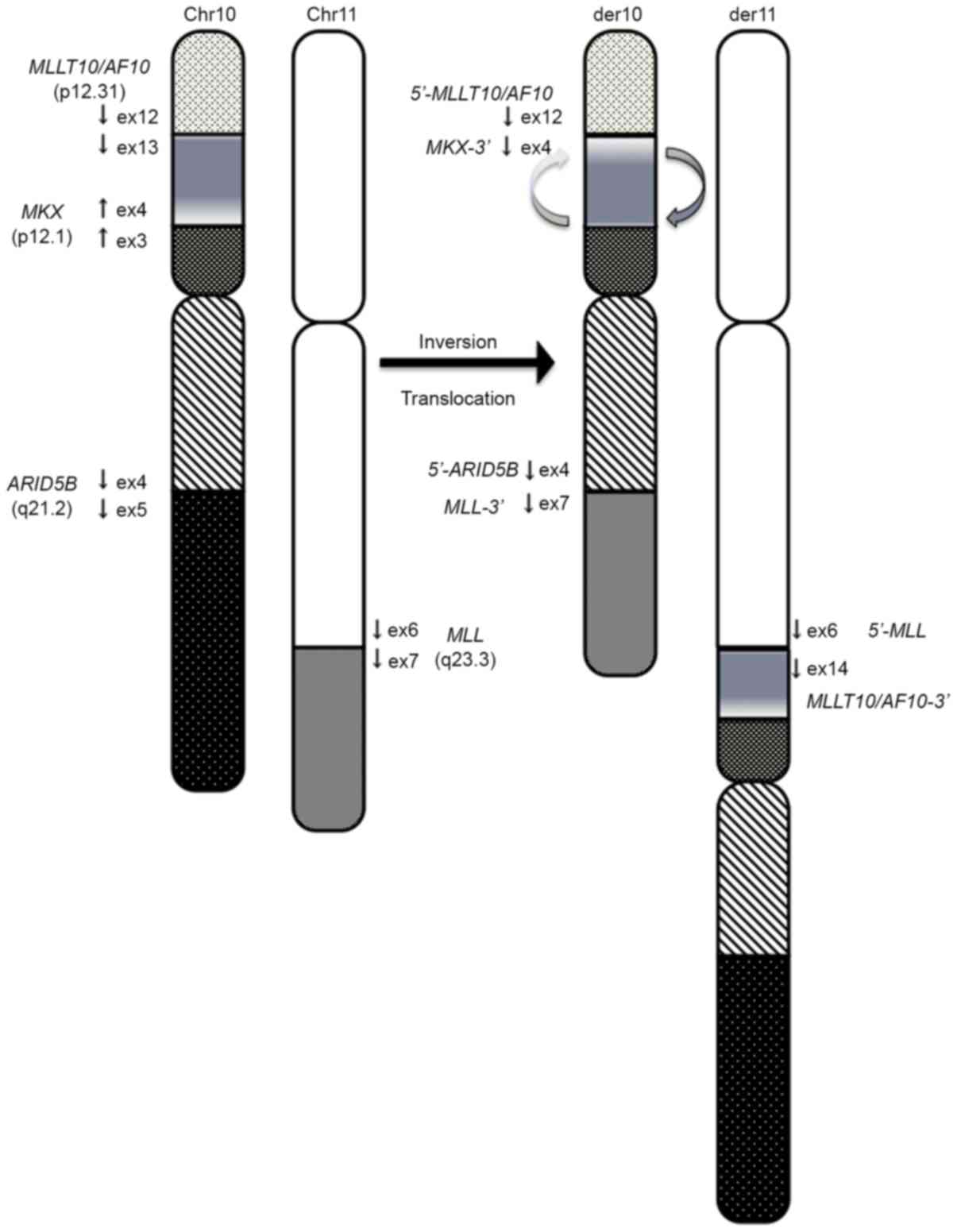
|
1
|
Felix CA: Secondary leukemias induced by
topoisomerase targeted drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1400:233–255.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y, Chen A, Yan XM and Huang G:
Disordered epigenetic regulation in MLL-related leukemia. Int J
Hematol. 96:428–437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meyer C, Kowarz E, Hofmann J, Renneville
A, Zuna J, Trka J, Ben Abdelali R, Macintyre E, De Braekeleer E, De
Braekeleer M, et al: New insights to the MLL recombinome of acute
leukemias. Leukemia. 23:1490–1499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hiwatari M, Taki T, Taketani T, Taniwaki
M, Sugita K, Okuya M, Eguchi M, Ida K and Hayashi Y: Fusion of an
AF4-related gene, LAF4, to MLL in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia with t(2;11)(q11;q23). Oncogene. 22:2851–2855. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chaplin T, Ayton P, Bernard OA, Saha V,
Valle V Della, Hillion J, Gregorini A, Lillington D, Berger R and
Young BD: A novel class of zinc finger/leucine zipper genes
identified from the molecular cloning of the t(10;11) translocation
in acute leukemia. Blood. 85:1435–1441. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu H, Cheng C, Devidas M, Pei D, Fan Y,
Yang W, Neale G, Scheet P, Burchard EG, Torgerson DG, et al: ARID5B
genetic polymorphisms contribute to racial disparities in the
incidence and treatment outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 30:751–757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Limbergen H, Poppe B, Janssens A, De
Bock R, De Paepe A, Noens L and Speleman F: Molecular cytogenetic
analysis of 10;11 rearrangements in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 16:344–351. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meyer C, Hofmann J, Burmeister T, Gröger
D, Park TS, Emerenciano M, de Oliveira M Pombo, Renneville A,
Villarese P, Macintyre E, et al: The MLL recombinome of acute
leukemias in 2013. Leukemia. 27:2165–2176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashihara E, Nakamura S, Inaba T, Taki T,
Hayashi Y and Shimazaki C: A novel AF10-CALM fusion transcript in
gamma/delta-T cell type lymphoblastic lymphoma. Am J Hematol.
82:859–860. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Silliman CC, McGavran L, Wei Q, Miller LA,
Li S and Hunger SP: Alternative splicing in wild-type AF10 and CALM
cDNAs and in AF10-CALM and CALM-AF10 fusion cDNAs produced by the
t(10;11)(p13-14;q14-q21) suggests a potential role for truncated
AF10 polypeptides. Leukemia. 12:1404–1410. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saha V, Chaplin T, Gregorini A, Ayton P
and Young BD: The leukemia-associated-protein (LAP) domain, a
cysteine-rich motif, is present in a wide range of proteins,
including MLL, AF10, and MLLT6 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
92:pp. 9737–9741. 1995; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kumon K, Kobayashi H, Maseki N, Sakashita
A, Sakurai M, Tanizawa A, Imashuku S and Kaneko Y: Mixed-lineage
leukemia with t(10;11)(p13;q21): An analysis of AF10-CALM and
CALM-AF10 fusion mRNAs and clinical features. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 25:33–39. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mroczkowski HJ, Arnold G, Schneck FX,
Rajkovic A and Yatsenko SA: Interstitial 10p11.23-p12.1
microdeletions associated with developmental delay, craniofacial
abnormalities, and cryptorchidism. Am J Med Genet A 164A. 1–2626.
2014.
|
|
14
|
Anderson DM, George R, Noyes MB, Rowton M,
Liu W, Jiang R, Wolfe SA, Wilson-Rawls J and Rawls A:
Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the Mohawk
homeobox transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 287:35351–35359. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Noyes MB, Christensen RG, Wakabayashi A,
Stormo GD, Brodsky MH and Wolfe SA: Analysis of homeodomain
specificities allows the family-wide prediction of preferred
recognition sites. Cell. 133:1277–1289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papaemmanuil E, Hosking FJ, Vijayakrishnan
J, Price A, Olver B, Sheridan E, Kinsey SE, Lightfoot T, Roman E,
Irving JA, et al: Loci on 7p12.2, 10q21.2 and 14q11.2 are
associated with risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat
Genet. 41:1006–1010. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Emerenciano M, Barbosa TC, Lopes BA,
Blunck CB, Faro A, Andrade C, Meyer C, Marschalek R and
Pombo-de-Oliveira MS; Brazilian Collaborative Study Group of Infant
Acute Leukemia, : ARID5B polymorphism confers an increased risk to
acquire specific MLL rearrangements in early childhood leukemia.
BMC Cancer. 14:1272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Prasad RB, Hosking FJ, Vijayakrishnan J,
Papaemmanuil E, Koehler R, Greaves M, Sheridan E, Gast A, Kinsey
SE, Lightfoot T, et al: Verification of the susceptibility loci on
7p12.2, 10q21.2, and 14q11.2 in precursor B-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. Blood. 115:1765–1767. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patsialou A, Wilsker D and Moran E:
DNA-binding properties of ARID family proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:66–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Webb CF, Bryant J, Popowski M, Allred L,
Kim D, Harriss J, Schmidt C, Miner CA, Rose K, Cheng HL, et al: The
ARID family transcription factor bright is required for both
hematopoietic stem cell and B lineage development. Mol Cell Biol.
31:1041–1053. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Will B, Vogler TO, Bartholdy B,
Garrett-Bakelman F, Mayer J, Barreyro L, Pandolfi A, Todorova TI,
Okoye-Okafor UC, Stanley RF, et al: Satb1 regulates the
self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells by promoting quiescence
and repressing differentiation commitment. Nat Immunol. 14:437–445.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Satoh Y, Yokota T, Sudo T, Kondo M, Lai A,
Kincade PW, Kouro T, Iida R, Kokame K, Miyata T, et al: The Satb1
protein directs hematopoietic stem cell differentiation toward
lymphoid lineages. Immunity. 38:1105–1115. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yokota T and Kanakura Y: Role of
tissue-specific AT-rich DNA sequence-binding proteins in lymphocyte
differentiation. Int J Hematol. 100:238–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bursen A, Schwabe K, Rüster B, Henschler
R, Ruthardt M, Dingermann T and Marschalek R: The AF4.MLL fusion
protein is capable of inducing ALL in mice without requirement of
MLL.AF4. Blood. 115:3570–3579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Emerenciano M, Kowarz E, Karl K, de
Almeida Lopes B, Scholz B, Bracharz S, Meyer C, Pombo-de-Oliveira
MS and Marschalek R: Functional analysis of the two reciprocal
fusion genes MLL-NEBL and NEBL-MLL reveal their oncogenic
potential. Cancer Lett. 332:30–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kowarz E, Burmeister T, Lo Nigro L, Jansen
MW, Delabesse E, Klingebiel T, Dingermann T, Meyer C and Marschalek
R: Complex MLL rearrangements in t(4;11) leukemia patients with
absent AF4.MLL fusion allele. Leukemia. 21:1232–1238. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scharf S, Zech J, Bursen A, Schraets D,
Oliver PL, Kliem S, Pfitzner E, Gillert E, Dingermann T and
Marschalek R: Transcription linked to recombination: A
gene-internal promoter coincides with the recombination hot spot II
of the human MLL gene. Oncogene. 26:1361–1371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|