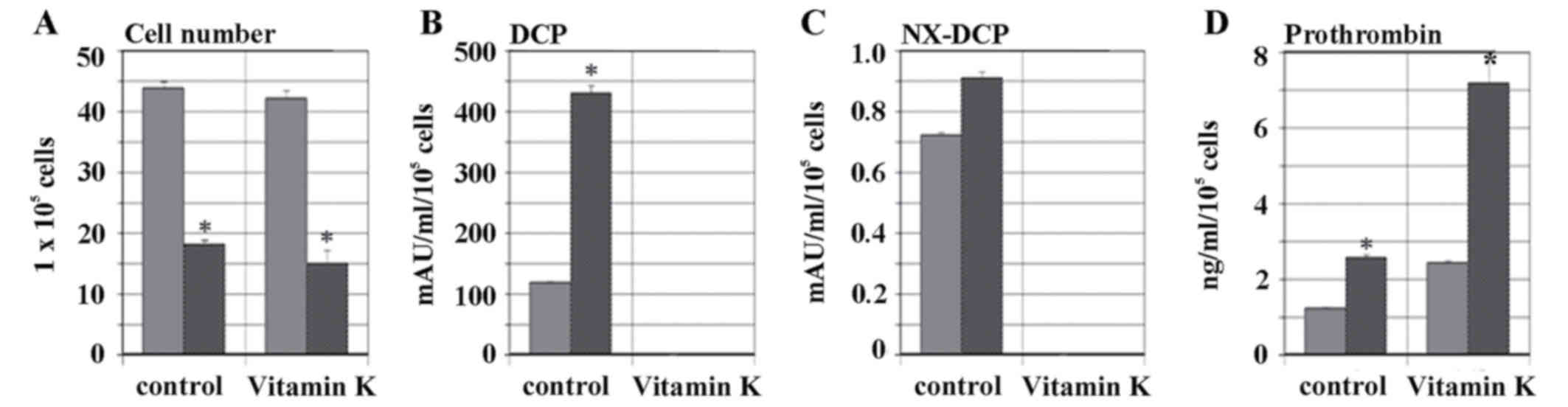
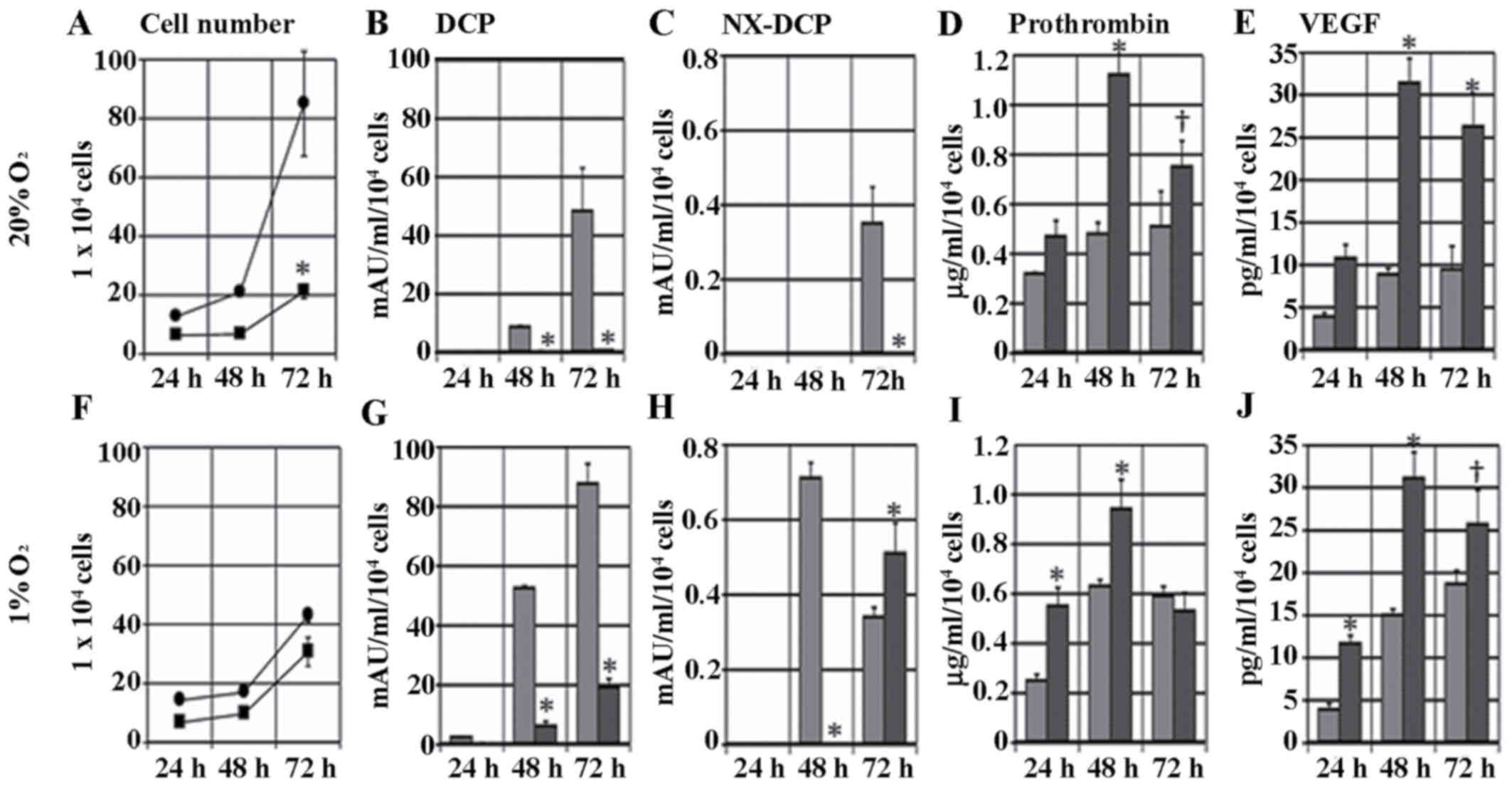
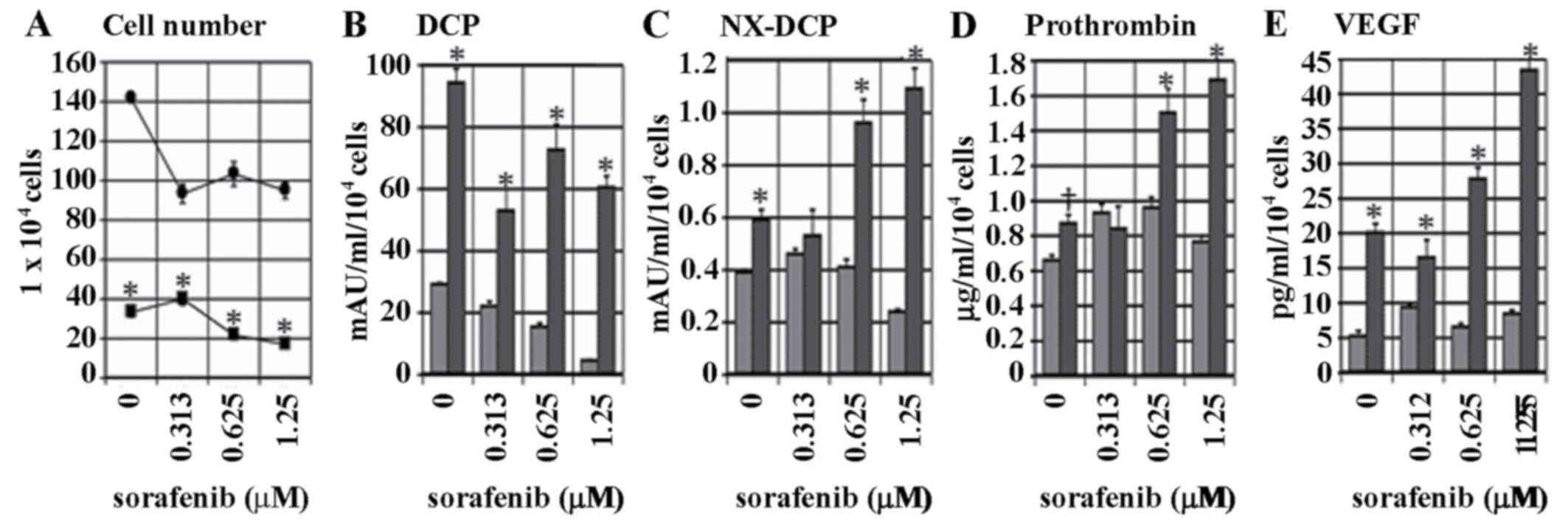
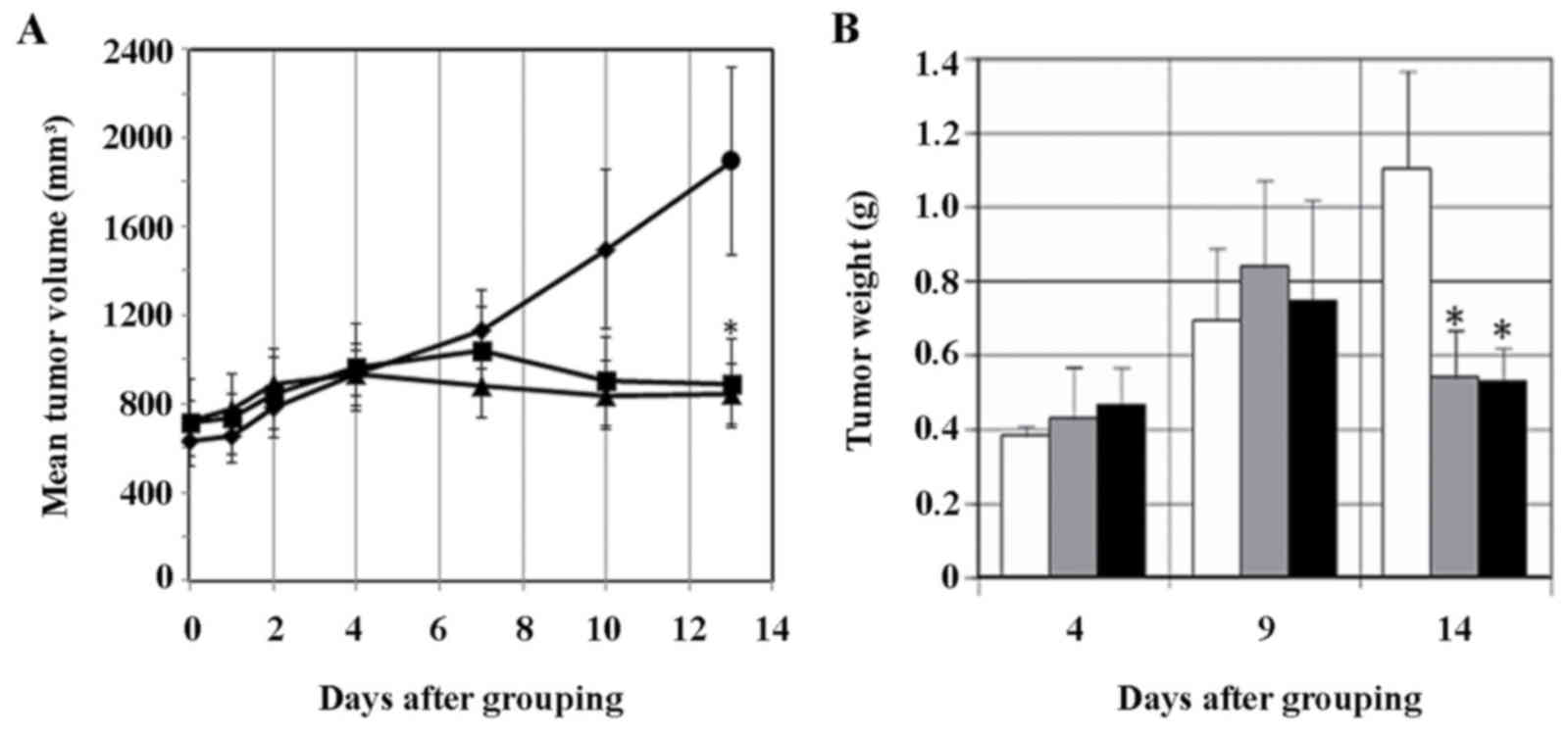
|
1
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stanler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Staehler M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Desai AA, Rolland
F, et al: Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Final
efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches
in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol.
27:3312–3318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carlomagno F, Anaganti S, Guida T,
Salvatore G, Troncone G, Wilhelm SM and Santoro M: BAY 43-9006
inhibition of oncogenic RET mutants. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:326–334. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liebman HA, Furie BC, Tong MJ, Blanchard
RA, Lo KJ, Lee SD, Coleman MS and Furie B: Des-gamma-carboxy
(abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 310:1427–1431. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakon M, Monden M, Gotoh M, Kanai T,
Umeshita K, Nakano Y, Mori T, Sakurai M and Wakasa K: Relationship
between pathologic prognostic factors and abnormal levels of
des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg. 163:251–256. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suehiro T, Sugimachi K, Matsumata T,
Itasaka H, Taketomi A and Maeda T: Protein induced by vitamin K
absence or antagonist II as a prognostic marker in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Comparison with alpha-fetoprotein. Cancer. 73:2464–2471.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sakamoto N: NX-PVKA assay, a conventional
but refined prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:755–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sumi A, Akiba J, Ogasawara S, Nakayama M,
Nomura Y, Yasumoto M, Sanada S, Nakashima O, Abe T and Yano H:
Des-γ-carboxyprothrombin (DCP) and NX-DCP expressions and their
relationship with clinicopathological features in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01184522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim BK, Ahn SH, Seong JS, Park JY, Kim DY,
Kim JK, Lee DY, Lee KH and Han KH: Early α-fetoprotein response as
a predictor for clinical outcome after localized concurrent
chemoradiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int.
31:369–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Johnson PJ: The role of serum
alpha-fetoprotein estimation in the diagnosis and management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 5:145–159. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou L, Liu J and Luo F: Serum tumor
markers for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:1175–1181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malaguarnera G, Giordano M, Paladina I,
Berretta M, Cappellani A and Malaguarnera M: Serum markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2744–2755. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuzuya T, Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Tanaka K,
Suzuki Y, Hoshioka T, Tamaki S, Kato T, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, et al:
Early decrease in α-fetoprotein, but not des-γ-carboxy prothrombin,
predicts sorafenib efficacy in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 81:251–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakazawa T, Hidaka H, Shibuya A and
Koizumi W: Rapid regression of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
associated with elevation of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin after
short-term treatment with sorafenib-a report of two cases. Case Rep
Oncol. 3:298–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueshima K, Kudo M, Takita M, Nagai T,
Tatsumi C, Ueda T, Kita S, Ishikawa E, Yada N, Inoue T, et al:
Des-γ-carboxyprothrombin may be a promising biomarker to determine
the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Dig Dis. 29:321–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murakami T: Establishment and
characterization of human hepatoma cell line (KIM-1). Acta Hepatol
Jpn. 25:532–539. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yano H, Kojiro M and Nakashima T: A new
human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (KYN-1) with a
transformation to adenocarcinoma. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol.
22:637–646. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yano H, Maruiwa M, Murakami T, Fukuda K,
Ito Y, Sugihara S and Kojiro M: A new human pleomorphic
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, KYN-2. Acta Pathol Jpn.
38:953–966. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murakami T, Maruiwa M, Fukuda K, Kojiro M,
Tanaka M and Tanikawa K: Establishment and characterization of a
new human hepatoma cell line (KYN-3) derived from the ascites of
the hepatoma paitient. Proceedings of the Japanese Cancer
Association. Jpn J Cancer Res. 292:1988;
|
|
22
|
Yano H, Iemura A, Fukuda K, Mizoguchi A,
Haramaki M and Kojiro M: Establishment of two distinct human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines from a single nodule showing
clonal dedifferentiation of cancer cells. Hepatology. 18:320–327.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Haramaki M, Yano H, Iemura A, Momosaki S,
Ogasawara S, Inoue M, Yamaguchi R, Kusaba A, Utsunomiya I and
Kojiro M: A new human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HAK-2)
forms various structures in collagen gel matrices. Hum Cell.
10:183–192. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Utsunomiya I, Iemura A, Yano H, Akiba J
and Kojiro M: Establishment and characterization of a new human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HAK-3, and its response to
growth factors. Int J Oncol. 15:669–675. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Murakami T, Yano H, Maruiwa M, Sugihara S
and Kojiro M: Establishment and characterization of a human
combined hepatocholangiocarcinoma cell line and its heterologous
transplantation in nude mice. Hepatology. 7:551–556. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yano H, Iemura A, Haramaki M, Momosaki S,
Ogasawara S, Higaki K and Kojiro M: A human combined hepatocellular
and cholangiocarcinoma cell line (KMCH-2) that shows the features
of hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma under different
growth conditions. J Hepatol. 24:413–422. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shah DV, Engelke JA and Suttie JW:
Abnormal prothrombin in the plasma of rats carrying hepatic tumors.
Blood. 69:850–854. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shah DV, Zhang P, Engelke JA, Bach AU and
Suttie JW: Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase activity, prothrombin
mRNA, and prothrombin production in two cultured rat hepatoma cell
lines. Thromb Res. 70:365–373. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ono M, Ohta H, Ohhira M, Sekiya C and
Namiki M: Measurement of immunoreactive prothrombin,
des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, and vitamin K in human liver
tissues: Overproduction of immunoreactive prothrombin in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 85:1149–1154.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamagata H, Nakanishi T, Furukawa M, Okuda
H and Obata H: Levels of vitamin K, immunoreactive prothrombin,
des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
activity in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 10:8–13. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Wang M, Finn F and Carr BI: The
growth inhibitory effects of vitamins K and their actions on gene
expression. Hepatology. 22:876–882. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okuda H, Obata H, Nakanishi T, Furukawa R
and Hashimoto E: Production of abnormal prothrombin
(des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin) by hepatocellular carcinoma. A
clinical and experimental study. J Hepatol. 4:357–363. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sakon M, Monden M, Gotoh M, Kobayashi K,
Kanai T, Umeshita K, Endoh W and Mori T: The effects of vitamin K
on the generation of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (PIVKA-II) in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol.
86:339–345. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuzuya T, Tsuchiya K, Tanaka K, Suzuki Y,
Hoshioka T, Tamaki S, Kato T, Yasui Y, Tanaka T, Hosokawa T, et al:
Significance of PIVKA-II in sorafenib therapy for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Kanzo. 51:403–404. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ueshima K and Kudo M: PIVKA-II is a
predictive marker in the treatment response of sorafenib to
hepatocellular carcinoma. Kanzo. 51:681–683. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Llobet D, Eritja N, Yeramian A, Pallares
J, Sorolla A, Domingo M, Santacana M, Gonzalez-Tallada FJ,
Matias-Guiu X and Dolcet X: The multikinase inhibitor Sorafenib
induces apoptosis and sensitises endometrial cancer cells to TRAIL
by different mechanisms. Eur J Cancer. 46:836–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fernando J, Sancho P, Fernández-Rodriguez
CM, Lledó JL, Caja L, Campbell JS, Fausto N and Fabregat I:
Sorafenib sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to
physiological apoptotic stimuli. J Cell Physio. 227:1319–1325.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Suzuki M, Shiraha H, Fujikawa T, Takaoka
N, Ueda N, Nakanishi Y, Koike K, Takaki A and Shiratori Y:
Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin is a potential autologous growth
factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 280:6409–6415.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao CF and Woude GF Vande: HGF/SF-Met
signaling in tumor progression. Cell Res. 15:49–51. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murata K, Suzuki H, Okano H, Oyamada T,
Yasuda Y and Sakamoto A: Hypoxia-induced des-gamma-carboxy
prothrombin production in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
36:161–170. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|