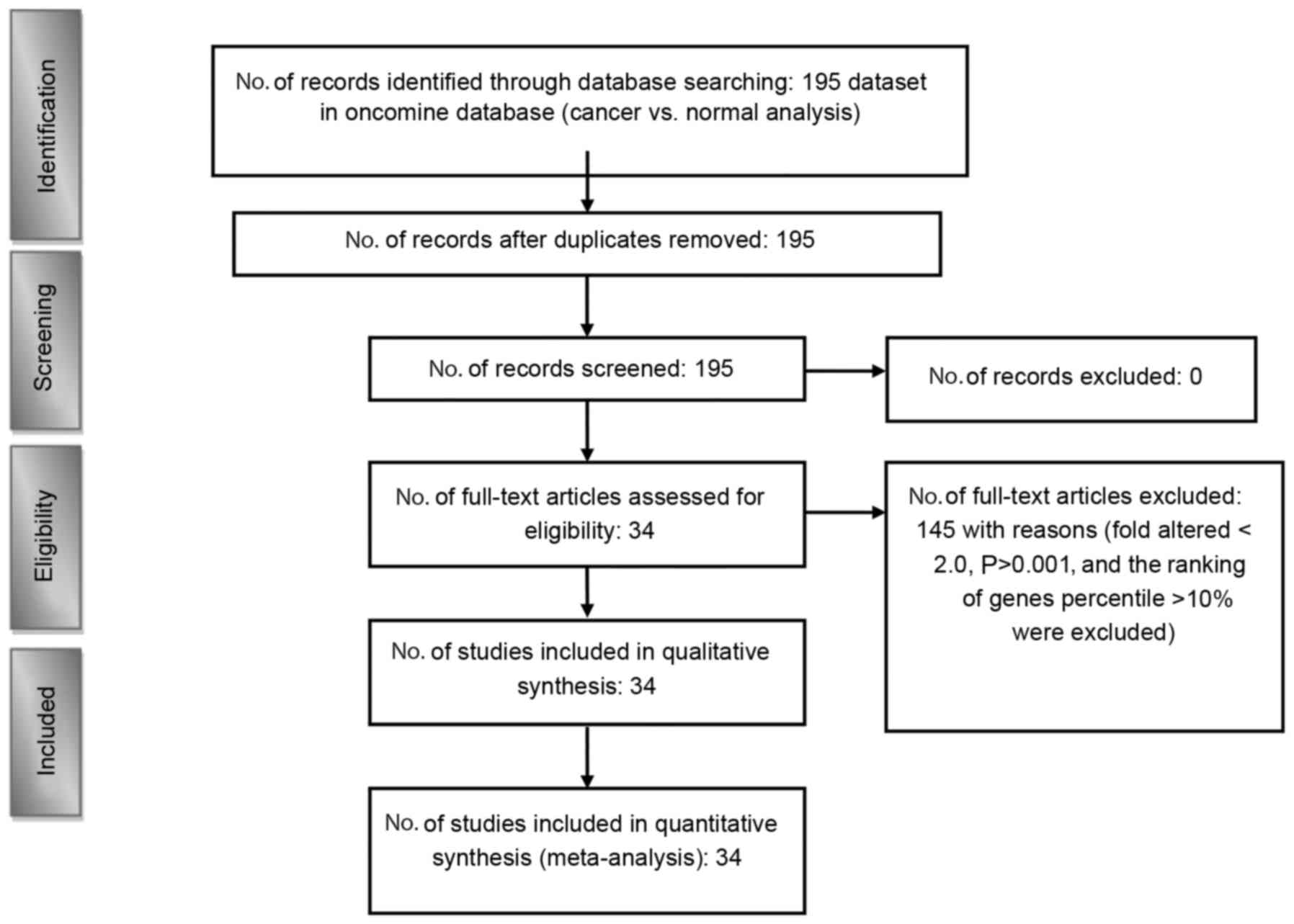
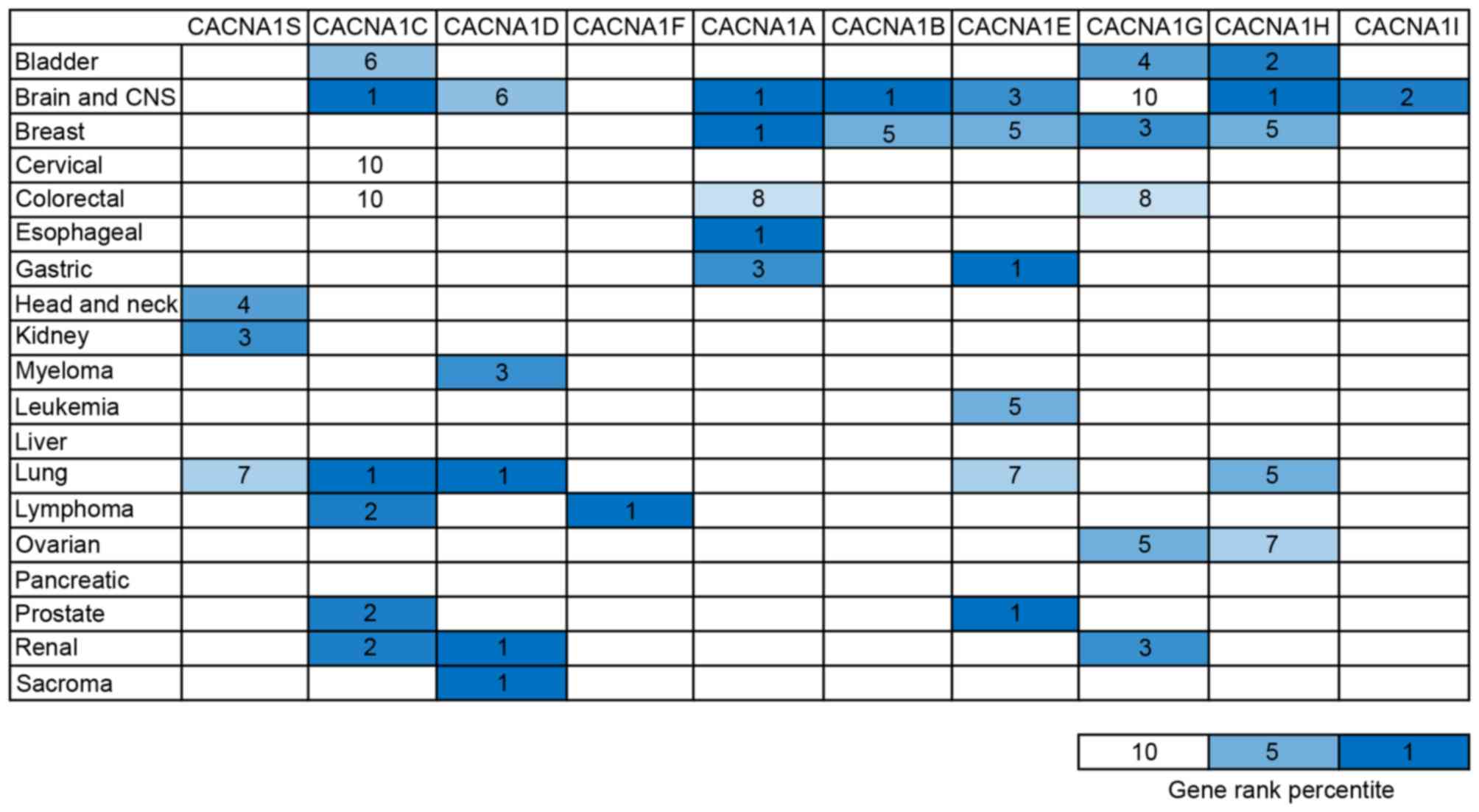
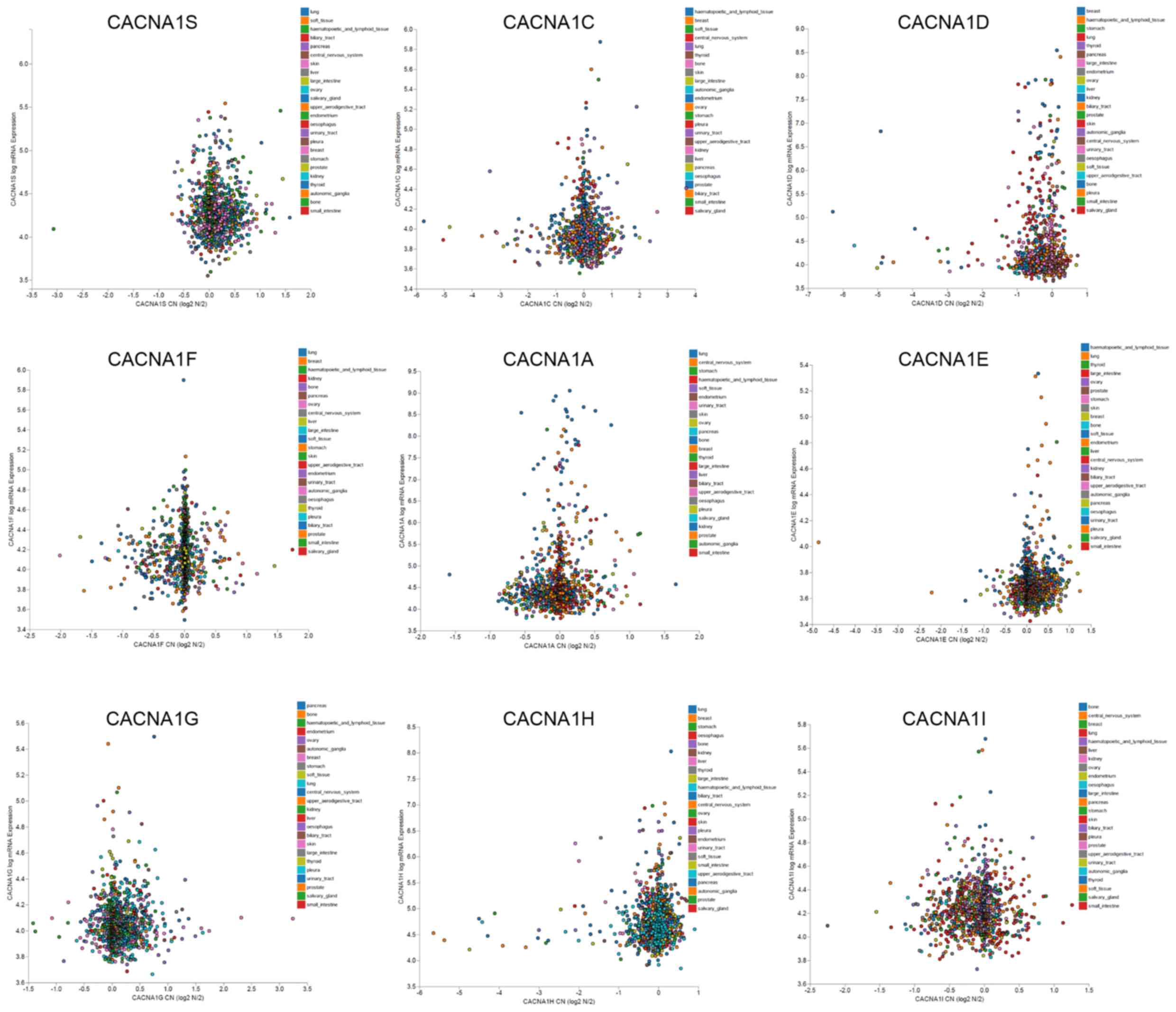
|
1
|
Sarkar P and Kumar S: Calcium sensing
receptor modulation for cancer therapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:3561–3568. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lang F, Föller M, Lang KS, Lang PA, Ritter
M, Gulbins E, Vereninov A and Huber SM: Ion channels in cell
proliferation and apoptotic cell death. J Membr Biol. 205:147–157.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cuddapah VA and Sontheimer H: Ion channels
and tranporters [corrected] in cancer. 2. Ion channels and the
control of cancer cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
301:C541–C549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Long J, Zhang ZB, Liu Z, Xu YH and Ge CL:
Loss of heterozygosity at the calcium regulation gene locus on
chromosome 10q in human pancreatic cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:2489–2493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Azimi I, Roberts-Thomson SJ and Monteith
GR: Calcium influx pathways in breast cancer: Opportunities for
pharmacological intervention. Br J Pharmacol. 171:945–960. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Loughlin KR: Calcium channel blockers and
prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 32:537–538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Q, Zhang Q, Zhong F, Guo S, Jin Z,
Shi W, Chen C and He J: Association between calcium channel
blockers and breast cancer: A meta-analysis of observational
studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 23:711–718. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
George GP, Ramesh V and Mittal RD: Impact
of total and ionized serum calcium on prostate cancer risk in North
Indian men. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1257–1260. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mahmoudi T, Karimi K, Arkani M, Farahani
H, Nobakht H, Dabiri R, Asadi A and Zali MR: Parathyroid hormone
gene rs6256 and calcium sensing receptor gene rs1801725 variants
are not associated with susceptibility to colorectal cancer in
Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6035–6039. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stegmaier K, Ross KN, Colavito SA,
O'Malley S, Stockwell BR and Golub TR: Gene expression-based
high-throughput screening (GE-HTS) and application to leukemia
differentiation. Nat Genet. 36:257–263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Sturla
LM, Angelo M, McLaughlin ME, Kim JY, Goumnerova LC, Black PM, Lau
C, et al: Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour
outcome based on gene expression. Nature. 415:436–442. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X,
Dhanasekaran SM, Khan AP, Quist MJ, Jing X, Lonigro RJ, Brenner JC,
et al: The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Nature. 487:239–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Storz MN, van de Rijn M, Kim YH,
Mraz-Gernhard S, Hoppe RT and Kohler S: Gene expression profiles of
cutaneous B cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 120:865–870. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bonome T, Levine DA, Shih J, Randonovich
M, Pise-Masison CA, Bogomolniy F, Ozbun L, Brady J, Barrett JC,
Boyd J and Birrer MJ: A gene signature predicting for survival in
suboptimally debulked patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
68:5478–5486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barretina J, Taylor BS, Banerji S, Ramos
AH, Lagos-Quintana M, Decarolis PL, Shah K, Socci ND, Weir BA, Ho
A, et al: Subtype-specific genomic alterations define new targets
for soft-tissue sarcoma therapy. Nat Genet. 42:715–721. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Skotheim RI, Lind GE, Monni O, Nesland JM,
Abeler VM, Fosså SD, Duale N, Brunborg G, Kallioniemi O, Andrews PW
and Lothe RA: Differentiation of human embryonal carcinomas in
vitro and in vivo reveals expression profiles relevant to normal
development. Cancer Res. 65:5588–5598. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cutcliffe C, Kersey D, Huang CC, Zeng Y,
Walterhouse D and Perlman EJ; Renal Tumor Committee of the
Children's Oncology Group, : Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney:
Up-regulation of neural markers with activation of the sonic
hedgehog and Akt pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7986–7994. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S,
Souleimanova M, Zhao H, Chen H, Omeroglu G, Meterissian S, Omeroglu
A, et al: Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in
breast cancer. Nat Med. 14:518–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crabtree JS, Jelinsky SA, Harris HA, Choe
SE, Cotreau MM, Kimberland ML, Wilson E, Saraf KA, Liu W,
McCampbell AS, et al: Comparison of human and rat uterine
leiomyomata: Identification of a dysregulated mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway. Cancer Res. 69:6171–6178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hao Y, Triadafilopoulos G, Sahbaie P,
Young HS, Omary MB and Lowe AW: Gene expression profiling reveals
stromal genes expressed in common between Barrett's esophagus and
adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 131:925–933. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szatkowski C, Parys JB, Ouadid-Ahidouch H
and Matifat F: Research Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+
signalling is involved in estradiol-induced breast cancer
epithelial cell growth. Mol Cancer. 9:1562010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mariot P, Prevarskaya N, Roudbaraki MM, Le
Bourhis X, Van Coppenolle F, Vanoverberghe K and Skryma R: Evidence
of functional ryanodine receptor involved in apoptosis of prostate
cancer (LNCaP) cells. Prostate. 43:205–214. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Galione A, Evans AM, Ma J, Parrington J,
Arredouani A, Cheng X and Zhu MX: The acid test: The discovery of
two-pore channels (TPCs) as NAADP-gated endolysosomal Ca(2+)
release channels. Pflugers Arch. 458:869–876. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lipkin M and Newmark H: Effect of added
dietary calcium on colonic epithelial-cell proliferation in
subjects at high risk for familial colonic cancer. N Engl J Med.
313:1381–1384. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin T, Zhang Z, Yang XF and Luo JS: S100A4
expression is closely linked to genesis and progression of glioma
by regulating proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2883–2887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD and Roderick HL:
Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 4:517–529. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takeshige N, Yin G, Ohnaka K, Kono S, Ueki
T, Tanaka M, Maehara Y, Okamura T, Ikejiri K, Maekawa T, et al:
Associations between vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms
and colorectal cancer risk and effect modifications of dietary
calcium and vitamin D in a Japanese population. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:2019–2026. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Panner A and Wurster RD: T-type calcium
channels and tumor proliferation. Cell Calcium. 40:253–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Linja MJ, Savinainen KJ, Saramäki OR,
Tammela TL, Vessella RL and Visakorpi T: Amplification and
overexpression of androgen receptor gene in hormone-refractory
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 61:3550–3555. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gillett C, Fantl V, Smith R, Fisher C,
Bartek J, Dickson C, Barnes D and Peters G: Amplification and
overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer detected by
immunohistochemical staining. Cancer Res. 54:1812–1817.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cole S, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach J, Mackie JE,
Grant CE, Almquist KC, Stewart AJ, Kurz EU, Duncan AM and Deeley
RG: Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant
human lung cancer cell line. Science. 258:1650–1654. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu TH, Guo K, Liu RQ, Zhang S, Huang ZH
and Liu YK: The high expressed serum soluble neural cell adhesion
molecule, a high risk factor indicating hepatic encephalopathy in
hepatocelular carcinoma patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:3131–3135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mao YY, Jing FY, Jin MJ, Li YJ, Ding Y,
Guo J, Wang FJ, Jiang LF and Chen K: rs12904 polymorphism in the
3′UTR of EFNA1 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility
in a Chinese population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5037–5041.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martino-Echarri E, Fernández-Rodríguez R,
Rodríguez-Baena FJ, Barrientos-Durán A, Torres-Collado AX,
Plaza-Calonge Mdel C, Amador-Cubero S, Cortés J, Reynolds LE,
Hodivala-Dilke KM and Rodríguez-Manzaneque JC: Contribution of
ADAMTS1 as a tumor suppressor gene in human breast carcinoma.
Linking its tumor inhibitory properties to its proteolytic activity
on nidogen-1 and nidogen-2. Int J Cancer Cancer Cancer.
133:2315–2324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li YP, Tian FG, Shi PC, Guo LY, Wu HM,
Chen RQ and Xue JM: 4-Hydroxynonenal promotes growth and
angiogenesis of breast cancer cells through HIF-1α stabilization.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:10151–10156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim HS, Patel K, Muldoon-Jacobs K, Bisht
KS, Aykin-Burns N, Pennington JD, van der Meer R, Nguyen P, Savage
J, Owens KM, et al: SIRT3 is a mitochondria-localized tumor
suppressor required for maintenance of mitochondrial integrity and
metabolism during stress. Cancer Cell. 17:41–52. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dziegielewska B, Gray LS and Dziegielewski
J: T-type calcium channels blockers as new tools in cancer
therapies. Pflugers Arch. 466:801–810. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee JY, Park SJ, Park SJ, Lee MJ, Rhim H,
Seo SH and Kim KS: Growth inhibition of human cancer cells in vitro
by T-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
16:5014–5017. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bertolesi GE, Shi CJ, Elbaum L, Jollimore
C, Rozenberg G, Barnes S and Kelly ME: The Ca(2+) channel
antagonists mibefradil and pimozide inhibit cell growth via
different cytotoxic mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol. 62:210–219. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Toyota M, Ho C, Ohe-Toyota M, Baylin SB
and Issa JP: Inactivation of CACNA1G, a T-type calcium channel
gene, by aberrant methylation of its 5′ CpG island in human tumors.
Cancer Res. 59:4535–4541. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Díaz-Lezama N, Hernández-Elvira M,
Sandoval A, Monroy A, Felix R and Monjaraz E: Ghrelin inhibits
proliferation and increases T-type Ca2+ channel expression in PC-3
human prostate carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
403:24–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang CY, Lai MD, Phan NN, Sun ZD and Lin
YC: Meta-analysis of public microarray datasets reveals
voltage-gated calcium gene signatures in clinical cancer patients.
PLoS One. 10:e01257662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rhodes DR and Chinnaiyan AM: Integrative
analysis of the cancer transcriptome. Nat Genet. 37 Suppl:S31–S37.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou C, Ren Y, Wang K, Liu J, He JJ and
Liu PJ: Intra-operative rectal washout with saline solution can
effectively prevent anastomotic recurrence: A meta-analysis. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7155–7159. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alqumber MA, Dar SA, Haque S, Wahid M,
Singh R and Akhter N: No association of the TGF-β1 29T/C
polymorphism with breast cancer risk in caucasian and Asian
populations: Evidence from a meta-analysis involving 55, 841
subjects. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:8725–8734. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ni M, Chen Y, Lim E, Wimberly H, Bailey
ST, Imai Y, Rimm DL, Liu XS and Brown M: Targeting androgen
receptor in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell.
20:119–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
D'Ambrogio A, Nagaoka K and Richter JD:
Translational control of cell growth and malignancy by the CPEBs.
Nat Rev Cancer. 13:283–290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N,
Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV,
Sonkin D, et al: The cancer cell line encyclopedia enables
predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature.
483:603–607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ertel EA, Campbell KP, Harpold MM, Hofmann
F, Mori Y, Perez-Reyes E, Schwartz A, Snutch TP, Tanabe T,
Birnbaumer L, et al: Nomenclature of voltage-gated calcium
channels. Neuron. 25:533–535. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cain SM and Snutch TP: Voltage-gated
calcium channels and disease. Biofactors. 37:197–205. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bidaud I, Mezghrani A, Swayne LA, Monteil
A and Lory P: Voltage-gated calcium channels in genetic diseases.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763:1169–1174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kavianpour M, Ahmadzadeh A, Shahrabi S and
Saki N: Significance of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in AML
prognosis. Tumour Biol. 37:10041–10052. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cooper GM and Hausman RE: The cell.
Sinauer Associates Sunderland; 2000, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Marta SC, Nicholas S, Juanjo L, Fabien S
and Carlos CC: Defining molecular profiles of poor outcome in
patients with invasive bladder cancer using oligonucleotide
microarrays. Tumor Biol. 27:47. 2006.
|
|
57
|
Schaldemose EL, Horjales-Araujo E,
Demontis D, Børglum AD, Svensson P and Finnerup NB: No association
of polymorphisms in the serotonin transporter gene with thermal
pain sensation in healthy individuals. Mol Pain. 10:762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stunnenberg BC, Deinum J, Links TP, Wilde
AA, Franssen H and Drost G: Cardiac arrhythmias in hypokalemic
periodic paralysis: Hypokalemia as only cause? Muscle Nerve.
50:327–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Beitelshees AL, Navare H, Wang D, Gong Y,
Wessel J, Moss JI, Langaee TY, Cooper-DeHoff RM, Sadee W, Pepine
CJ, et al: CACNA1C gene polymorphisms, cardiovascular disease
outcomes, and treatment response. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2:362–370.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Baig SM, Koschak A, Lieb A, Gebhart M,
Dafinger C, Nürnberg G, Ali A, Ahmad I, Sinnegger-Brauns MJ, Brandt
N, et al: Loss of Cav1. 3 (CACNA1D) function in a human
channelopathy with bradycardia and congenital deafness. Nat
Neurosci. 14:77–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Johnson AD, Newton-Cheh C, Chasman DI,
Ehret GB, Johnson T, Rose L, Rice K, Verwoert GC, Launer LJ,
Gudnason V, et al: Association of hypertension drug target genes
with blood pressure and hypertension in 86 588 individuals.
Hypertension. 57:903–910. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Madden E: Differential gene remodeling in
overweight and obese patients with heart failure. 2013.
|
|
63
|
Kang H, Yang X, Chen R, Zhang B, Corona E,
Schadt EE and Butte AJ: Integration of disease-specific single
nucleotide polymorphisms, expression quantitative trait loci and
coexpression networks reveal novel candidate genes for type 2
diabetes. Diabetologia. 55:2205–2213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Reinbothe TM, Alkayyali S, Ahlqvist E,
Tuomi T, Isomaa B, Lyssenko V and Renström E: The human L-type
calcium channel Cav1. 3 regulates insulin release and polymorphisms
in CACNA1D associate with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia.
56:340–349. 2013.
|
|
65
|
Reinbothe T, Lyssenko V, Lang S and
Renström E: Polymorphisms in CACNA1D affect insulin release and
channel expression and associate with type 2 diabetes46th Annual
Meeting of the European-Association-for-the-Study-of-Diabetes
(EASD). Springer; pp. 2962010;
|
|
66
|
Qiu ZX, Zhao S, Li L and Li WM: Loss of
expression of PTEN is associated with worse prognosis in patients
with cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:4691–4698. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kamp TJ and Hell JW: Regulation of cardiac
L-type calcium channels by protein kinase A and protein kinase C.
Cir Res. 87:1095–1102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Moosmang S, Schulla V, Welling A, Feil R,
Feil S, Wegener JW, Hofmann F and Klugbauer N: Dominant role of
smooth muscle L-type calcium channel Cav1. 2 for blood pressure
regulation. EMBO J. 22:6027–6034. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bhat S, Dao DT, Terrillion CE, Arad M,
Smith RJ, Soldatov NM and Gould TD: CACNA1C (Ca v 1.2) in the
pathophysiology of psychiatric disease. Prog Neurobiol. 99:1–14.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sun L, Hui AM, Su Q, Vortmeyer A,
Kotliarov Y, Pastorino S, Passaniti A, Menon J, Walling J, Bailey
R, et al: Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces
angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell. 9:287–300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Murat A, Migliavacca E, Gorlia T, Lambiv
WL, Shay T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Regli L, Wick W, Kouwenhoven
MC, et al: Stem cell-related ‘self-renewal’ signature and high
epidermal growth factor receptor expression associated with
resistance to concomitant chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma. J Clin
Oncol. 26:3015–3024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Uchitel OD, Protti DA, Sanchez V, Cherksey
BD, Sugimori M and Llinás R: P-type voltage-dependent calcium
channel mediates presynaptic calcium influx and transmitter release
in mammalian synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:pp. 3330–3333.
1992; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Catterall WA: Structure and function of
neuronal Ca2+ channels and their role in neurotransmitter release.
Cell Calcium. 24:307–323. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Piccaluga PP, Agostinelli C, Califano A,
Rossi M, Basso K, Zupo S, Went P, Klein U, Zinzani PL, Baccarani M,
et al: Gene expression analysis of peripheral T cell lymphoma,
unspecified, reveals distinct profiles and new potential
therapeutic targets. J Clin Invest. 117:823–834. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Gazulla J and Tintore M: P/Q-type
voltage-dependent calcium channels in neurological disease.
Neurologia. 22:511–516. 2007.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jensen RL, Petr M and Wurster RD: Calcium
channel antagonist effect on in vitro meningioma signal
transduction pathways after growth factor stimulation.
Neurosurgery. 46:692–703. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lee YS, Sayeed MM and Wurster RD:
Inhibition of cell growth and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in
human brain tumor cells by Ca2+ channel antagonists. Mol Chem
Neuropathol. 22:81–95. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jensen RL, Origitano TC, Lee YS, Weber M
and Wurster RD: In vitro growth inhibition of growth
factor-stimulated meningioma cells by calcium channel antagonists.
Neurosurgery. 36:365–374. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Latour I, Louw DF, Beedle AM, Hamid J,
Sutherland GR and Zamponi GW: Expression of T-type calcium channel
splice variants in human glioma. Glia. 48:112–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Schorge S and Rajakulendran S: The P/Q
channel in human disease: untangling the genetics and physiology.
WIREs Membr Transp Signal. 1:311–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, van
Eijk R, Oefner PJ, Hoffman SM, Lamerdin JE, Mohrenweiser HW, Bulman
DE, Ferrari M, et al: Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic
ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene
CACNL1A4. Cell. 87:543–552. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhuchenko O, Bailey J, Bonnen P, Ashizawa
T, Stockton DW, Amos C, Dobyns WB, Subramony SH, Zoghbi HY, Lee CC,
et al: Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (SCA6) associated with
small polyglutamine expansions in the alpha1A-voltage-dependent
calcium channel. Nat Genet. 15:62–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bürk K, Kaiser FJ, Tennstedt S, Schöls L,
Kreuz FR, Wieland T, Strom TM, Büttner T, Hollstein R, Braunholz D,
et al: A novel missense mutation in CACNA1A evaluated by in silico
protein modeling is associated with non-episodic spinocerebellar
ataxia with slow progression. Eur J Med Genet. 57:207–211. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sintas C, Carreño O, Corominas R, Serra
SA, Vila M, Fernández-Castillo N, Toma C, Pons R, Llaneza M,
Sobrido MJ, et al: Screening of cacna1a and ATP1A2 genes in
hemiplegic migraine: Clinical, genetic and functional studies. J
Headache Pain. 14 Suppl 1:P262013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Verschuur-Maes AH, de Bruin PC and van
Diest PJ: Epigenetic progression of columnar cell lesions of the
breast to invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
136:705–715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Castro M, Grau L, Puerta P, Gimenez L,
Venditti J, Quadrelli S and Sánchez-Carbayo M: Multiplexed
methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes and clinical outcome
in lung cancer. J Transl Med. 8:862010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Burger PC, Yu I, Tihan T, et al: Atypical
teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system: A highly
malignant tumor of infancy and childhood frequently mistaken for
medulloblastoma: A pediatric oncology group study. Am J Surg
Pathol. 22:1083–1092. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Roderick HL and Cook SJ: Ca2+ signalling
checkpoints in cancer: Remodelling Ca2+ for cancer cell
proliferation and survival. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:361–375. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Varambally S, Cao X,
Yu J, Helgeson BE, Cao Q, Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Shah RB, et al:
Role of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia.
10:177–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chen R, Zeng X, Zhang R, Huang J, Kuang X,
Yang J, Liu J, Tawfik O, Thrasher JB and Li B: Cav1.3 channel α1D
protein is overexpressed and modulates androgen receptor
transactivation in prostate cancers. Urol Oncol. 32:524–536. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Liu Z, Christudass C, Zhang H, et al: A
novel quantitative histomorphological tool to assess multiple
biomarkers to predict prostate cancer aggression. Cancer Res. 74 19
Suppl:S40132014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ricci M, Xu Y, Hammond HL, Willoughby DA,
Nathanson L, Rodriguez MM, Vatta M, Lipshultz SE and Lincoln J:
Myocardial alternative RNA splicing and gene expression profiling
in early stage hypoplastic left heart syndrome. PLoS One.
7:e297842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dutton Regester K and Hayward NK:
Reviewing the somatic genetics of melanoma: From current to future
analytical approaches. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 25:144–154. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jones J, Otu H, Spentzos D, Kolia S, Inan
M, Beecken WD, Fellbaum C, Gu X, Joseph M, Pantuck AJ, et al: Gene
signatures of progression and metastasis in renal cell cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:5730–5739. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ginos MA, Page GP, Michalowicz BS, Patel
KJ, Volker SE, Pambuccian SE, Ondrey FG, Adams GL and Gaffney PM:
Identification of a gene expression signature associated with
recurrent disease in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Cancer Res. 64:55–63. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Estilo CL, O-charoenrat P, Talbot S, Socci
ND, Carlson DL, Ghossein R, Williams T, Yonekawa Y, Ramanathan Y,
Boyle JO, et al: Oral tongue cancer gene expression profiling:
Identification of novel potential prognosticators by
oligonucleotide microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 9:112009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Talbot SG, Estilo C, Maghami E, Sarkaria
IS, Pham DK, O-charoenrat P, Socci ND, Ngai I, Carlson D, Ghossein
R, et al: Gene expression profiling allows distinction between
primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinomas in the lung. Cancer
Res. 65:3063–3071. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Basso K, Margolin AA, Stolovitzky G, Klein
U, Dalla-Favera R and Califano A: Reverse engineering of regulatory
networks in human B cells. Nat Genet. 37:382–390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yoshihara K, Tajima A, Komata D, et al:
Gene expression profiling of advanced-stage serous ovarian cancers
distinguishes novel subclasses and implicates ZEB2 in tumor
progression and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 100:1421–1428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Rhodes DR, et al:
Integrative molecular concept modeling of prostate cancer
progression. Nat Genet. 39:41–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yusenko MV, Kuiper RP, Boethe T, Ljungberg
B, van Kessel AG and Kovacs G: High-resolution DNA copy number and
gene expression analyses distinguish chromophobe renal cell
carcinomas and renal oncocytomas. BMC Cancer. 9:1522009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Frierson HF Jr, El-Naggar AK, Welsh JB,
Sapinoso LM, Su AI, Cheng J, Saku T, Moskaluk CA and Hampton GM:
Large scale molecular analysis identifies genes with altered
expression in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Am J Pathol.
161:1315–1323. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Biewenga P, Buist MR, Moerland PD, Ver
Loren van Themaat E, van Kampen AH, ten Kate FJ and Baas F: Gene
expression in early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
108:520–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Hou J, Aerts J, den Hamer B, van Ijcken W,
den Bakker M, Riegman P, van der Leest C, van der Spek P, Foekens
JA, Hoogsteden HC, et al: Gene expression-based classification of
non-small cell lung carcinomas and survival prediction. PLoS One.
5:e103122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, Shimada Y,
Shiraishi K, Iwakawa R, Furuta K, Tsuta K, Shibata T, Yamamoto S,
et al: Identification of genes upregulated in ALK-positive and
EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res.
72:100–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W,
Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Fiel I, Thung S, Mazzaferro V, Bruix J, et
al: Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 45:938–947. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Detwiller KY, Fernando NT, Segal NH, Ryeom
SW, D'Amore PA and Yoon SS: Analysis of hypoxia-related gene
expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of
vascular endothelial cell growth factor A. Cancer Res.
65:5881–5889. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Rickman DS, Bobek MP, Misek DE, Kuick R,
Blaivas M, Kurnit DM, Taylor J and Hanash SM: Distinctive molecular
profiles of high-grade and low-grade gliomas based on
oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 61:6885–6891.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Shai R, Shi T, Kremen TJ, Horvath S, Liau
LM, Cloughesy TF, Mischel PS and Nelson SF: Gene expression
profiling identifies molecular subtypes of gliomas. Oncogene.
22:4918–4923. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hong Y, Downey T, Eu KW, Koh PK and Cheah
PY: A ‘metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair
proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications
for possible therapeutics. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:83–90. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Sabates-Bellver J, van der Flier LG, de
Palo M, et al: Transcriptome profile of human colorectal adenomas.
Mol Cancer Res. 5:1263–1275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
D'Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, Viti
V, Falchetti M, Calcagnile A, Sera F, Saieva C, Ottini L, Palli D,
et al: Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers
with microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 45:461–469. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Baumforth K, Wei
W, Dziechciarkova M, Ehrmann J, Klein J, Fridman E, Skarda J,
Srovnal J, et al: Novel markers for differentiation of lobular and
ductal invasive breast carcinomas by laser microdissection and
microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 7:552007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Li A, Su
Q, Donin NM, Pastorino S, Purow BW, Christopher N, Zhang W, et al:
Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and
EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary
tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 9:391–403.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Lee JS, Leem SH, Lee SY, Kim SC, Park ES,
Kim SB, Kim SK, Kim YJ, Kim WJ and Chu IS: Expression signature of
E2F1 and its associated genes predict superficial to invasive
progression of bladder tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:2660–2667. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J,
Li C, Monti S, Vasa P, Ladd C, Beheshti J, Bueno R, Gillette M, et
al: Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression
profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:pp. 13790–13795. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Gluck S, Ross JS, Royce M, McKenna EF Jr,
Perou CM, Avisar E and Wu L: TP53 genomics predict higher clinical
and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer
treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 132:781–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
French PJ, Swagemakers SM, Nagel JH,
Kouwenhoven MC, Brouwer E, van der Spek P, Luider TM, Kros JM, van
den Bent MJ and Smitt PA Sillevis: Gene expression profiles
associated with treatment response in oligodendrogliomas. Cancer
Res. 65:11335–11344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wang Q, Wen YG, Li DP, Xia J, Zhou CZ, Yan
DW, Tang HM and Peng ZH: Upregulated INHBA expression is associated
with poor survival in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 29:77–83. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Haslinger C, Schweifer N, Stilgenbauer S,
Döhner H, Lichter P, Kraut N, Stratowa C and Abseher R: Microarray
gene expression profiling of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
subgroups defined by genomic aberrations and VH mutation status. J
Clin Oncol. 22:3937–3949. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|