|
1
|
Cunningham SC, Suh HS, Winter JM,
Montgomery E, Schulick RD, Cameron JL and Yeo CJ: Retroperitoneal
paraganglioma: Single-institution experience and review of the
literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 10:1156–1163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lack EE, Cubilla AL, Woodruff JM and
Lieberman PH: Extra-adrenal paragangliomas of the retroperitoneum:
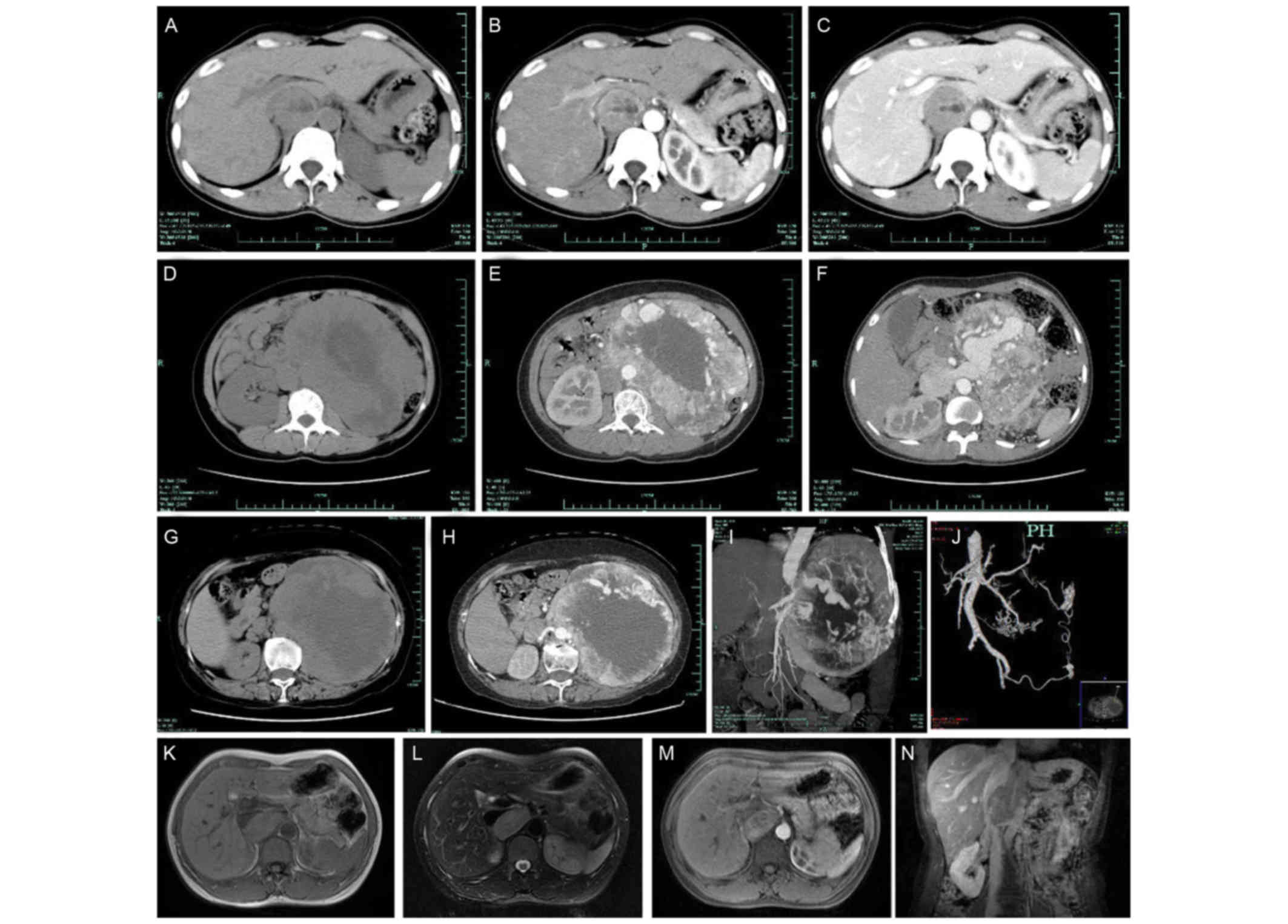
A clinicopathologic study of 12 tumors. Am J Surg Pathol.
4:109–120. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Noda T, Nagano H, Miyamoto A, Wada H,
Murakami M, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Takeda Y, Dono K, Umeshita K,
et al: Successful outcome after resection of liver metastasis
arising from an extraadrenal retroperitoneal paraganglioma that
appeared 9 years after surgical excision of the primary lesion. Int
J Clin Oncol. 14:473–477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sclafani LM, Woodruff JM and Brennan MF:
Extraadrenal retroperitoneal paragangliomas: Natural history and
response to treatment. Surgery. 108:1124–1130. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Melicow MM: One hundred cases of
pheochromocytoma (107 tumors) at the columbia-presbyterian medical
center, 1926–1976: A clinicopathological analysis. Cancer.
40:1987–2004. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Joynt KE, Moslehi JJ and Baughman KL:
Paragangliomas: Etiology, presentation and management. Cardiol Rev.
17:159–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boltze C, Mundschenk J, Unger N,
Schneider-Stock R, Peters B, Mawrin C, Hoang-Vu C, Roessner A and
Lehnert H: Expression profile of the telomeric complex
discriminates between benign and malignant pheochromocytoma. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:4280–4286. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strauss DC, Hayes AJ and Thomas JM:
Retroperitoneal tumours: Review of management. Ann R Coll Surg
Engl. 93:275–280. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Van Roggen JF and Hogendoorn PC: Soft
tissue tumours of the retroperitoneum. Sarcoma. 4:17–26. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Riordain DS, Young WF Jr, Grant CS,
Carney JA and van Heerden JA: Clinical spectrum and outcome of
functional extraadrenal paraganglioma. World J Surg. 20:916–922.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barski D: Management and follow up of
extra-adrenal phaeochromocytoma. Cent European J Urol. 67:156–161.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Manger WM: The vagaries of
pheochromocytomas. Am J Hypertens. 18:1266–1270. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baez JC, Jagannathan JP, Krajewski K,
O'Regan K, Zukotynski K, Kulke M and Ramaiya NH: Pheochromocytoma
and paraganglioma: Imaging characteristics. Cancer Imaging.
12:153–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brink I, Hoegerle S, Klisch J and Bley TA:
Imaging of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Fam Cancer. 4:61–68.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahdev A, Sohaib A, Monson JP, Grossman
AB, Chew SL and Reznek RH: CT and MR imaging of unusual locations
of extra-adrenal paragangliomas (pheochromocytomas). Eur Radiol.
15:85–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ji XK, Zeng QQ, Wu XL, Huang YP, Zhou MT,
Huang KT, Yu ZP, Han SL and Zhang QY: Surgical treatment and
prognostic analysis of retroperitoneal paragangliomas: A study of
19 cases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 90:2385–2388. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kimura N, Ishidate T, Kogawa T, Miura Y,
Ishizaka M and Ogita M: A retroperitoneal sympathetic paraganglioma
invading the duodenum and mimicking a submucosal tumor. Endocr
Pathol. 19:128–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inzani F, Rindi G, Tamborrino E, Cobelli R
and Bordi C: Extra-adrenal composite paraganglioma with
ganglioneuroma component presenting as a pancreatic mass. Endocr
Pathol. 20:191–195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
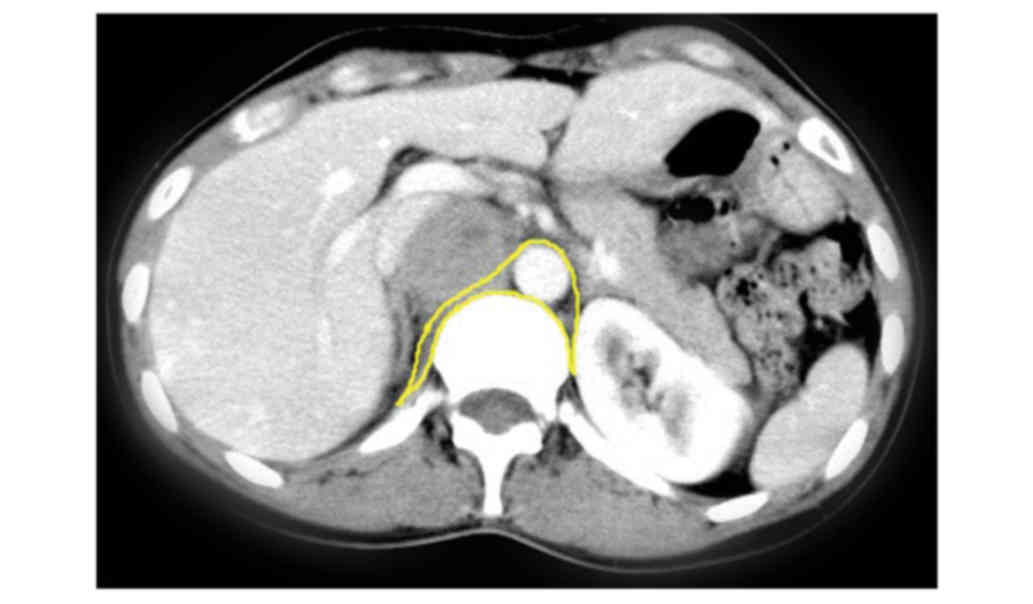
Sangster G, Do D, Previgliano C, Li B,
LaFrance D and Heldmann M: Primary retroperitoneal paraganglioma
simulating a pancreatic mass: A case report and review of the
literature. HPB Surg. 2010:6457282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Caumont-Prim A,
Houzard C, Hignette C, Hernigou A, Halimi P, Niccoli P, Leboulleux
S, Amar L, Borson-Chazot F, et al: Imaging work-up for screening of
paraganglioma and pheochromocytoma in SDHx mutation carriers: A
multicenter prospective study from the PGL.EVA investigators. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E162–E173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dalal T, Maher MM, Kalra MK and Mueller
PR: Extraadrenal pheochromocytoma: A rare cause of tachycardia and
hypertension during percutaneous biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
185:554–555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sood SK, Balasubramanian SP and Harrison
BJ: Percutaneous biopsy of adrenal and extra-adrenal
retroperitoneal lesions: Beware of catecholamine secreting tumours!
Surgeon. 5:1–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
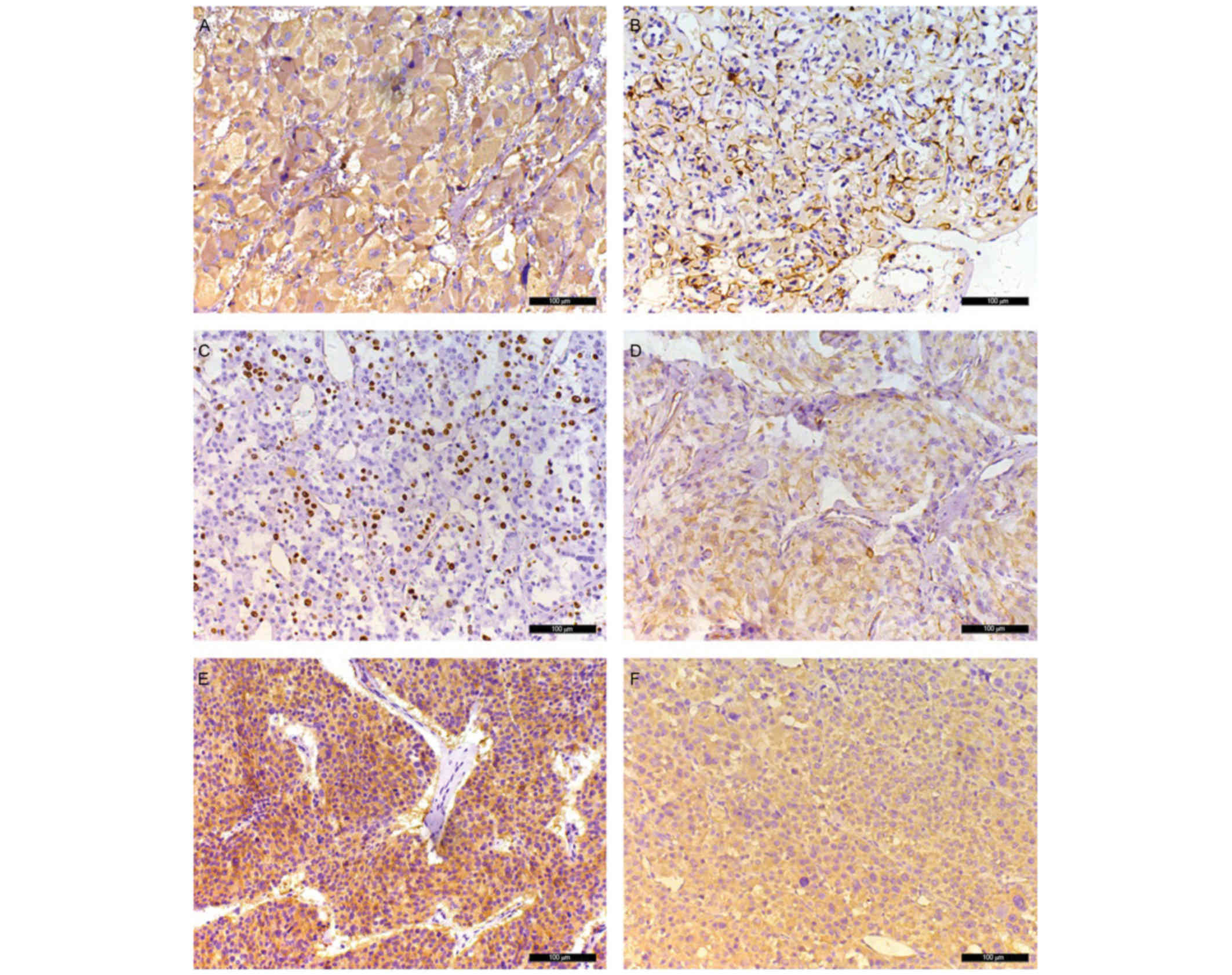
Kliewer KE, Wen DR, Cancilla PA and
Cochran AJ: Paragangliomas: Assessment of prognosis by histologic,
immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural techniques. Hum Pathol.
20:29–39. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Achilles E, Padberg BC, Holl K, Klöppel G
and Schröder S: Immunocytochemistry of paragangliomas-value of
staining for S-100 protein and glial fibrillary acid protein in
diagnosis and prognosis. Histopathology. 18:453–458. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pávai Z, Orosz Z, Horváth E, Seres-Sturm L
and Jung J: Immunohistochemical features of paragangliomas. J Cell
Mol Med. 5:311–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elder EE, Xu D, Höög A, Enberg U, Hou M,
Pisa P, Gruber A, Larsson C and Bäckdahl M: KI-67 and hTERT
expression can aid in the distinction between malignant and benign
pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Mod Pathol. 16:246–255. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feng N, Zhang WY and Wu XT:
Clinicopathological analysis of paraganglioma with literature
review. World J Gastroenterol. 15:3003–3008. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Korevaar TI and Grossman AB:
Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas: Assessment of malignant
potential. Endocrine. 40:354–365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varma K, Jain S and Mandal S:
Cytomorphologic spectrum in paraganglioma. Acta Cytol. 52:549–556.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thompson LD: Pheochromocytoma of the
adrenal gland scaled score (PASS) to separate benign from malignant
neoplasms: A clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 100
cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 26:551–566. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Agarwal A, Mehrotra PK, Jain M, Gupta SK,
Mishra A, Chand G, Agarwal G, Verma AK, Mishra SK and Singh U: Size
of the tumor and pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland scaled score
(PASS): Can they predict malignancy? World J Surg. 34:3022–3028.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu D, Tischler AS, Lloyd RV, DeLellis RA,
de Krijger R, van Nederveen F and Nosé V: Observer variation in the
application of the pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland scaled
score. Am J Surg Pathol. 33:599–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Somasundar P, Krouse R, Hostetter R,
Vaughan R and Covey T: Paragangliomas- a decade of clinical
experience. J Surg Oncol. 74:286–290. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Altergott R, Barbato A, Lawrence A,
Paloyan E, Freeark RJ and Prinz RA: Spectrum of
catecholamine-secreting tumors of the organ of Zuckerkandl.
Surgery. 98:1121–1126. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Heerden JA, Roland CF, Carney JA,
Sheps SG and Grant CS: Long-term evaluation following resection of
apparently benign pheochromocytoma(s)/paraganglioma(s). World J
Surg. 14:325–329. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Matsui H, Ikeuchi S, Onoda N and Tsutsumi
Y: Malignant paraganglioma of the retroperitoneum with lung
metastases: A 13-year survivor after radical surgery. Asian J Surg.
30:75–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pacak K: Preoperative management of the
pheochromocytoma patient. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 92:4069–4079.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lebuffe G, Dosseh ED, Tek G, Tytgat H,
Moreno S, Tavernier B, Vallet B and Proye CA: The effect of calcium
channel blockers on outcome following the surgical treatment of
phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Anaesthesia. 60:439–444.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|