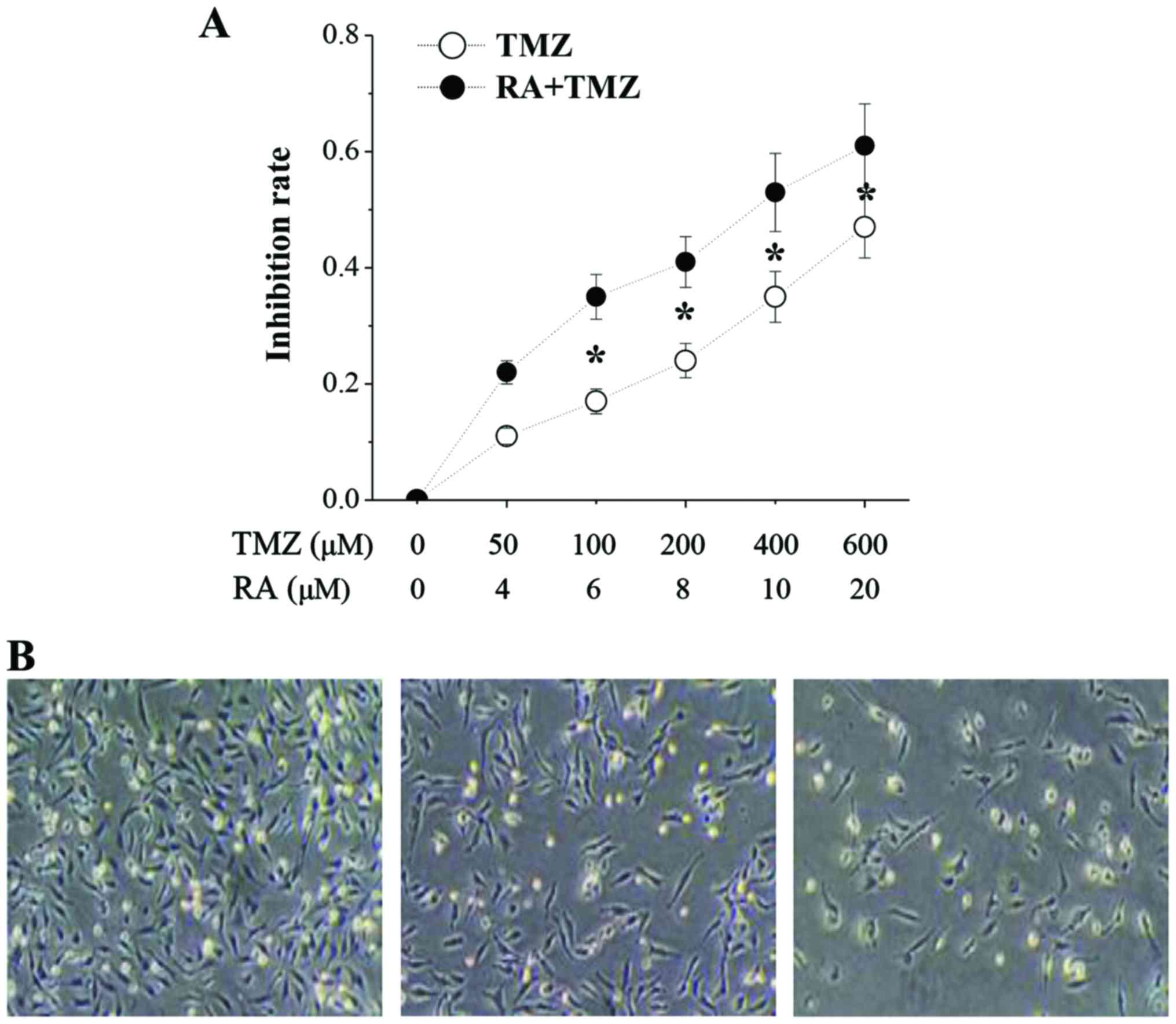
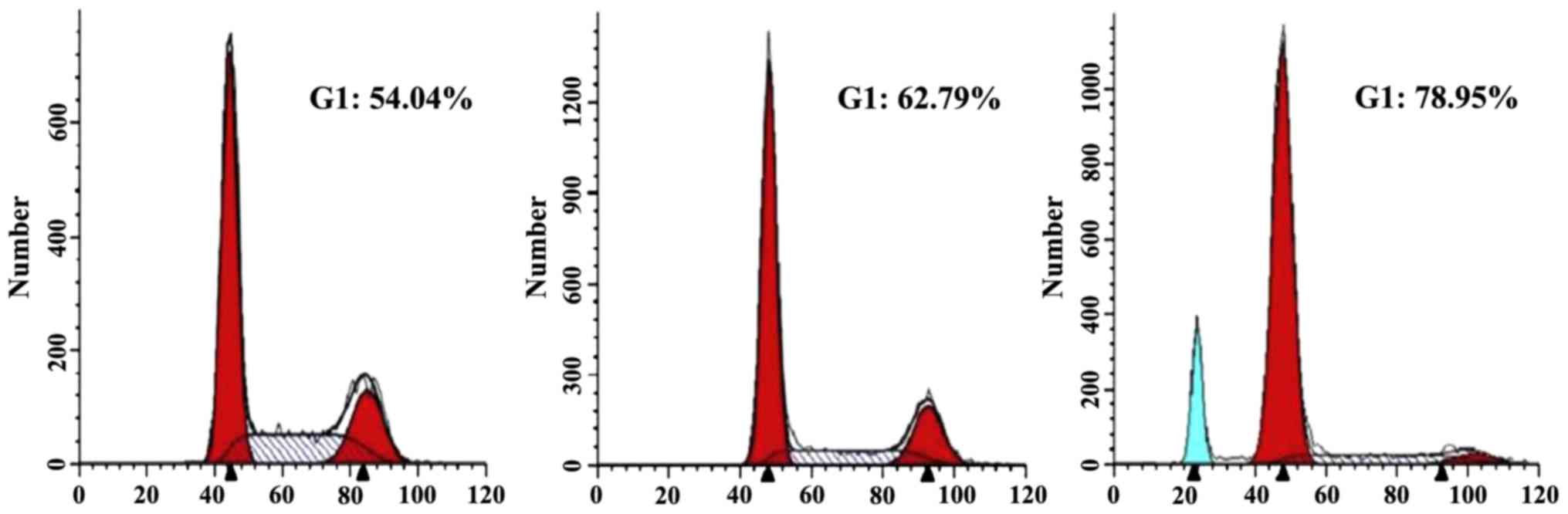
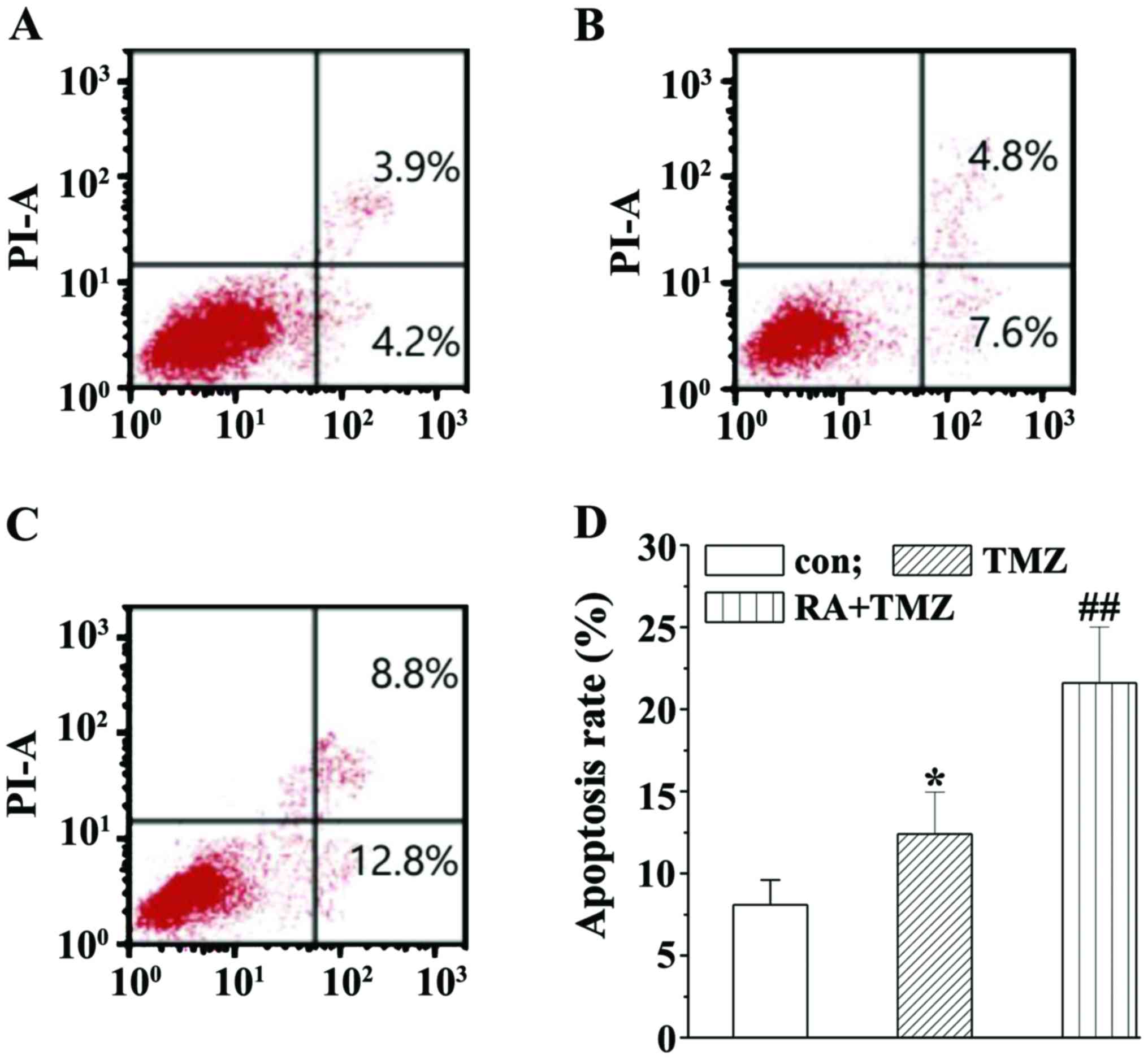
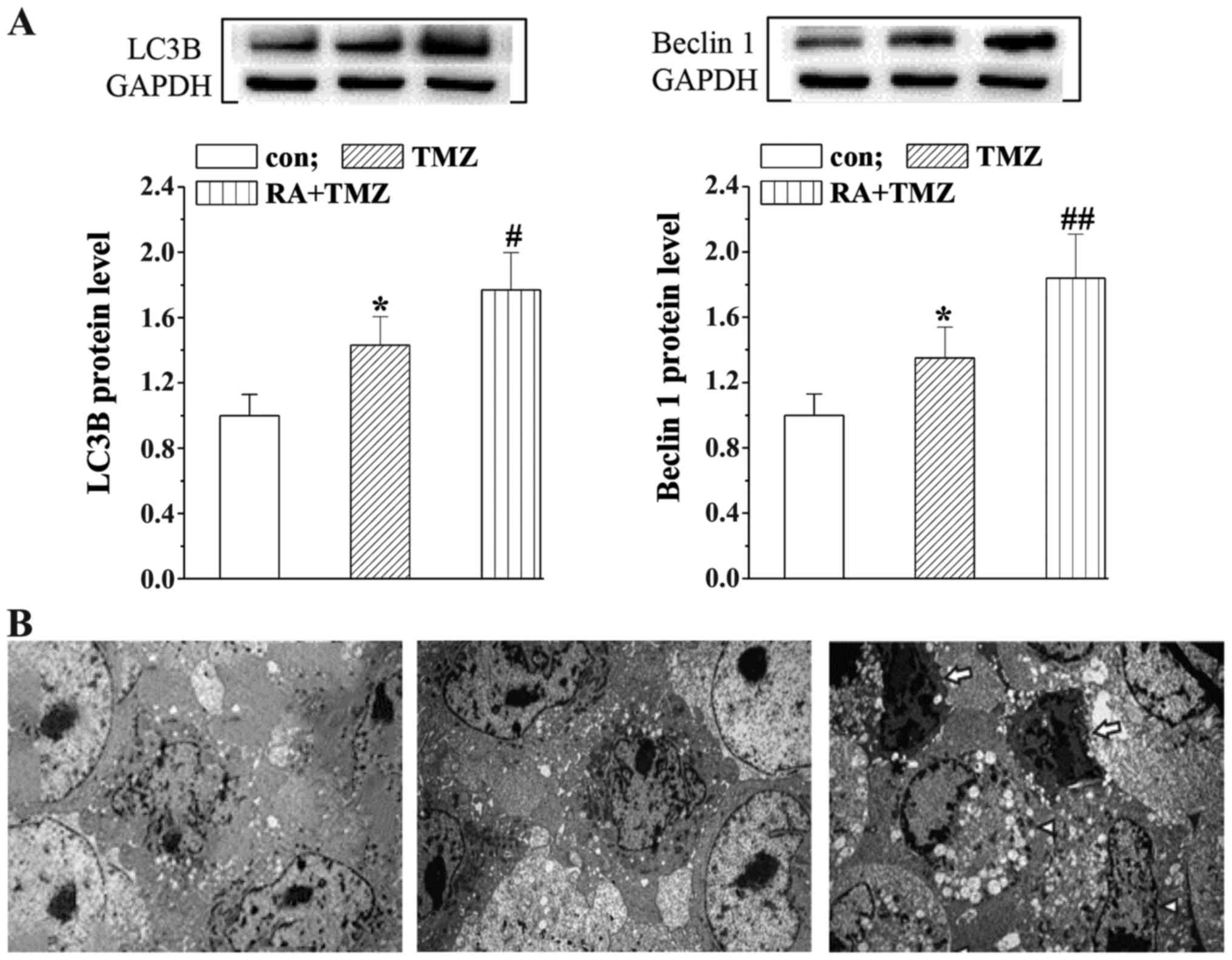
|
1
|
Hathout L, Ellingson BM, Cloughesy T and
Pope WB: A novel bicompartmental mathematical model of glioblastoma
multiforme. Int J Oncol. 46:825–832. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huse JT and Holland EC: Targeting brain
cancer: Advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and
medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:319–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bryukhovetskiy IS, Dyuizen IV, Shevchenko
VE, Bryukhovetski AS, Mischenko PV, Milkina EV and Khotimchenko YS:
Hematopoietic stem cells as a tool for the treatment of
glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Med Rep. 14:4511–4520. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Knisely JP and Baehring JM: A silver
lining on the horizon for glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 10:434–435.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nanegrungsunk D, Onchan W, Chattipakorn N
and Chattipakorn SC: Current evidence of temozolomide and
bevacizumab in treatment of gliomas. Neurol Res. 37:167–183. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Messaoudi K, Clavreul A and Lagarce F:
Toward an effective strategy in glioblastoma treatment. Part II:
RNA interference as a promising way to sensitize glioblastomas to
temozolomide. Drug Discov Today. 20:772–779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wait SD, Prabhu RS, Burri SH, Atkins TG
and Asher AL: Polymeric drug delivery for the treatment of
glioblastoma. Neuro-oncol. 17 Suppl 2:ii9–ii23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu YS, Wang Q, Ma JX, Yang XH, Wu ML,
Zhang KL, Kong QY, Chen XY, Sun Y, Chen NN, et al: CRABP-II
methylation: A critical determinant of retinoic acid resistance of
medulloblastoma cells. Mol Oncol. 6:48–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sakoe Y, Sakoe K, Kirito K, Ozawa K and
Komatsu N: FOXO3A as a key molecule for all-trans retinoic
acid-induced granulocytic differentiation and apoptosis in acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 115:3787–3795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Manor D, Shmidt EN, Budhu A,
Flesken-Nikitin A, Zgola M, Page R, Nikitin AY and Noy N: Mammary
carcinoma suppression by cellular retinoic acid binding protein-II.
Cancer Res. 63:4426–4433. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Niederreither K, Abu-Abed S, Schuhbaur B,
Petkovich M, Chambon P and Dollé P: Genetic evidence that oxidative
deriva tives of retinoic acid are not involved in retinoid
signaling during mouse development. Nat Genet. 31:84–88.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jacobs S, Lie DC, DeCicco KL, Shi Y,
DeLuca LM, Gage FH and Evans RM: Retinoic acid is required early
during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:pp. 3902–3907. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N,
Zhang M, Han W, Lou F, Yang J, Zhang Q, et al: Autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer
treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett
N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D and Yahalom J: A novel response
of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of
acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fulda S and Kögel D: Cell death by
autophagy: Emerging molecular mechanisms and implications for
cancer therapy. Oncogene. 34:5105–5113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Vicencio JM, Kepp
O, Joza N, Tajeddine N and Kroemer G: Life, death and burial:
Multifaceted impact of autophagy. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:786–790.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Autophagy and
signaling: Their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 12 Suppl 2:1509–1518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Jia X, Wang K, Bao J, Li P, Chen
M, Wan JB, Su H, Mei Z and He C: Polyphyllin VII induces an
autophagic cell death by activation of the JNK pathway and
inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in HepG2 cells. PLoS One.
11:e01474052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cao Y and Klionsky DJ: Physiological
functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: A unique autophagy-related protein.
Cell Res. 17:839–849. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan Y, Xu Z, Dai S, Qian L, Sun L and Gong
Z: Targeting autophagy to sensitive glioma to temozolomide
treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang C, Zhu Q, He H, Jiang L, Qiang Q, Hu
L, Hu G, Jiang Y, Ding X and Lu Y: RIZ1: A potential tumor
suppressor in glioma. BMC Cancer. 15:9902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang C, Cai Z, Liang Q, Wang Q, Lu Y, Hu
L and Hu G: RLIP76 depletion enhances autophagic flux in U251
cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:555–562. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced
cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ.
11:448–457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shinojima N, Yokoyama T, Kondo Y and Kondo
S: Roles of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in
curcumin-induced autophagy. Autophagy. 3:635–637. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Natsumeda M, Maitani K, Liu Y, Miyahara H,
Kaur H, Chu Q, Zhang H, Kahlert UD and Eberhart CG: Targeting notch
signaling and autophagy increases cytotoxicity in glioblastoma
neurospheres. Brain Pathol. 26:713–723. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Meng D, Wang H, Sun R, Wang D,
Wang S, Fan J, Zhao Y, Wang J, Yang S, et al: VAMP8 facilitates
cellular proliferation and temozolomide resistance in human glioma
cells. Neuro Oncol. 17:407–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pratt J and Annabi B: Induction of
autophagy biomarker BNIP3 requires a JAK2/STAT3 and MT1-MMP
signaling interplay in Concanavalin-A-activated U87 glioblastoma
cells. Cell Signal. 26:917–924. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bordin DL, Lima M, Lenz G, Saffi J, Meira
LB, Mésange P, Soares DG, Larsen AK, Escargueil AE and Henriques
JA: DNA alkylation damage and autophagy induction. Mutat Res.
753:91–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wagner E, Luo T, Sakai Y, Parada LF and
Dräger UC: Retinoic acid delineates the topography of neuronal
plasticity in postnatal cerebral cortex. Eur J Neurosci.
24:329–340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baharvand H, Mehrjardi NZ, Hatami M, Kiani
S, Rao M and Haghighi MM: Neural differentiation from human
embryonic stem cells in a defined adherent culture condition. Int J
Dev Biol. 51:371–378. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|