|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mangeksdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M,
Herrlich P, Schütz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M,
Chambon P and Evans RM: The nuclear receptor superfamily: The
second decade. Cell. 83:835–839. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McKenna NJ, Cooney AJ, DeMayo FJ, Downes
M, Glass CK, Lanz RB, Lazar MA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Moore DD, Qin J, et
al: Minireview: Evolution of NURSA, the nuclear receptor signaling
atlas. Mol Endocrinol. 23:740–746. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chuu CP, Kokontis JM, Hilpakka RA and Liao
S: Modulation of liver X receptor signaling as novel therapy for
prostate cancer. J Biomed Sci. 14:543–553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wójcicka G, Jamroz-Wisniewska A,
Horoszewicz K and Beltowski J: Liver X receptors (LXRs). Part I:
Structure, function, regulation of activity, and role in lipid
metabolism. Postepy Hig Med Dows (Online). 61:736–759. 2007.
|
|
7
|
Lo Sasso G, Bovenga F, Murzili S,
Salvatore L, Di Tullio G, Martelli N, D'Orazio A, Rainaldi S, Vacca
M, Mangia A, et al: Liver X receptors inhibit proliferation of
human colorectal cancer cells and growth of intestinal tumors in
mice. Gastroenterology. 144(1497–1507): e1–e13. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Fukuchi J, Kokontis JM, Hiipakka RA, Chuu
CP and Liao S: Antiproliferative effect of liver X receptor
agonists on LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
64:7686–7689. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chuu CP, Hiipakka RA, Kokontis JM, Fukuchi
J, Chen RY and Liao S: Inhibition of tumor growth and progression
of LNCaP prostate cancer cells in athymic mice by androgen and
liver X receptor agonist. Cancer Res. 66:6482–6486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pommier AJ, Alves G, Viennois E, Bernard
S, Communal Y, Sion B, Marceau G, Damon C, Mouzat K, Caira F, et
al: Liver X receptor activation downregulates AKT survival
signaling in lipid rafts and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer
cells. Oncogene. 29:2712–2723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vedin LL, Lewandowski SA, Parini P,
Gustafsson JA and Steffensen KR: The oxysterol receptor LXR
inhibits proliferation of human breast cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 30:575–579. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Uno S, Endo K, Jeong Y, Kawana K, Miyachi
H, Hashimoto Y and Makishima M: Suppression of beta-catenin
signaling by liver X receptor ligands. Biochem Pharmacol.
77:186–195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Scoles DR, Xu X, Wang H, Tran H,
Taylor-Harding B, Li A and Karlan BY: Liver X receptor agonist
inhibits proliferation of ovarian carcinoma cells stimulated by
oxidized low density lipoprotein. Gynecol Oncol. 116:109–116. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Geyeregger R, Shehata M, Zeyda M, Kiefer
FW, Stuhlmeier KM, Porpaczy E, Zlabinger GJ, Jäger U and Stulnig
TM: Liver X receptors interfere with cytokine-induced proliferation
and cell survival in normal and leukemic lymphocytes. J Leukoc
Biol. 86:1039–1048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakayama K, Nagahama H, Minamishima YA,
Matsumoto M, Nakamichi I, Kitagawa K, Shirane M, Tsunematsu R,
Tsukiyama T, Ishida N, et al: Targeted disruption of Skp2 results
in accumulation of cyclin E and (p27)Kip, polyploidy and centrosome
overduplication. EMBO J. 19:2069–2081. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blaschke F, Leppanen O, Takata Y, Caglayan
E, Liu J, Fishbein MC, Kappert K, Nakayama KI, Collins AR, Fleck E,
et al: Liver X receptor agonists suppress vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation and inhibit neointima formation in
balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Cir Res. 95:e110–e123. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fan YY, Spencer TE, Wang N, Moyer MP and
Chapkin RS: Chemopreventive n-3 fatty acids activate RXRalpha in
colonocytes. Carcinogenesis. 24:1541–1548. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang SY, Shen SR, Shyu RY, Yu JC, Harn
HJ, Yeh MY, Lee MM and Chang YC: Expression of nuclear retinoid
receptors in normal, premalignant and malignant gastric tissues
determined by in situ hybridization. Br J Cancer. 80:206–214. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar R, Shoemaker AR and Verma AK:
Retinoic acid nuclear receptors and tumor promotion: Decreased
expression of retinoic acid nuclear receptors by the tumor promoter
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Carcinogenesis. 15:701–705.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu XC, Sozzi G, Lee JS, Lee JJ, Pastorino
U, Pilotti S, Kurie JM, Hong WK and Lotan R: Suppression of
retinoic acid receptor beta in non-small-cell lung cancer in vivo:
Implications for lung cancer development. J Natl Cancer Inst.
89:624–629. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang YA, Han WF, Morin PJ, Chrest FJ and
Pizer ES: Activation of fatty acid synthesis during neoplastic
transformation: Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Exp Cell Res. 279:80–90. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Yu, Morin PJ, Han WF, Chen T, Bomman
DM, Gabrielson EW and Pizer ES: Regulation of fatty acid synthase
expression in breast cancer by sterol regulatory element binding
protein-1c. Exp Cell Res. 282:132–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun Y, He W, Luo M, Zhou Y, Chang G, Ren
W, Wu K, Li X, Shen J, Zhao X and Hu Y: SREBP1 regulates
tumorigenesis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer through targeting
lipid metabolism. Tumour Biol. 36:4133–4141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smirnov DA, Hou S, Liu X, Claudio E,
Siebenlist UK and Ricciardi RP: COUP-TFII is up-regulated in
adenovirus type 12 tumorigenic cells and is a repressor of MHC
class I transcription. Virology. 284:13–19. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Navab R, Wang Y, Chow YH, Wang A, Jankov
RP, Takamoto N, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, Tanswell AK and Hu J: Regulation
of human Clara cell 10 kD protein expression by chicken ovalbumin
upstream promoter transcription factors (COUP-TFs). Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 27:273–285. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai MJ and O'Malley BW: Molecular
mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily
members. Annu Rev Biochem. 63:451–486. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Navab R, Gonzalez-Santos JM, Johnston MR,
Liu J, Brodt P, Tsao MS and Hu J: Expression of chicken ovalbumin
upstream promoter-transcription factor II enhances invasiveness of
human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 64:5097–5105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakshatri H, Mendonca MS, Bhat-Nakshatri
P, Patel NM, Goulet RJ Jr and Cornetta K: The orphan receptor
COUP-TFII regulates G2/M progression of breast cancer cells by
modulating the expression/activity of p21(WAF1/CIP1), cyclin D1,
and cdk2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 270:1144–1153. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Safe S, Jin UH, Hedrick E, Reeder A and
Lee SO: Minireview: Role of orphan nuclear receptors in cancer and
potential as drug targets. Mol Endocrinol. 28:157–172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Litchfield LM and Klinge CM: Multiple
roles of COUP-TFII in cancer initiation and progression. J Mol
Endocrinol. 49:R135–R148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin J, Tsai SY and Tsai MJ: The critical
roles of COUP-TFII in tumor progression and metastasis. Cell
Biosci. 4:582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boudot A, Le Dily F and Pakdel F:
Involvement of COUP-TFs in cancer progression. Cancers (Basel).
3:700–715. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shin SW, Kwon HC, Rho MS, Choi HJ, Kwak JY
and Park JI: Clinical significance of chicken ovalbumin upstream
promoter-transcription factor II expression in human colorectal
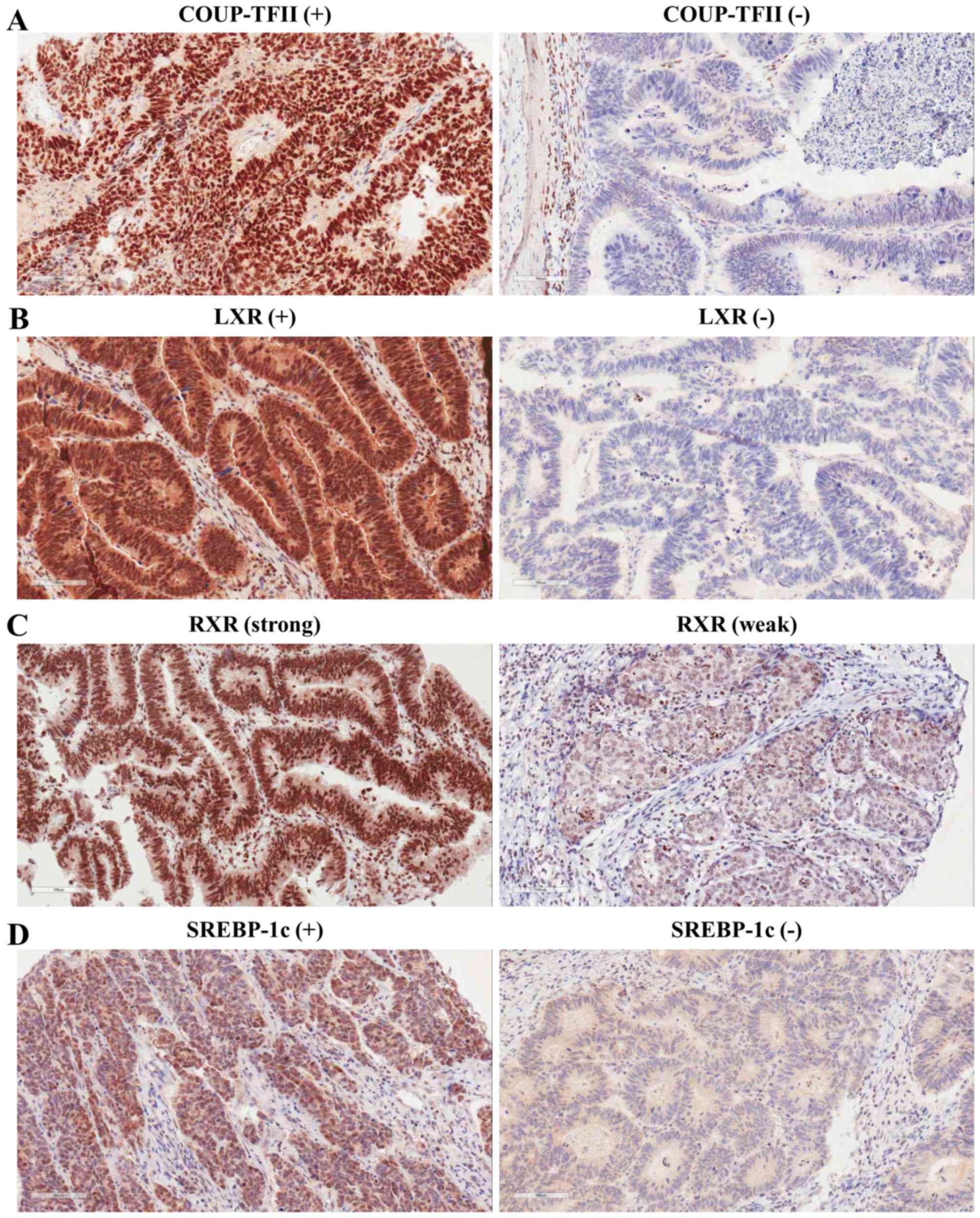
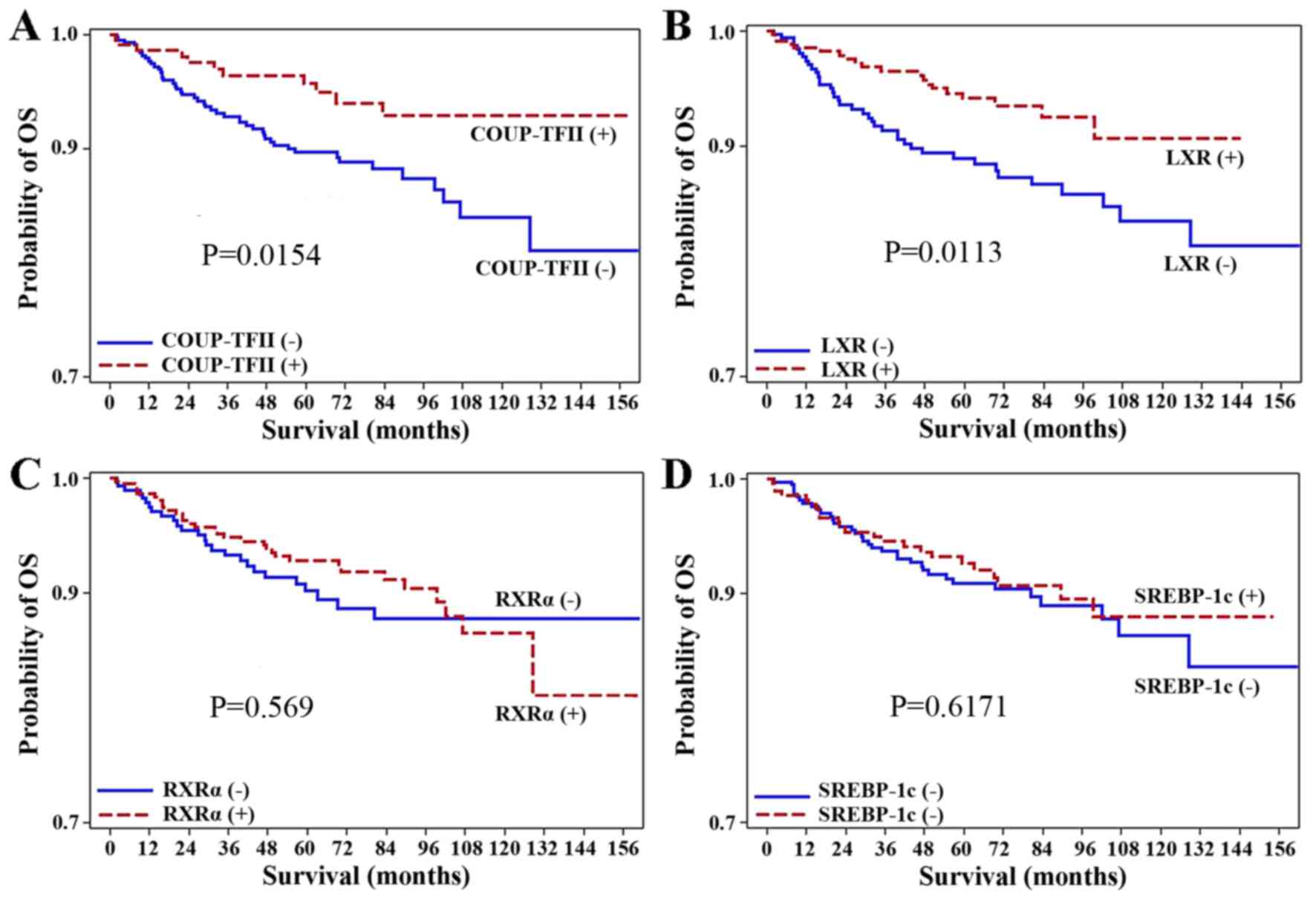
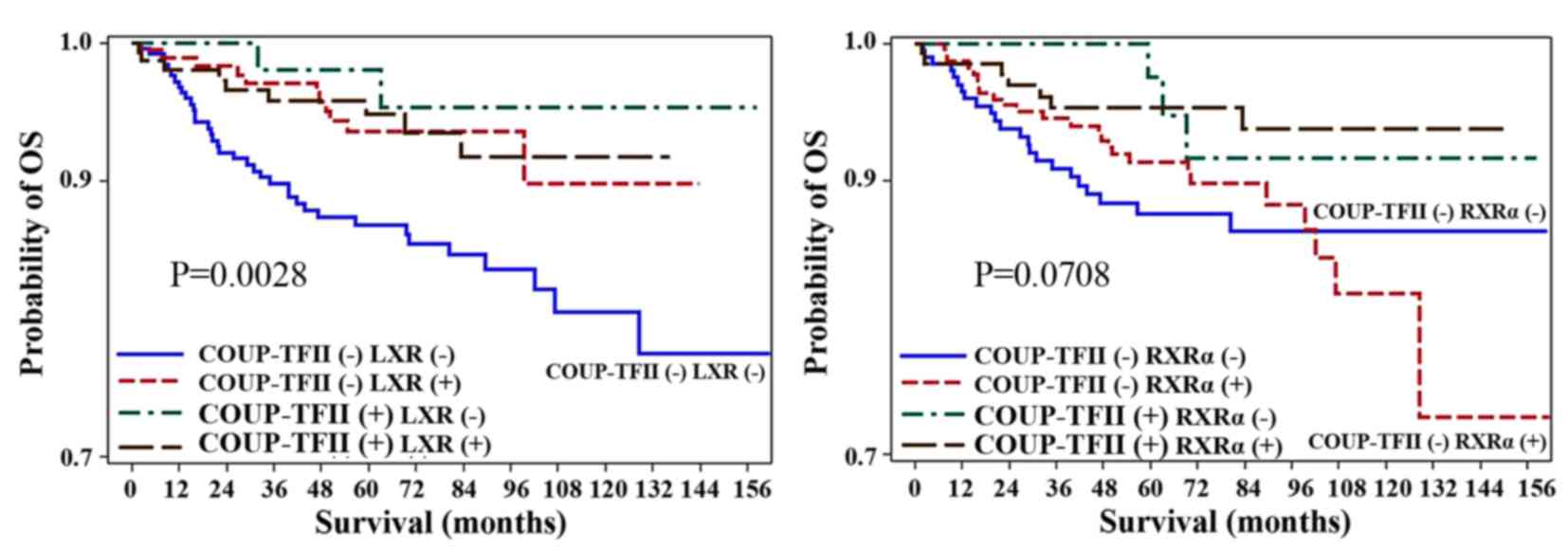
cancer. Oncol Rep. 21:101–106. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lan YT, Yang SH, Chang SC, Liang WY, Li
AF, Wang HS, Jiang JK, Chen WS, Lin TC and Lin JK: Analysis of the
seventh edition of American Joint Committee on colon cancer
staging. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:657–663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hsu FD, Nielsen TO, Alkushi A, Dupuis B,
Huntsman D, Liu CL, van de Rijn M and Gilks CB: Tissue microarrays
are an effective quality assurance tool for diagnostic
immunohistochemistry. Mod Pathol. 15:1374–1380. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang C, Han Y, Huang H, Qu L and Shou C:
High NR2F2 transcript is associated with increased survival and its
expression inhibits TGF-β-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 147:265–281.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bao Y, Gu D, Feng W, Sun X, Wang X, Zhang
X, Shi Q, Cui G, Yu H, Tang C and Deng A: COUP-TFII regulates
metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells by modulating Snail1.
Br J Cancer. 111:933–943. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bringuier PP, Schalken JA, Hervieu V and
Giroldi LA: Involvement of orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII in
cadherin-6 and cadherin-11 regulation: implications in development
and cancer. Mech Dev. 136:64–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|