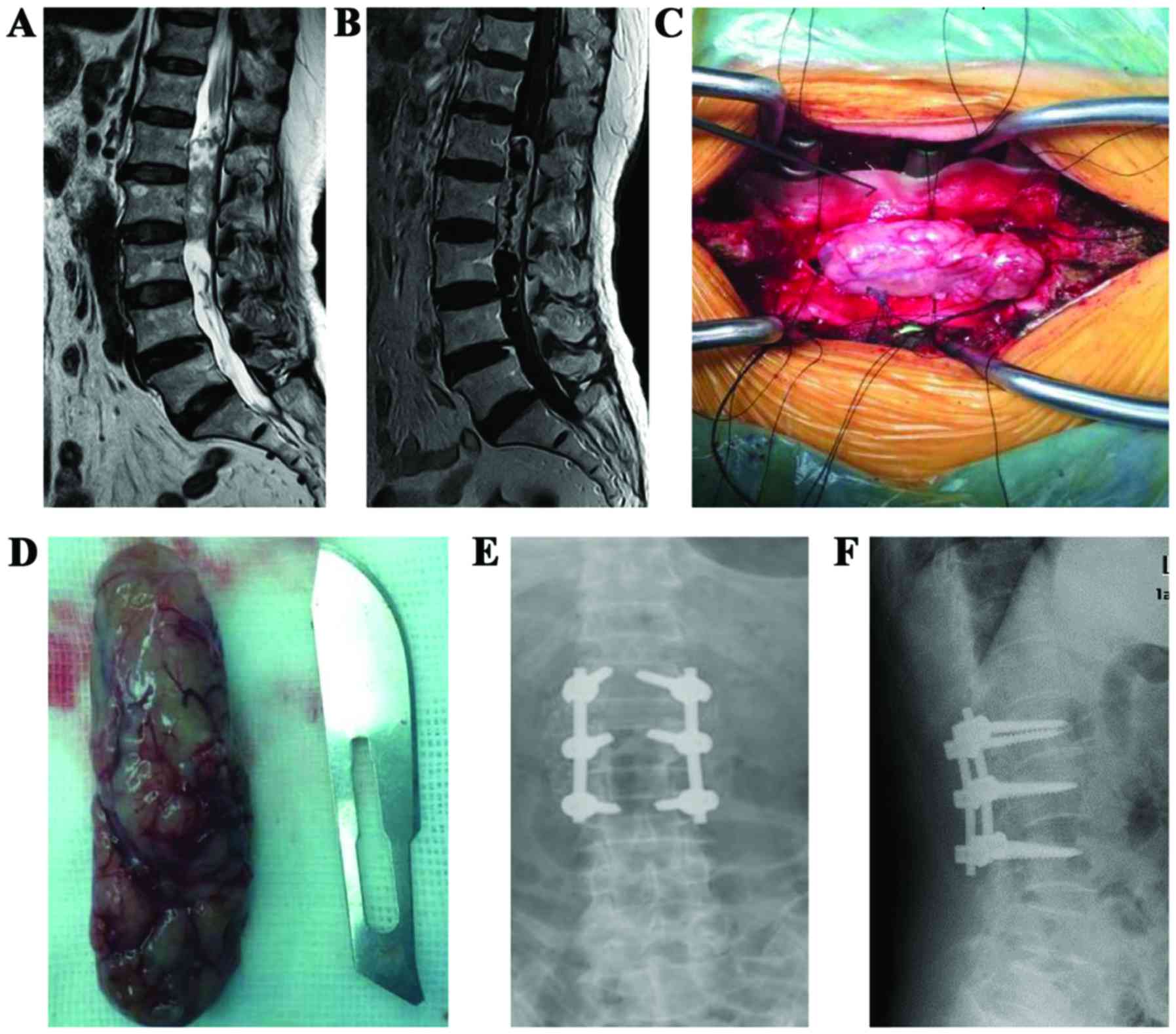
|
1
|
Weber C, Gulati S, Jakola AS, Habiba S,
Nygaard ØP, Johannesen TB and Solheim O: Incidence rates and
surgery of primary intraspinal tumors in the era of modern
neuroimaging: A national population-based study. Spine.
39:E967–E973. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan Z, Yang G, He H, Zhao G, Yuan T and Li
Y, Shi W, Gao P, Dong L and Li Y: Concurrent radiotherapy and
intrathecal methotrexate for treating leptomeningeal metastasis
from solid tumors with adverse prognostic factors: A prospective
and single-arm study. Int J Cancer. 139:1864–1872. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sowash M, Barzilai O, Kahn S, McLaughlin
L, Boland P, Bilsky MH and Laufer I: Clinical outcomes following
resection of giant spinal schwannomas: A case series of 32
patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 26:494–500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merhemic Z, Stosic-Opincal T and Thurnher
MM: Neuroimaging of Spinal Tumors. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am.
24:563–579. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Safaee MM, Lyon R, Barbaro NM, Chou D,
Mummaneni PV, Weinstein PR, Chin CT, Tihan T and Ames CP:
Neurological outcomes and surgical complications in 221 spinal
nerve sheath tumors. J Neurosurg Spine. 26:103–111. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
dos Santos MP, Zhang J, Ghinda D,
Glikstein R, Agid R, Rodesch G, Tampieri D and terBrugge KG:
Imaging diagnosis and the role of endovascular embolization
treatment for vascular intraspinal tumors. Neurosurg Focus.
39:E162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masaryk TJ: Neoplastic disease of the
spine. Radiol Clin North Am. 29:829–845. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bendszus M, Urbach H, Wolf HK, Schramm J
and Solymosi L: Magnetic resonance imaging of intraspinal melanotic
schwannoma. Eur Radiol. 8:11971998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee RR: MR imaging of intradural tumors of
the cervical spine. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 8:529–540.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahn DK, Park HS, Choi DJ, Kim KS, Kim TW
and Park SY: The surgical treatment for spinal intradural
extramedullary tumors. Clin Orthop Surg. 1:165–172. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zong S, Wu Y, Tao Y, Chen X, Fang Y, Du L,
Zhao J and Zeng G: Treatment results in different surgical
approaches for intraspinal tumor in 51 patients. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:16627–16633. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Viereck MJ, Ghobrial GM, Beygi S and
Harrop JS: Improved patient quality of life following intradural
extramedullary spinal tumor resection. J Neurosurg Spine.
25:640–645. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Ni M, Liu WM, Jia W, Jia GJ and
Zhang JT: Intra- and extramedullary dumbbell-shaped schwannoma of
the medulla oblongata: A case report and review of the literature.
World Neurosurg. 98:873.e1–873.e7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Iacopino DG, Giugno A, Gulì C, Basile L,
Graziano F and Maugeri R: Surgical nuances on the treatment of
giant dumbbell cervical spine schwannomas: Description of a
challenging case and review of the literature. Spinal Cord Ser
Cases. 2:150422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Das JM and Peethambaran A: Total excision
of a giant ventral midline cervical spinal intradural schwannoma
via posterior approach. Asian Spine J. 10:153–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schultheiss R and Gullotta G: Resection of
relevant nerve roots in surgery of spinal neurinomas without
persisting neurological deficit. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 122:91–96.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Celli P: Treatment of relevant nerve roots
involved in nerve sheath tumors: Removal or preservation?
Neurosurgery. 51:684–692. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang P, He X, Li H, Zang Q and Wang G:
Therapy for thoracic lumbar and sacral vertebrae tumors using total
spondylectomy and spine reconstruction through posterior or
combined anterior-posterior approaches. Oncol Lett. 11:1778–1782.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hussein HA and Goda HA: Paravertebral
neurogenic tumors with intraspinal extension: Preoperative
evaluation and surgical approach. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 21:12–22.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang B, Wang Y, He X and Li H: Treatment
for thoracic ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament with
posterior circumferential decompression: Complications and
managements. J Orthop Surg. 11:1532016. View Article : Google Scholar
|