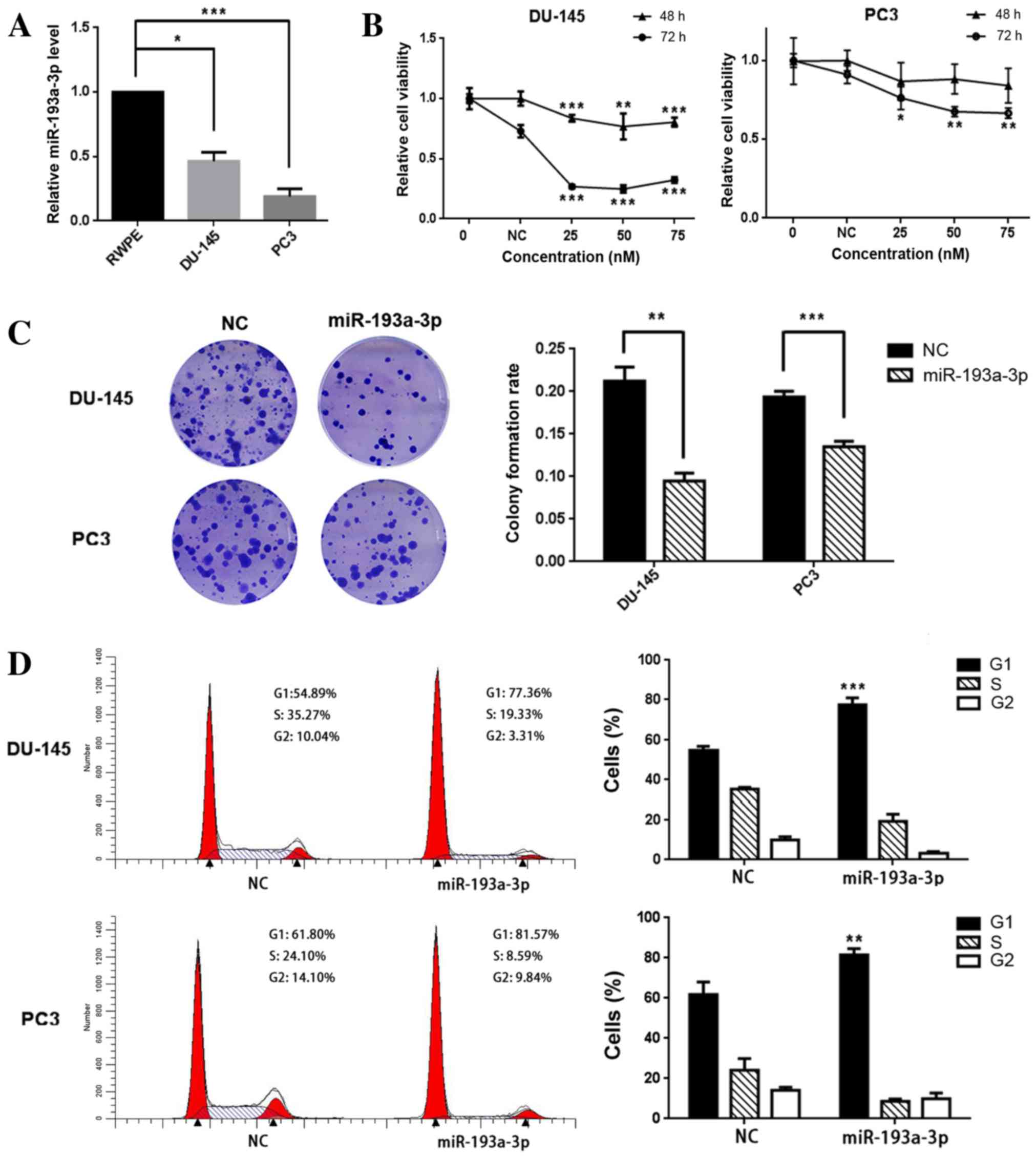
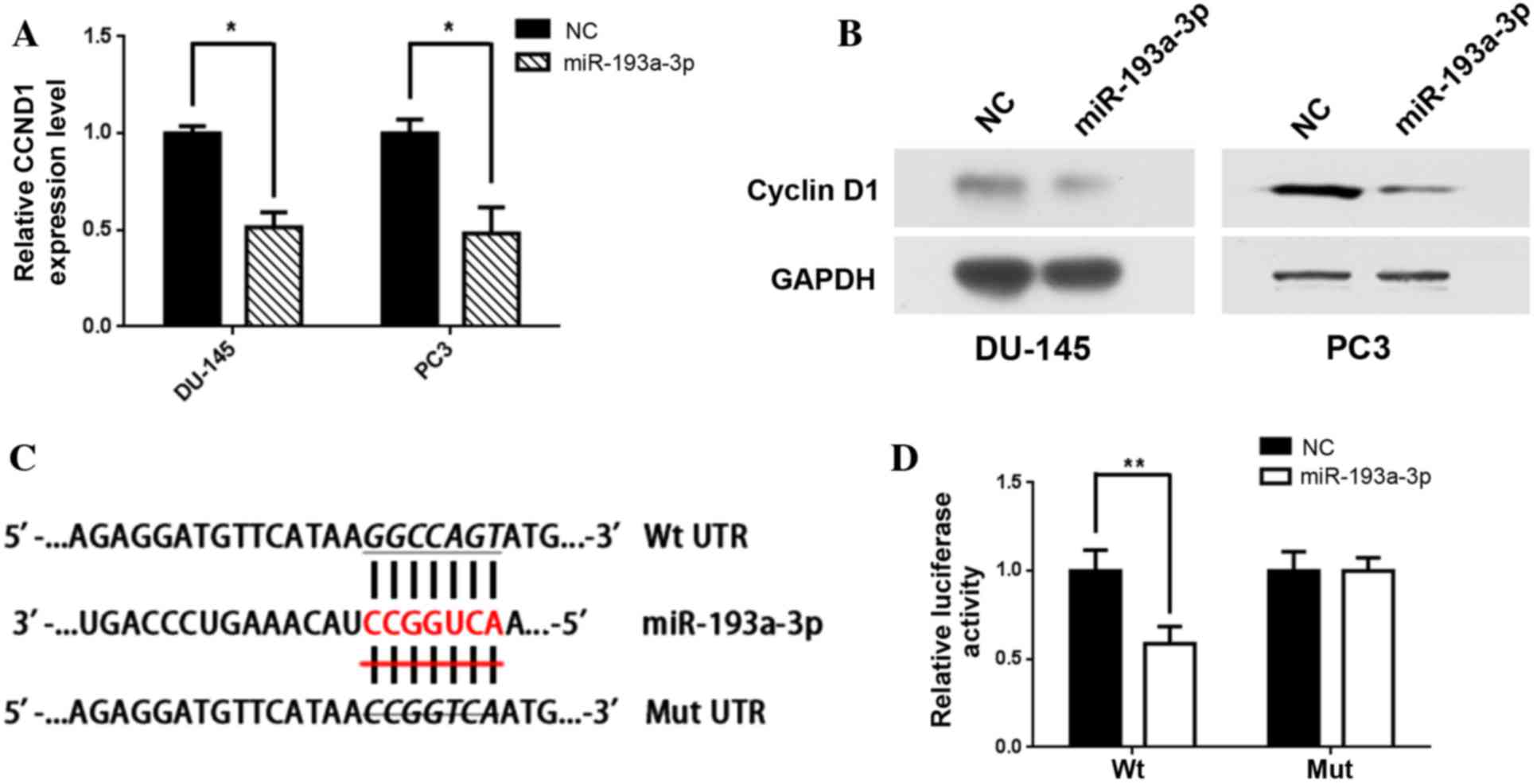
|
1
|
NCI: SEER stat fact sheets: Prostate
cancer. In: Surveillance, epidemiology and end results program.
National Institute of Health. 2013 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE36802Accessed.
September 4–2013.
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fendler A, Jung M, Stephan C, Erbersdobler
A, Jung K and Yousef GM: The antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in
prostate cancer by inhibition of FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e808072013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kojima S, Enokida H, Yoshino H, Itesako T,
Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Naya Y, et
al: The tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster inhibits cell
migration and invasion by targeting GOLM1 in prostate cancer. J Hum
Genet. 59:78–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arora S, Saini S, Fukuhara S, Majid S,
Shahryari V, Yamamura S, Chiyomaru T, Deng G, Tanaka Y and Dahiya
R: MicroRNA-4723 inhibits prostate cancer growth through
inactivation of the abelson family of nonreceptor protein tyrosine
kinases. PLoS One. 8:e780232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang L, Li B, Li L and Wang T:
MicroRNA-497 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
prostate cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3499–3502. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He L, Yao H, Fan LH, Liu L, Qiu S, Li X,
Gao JP and Hao CQ: MicroRNA-181b expression in prostate cancer
tissues and its influence on the biological behavior of the
prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Genet Mol Res. 12:1012–1021. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao Y, Chen H, Lin Y, Xu X, Hu Z, Zhu Y,
Wu J, Xu X, Zheng X and Xie L: MicroRNA-330 inhibits cell motility
by downregulating Sp1 in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
30:327–333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Meyer J,
Borkhardt A and Tuschl T: New microRNAs from mouse and human. RNA.
9:175–179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kozaki K, Imoto I, Mogi S, Omura K and
Inazawa J: Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by
DNA hypermethylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68:2094–2105.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kietzmann L, Guhr SS, Meyer TN, Ni L,
Sachs M, Panzer U, Stahl RA, Saleem MA, Kerjaschki D, Gebeshuber CA
and Meyer-Schwesinger C: MicroRNA-193a regulates the
transdifferentiation of human parietal epithelial cells toward a
podocyte phenotype. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:1389–1401. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin PC, Chiu YL, Banerjee S, Park K,
Mosquera JM, Giannopoulou E, Alves P, Tewari AK, Gerstein MB,
Beltran H, et al: Epigenetic repression of miR-31 disrupts androgen
receptor homeostasis and contributes to prostate cancer
progression. Cancer Res. 73:1232–1244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allegra A, Alonci A, Campo S, Penna G,
Petrungaro A, Gerace D and Musolino C: Circulating microRNAs: New
biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer
(review). Int J Oncol. 41:1897–1912. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tay FC, Lim JK, Zhu H, Hin LC and Wang S:
Using artificial microRNA sponges to achieve microRNA
loss-of-function in cancer cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:117–127.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wojcicka A, de la Chapelle A and
Jazdzewski K: MicroRNA-related sequence variations in human
cancers. Hum Genet. 133:463–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim WT and Kim WJ: MicroRNAs in prostate
cancer. Prostate Int. 1:3–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiang XF, Zhang ZW, Liu Q, Sun N, Pan LL,
Shen J, Li T, Yun C, Li H and Shi LH: MiR-20a promotes prostate
cancer invasion and migration through targeting ABL2. J Cell
Biochem. 115:1269–1276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peters G: The D-type cyclins and their
role in tumorigenesis. J Cell Sci Suppl. 18:89–96. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee EY and Muller WJ: Oncogenes and tumor
suppressor genes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0032362010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jares P, Colomer D and Campo E: Molecular
pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 122:3416–3423.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaki T and Pestell
RG: Minireview: Cyclin D1: Normal and abnormal functions.
Endocrinology. 145:5439–5447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bienvenu F, Jirawatnotai S, Elias JE,
Meyer CA, Mizeracka K, Marson A, Frampton GM, Cole MF, Odom DT,
Odajima J, et al: Transcriptional role of cyclin D1 in development
revealed by a genetic-proteomic screen. Nature. 463:374–378. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aggarwal P, Vaites LP, Kim JK, Mellert H,
Gurung B, Nakagawa H, Herlyn M, Hua X, Rustgi AK, McMahon SB and
Diehl JA: Nuclear cyclin D1/CDK4 kinase regulates CUL4 expression
and triggers neoplastic growth via activation of the PRMT5
methyltransferase. Cancer Cell. 18:329–340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Casimiro MC, Crosariol M, Loro E, Ertel A,
Yu Z, Dampier W, Saria EA, Papanikolaou A, Stanek TJ, Li Z, et al:
ChIP sequencing of cyclin D1 reveals a transcriptional role in
chromosomal instability in mice. J Clin Invest. 122:833–843. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jirawatnotai S, Hu Y, Michowski W, Elias
JE, Becks L, Bienvenu F, Zagozdzon A, Goswami T, Wang YE, Clark AB,
et al: A function for cyclin D1 in DNA repair uncovered by protein
interactome analyses in human cancers. Nature. 474:230–234. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Z, Chen K, Jiao X, Wang C, Willmarth
NE, Casimiro MC, Li W, Ju X, Kim SH, Lisanti MP, et al: Cyclin D1
integrates estrogen-mediated DNA damage repair signaling. Cancer
Res. 74:3959–3970. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian L, Fang YX, Xue JL and Chen JZ: Four
microRNAs promote prostate cell proliferation with regulation of
PTEN and its downstream signals in vitro. PLoS One. 8:e758852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|