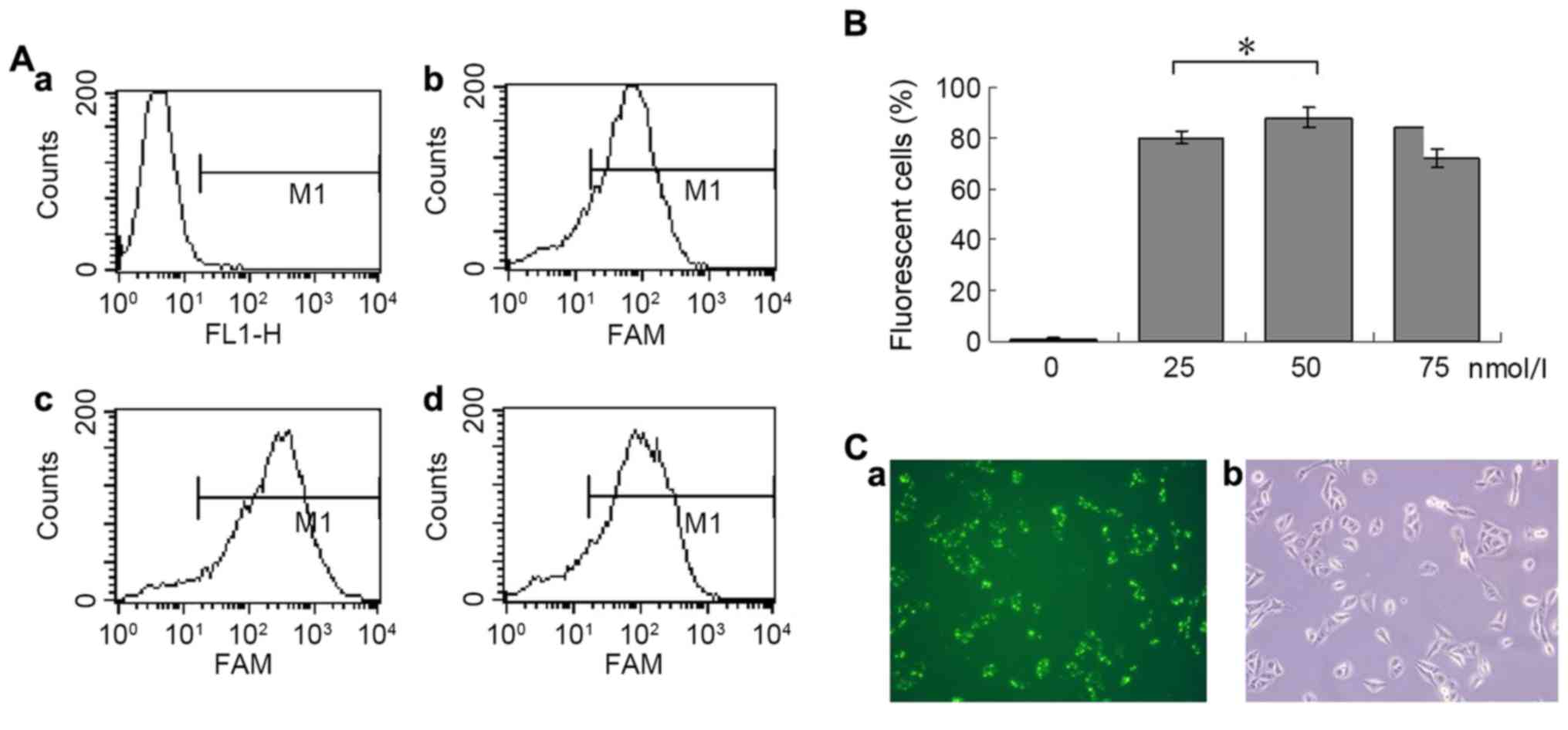
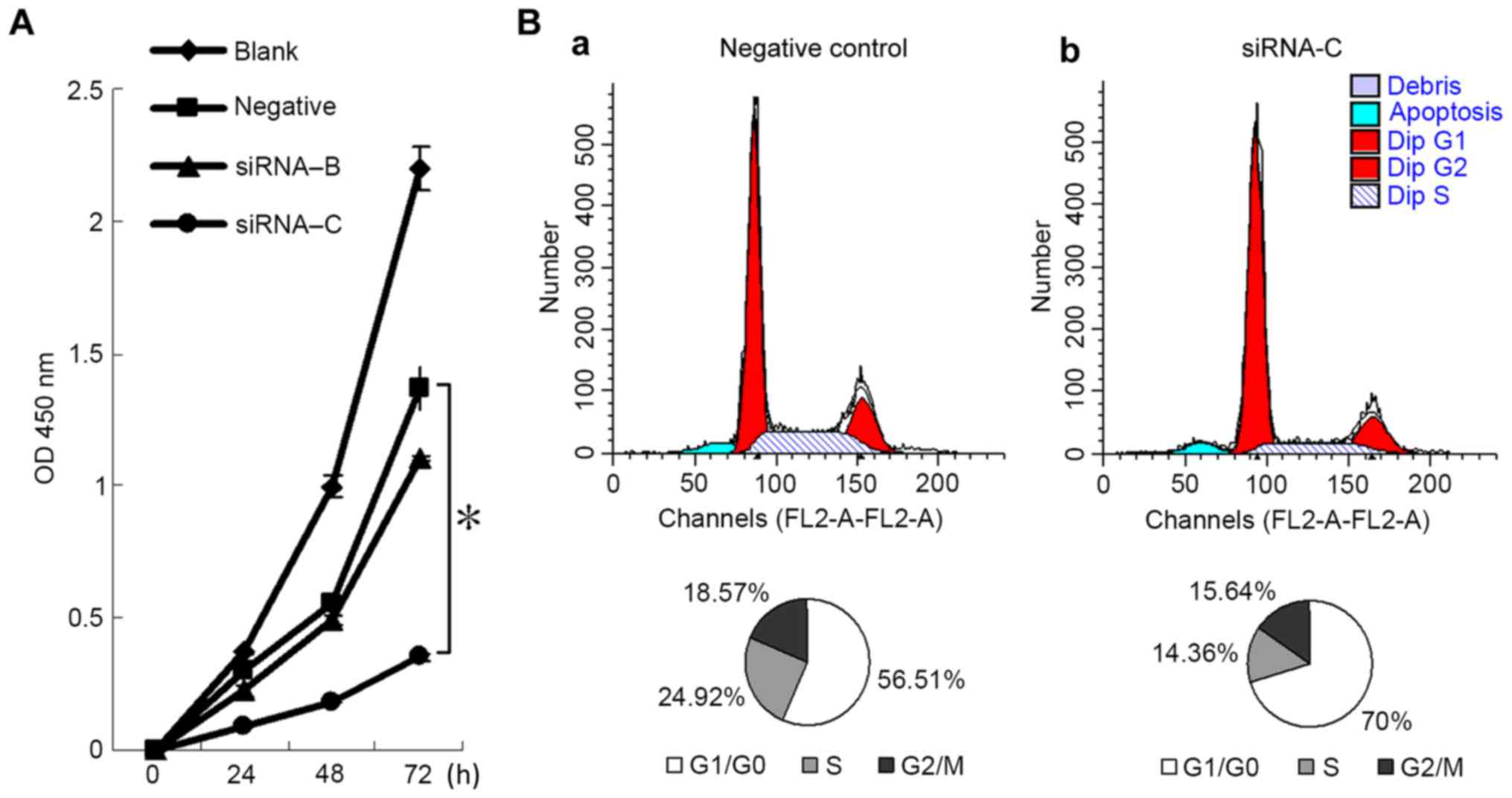
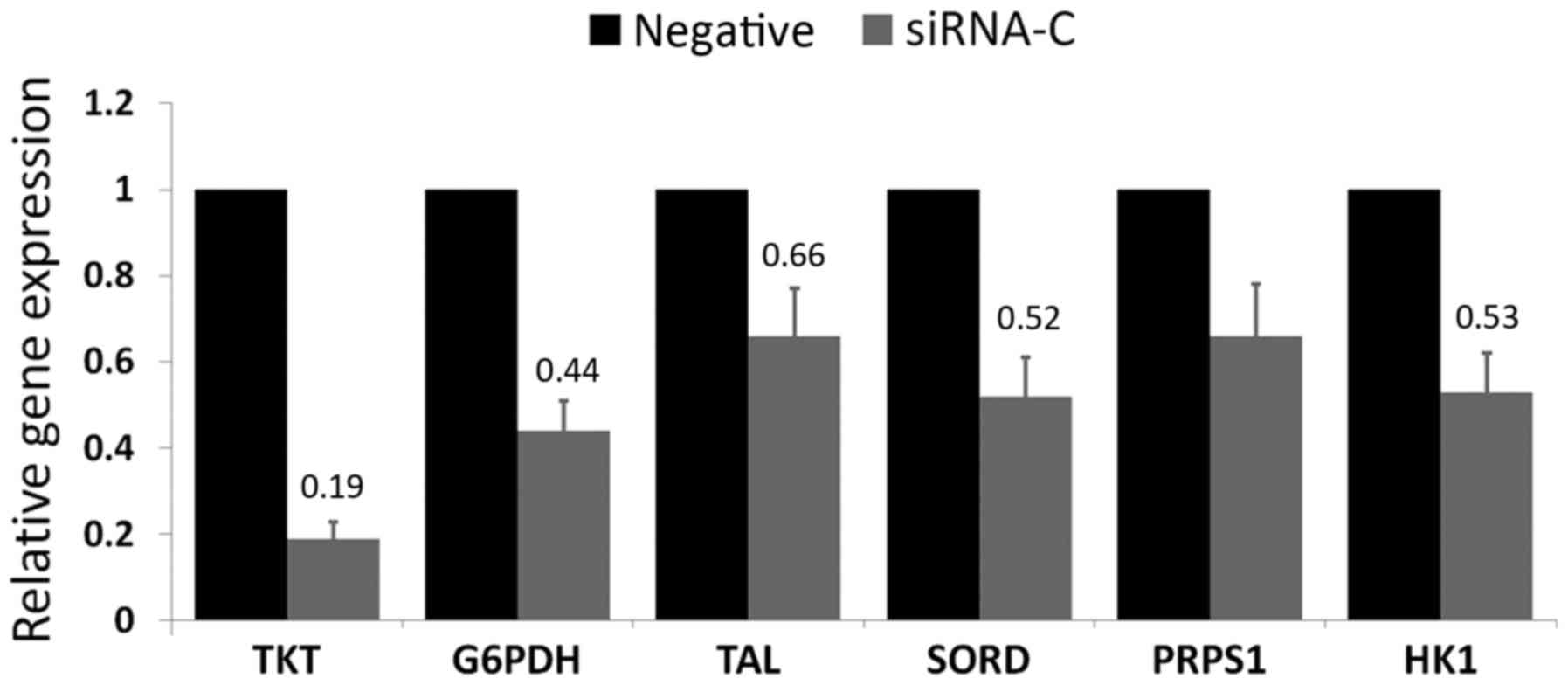
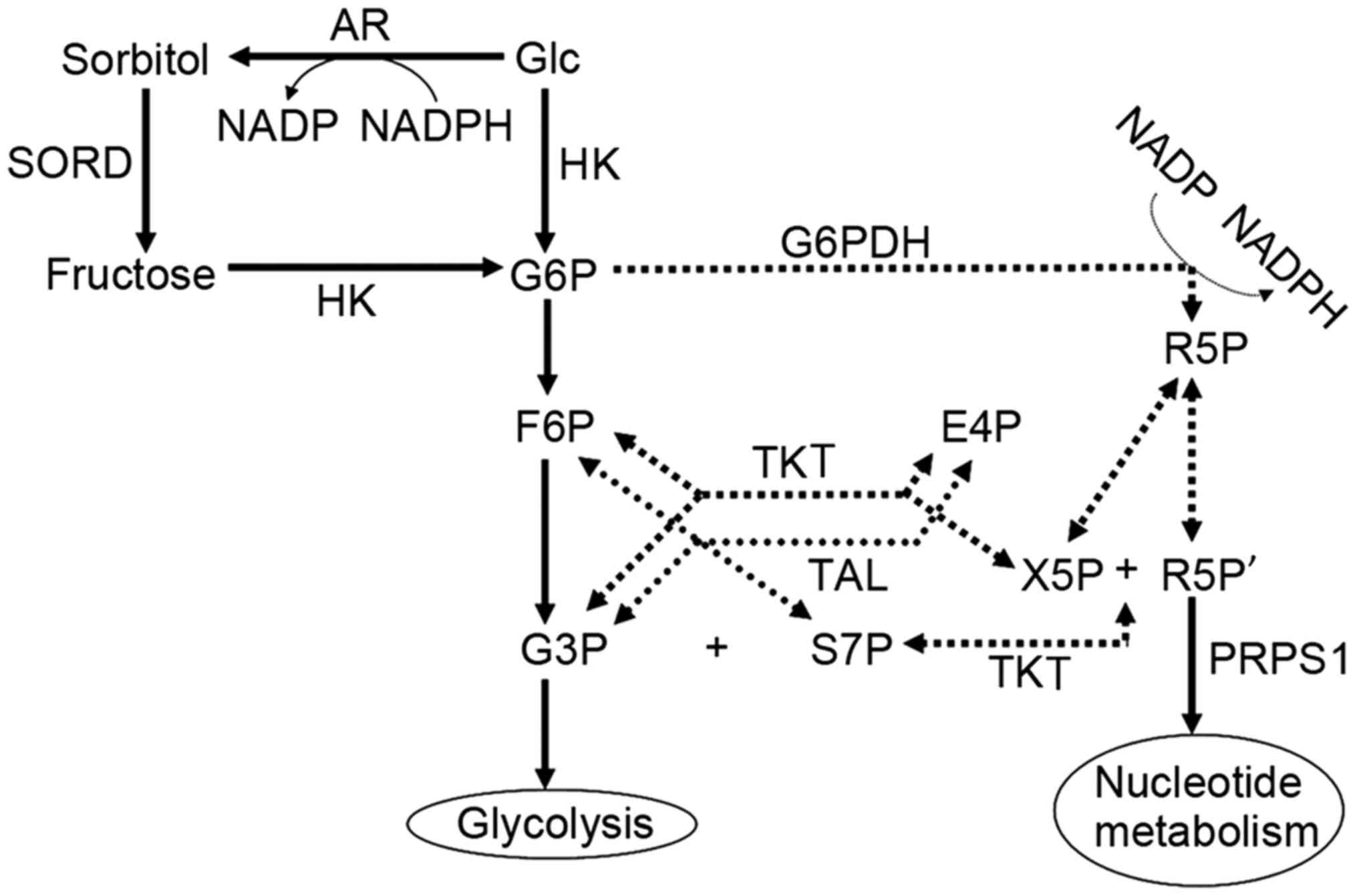
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H
and Zou X: Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010.
Ann Transl Med. 2:612014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patra KC and Hay N: The pentose phosphate
pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:347–354. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Raïs B, Comin B, Puigjaner J, Brandes JL,
Creppy E, Saboureau D, Ennamany R, Lee WN, Boros LG and Cascante M:
Oxythiamine and dehydroepiandrosterone induce a G1 phase cycle
arrest in Ehrlich's tumor cells through inhibition of the pentose
cycle. FEBS Lett. 456:113–118. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salas E, Roy S, Marsh T, Rubin B and
Debnath J: Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway inhibition is a key
determinant of antimalarial induced cancer cell death. Oncogene.
35:2913–2922. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Williams JF, Arora KK and Longenecker JP:
The pentose pathway: A random harvest. Impediments which oppose
acceptance of the classical (F-type) pentose cycle for liver, some
neoplasms and photosynthetic tissue. The case for the L-type
pentose pathway. Int J Biochem. 19:749–817. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu H, Lan WX, Bo L, Niu C, Zhou JJ and Zhu
HL: Metabolic response of LLC xenografted mice to oxythiamine, as
measured by [1H] NMR spectroscopy. Genet Mol Res. 14:11043–11051.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boros LG, Torday JS, Lim S, Bassilian S,
Cascante M and Lee WN: Transforming growth factor beta2 promotes
glucose carbon incorporation into nucleic acid ribose through the
nonoxidative pentose cycle in lung epithelial carcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 60:1183–1185. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin CC, Chen LC, Tseng VS, Yan JJ, Lai WW,
Su WP, Lin CH, Huang CY and Su WC: Malignant pleural effusion cells
show aberrant glucose metabolism gene expression. Eur Respir J.
37:1453–1465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ricciardelli C, Lokman NA, Cheruvu S, Tan
IA, Ween MP, Pyragius CE, Ruszkiewicz A, Hoffmann P and Oehler MK:
Transketolase is upregulated in metastatic peritoneal implants and
promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Clin Exp Metastasis.
32:441–455. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang CM, Liu YZ, Liao JW and Hu ML: The in
vitro and in vivo anti-metastatic efficacy of oxythiamine and the
possible mechanisms of action. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:341–349.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pekovich SR, Martin PR and Singleton CK:
Thiamine deficiency decreases steady-state transketolase and
pyruvate dehydrogenase but not alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
mRNA levels in three human cell types. J Nutr. 128:683–687.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sánchez-Tena S, Alcarraz-Vizán G, Marín S,
Torres JL and Cascante M: Epicatechin gallate impairs colon cancer
cell metabolic productivity. J Agric Food Chem. 61:4310–4317. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung SN, Shin DS, Kim HN, Jeon YJ, Yun J,
Lee YJ, Kang JS, Han DC and Kwon BM: Sugiol inhibits STAT3 activity
via regulation of transketolase and ROS-mediated ERK activation in
DU145 prostate carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 97:38–50. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uzozie A, Nanni P, Staiano T, Grossmann J,
Barkow-Oesterreicher S, Shay JW, Tiwari A, Buffoli F, Laczko E and
Marra G: Sorbitol dehydrogenase overexpression and other aspects of
dysregulated protein expression in human precancerous colorectal
neoplasms: A quantitative proteomics study. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:1198–1218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coy JF, Dressler D, Wilde J and Schubert
P: Mutations in the transketolase-like gene TKTL1: Clinical
implications for neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes and cancer.
Clin Lab. 51:257–273. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mayer A, Von Wallbrunn A and Vaupel P:
Glucose metabolism of malignant cells is not regulated by
transketolase-like (TKTL)-1. Int J Oncol. 37:265–271. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hartmannsberger D, Mack B, Eggert C,
Denzel S, Stepp H, Betz CS and Gires O: Transketolase-like protein
1 confers resistance to serum withdrawal in vitro. Cancer Lett.
300:20–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|