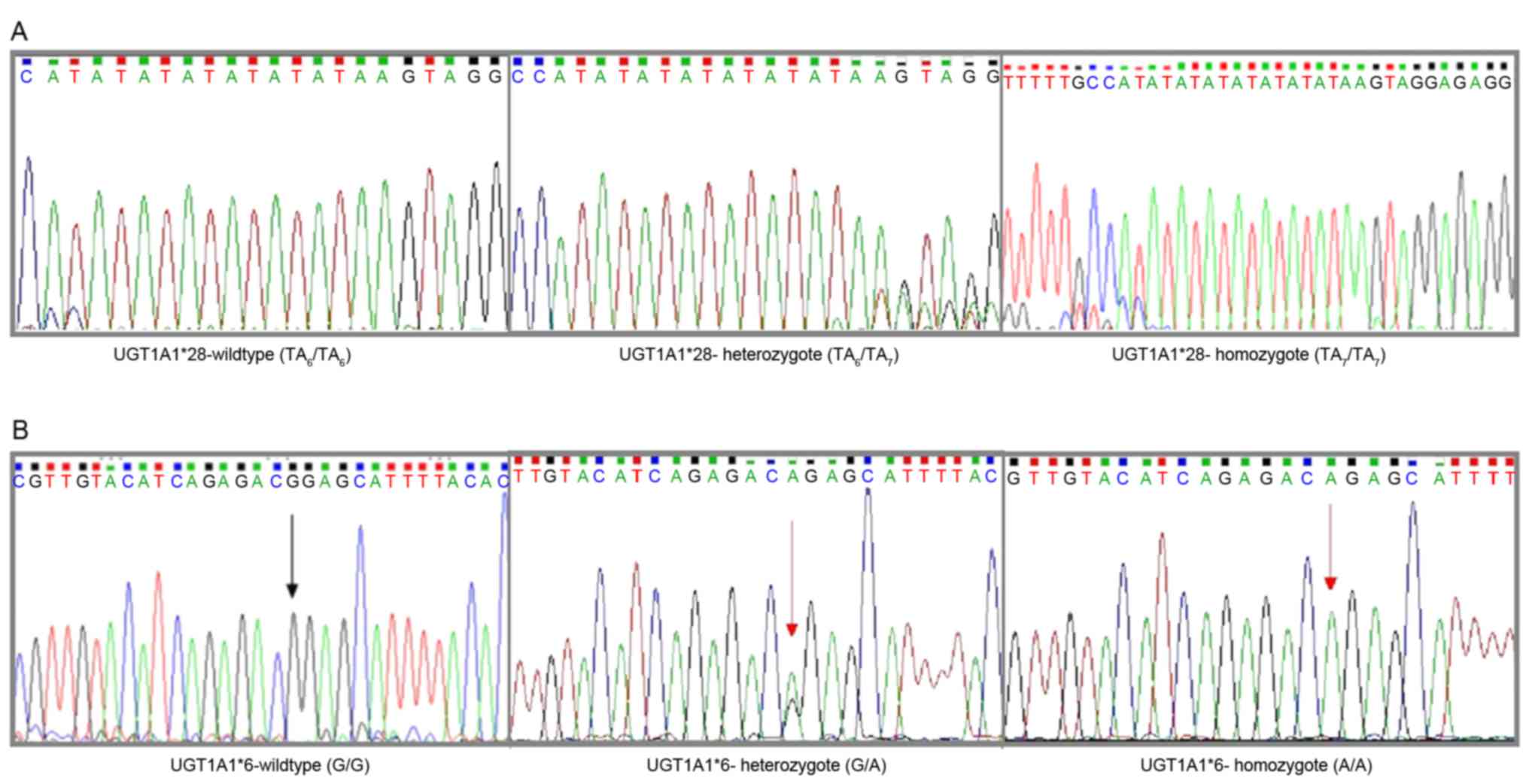
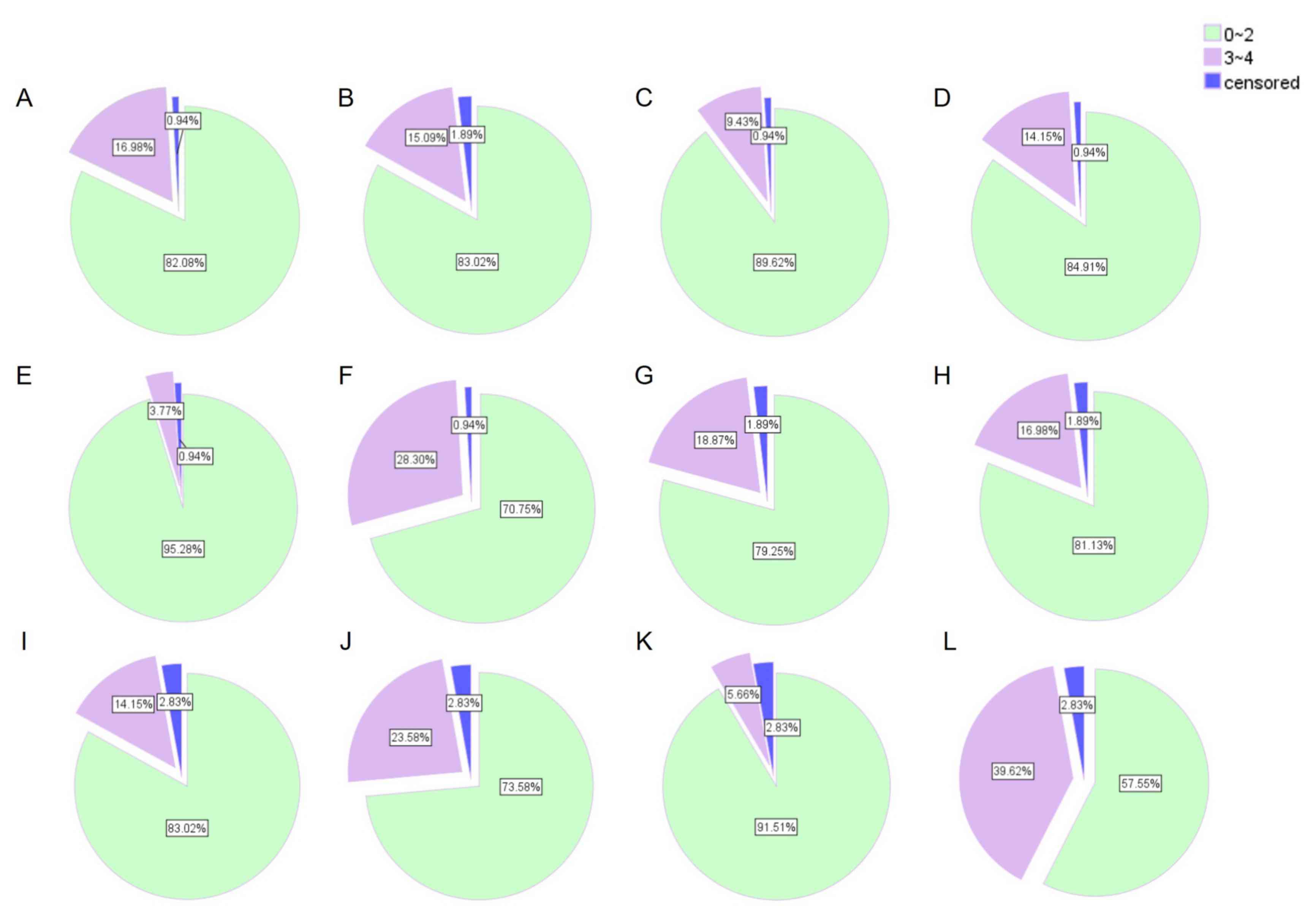
|
1
|
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD,
Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J,
Alakl M, et al: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with
fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic
colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet.
355:1041–1047. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akie K, Oizumi S, Ogura S, Shinagawa N,
Kikuchi E, Fukumoto S, Harada M, Kinoshita I, Kojima T, Harada T,
et al: Phase II study of irinotecan plus S-1 combination for
previously untreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Hokkaido
Lung Cancer Clinical Study Group Trial (HOT) 0601. Oncology.
81:84–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takakura S, Takano M, Takahashi F, Saito
T, Aoki D, Inaba N, Noda K, Sugiyama T and Ochiai K: Japanese
Gynecologic Oncology Group: Randomized phase II trial of paclitaxel
plus carboplatin therapy versus irinotecan plus cisplatin therapy
as first-line chemotherapy for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the
ovary: A JGOG study. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 20:240–247. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo HY, Wang ZQ, Wang FH, Qiu MZ, Teng KY,
Ruan DY, He YJ, Li YH and Xu RH: Phase 2 study of capecitabine and
irinotecan combination chemotherapy (modified XELIRI regimen) in
patients with advanced gastric cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 34:555–560.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glimelius B: Benefit-risk assessment of
irinotecan in advanced colorectal cancer. Drug Saf. 28:417–433.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith NF, Figg WD and Sparreboom A:
Pharmacogenetics of irinotecan metabolism and transport: An update.
Toxicol In Vitro. 20:163–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mathijssen RH, van Alphen RJ, Verweij J,
Loos WJ, Nooter K, Stoter G and Sparreboom A: Clinical
pharmacokinetics and metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11). Clin Cancer
Res. 7:2182–2194. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iyer L, Das S, Janisch L, Wen M, Ramírez
J, Karrison T, Fleming GF, Vokes EE, Schilsky RL and Ratain MJ:
UGT1A1*28 polymorphism as a determinant of irinotecan disposition
and toxicity. Pharmacogenomics J. 2:43–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Innocenti F and Ratain MJ: ‘Irinogenetics’
and UGT1A: From genotypes to haplotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
75:495–500. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perera MA, Innocenti F and Ratain MJ:
Pharmacogenetic testing for uridine diphosphate
glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 polymorphisms: Are we there yet?
Pharmacotherapy. 28:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ramchandani RP, Wang Y, Booth BP, Ibrahim
A, Johnson JR, Rahman A, Mehta M, Innocenti F, Ratain MJ and
Gobburu JV: The role of SN-38 exposure, UGT1A1*28 polymorphism and
baseline bilirubin level in predicting severe irinotecan toxicity.
J Clin Pharmacol. 47:78–86. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deeken JF, Slack R and Marshall JL:
Irinotecan and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1
pharmacogenetics: To test or not to test, that is the question.
Cancer. 113:1502–1510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ando Y, Saka H, Ando M, Sawa T, Muro K,
Ueoka H, Yokoyama A, Saitoh S, Shimokata K and Hasegawa Y:
Polymorphisms of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene and irinotecan
toxicity: A pharmacogenetic analysis. Cancer Res. 60:6921–6926.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han JY, Lim HS, Shin ES, Yoo YK, Park YH,
Lee JE, Jang IJ, Lee DH and Lee JS: Comprehensive analysis of UGT1A
polymorphisms predictive for pharmacokinetics and treatment outcome
in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with irinotecan
and cisplatin. J Clin Oncol. 24:2237–2244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jada SR, Lim R, Wong CI, Shu X, Lee SC,
Zhou Q, Goh BC and Chowbay B: Role of UGT1A1*6, UGT1A1*28 and ABCG2
c.421C>A polymorphisms in irinotecan-induced neutropenia in
Asian cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 98:1461–1467. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Onoue M, Terada T, Kobayashi M, Katsura T,
Matsumoto S, Yanagihara K, Nishimura T, Kanai M, Teramukai S,
Shimizu A, et al: UGT1A1*6 polymorphism is most predictive of
severe neutropenia induced by irinotecan in Japanese cancer
patients. Int J Clin Oncol. 14:136–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamamoto N, Takahashi T, Kunikane H,
Masuda N, Eguchi K, Shibuya M, Takeda Y, Isobe H, Ogura T, Yokoyama
A and Watanabe K: Phase I/II pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic
study of UGT1A1 polymorphism in elderly patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer treated with irinotecan. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 85:149–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu YY, Huang XE, Wu XY, Cao J, Liu J, Wang
L and Xiang J: Clinical observations on associations between the
UGT1A1 genotype and severe toxicity of irinotecan. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3335–3341. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Te HS, Schiano TD, Das S, Kuan SF,
DasGupta K, Conjeevaram HS and Baker AL: Donor liver uridine
diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronosyltransferase-1A1 deficiency causing
Gilbert's syndrome in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation.
69:1882–1886. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Shen L, Xu N, Wang JW, Jiao SC,
Liu ZY and Xu JM: UGT1A1 predicts outcome in colorectal cancer
treated with irinotecan and fluorouracil. World J Gastroenterol.
18:6635–6644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friendlander AH and Ettinger RL: Karnofsky
performance status scale. Spec Care Dentist. 29:147–148. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
CTCAE, . Cancer Therapy Evaluation
Program: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version
4.0. DCTD, NCI, NIH, DHHS. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Hoskins JM, Goldberg RM, Qu P, Ibrahim JG
and McLeod HL: UGT1A1*28 genotype and irinotecan-induced
neutropenia: Dose matters. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1290–1295. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yong WP, Innocenti F and Ratain MJ: The
role of pharmacogenetics in cancer therapeutics. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 62:35–46. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Premawardhena A, Fisher CA, Liu YT, Verma
IC, de Silva S, Arambepola M, Clegg JB and Weatherall DJ: The
global distribution of length polymorphisms of the promoters of the
glucuronosyltransferase 1 gene (UGT1A1): Hematologic and
evolutionary implications. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 31:98–101. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang A, Xing Q, Qin S, Du J, Wang L, Yu
L, Li X, Xu L, Xu M, Feng G and He L: Intra-ethnic differences in
genetic variants of the UGT-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene in
Chinese populations. Pharmacogenomics J. 7:333–338. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Glimelius B, Garmo H, Berglund A,
Fredriksson LA, Berglund M, Kohnke H, Byström P, Sørbye H and
Wadelius M: Prediction of irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil toxicity
and response in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Pharmacogenomics J. 11:61–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McLeod HL, Sargent DJ, Marsh S, Green EM,
King CR, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, Findlay BP,
Thibodeau SN, et al: Pharmacogenetic predictors of adverse events
and response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
Results from North American Gastrointestinal Intergroup Trial
N9741. J Clin Oncol. 28:3227–3233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shulman K, Cohen I, Barnett-Griness O,
Kuten A, Gruber SB, Lejbkowicz F and Rennert G: Clinical
implications of UGT1A1*28 genotype testing in colorectal cancer
patients. Cancer. 117:3156–3162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stewart CF, Panetta JC, O'Shaughnessy MA,
Throm SL, Fraga CH, Owens T, Liu T, Billups C, Rodriguez-Galindo C,
Gajjar A, et al: UGT1A1 promoter genotype correlates with SN-38
pharmacokinetics, but not severe toxicity in patients receiving
low-dose irinotecan. J Clin Oncol. 25:2594–2600. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu ZY, Yu Q, Pei Q and Guo C:
Dose-dependent association between UGT1A1*28 genotype and
irinotecan-induced neutropenia: Low doses also increase risk. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:3832–3842. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marcuello E, Altés A, Menoyo A, Del Rio E,
Gómez-Pardo M and Baiget M: UGT1A1 gene variations and irinotecan
treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J
Cancer. 91:678–682. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu ZY, Yu Q and Zhao YS: Dose-dependent
association between UGT1A1*28 polymorphism and irinotecan-induced
diarrhoea: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 46:1856–1865. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Braun MS, Richman SD, Thompson L, Daly CL,
Meade AM, Adlard JW, Allan JM, Parmar MK, Quirke P and Seymour MT:
Association of molecular markers with toxicity outcomes in a
randomized trial of chemotherapy for advanced colorectal cancer:
The FOCUS trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:5519–5528. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Okuyama Y, Hazama S, Nozawa H, Kobayashi
M, Takahashi K, Fujikawa K, Kato T, Nagata N, Kimura H, Oba K, et
al: Prospective phase II study of FOLFIRI for mCRC in Japan,
including the analysis of UGT1A1 28/6 polymorphisms. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 41:477–482. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sunakawa Y, Ichikawa W, Fujita K,
Nagashima F, Ishida H, Yamashita K, Mizuno K, Miwa K, Kawara K,
Akiyama Y, et al: UGT1A1*1/*28 and *1/*6 genotypes have no effects
on the efficacy and toxicity of FOLFIRI in Japanese patients with
advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:279–284.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meyerhardt JA, Kwok A, Ratain MJ, McGovren
JP and Fuchs CS: Relationship of baseline serum bilirubin to
efficacy and toxicity of single-agent irinotecan in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:1439–1446. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han JY, Lim HS, Shin ES, Yoo YK, Park YH,
Lee JE, Kim HT and Lee JS: Influence of the organic
anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) polymorphisms on
irinotecan-pharmacokinetics and clinical outcome of patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 59:69–75. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
de Jong FA, Scott-Horton TJ, Kroetz DL,
McLeod HL, Friberg LE, Mathijssen RH, Verweij J, Marsh S and
Sparreboom A: Irinotecan-induced diarrhea: Functional significance
of the polymorphic ABCC2 transporter protein. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
81:42–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lankisch TO, Schulz C, Zwingers T,
Erichsen TJ, Manns MP, Heinemann V and Strassburg CP: Gilbert's
Syndrome and irinotecan toxicity: Combination with
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 variants increases risk. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:695–701. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|