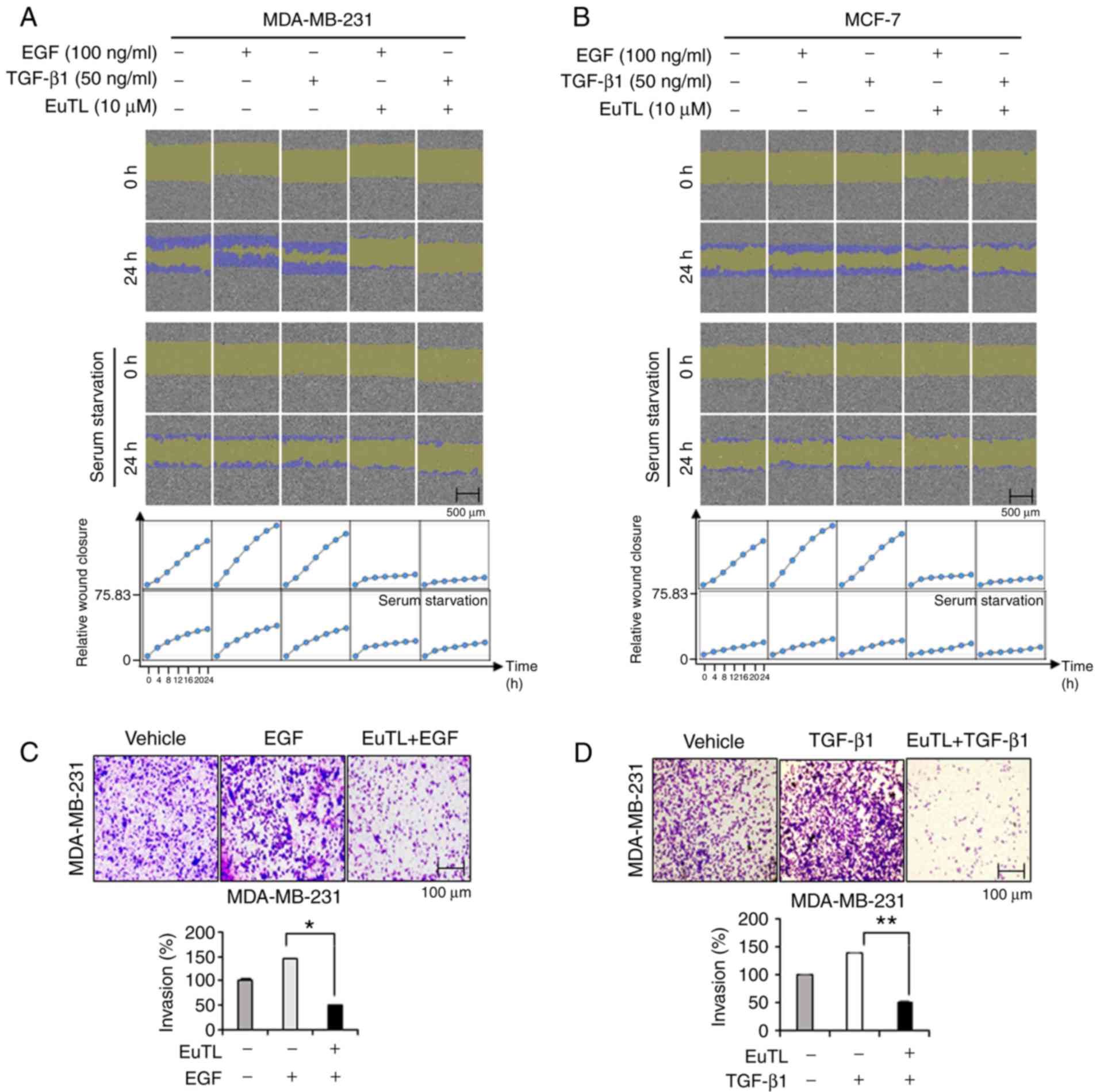
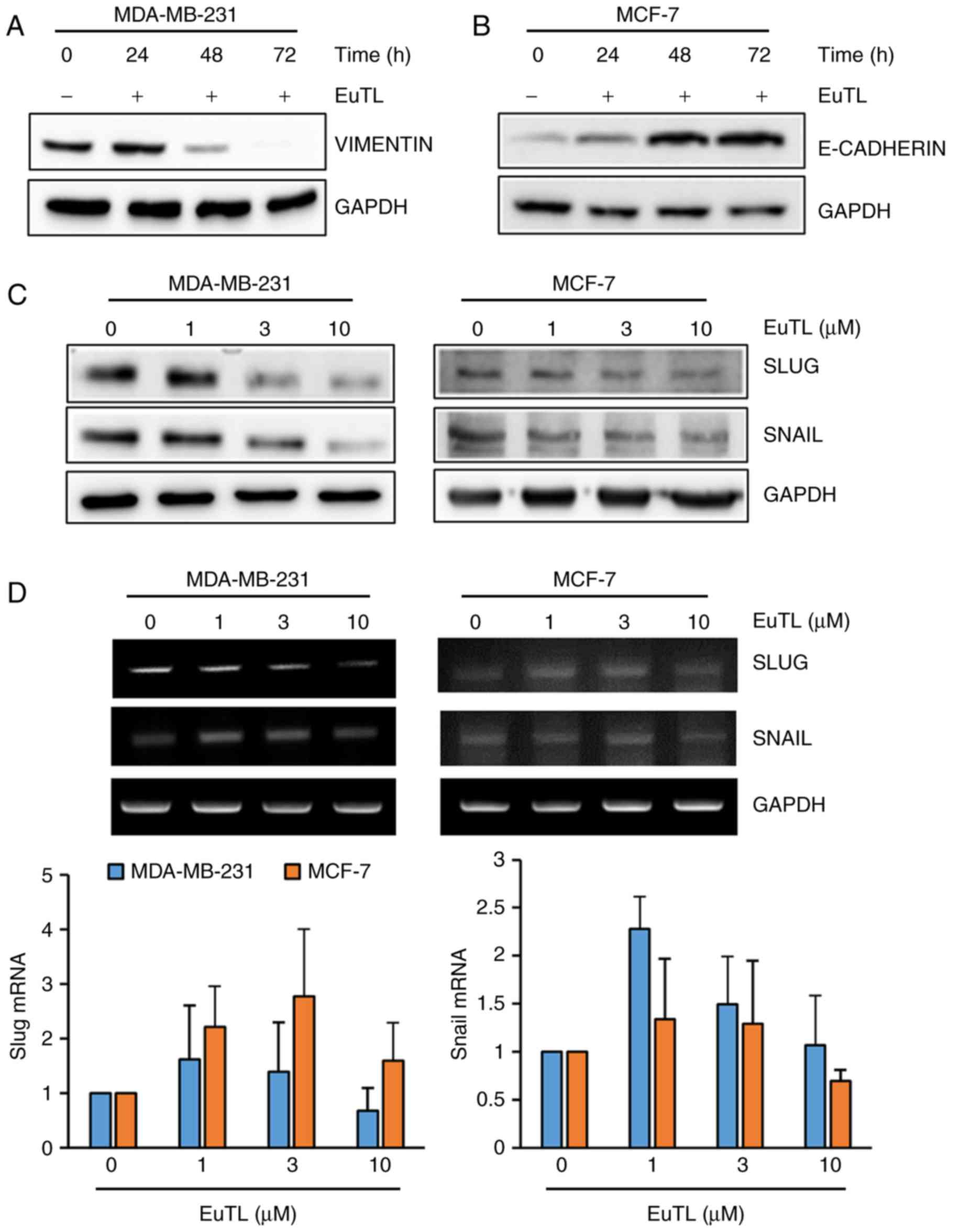
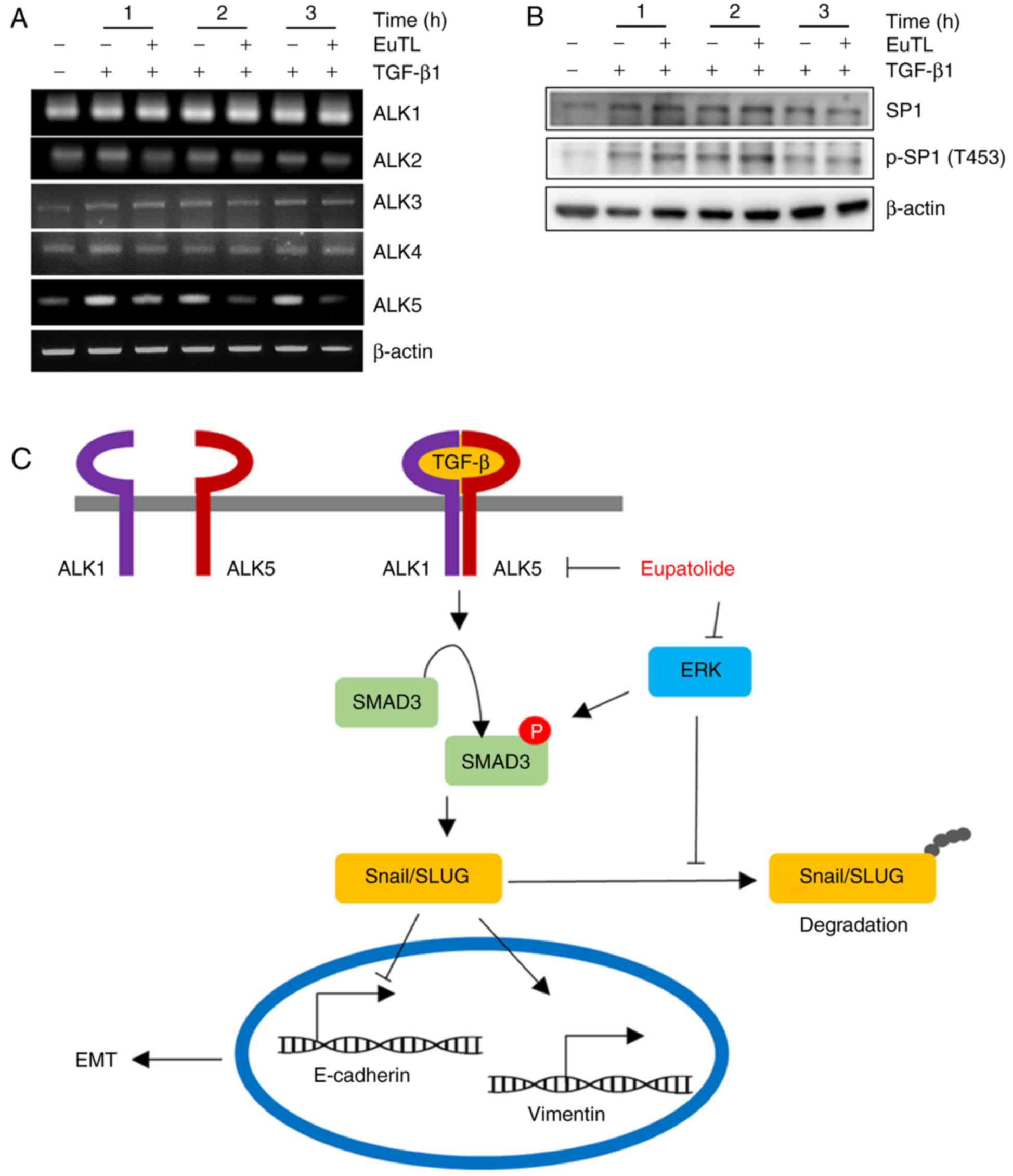
|
1
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchytnal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tam WL and Weinberg RA: The epigenetics of
epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nat Med. 19:1438–1449.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin YC, Lee YC, Li LH, Cheng CJ and Yang
RB: Tumor suppressor SCUBE2 inhibits breast-cancer cell migration
and invasion through the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Sci. 127:85–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: Snail: More than EMT.
Cell Adh Migr. 4:199–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marcucci F, Stassi G and De Maria R:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A new target in anticancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:311–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heldin CH, Vanlandewijck M and Moustakas
A: Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer. FEBS Lett. 586:1959–1970.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wakefield LM and Roberts AB: TGF-beta
signaling: Positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 12:22–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubiczkova L, Sedlarikova L, Hajek R and
Sevcikova S: TGF-β - an excellent servant but a bad master. J
Transl Med. 10:1832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cunha SI and Pietras K: ALK1 as an
emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer. Blood.
117:6999–7006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Whitman M and Raftery L: TGFbeta signaling
at the summit. Development. 132:4205–4210. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Curado F, Spuul P, Egaña I, Rottiers P,
Daubon T, Veillat V, Duhamel P, Leclercq A, Gontier E and Génot E:
ALK5 and ALK1 play antagonistic roles in transforming growth factor
β-induced podosome formation in aortic endothelial cells. Mol Cell
Biol. 34:4389–4403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schniewind B, Groth S, Müerköster S
Sebens, Sipos B, Schäfer H, Kalthoff H, Fändrich F and Ungefroren
H: Dissecting the role of TGF-beta type I receptor/ALK5 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Smad activation is crucial for
both the tumor suppressive and prometastatic function. Oncogene.
26:4850–4862. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Khan AL, Hussain J, Hamayun M, Gilani SA,
Ahmad S, Rehman G, Kim YH, Kang SM and Lee IJ: Secondary
metabolites from Inula britannica L. and their biological
activities. Molecules. 15:1562–1577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee YH, Lee NK and Paik HD: Antimicrobial
characterization of inula britannica against helicobacter pylori on
gastric condition. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 26:1011–1017. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Hwangbo C, Lee JJ, Seo J and Lee
JH: The sesquiterpene lactone eupatolide sensitizes breast cancer
cells to TRAIL through down-regulation of c-FLIP expression. Oncol
Rep. 23:229–237. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim N, Hwangbo C, Lee S and Lee JH:
Eupatolide inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of
aortic smooth muscle cells through ROS-dependent heme oxygenase-1
induction. Phytother Res. 27:1700–1707. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee S, Jeong AL, Park JS, Han S, Jang CY,
Kim KI, Kim Y, Park JH, Lim JS, Lee MS and Yang Y: IK-guided PP2A
suppresses Aurora B activity in the interphase of tumor cells. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 73:3375–3386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin HZ, Lee D, Lee JH, Lee K, Hong YS,
Choung DH, Kim YH and Lee JJ: New sesquiterpene dimers from Inula
britannica inhibit NF-kappaB activation and NO and TNF-alpha
production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Planta Med. 72:40–45.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee S, Han S, Jeong AL, Park JS and Yang
Y: Depletion of IK causes mitotic arrest through aberrant
regulation of mitotic kinases and phosphatases. FEBS Lett.
588:2844–2850. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sinha C, Ren A, Arora K, Moon CS,
Yarlagadda S, Zhang W, Cheepala SB, Schuetz JD and Naren AP:
Multi-drug resistance protein 4 (MRP4)-mediated regulation of
fibroblast cell migration reflects a dichotomous role of
intracellular cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 288:3786–3794. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Qi L, Liang Z, Song W, Liu Y, Wang
Y, Sun B, Zhang B and Cao W: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces
EMT by the transactivation of epidermal growth factor signaling
through HA/CD44 in lung and breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med.
36:113–122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guttilla IK, Phoenix KN, Hong X, Tirnauer
JS, Claffey KP and White BA: Prolonged mammosphere culture of MCF-7
cells induces an EMT and repression of the estrogen receptor by
microRNAs. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 132:75–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vergara D, Valente CM, Tinelli A,
Siciliano C, Lorusso V, Acierno R, Giovinazzo G, Santino A,
Storelli C and Maffia M: Resveratrol inhibits the epidermal growth
factor-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition in MCF-7 cells.
Cancer Lett. 310:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chao YL, Shepard CR and Wells A: Breast
carcinoma cells re-express E-cadherin during mesenchymal to
epithelial reverting transition. Mol Cancer. 9:1792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kocic J, Bugarski D and Santibanez JF:
SMAD3 is essential for transforming growth factor-β1-induced
urokinase type plasminogen activator expression and migration in
transformed keratinocytes. Eur J Cancer. 48:1550–1557. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pannu J, Nakerakanti S, Smith E, ten Dijke
P and Trojanowska M: Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type
I-dependent fibrogenic gene program is mediated via activation of
Smad1 and ERK1/2 pathways. J Biol Chem. 282:10405–10413. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wrighton KH, Lin X and Feng XH:
Phospho-control of TGF-beta superfamily signaling. Cell Res.
19:8–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cantelli G, Crosas-Molist E, Georgouli M
and Sanz-Moreno V: TGFBeta-induced transcription in cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 42:60–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee J, Tae N, Lee JJ, Kim T and Lee JH:
Eupatolide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced COX-2 and iNOS
expression in RAW264.7 cells by inducing proteasomal degradation of
TRAF6. Eur J Pharmacol. 636:173–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmierer B and Hill CS: TGFbeta-SMAD
signal transduction: Molecular specificity and functional
flexibility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:970–982. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Daly AC, Randall RA and Hill CS:
Transforming growth factor beta-induced Smad1/5 phosphorylation in
epithelial cells is mediated by novel receptor complexes and is
essential for anchorage-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol.
28:6889–6902. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support
transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1987–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Connolly EC, Freimuth J and Akhurst RJ:
Complexities of TGF-β targeted cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci.
8:964–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schlingensiepen KH, Schlingensiepen R,
Steinbrecher A, Hau P, Bogdahn U, Fischer-Blass B and Jachimczak P:
Targeted tumor therapy with the TGF-beta 2 antisense compound AP
12009. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:129–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Akhurst RJ: Large- and small-molecule
inhibitors of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 7:513–521. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ling LE and Lee WC: Tgf-beta type I
receptor (Alk5) kinase inhibitors in oncology. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 12:2190–2202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Smith AL, Robin TP and Ford HL: Molecular
pathways: Targeting the TGF-β pathway for cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:4514–4521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Grignani F,
McGlade J, Cavallo F, Forni G, Nicoletti I, Grignani F, Pawson T
and Pelicci PG: A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2
domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell.
70:93–104. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee MK, Pardoux C, Hall MC, Lee PS,
Warburton D, Qing J, Smith SM and Derynck R: TGF-beta activates Erk
MAP kinase signalling through direct phosphorylation of ShcA. EMBO
J. 26:3957–3967. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo X and Wang XF: Signaling cross-talk
between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 19:71–88. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|