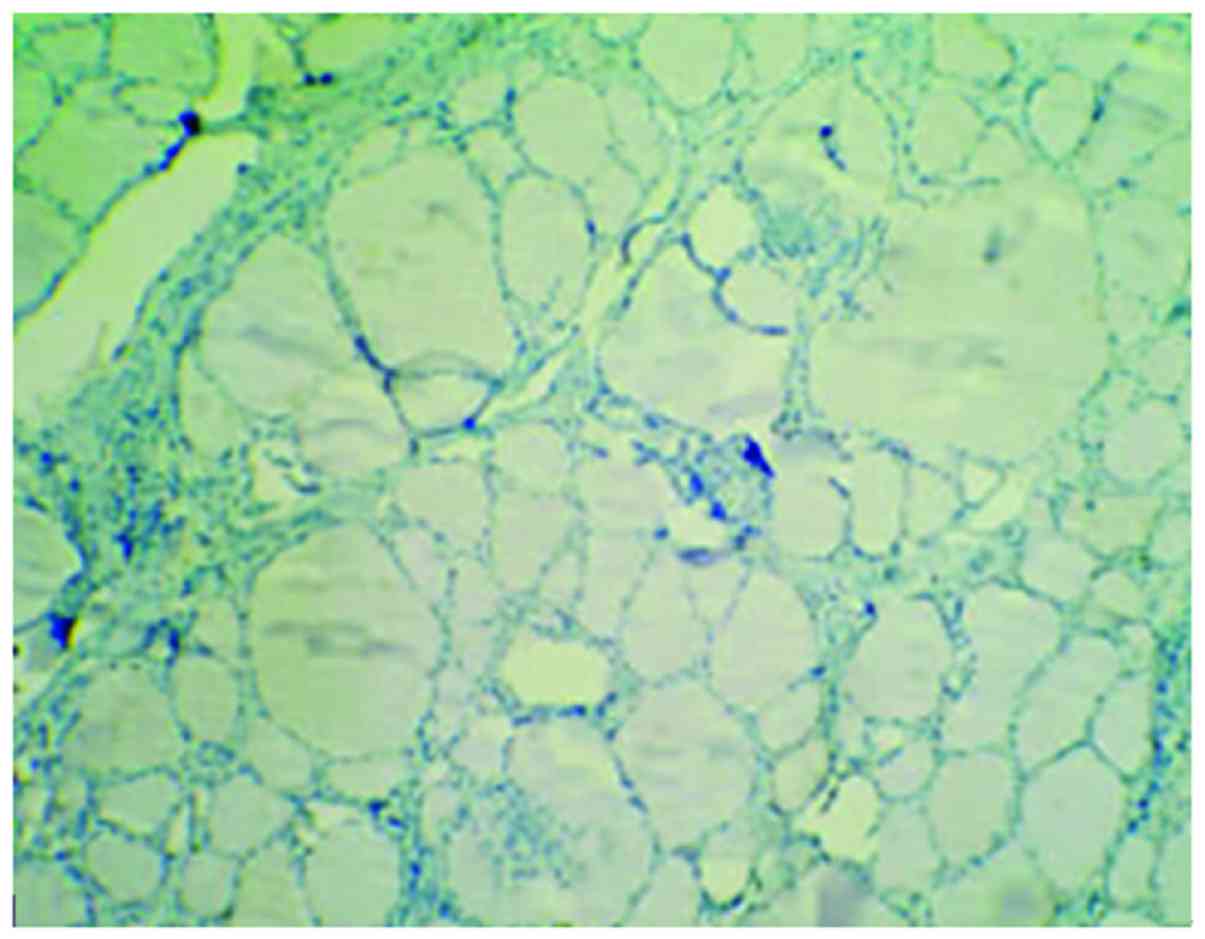
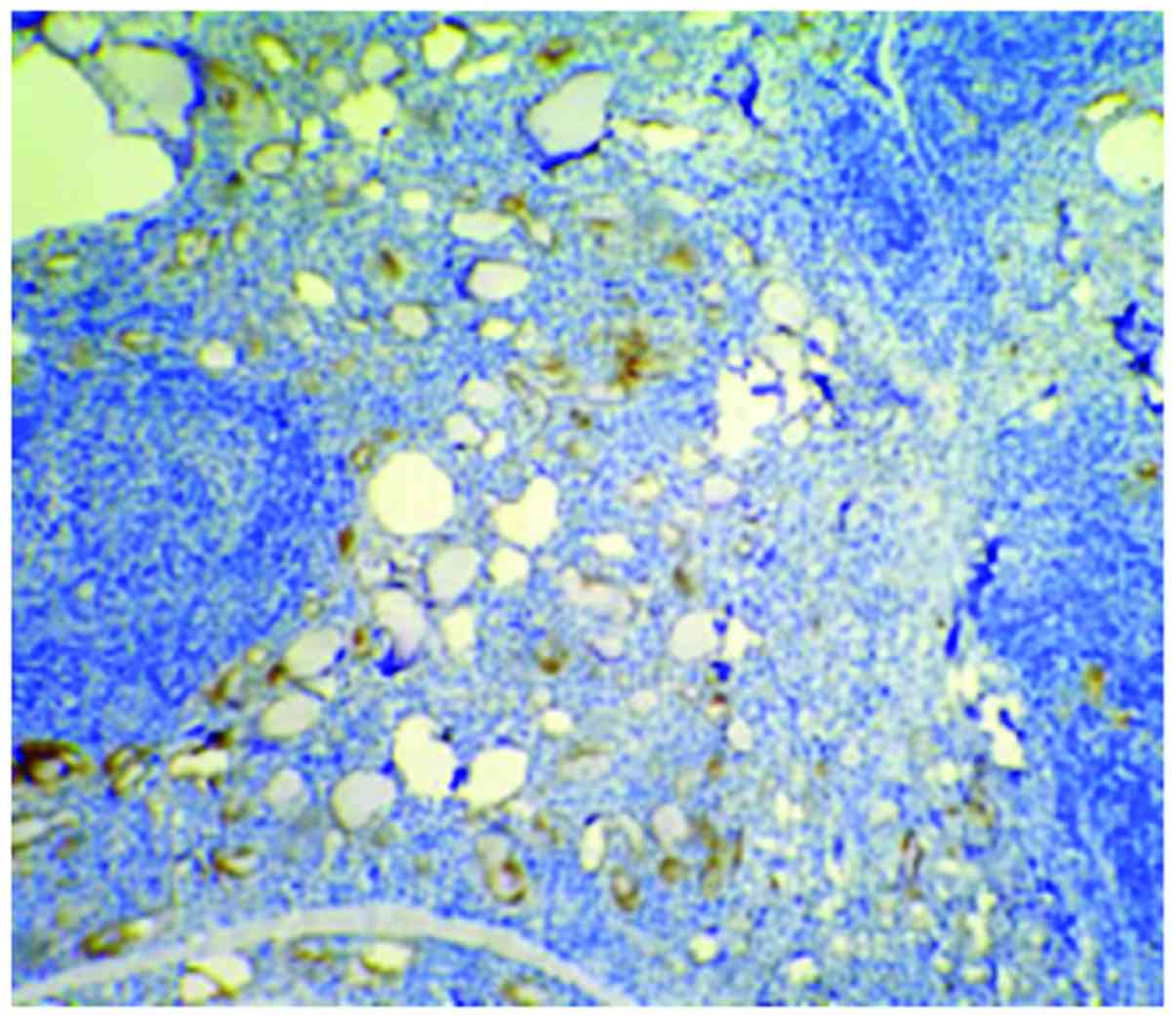
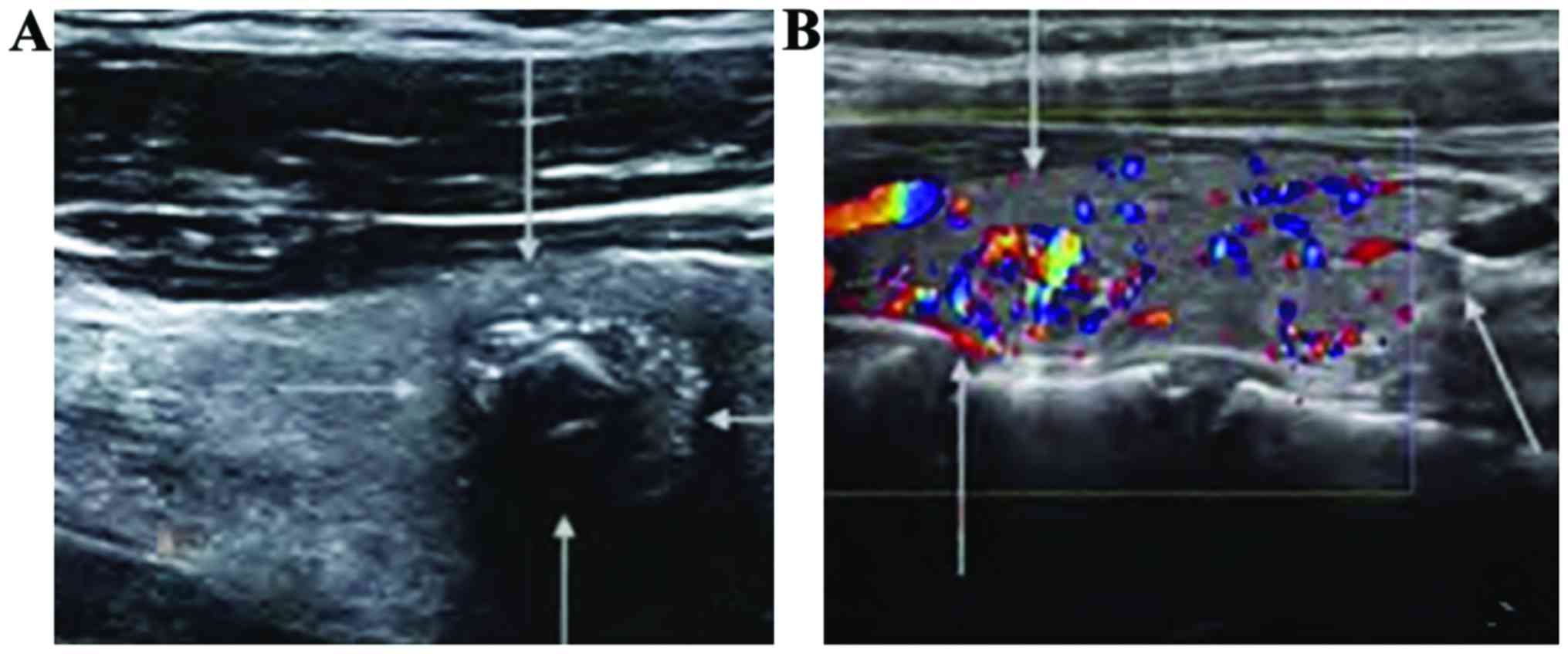
|
1
|
Asa SL, Giordano TJ and LiVolsi VA:
Implications of the TCGA genomic characterization of papillary
thyroid carcinoma for thyroid pathology: Does follicular variant
papillary thyroid carcinoma exist? Thyroid. 25:1–2. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mebed AH: Aggressive surgical therapy for
locally invasive differentiated thyroid carcinoma: An experience of
nineteen (19) cases. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 19:282–291.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paschke R, Lincke T, Müller SP, Kreissl
MC, Dralle H and Fassnacht M: The Treatment of Well-Differentiated
Thyroid Carcinoma. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 112:452–458. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu D, Wang L, Long B, Ye X, Ge M, Wang K,
Guo L and Li L: Radiofrequency ablation for postsurgical thyroid
removal of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
8:1876–1885. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cantisani V, Maceroni P, DAndrea V,
Patrizi G, Di Segni M, De Vito C, Grazhdani H, Isidori AM,
Giannetta E, Redler A, et al: Strain ratio ultrasound elastography
increases the accuracy of colour-Doppler ultrasound in the
evaluation of Thy-3 nodules. A bi-centre university experience. Eur
Radiol. 26:1441–1449. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
de Matos PS, Ferreira AP, de Oliveira
Facuri F, Assumpção LV, Metze K and Ward LS: Usefulness of HBME-1,
cytokeratin 19 and galectin-3 immunostaining in the diagnosis of
thyroid malignancy. Histopathology. 47:391–401. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sadamori H, Yagi T, Iwagaki H, Matsuda H,
Shinoura S, Umeda Y, Ohara N, Yanai H, Ogino T and Tanaka N:
Immunohistochemical staining of liver grafts with a monoclonal
antibody against HCV-Envelope 2 for recurrent hepatitis C after
living donor liver transplantation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:574–580. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Verslype C, Nevens F, Sinelli N, Clarysse
C, Pirenne J, Depla E, Maertens G, van Pelt J, Desmet V, Fevery J,
et al: Hepatic immunohistochemical staining with a monoclonal
antibody against HCV-E2 to evaluate antiviral therapy and
reinfection of liver grafts in hepatitis C viral infection. J
Hepatol. 38:208–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Casey MB, Lohse CM and Lloyd RV:
Distinction between papillary thyroid hyperplasia and papillary
thyroid carcinoma by immunohistochemical staining for cytokeratin
19, galectin-3, and HBME-1. Endocr Pathol. 14:55–60. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee YS, Yun JS, Jeong JJ, Nam KH, Chung WY
and Park CS: Thyroid hemiagenesis associated with thyroid
adenomatous hyperplasia and papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid.
18:381–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dong S, Song XS, Chen G and Liu J: Mixed
primary squamous cell carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, and
micropapillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland: A case report. Auris
Nasus Larynx. 43:455–459. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bychkov A, Sampatanukul P, Shuangshoti S
and Keelawat S: TROP-2 immunohistochemistry: A highly accurate
method in the differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Pathology. 48:425–433. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erdogan-Durmus S, Ozcan D, Yarikkaya E,
Kurt A and Arslan A: CD56, HBME-1 and cytokeratin 19 expressions in
papillary thyroid carcinoma and nodular thyroid lesions. J Res Med
Sci. 21:49–54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen YJ, Zhao RM, Zhao Q, Li BY, Ma QY, Li
X and Chen X: Diagnostic significance of elevated expression of
HBME-1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:8715–8720.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu X, Sun T, Lu H, Zhou X, Lu Y, Cai X
and Zhu X: Diagnostic significance of CK19, RET, galectin-3 and
HBME-1 expression for papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Pathol.
63:786–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Z, Yu P, Xiong Y, Zeng W, Li X,
Maiaiti Y, Wang S, Song H, Shi L, Liu C, et al: Significance of
CK19, TPO, and HBME-1 expression for diagnosis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:4369–4374. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El-Mahdy MM, Mabrouk SH, El-Din ZS, Ghazal
FA and Mohamed HH: Diagnostic value of HBME-1 and CK19 expression
in papillary thyroid carcinoma, well-differentiated tumors of
uncertain malignant potential, and benign thyroid nodules. Egypt J
Pathol. 31:68–74. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chao TT, Maa HC, Wang CY, Pei D, Liang YJ,
Yang YF, Chou SJ and Chen YL: CIP2A is a poor prognostic factor and
can be a diagnostic marker in papillary thyroid carcinoma. APMIS.
124:1031–1037. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeşil C, Kandemir O, Haksever H and
Dabakoğlu T: Is BECLIN-1 immunoreactivity more effective than
HBME-1 in diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer? Acta Chir Belg.
115:299–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|