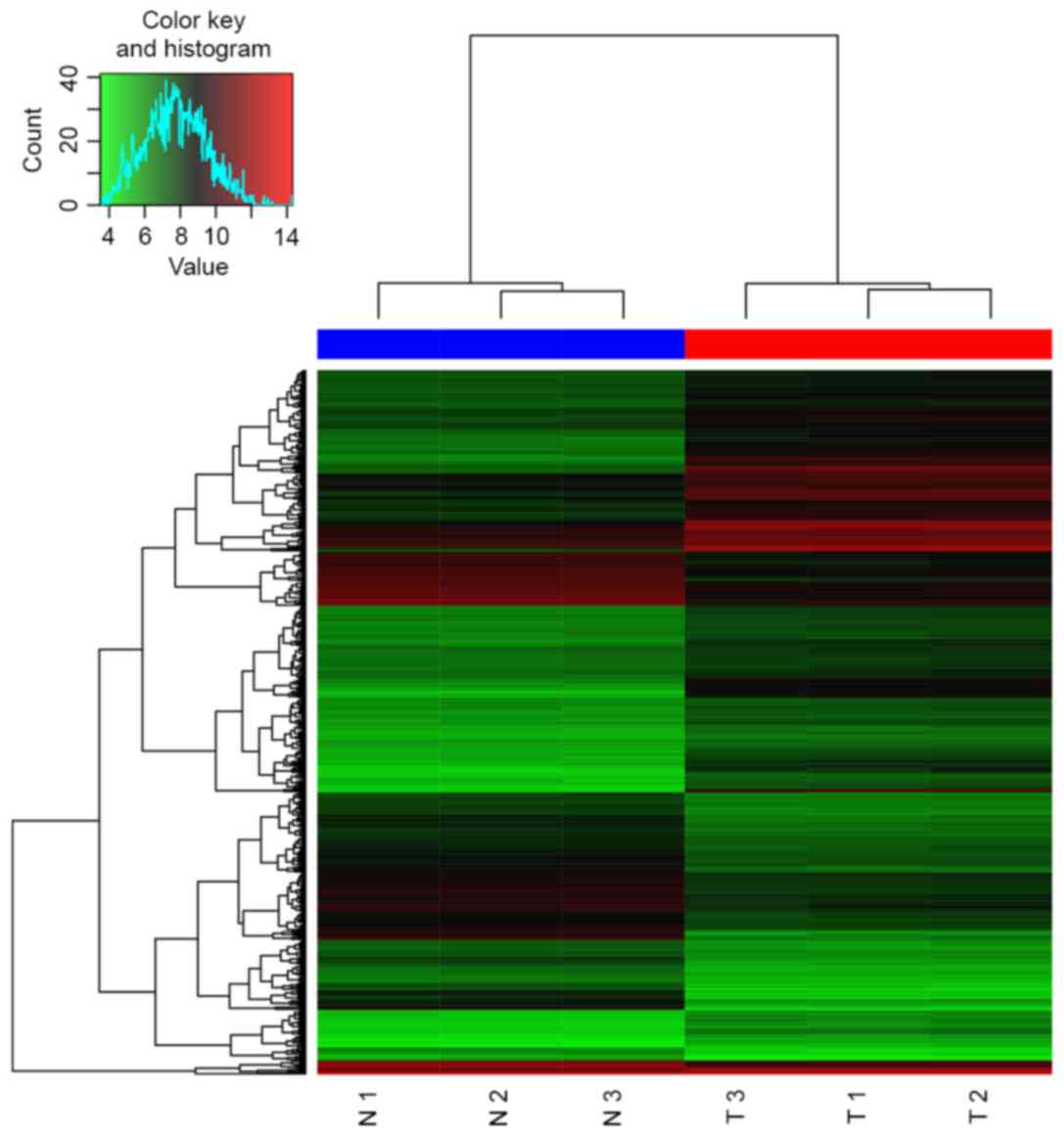
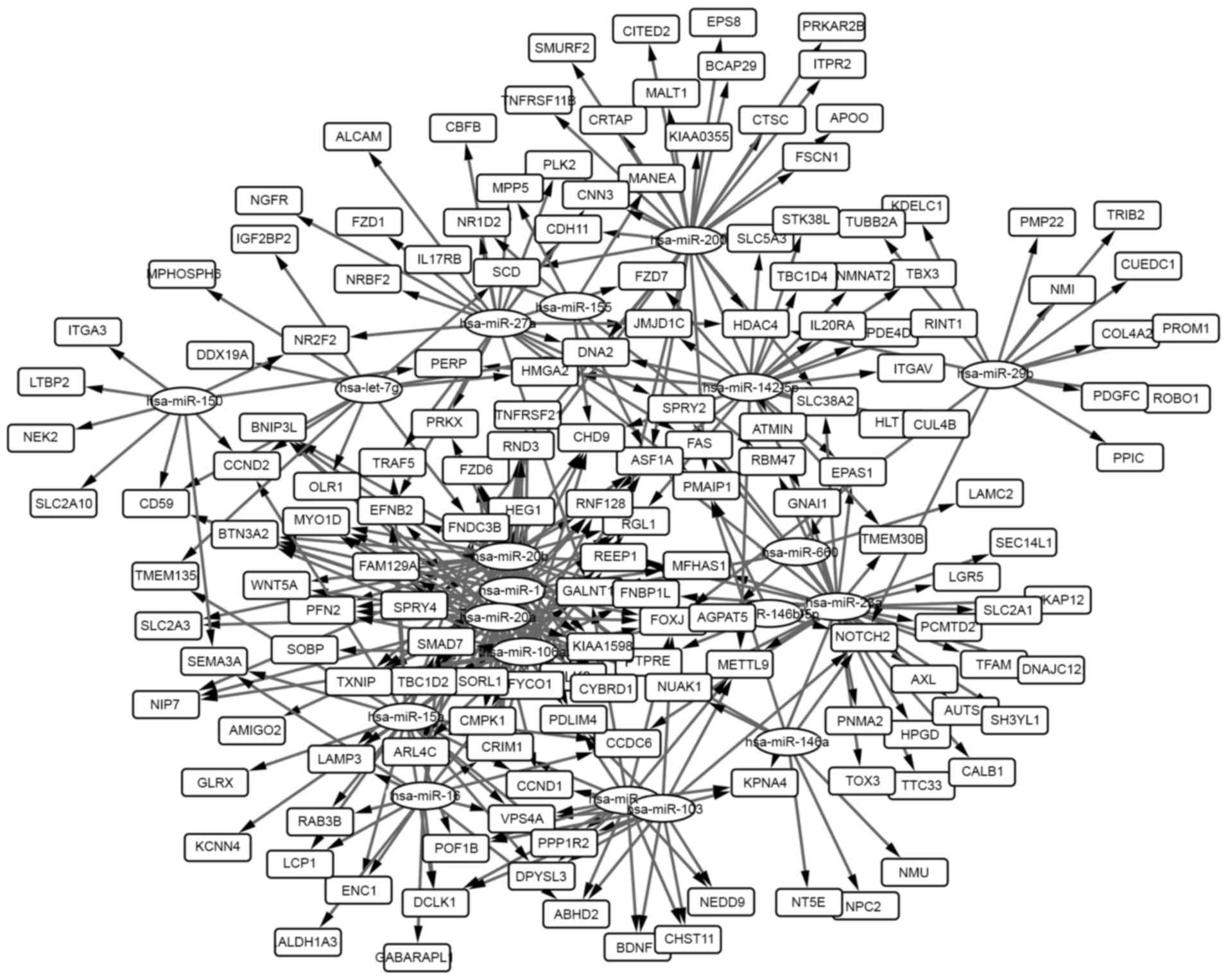
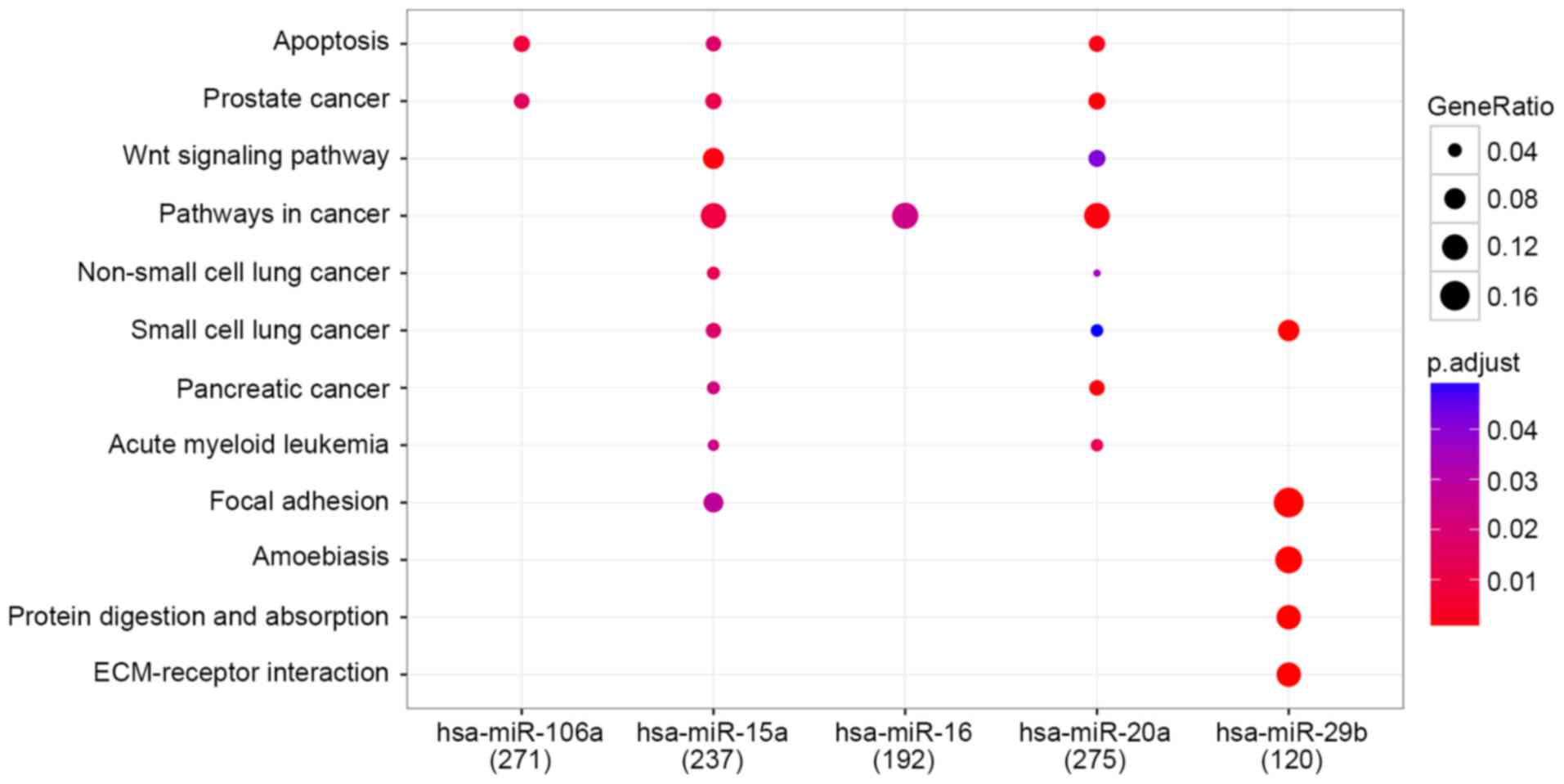
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shike M, Winawer SJ, Greenwald PH, Bloch
A, Hill MJ and Swaroop SV: Primary prevention of colorectal cancer.
The WHO collaborating centre for the prevention of colorectal
cancer. Bull World Health Organ. 68:377–385. 1990.
|
|
3
|
Matsuda T, Ono A, Kakugawa Y, Matsumoto M
and Saito Y: Impact of screening colonoscopy on outcomes in
colorectal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 45:900–905. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sabatino SA, Lawrence B, Elder R, Mercer
SL, Wilson KM, DeVinney B, Melillo S, Carvalho M, Taplin S, Bastani
R, et al: Effectiveness of interventions to increase screening for
breast, cervical and colorectal cancers: Nine updated systematic
reviews for the guide to community preventive services. Am J Prev
Med. 43:97–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Board PDQATE: Colon Cancer Treatment
(PDQ®): Health professional versionPDQ Cancer
Information Summaries. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD:
2002
|
|
6
|
Cao H, Xu E, Liu H, Wan L and Lai M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis:
A system review. Pathol Res Pract. 211:557–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Christofori G: New signals from the
invasive front. Nature. 441:444–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kanthan R, Senger JL and Kanthan SC:
Molecular events in primary and metastatic colorectal carcinoma: A
review. Patholog Res Int. 2012:5974972012.
|
|
10
|
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K,
Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, et al:
Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J
Clin. 62:220–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Grothey A and Schmoll HJ: New chemotherapy
approaches in colorectal cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 13:275–286. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cui YM, Jiao HL, Ye YP, Chen CM, Wang JX,
Tang N, Li TT, Lin J, Qi L, Wu P, et al: FOXC2 promotes colorectal
cancer metastasis by directly targeting MET. Oncogene.
34:4379–4390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yuan R, Ke J, Sun L, He Z, Zou Y, He X,
Chen Y, Wu X, Cai Z, Wang L, et al: HES1 promotes metastasis and
predicts poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 32:169–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Z, Liu X, Feng B, Liu N, Wu Q, Han
Y, Nie Y, Wu K, Shi Y and Fan D: STIM1, a direct target of
microRNA-185, promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with poor
prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 34:4808–4820. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhou ZH, Rao J, Yang J, Wu F, Tan J, Xu
SL, Ding Y, Zhan N, Hu XG, Cui YH, et al: SEMA3F prevents
metastasis of colorectal cancer by PI3K-AKT-dependent
down-regulation of the ASCL2-CXCR4 axis. J Pathol. 236:467–478.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fang Y, Liang X, Jiang W, Li J, Xu J and
Cai X: Cyclin b1 suppresses colorectal cancer invasion and
metastasis by regulating e-cadherin. PLoS One. 10:e01268752015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li X, Chen T, Shi Q, Li J, Cai S, Zhou P,
Zhong Y and Yao L: Angiopoietin-like 4 enhances metastasis and
inhibits apoptosis via inducing bone morphogenetic protein 7 in
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:128–134.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Song B, Wang W, Zheng Y, Yang J and Xu Z:
P21-activated kinase 1 and 4 were associated with colorectal cancer
metastasis and infiltration. J Surg Res. 196:130–135. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Purnak T, Ozaslan E and Efe C: Molecular
basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 362:1246–1247. 2010.
|
|
22
|
Provenzani A, Fronza R, Loreni F, Pascale
A, Amadio M and Quattrone A: Global alterations in mRNA polysomal
recruitment in a cell model of colorectal cancer progression to
metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 27:1323–1333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Drusco A, Nuovo GJ, Zanesi N, Di Leva G,
Pichiorri F, Volinia S, Fernandez C, Antenucci A, Costinean S,
Bottoni A, et al: MicroRNA profiles discriminate among colon cancer
metastasis. PLoS One. 9:e966702014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wiberg AO, Liu L, Tong Z, Myslivets E,
Ataie V, Kuo BP, Alic N and Radic S: Photonic preprocessor for
analog-to-digital-converter using a cavity-less pulse source. Opt
Express. 20:B419–B427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dweep H, Gretz N and Sticht C: miRWalk
database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1182:289–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Heuberger J and Birchmeier W: Interplay of
cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0029152010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tenbaum SP, Ordóñez-Morán P, Puig I,
Chicote I, Arqués O, Landolfi S, Fernández Y, Herance JR, Gispert
JD, Mendizabal L, et al: β-catenin confers resistance to PI3K and
AKT inhibitors and subverts FOXO3a to promote metastasis in colon
cancer. Nat Med. 18:892–901. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Qi J, Yu Y, Öztürk Ö Akilli, Holland JD,
Besser D, Fritzmann J, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Eckert K, Fichtner I and
Birchmeier W: New Wnt/β-catenin target genes promote experimental
metastasis and migration of colorectal cancer cells through
different signals. Gut. 65:1690–1701. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hu TH, Yao Y, Yu S, Han LL, Wang WJ, Guo
H, Tian T, Ruan ZP, Kang XM, Wang J, et al: SDF-1/CXCR4 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of colorectal
cancer by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer
Lett. 354:417–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ting WC, Chen LM, Pao JB, Yang YP, You BJ,
Chang TY, Lan YH, Lee HZ and Bao BY: Common genetic variants in Wnt
signaling pathway genes as potential prognostic biomarkers for
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e561962013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mariman EC and Wang P: Adipocyte
extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1277–1292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang HJ, Tao J, Sheng L, Hu X, Rong RM,
Xu M and Zhu TY: Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation
and invasion by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the
ECM-receptor interaction pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1801–1812.
2016.
|
|
38
|
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP,
Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S,
et al: Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of
tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell.
14:79–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Katoh D, Nishizuka M, Osada S and Imagawa
M: Fad104, a positive regulator of adipocyte differentiation,
suppresses invasion and metastasis of melanoma cells by inhibition
of STAT3 activity. PLoS One. 10:e01171972015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nishizuka M, Kishimoto K, Kato A, Ikawa M,
Okabe M, Sato R, Niida H, Nakanishi M, Osada S and Imagawa M:
Disruption of the novel gene fad104 causes rapid postnatal death
and attenuation of cell proliferation, adhesion, spreading and
migration. Exp Cell Res. 315:809–819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cai C, Rajaram M, Zhou X, Liu Q, Marchica
J, Li J and Powers RS: Activation of multiple cancer pathways and
tumor maintenance function of the 3q amplified oncogene FNDC3B.
Cell Cycle. 11:1773–1781. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zeng H and Tang L: CRIM1, the antagonist
of BMPs, is a potential risk factor of cancer. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 14:652–658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Nakashima Y, Morimoto M, Toda K, Shinya T,
Sato K and Takahashi S: Inhibition of the proliferation and
acceleration of migration of vascular endothelial cells by
increased cysteine-rich motor neuron 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
462:215–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Prenkert M, Uggla B, Tidefelt U and Strid
H: CRIM1 is expressed at higher levels in drug-resistant than in
drug-sensitive myeloid leukemia HL60 cells. Anticancer Res.
30:4157–4161. 2010.
|
|
45
|
Qiu X, Ji B, Yang L, Huang Q, Shi W, Ding
Z, He X, Ban N, Fan S, Zhang J and Tian Y: The role of FoxJ2 in the
migration of human glioma cells. Pathol Res Pract. 211:389–397.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Yang S, Ni Q, He S, Zhao Y, Yuan
Q, Li C, Chen H, Zhang L, Zou L, et al: Overexpression of forkhead
box J2 can decrease the migration of breast cancer cells. J Cell
Biochem. 113:2729–2737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Qiang Y, Wang F, Yan S, Zhang H, Zhu L and
Chen Z, Tu F, Wang D, Wang G, Wang W and Chen Z: Abnormal
expression of Forkhead Box J2 (FOXJ2) suppresses migration and
invasion in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and is associated with
prognosis. Int J Oncol. 46:2449–2458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|