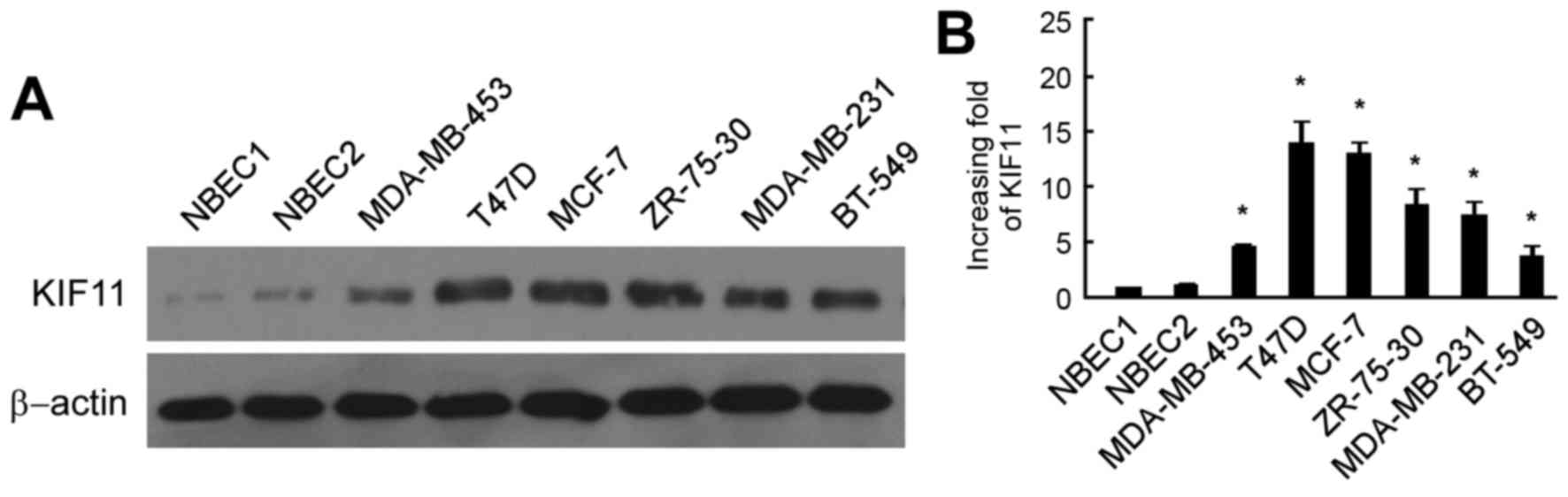
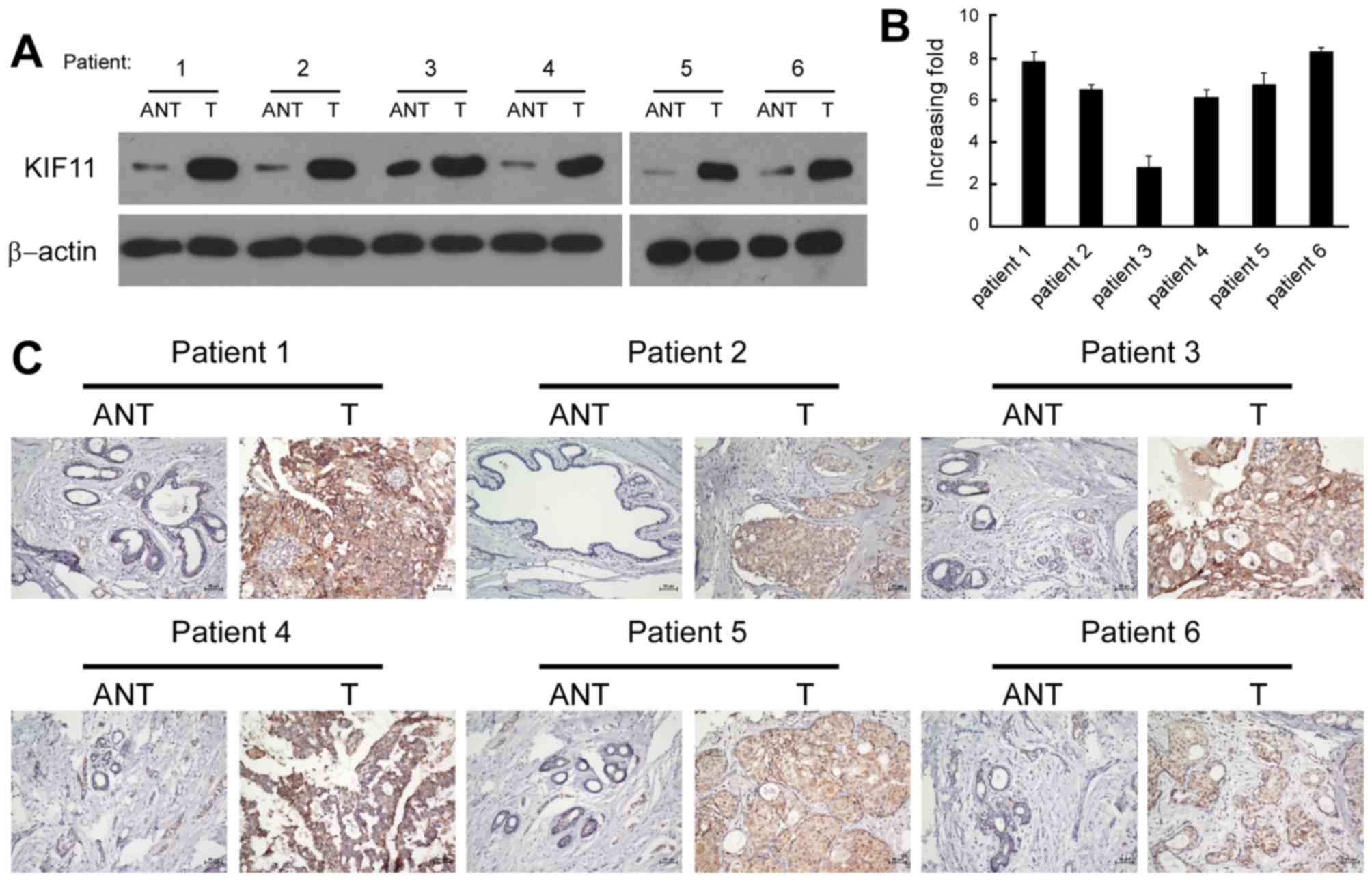
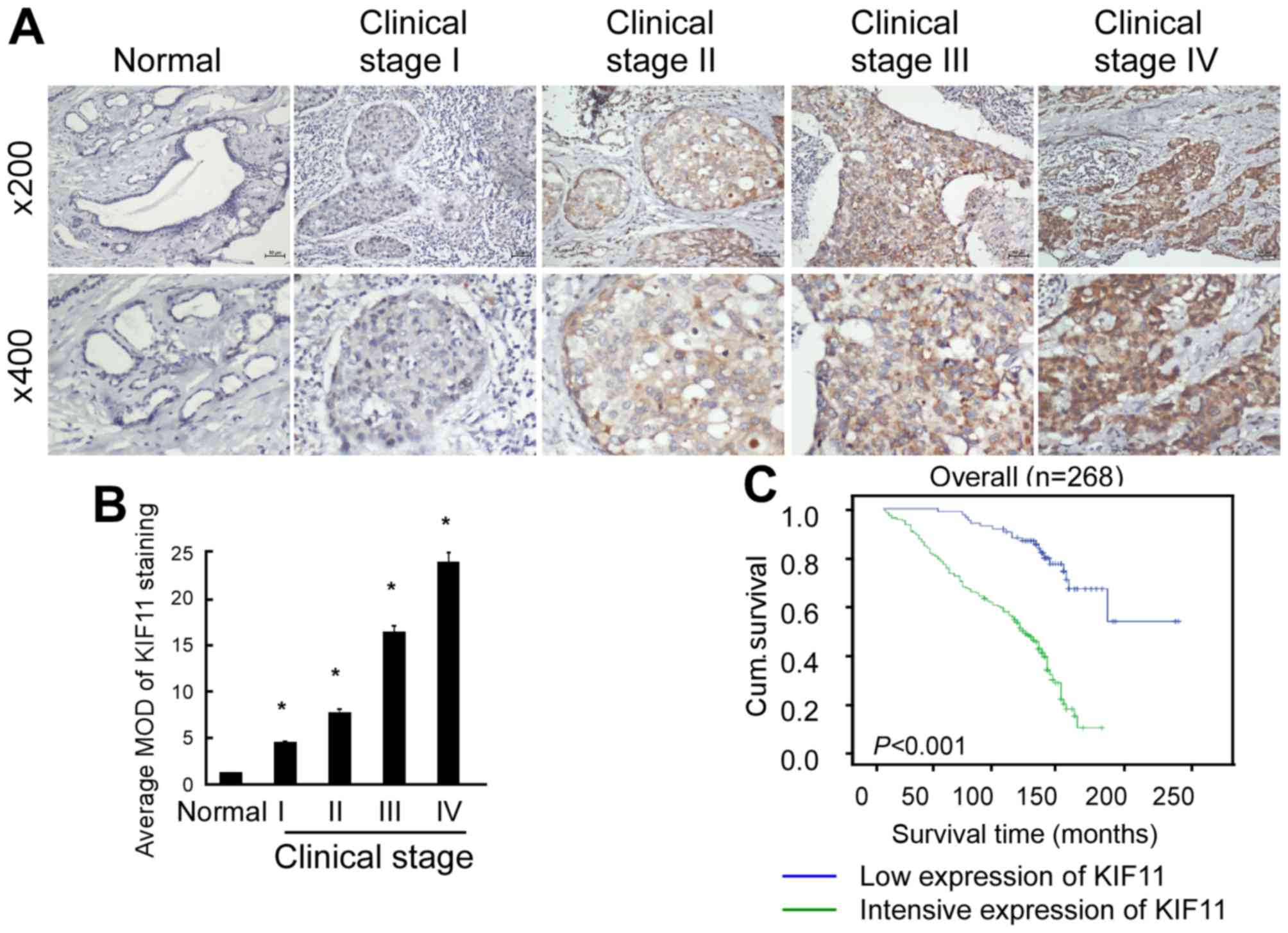
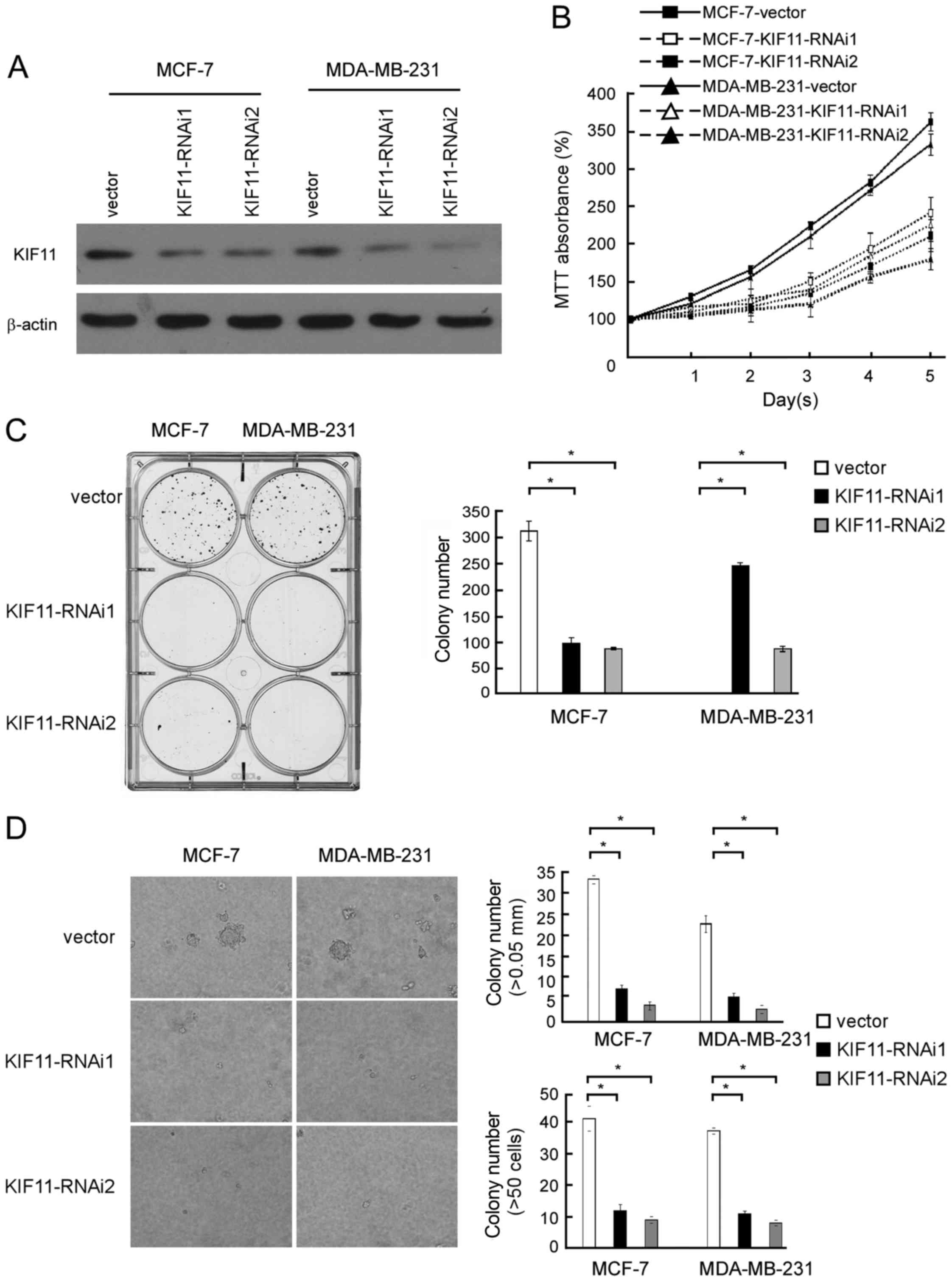
|
1
|
Stuckey AR and Onstad MA: Hereditary
breast cancer: An update on risk assessment and genetic testing in
2015. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213:161–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sutherland RL, Hamilton JA, Sweeney KJ,
Watts CK and Musgrove EA: Expression and regulation of cyclin genes
in breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 34:651–656. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sjöström J, Blomqvist C, Heikkilä P,
Boguslawski KV, Räisänen-Sokolowski A, Bengtsson NO, Mjaaland I,
Malmström P, Ostenstadt B, Bergh J, et al: Predictive value of p53,
mdm-2, p21, and mib-1 for chemotherapy response in advanced breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3103–3110. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartek J, Iggo R, Gannon J and Lane DP:
Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast
cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 5:893–899. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ertel A, Dean JL, Rui H, Liu C, Witkiewicz
AK, Knudsen KE and Knudsen ES: RB-pathway disruption in breast
cancer: Differential association with disease subtypes,
disease-specific prognosis and therapeutic response. Cell Cycle.
9:4153–4163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomas NM, Masur K, Piecha JC, Niggemann B
and Zänker KS: Akt and phospholipase Cγ are involved in the
regulation of growth and migration of MDA-MB-468 breast cancer and
SW480 colon cancer cells when cultured with diabetogenic levels of
glucose and insulin. BMC Res Notes. 5:2142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song L, Wang L, Li Y, Xiong H, Wu J, Li J
and Li M: Sam68 up-regulation correlates with, and its
down-regulation inhibits, proliferation and tumourigenicity of
breast cancer cells. J Pathol. 222:227–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iwakiri Y, Kamakura S, Hayase J and
Sumimoto H: Interaction of NuMA protein with the kinesin Eg5: It's
possible role in bipolar spindle assembly and chromosome alignment.
Biochem J. 451:195–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun L, Sun X, Xie S, Yu H and Zhong D:
Significant decrease of ADP release rate underlies the potent
activity of dimethylenastron to inhibit mitotic kinesin Eg5 and
cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 447:465–470.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McGrath MJ, Kuo IF, Hayashi S and Takada
S: Adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis mechanism in kinesin studied
by combined quantum-mechanical/molecular-mechanical metadynamics
simulations. J Am Chem Soc. 135:8908–8919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Robitaille JM, Gillett RM, LeBlanc MA,
Gaston D, Nightingale M, Mackley MP, Parkash S, Hathaway J, Thomas
A, Ells A, et al: Phenotypic overlap between familial exudative
vitreoretinopathy and microcephaly, lymphedema, and chorioretinal
dysplasia caused by KIF11 mutations. JAMA Ophthalmol.
132:1393–1399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hazan F, Ostergaard P, Ozturk T, Kantekin
E, Atlihan F, Jeffery S and Ozkinay F: A novel KIF11 mutation in a
Turkish patient with microcephaly, lymphedema, and chorioretinal
dysplasia from a consanguineous family. Am J Med Genet A.
158A:1–1689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riedl J, Voβmerbäumer U, Stoffelns B and
Elflein H: Total retinal detachment caused by a KIF11 mutation. Eur
J Ophthalmol. May 24–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jones GE, Ostergaard P, Moore AT, Connell
FC, Williams D, Quarrell O, Brady AF, Spier I, Hazan F, Moldovan O,
et al: Microcephaly with or without chorioretinopathy, lymphoedema,
or mental retardation (MCLMR): Review of phenotype associated with
KIF11 mutations. Eur J Hum Genet. 22:881–887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bullock JM, Medway C, Cortina-Borja M,
Turton JC, Prince JA, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Schuur M, Breteler MM,
van Duijn CM, Kehoe PG, et al: Discovery by the Epistasis Project
of an epistatic interaction between the GSTM3 gene and the
HHEX/IDE/KIF11 locus in the risk of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol
Aging. 34:1309.e1–e7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Qian Y, Lu F, Dong M, Lin Y, Li H, Chen J,
Shen C, Jin G, Hu Z and Shen H: Genetic variants of IDE-KIF11-HHEX
at 10q23.33 associated with type 2 diabetes risk: A fine-mapping
study in Chinese population. PLoS One. 7:e350602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan LJ, Saijo M, Kuraoka I, Narita T,
Takahata C, Iwai S and Tanaka K: Xeroderma pigmentosum group F
protein binds to Eg5 and is required for proper mitosis:
Implications for XP-F and XFE. Genes Cells. 17:173–185. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wakana Y, Villeneuve J, van Galen J,
Cruz-Garcia D, Tagaya M and Malhotra V: Kinesin-5/Eg5 is important
for transport of CARTS from the trans-Golgi network to the cell
surface. J Cell Biol. 202:241–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding S, Xing N, Lu J, Zhang H, Nishizawa
K, Liu S, Yuan X, Qin Y, Liu Y, Ogawa O, et al: Overexpression of
Eg5 predicts unfavorable prognosis in non-muscle invasive bladder
urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol. 18:432–438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsui M, Xie T, Orth JD, Carpenter AE,
Rudnicki S, Kim S, Shamu CE and Mitchison TJ: An intermittent live
cell imaging screen for siRNA enhancers and suppressors of a
kinesin-5 inhibitor. PLoS One. 4:e73392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Woessner R, Tunquist B, Lemieux C,
Chlipala E, Jackinsky S, Dewolf W Jr, Voegtli W, Cox A, Rana S, Lee
P and Walker D: ARRY-520, a novel KSP inhibitor with potent
activity in hematological and taxane-resistant tumor models.
Anticancer Res. 29:4373–4380. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Woessner R, Gross S,
Schober WD, Estrov Z, Kantarjian H and Andreeff M: Inhibition of
KSP by ARRY-520 induces cell cycle block and cell death via the
mitochondrial pathway in AML cells. Leukemia. 23:1755–1762. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim KH, Xie Y, Tytler EM, Woessner R, Mor
G and Alvero AB: KSP inhibitor ARRY-520 as a substitute for
Paclitaxel in Type I ovarian cancer cells. J Transl Med. 7:632009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asbaghi Y, Thompson LL, Lichtensztejn Z
and McManus KJ: KIF11 silencing and inhibition induces chromosome
instability that may contribute to cancer. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 56:668–680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schneider MA, Christopoulos P, Muley T,
Warth A, Klingmueller U, Thomas M, Herth FJ, Dienemann H, Mueller
NS, Theis F, et al: AURKA, DLGAP5, TPX2, KIF11 and CKAP5: Five
specific mitosis-associated genes correlate with poor prognosis for
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Oncol. 50:365–372. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Imai T, Oue N, Sentani K, Sakamoto N,
Uraoka N, Egi H, Hinoi T, Ohdan H, Yoshida K and Yasui W: KIF11 is
required for spheroid formation by oesophageal and colorectal
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37:47–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Imai T, Oue N, Nishioka M, Mukai S, Oshima
T, Sakamoto N, Sentani K, Matsusaki K, Yoshida K and Yasui W:
Overexpression of KIF11 in gastric cancer with intestinal mucin
phenotype. Pathobiology. 84:16–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL,
Gong LY, Wu J, Yuan J, Zhang HZ, Zeng MS and Li M: Astrocyte
elevated gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer
progression and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res.
14:3319–3326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J, Yang L, Song L, Xiong H, Wang L, Yan
X, Yuan J, Wu J and Li M: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a
proliferation promoter in breast cancer via suppressing
transcriptional factor FOXO1. Oncogene. 28:3188–3196. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Li J, Zheng H, Yu C, Chen J, Liu
Z, Li M, Zeng M, Zhou F and Song L: Expression and cytoplasmic
localization of SAM68 is a significant and independent prognostic
marker for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:2685–2693. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hayashi N, Koller E, Fazli L and Gleave
ME: Effects of Eg5 knockdown on human prostate cancer xenograft
growth and chemosensitivity. Prostate. 68:1283–1295. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu M, Li D, Sun L, Chen J, Sun X, Zhang
L, Huo L and Zhou J: Modulation of Eg5 activity contributes to
mitotic spindle checkpoint activation and Tat-mediated apoptosis in
CD4-positive T-lymphocytes. J Pathol. 233:138–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun D, Lu J, Ding K, Bi D, Niu Z, Cao Q,
Zhang J and Ding S: The expression of Eg5 predicts a poor outcome
for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:4762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bartoli KM, Jakovljevic J, Woolford JL Jr
and Saunders WS: Kinesin molecular motor Eg5 functions during
polypeptide synthesis. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3420–3430. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith E, Hégarat N, Vesely C, Roseboom I,
Larch C, Streicher H, Straatman K, Flynn H, Skehel M, Hirota T, et
al: Differential control of Eg5-dependent centrosome separation by
Plk1 and Cdk1. EMBO J. 30:2233–2245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang G, Gao X, Huang Y, Yao Z, Shi Q and
Wu M: Nucleophosmin/B23 inhibits Eg5-mediated microtubule
depolymerization by inactivating its ATPase activity. J Biol Chem.
285:19060–19067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cochran JC, Sontag CA, Maliga Z, Kapoor
TM, Correia JJ and Gilbert SP: Mechanistic analysis of the mitotic
kinesin Eg5. J Biol Chem. 279:38861–38870. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rosenfeld SS, Xing J, Jefferson GM and
King PH: Docking and rolling, a model of how the mitotic motor Eg5
works. J Biol Chem. 280:35684–35695. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martens-de Kemp SR, Nagel R, Stigter-van
Walsum M, Van der Meulen IH, van Beusechem VW, Braakhuis BJ and
Brakenhoff RH: Functional genetic screens identify genes essential
for tumor cell survival in head and neck and lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1994–2003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marra E, Palombo F, Ciliberto G and
Aurisicchio L: Kinesin spindle protein SiRNA slows tumor
progression. J Cell Physiol. 228:58–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Valensin S, Ghiron C, Lamanna C, Kremer A,
Rossi M, Ferruzzi P, Nievo M and Bakker A: KIF11 inhibition for
glioblastoma treatment: Reason to hope or a struggle with the
brain? BMC Cancer. 9:1962009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tao W, South VJ, Diehl RE, Davide JP,
Sepp-Lorenzino L, Fraley ME, Arrington KL and Lobell RB: An
inhibitor of the kinesin spindle protein activates the intrinsic
apoptotic pathway independently of p53 and de novo protein
synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 27:689–698. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|