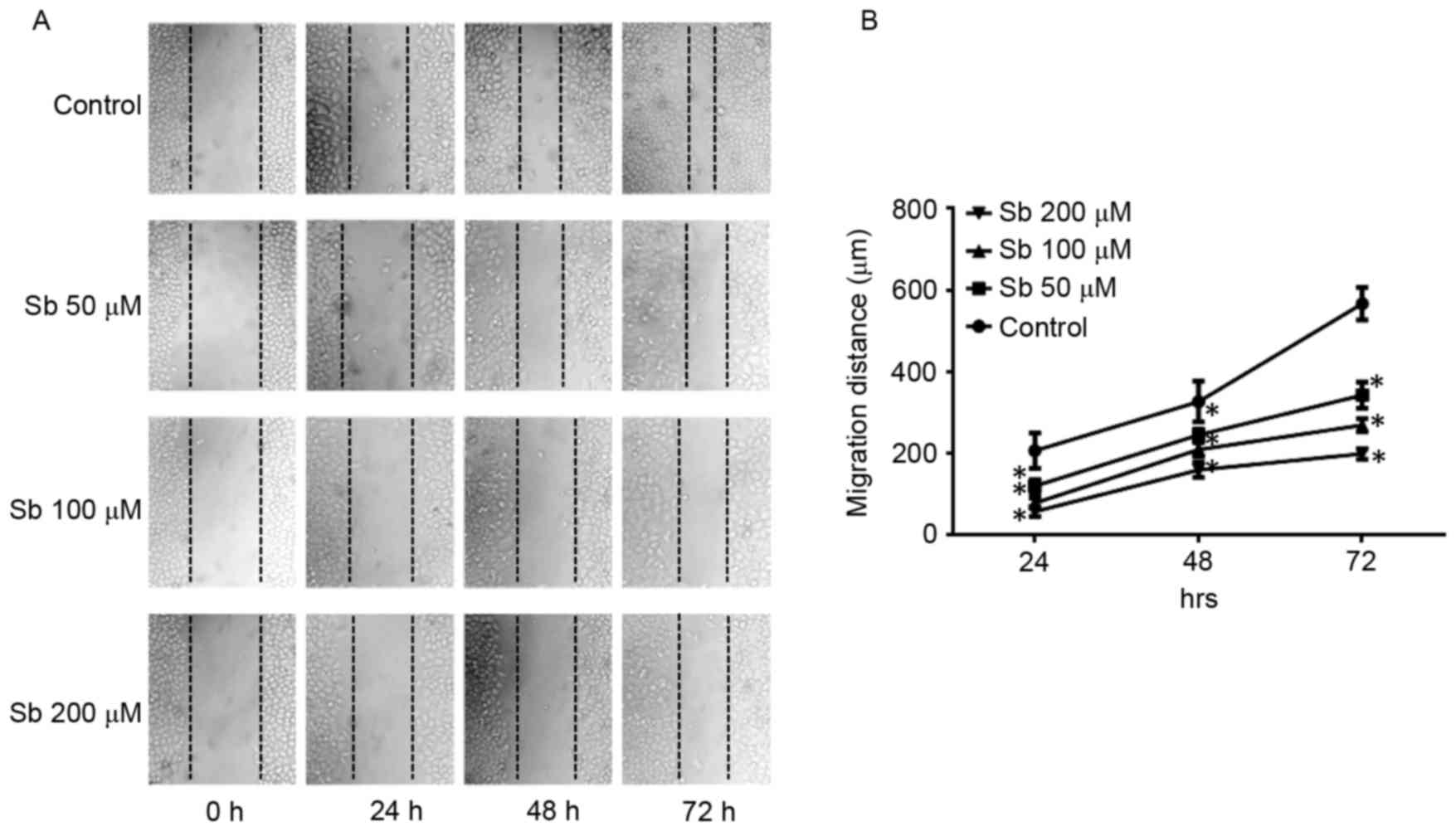
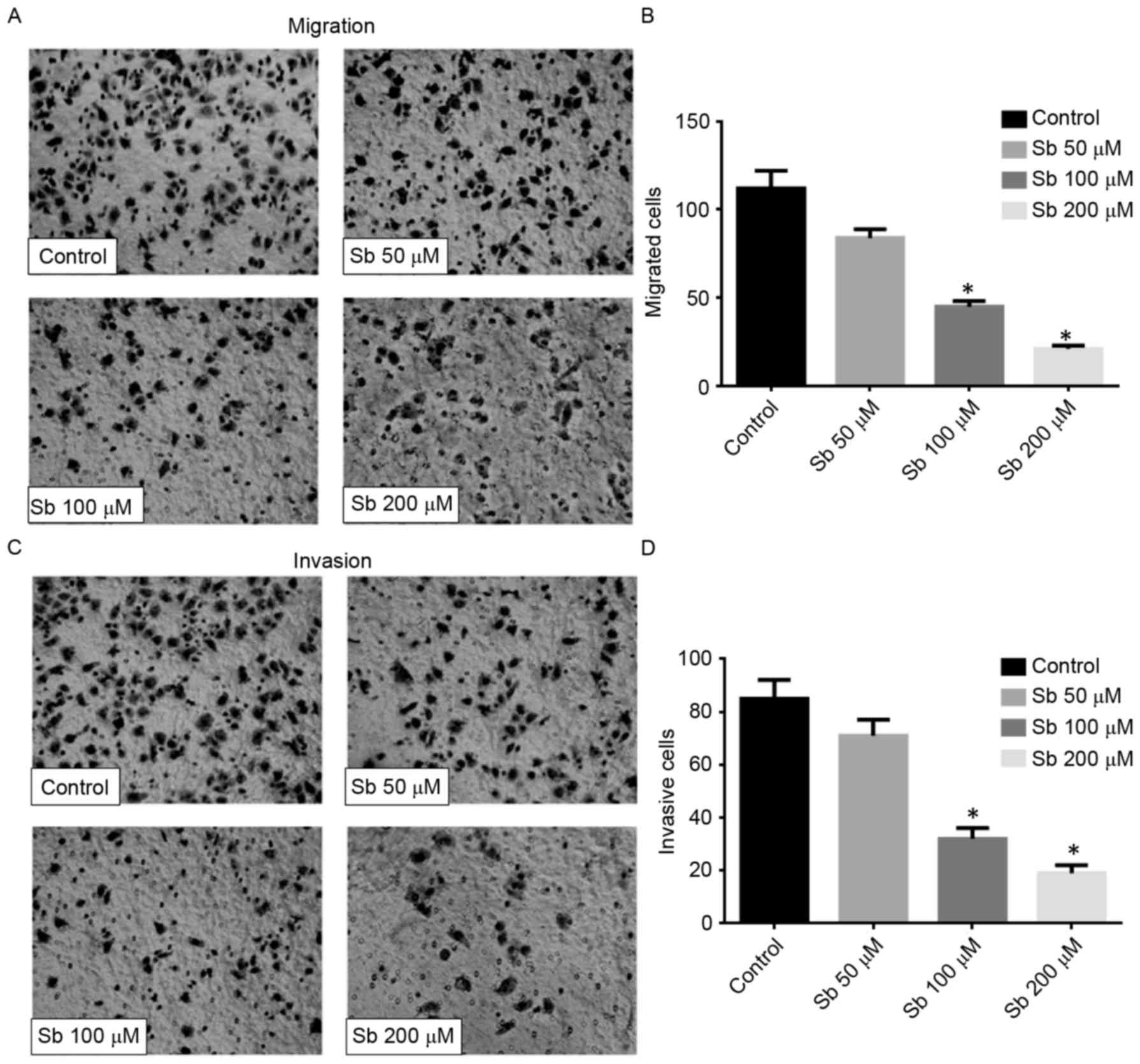
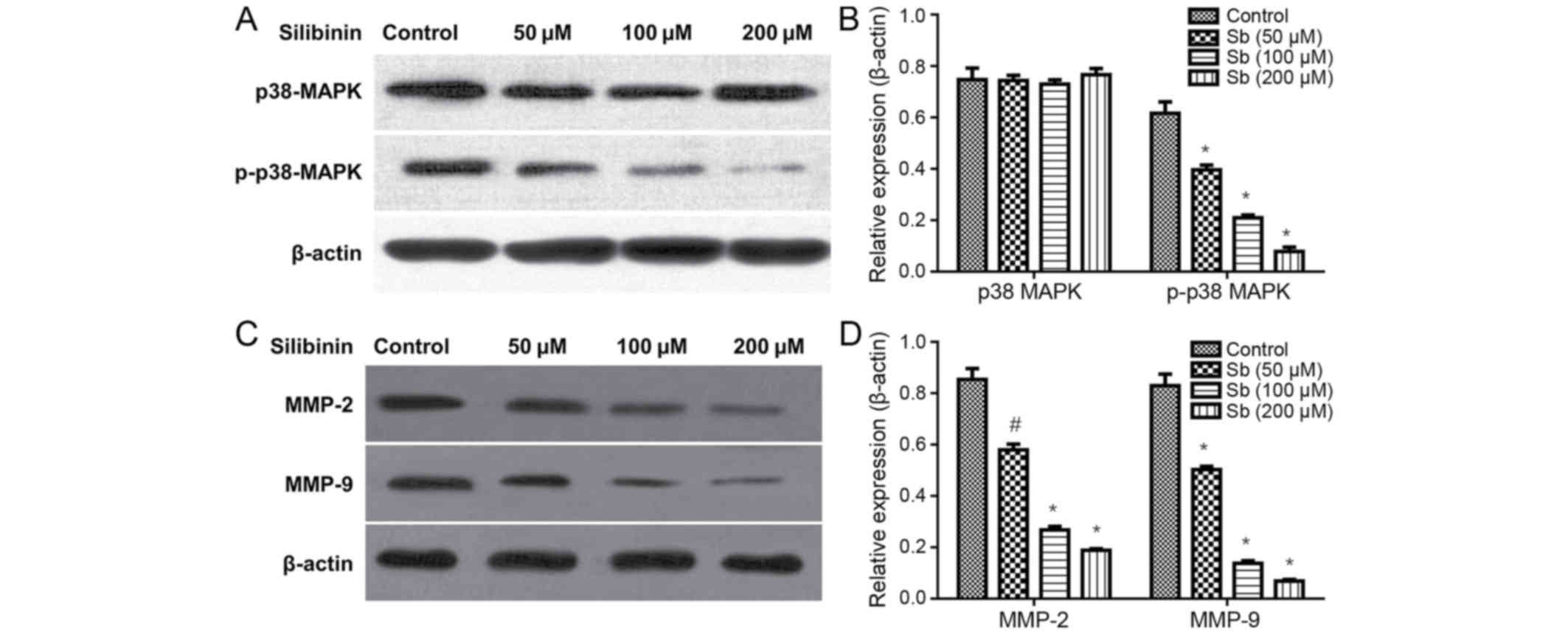
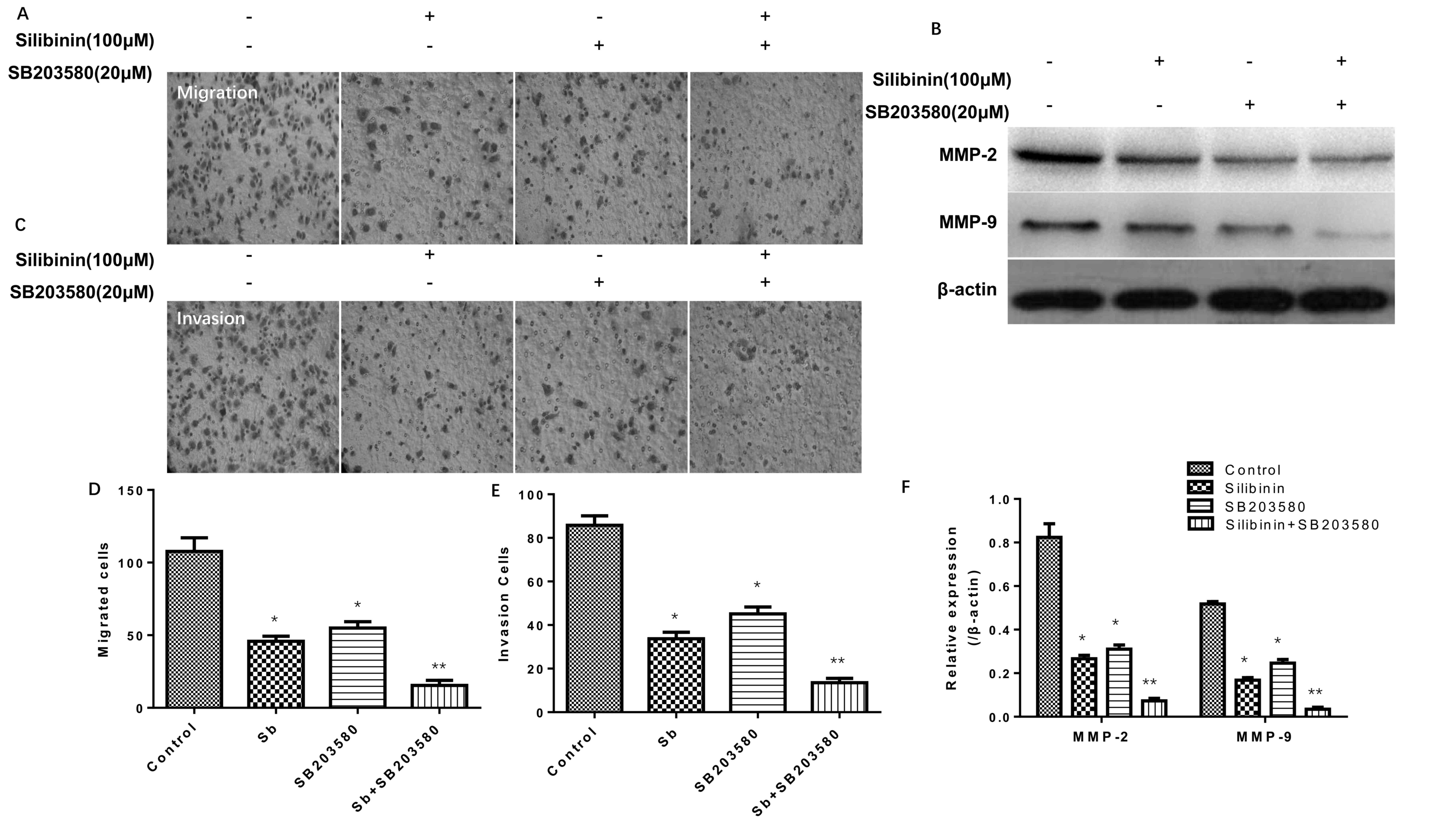
|
1
|
Mazzocca A and Carloni V: The metastatic
process: Methodological advances and pharmacological challenges.
Curr Med Chem. 16:1704–1717. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Hodgson L and Condeelis
J: Directed cell invasion and migration during metastasis. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 24:277–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hulkower KI and Herber RL: Cell migration
and invasion assays as tools for drug discovery. Pharmaceutics.
3:107–124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loukopoulos P, Mungall BA, Straw RC,
Thornton JR and Robinson WF: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −9
involvement in canine tumors. Vet Pathol. 40:382–394. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koul HK, Pal M and Koul S: Role of p38 MAP
kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer.
4:342–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dolado I and Nebreda AR: Regulation of
tumorigenesis by p38 MAP kinase. Topics Curr Genet. 20:99–128.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Emerling BM, Platanias LC, Black E,
Nebreda AR, Davis RJ and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is
required for hypoxia signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4853–4862. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee KH, Kim SW and Kim JR: Reactive oxygen
species regulate urokinase plasminogen activator expression and
cell invasion via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways after
treatment with hepatocyte growth factor in stomach cancer cells. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:732009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Boukerche H, Aissaoui H, Prévost C, Hirbec
H, Das SK, Su ZZ, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Src kinase activation is
mandatory for MDA-9/syntenin-mediated activation of nuclear
factor-kappaB. Oncogene. 29:3054–3066. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo X, Ma N, Wang J, Song J, Bu X, Cheng
Y, Sun K, Xiong H, Jiang G, Zhang B, et al: Increased p38-MAPK is
responsible for chemotherapy resistance in human gastric cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 8:3752008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chou RH, Hsieh SC, Yu YL, Huang MH, Huang
YC and Hsieh YH: Fisetin inhibits migration and invasion of human
cervical cancer cells by down-regulating urokinase plasminogen
activator expression through suppressing the p38 MAPK-dependent
NF-kB signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e719832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peng CY, Yang HW, Chu YH, Chang YC, Hsieh
MJ, Chou MY, Yeh KT, Lin YM, Yang SF and Lin CW: Caffeic Acid
phenethyl ester inhibits oral cancer cell metastasis by regulating
matrix metalloproteinase-2 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:7325782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XF, Zhou QM, Du J, Zhang H, Lu YY and
Su SB: Baicalin suppresses migration, invasion and metastasis of
breast cancer via p38MAPK signaling pathway. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 13:923–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
DE Oliveira DT, Savio AL, Marcondes JP,
Barros TM, Barbosa LC, Salvadori DM and DA Silva GN: Cytotoxic and
toxicogenomic effects of silibinin in bladder cancer cells with
different TP53 status. J Biosci. 42:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Polachi N, Bai G, Li T, Chu Y, Wang X, Li
S, Gu N, Wu J, Li W, Zhang Y, et al: Modulatory effects of
silibinin in various cell signaling pathways against liver
disorders and cancer-A comprehensive review. Eur J Med Chem.
123:577–595. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jahanafrooz Z, Motameh N and Bakhshandeh
B: Comparative evaluation of Silibinin effects on cell cycling and
apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 and T47D cell lines. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:2661–2665. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang HR, Chen PN, Yang SF, Sun YS, Wu SW,
Hung TW, Lian JD, Chu SC and Hsieh YS: Silibinin inhibits the
invasion and migration of renal carcinoma 786-O cells in vitro,
inhibits the growth of xenografts in vivo and enhances
chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel. Mol Carcinog.
50:811–823. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lali FV, Hunt AE, Turner SJ and Foxwell
BM: The pyridinyl imidazole inhibitor SB203580 blocks
phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase activity, protein kinase
B phosphorylation, and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation in
interleukin-2-stimulated T cells independently of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 275:7395–7402. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Birkenkamp KU, Tuyt LM, Lummen C, Wierenga
AT, Kruijer W and Vellenga E: The p38 MAP kinase inhibitor SB203580
enhances nuclear factor-kappa B transcriptional activity by a
non-specific effect upon the ERK pathway. Br J Pharmacol.
131:99–107. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barancik M, Htun P, Strohm C, Kilian S and
Schaper W: Inhibition of the cardiac p38-MAPK pathway by SB203580
delays ischemic cell death. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 35:474–483.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin N, Wang Q, Zhang X, Jiang D, Cheng H
and Zhu K: The selective p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
inhibitor, SB203580, improves renal disease in MRL/lpr mouse model
of systemic lupus. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:1319–1326. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang H, Wu S and Xing D: YAP accelerates
A(25–35)-induced apoptosis through upregulation of Bax expression
by interaction with p73. Apoptosis. 16:808–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lali FV, Hunt AE, Turner SJ and Foxwell
BM: The pyridinyl imidazole inhibitor SB203580 blocks
phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase activity, protein kinase
B phosphorylation, and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation in
interleukin-2-stimulated T cells independently of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 275:7395–7402. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu KJ, Zeng J, Zhu GD, Zhang LL, Zhang D,
Li L, Fan JH, Wang XY and He DL: Silibinin inhibits prostate cancer
invasion, motility and migration by suppressing vimentin and MMP-2
expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1162–1168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dastpeyman M, Motamed N, Azadmanesh K,
Mostafavi E, Kia V, Jahanian-Najafabadi A and Shokrgozar MA:
Inhibition of silibinin on migration and adhesion capacity of human
highly metastatic breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-231, by
evaluation of 1-integrin and downstream molecules, Cdc42, Raf-1 and
D4GDI. Med Oncol. 29:2512–2518. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metall oproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kleiner DE and Stetler-Stevenson WG:
Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 43 Suppl:S42–S51. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hidalgo M and Eckhardt SG: Development of
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 93:178–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gerstein ES, Sini L, Ryabov AB, Dvorova
EK, Yurchenko AA, Stilidi IS, Kushlinskii NE and Davydov MI:
Comparative enzyme immunoassay of matrix metalloproteinases-2,-7,-9
and their tissue inhibitor-2 in tumors and plasma of patients with
gastric cancer. Bull Exp Biol Med. 148:899–902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sampieri CL, de la Peña S, Ochoa-Lara M,
Zenteno-Cuevas R and León-Córdoba K: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in human gastric cancer and superficial
gastritis. World J Gastroenterol. 16:1500–1505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weng Y, Cai M, Zhu J, Geng J, Zhu K, Jin X
and Ding W: Matrix metalloproteinase activity in early-stage lung
cancer. Onkologie. 36:256–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dragutinović VV, Radonjić NV, Petronijević
ND, Tatić SB, Dimitrijević IB, Radovanović NS and Krivokapić ZV:
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and −9 (MMP-9) in preoperative
serum as independent prognostic markers in patients with colorectal
cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 355:173–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Ma J, Guo Q, Duan F, Tang F, Zheng
P, Zhao Z and Lu G: Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 22:664–667. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bradham C and McClay DR: p38 MAPK in
development and cancer. Cell Cycle. 5:824–828. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang C, Jacobson K and Schaller MD: MAP
kinases and migration. J Cell Sci. 117:4619–4628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang ZS, Luo P, Dai SH, Liu ZB, Zheng XR
and Chen T: Salvianolic acid B induces apoptosis in human glioma
U87 cells through p38-mediated ROS generation. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
33:921–928. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan F, Ma S, Cao W, Liu H, Chen F, Chen X
and Shi R: SDF-1 upregulation of MMP-2 is mediated by p38 MAPK
signaling in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep.
40:4139–4146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|