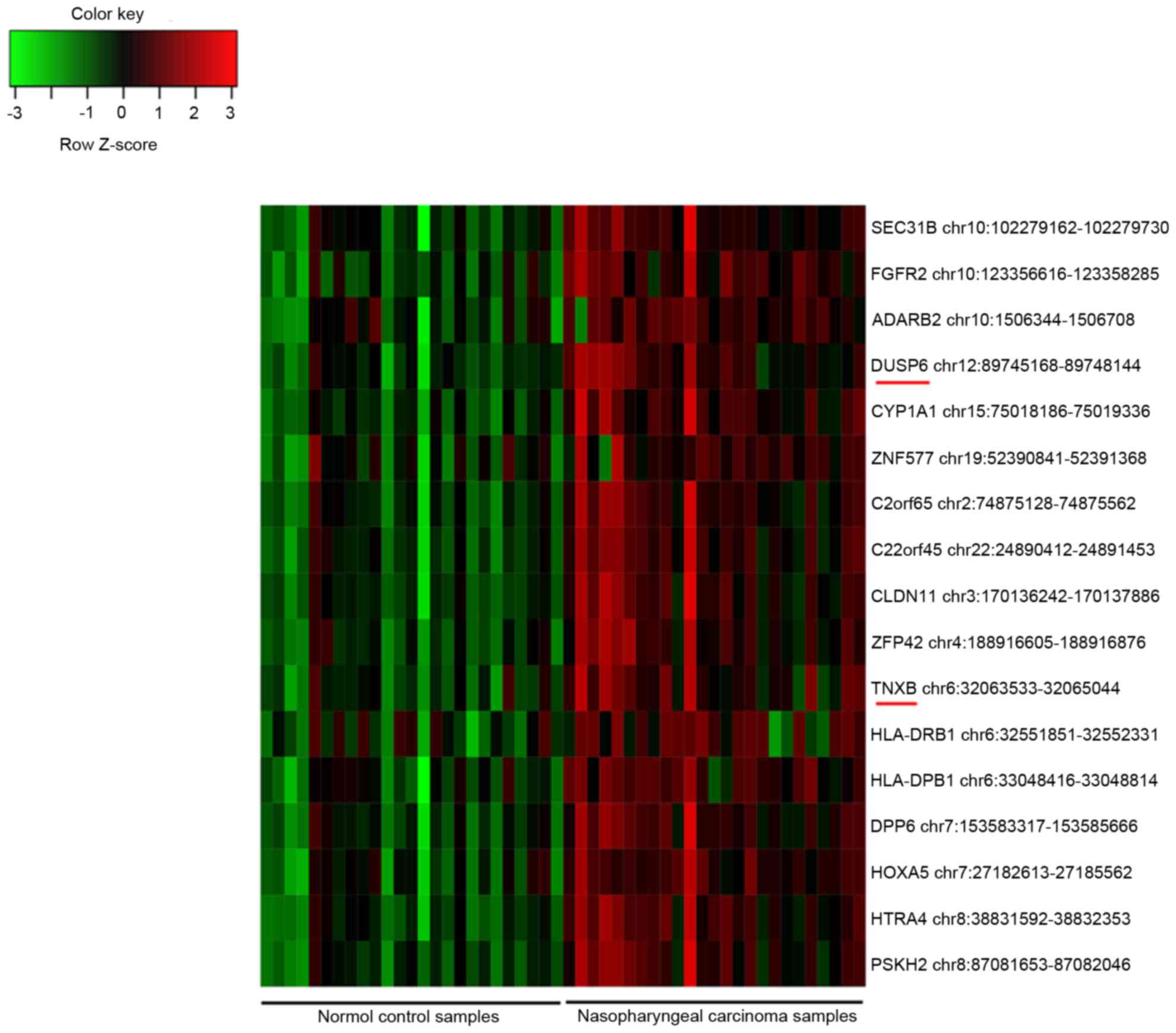
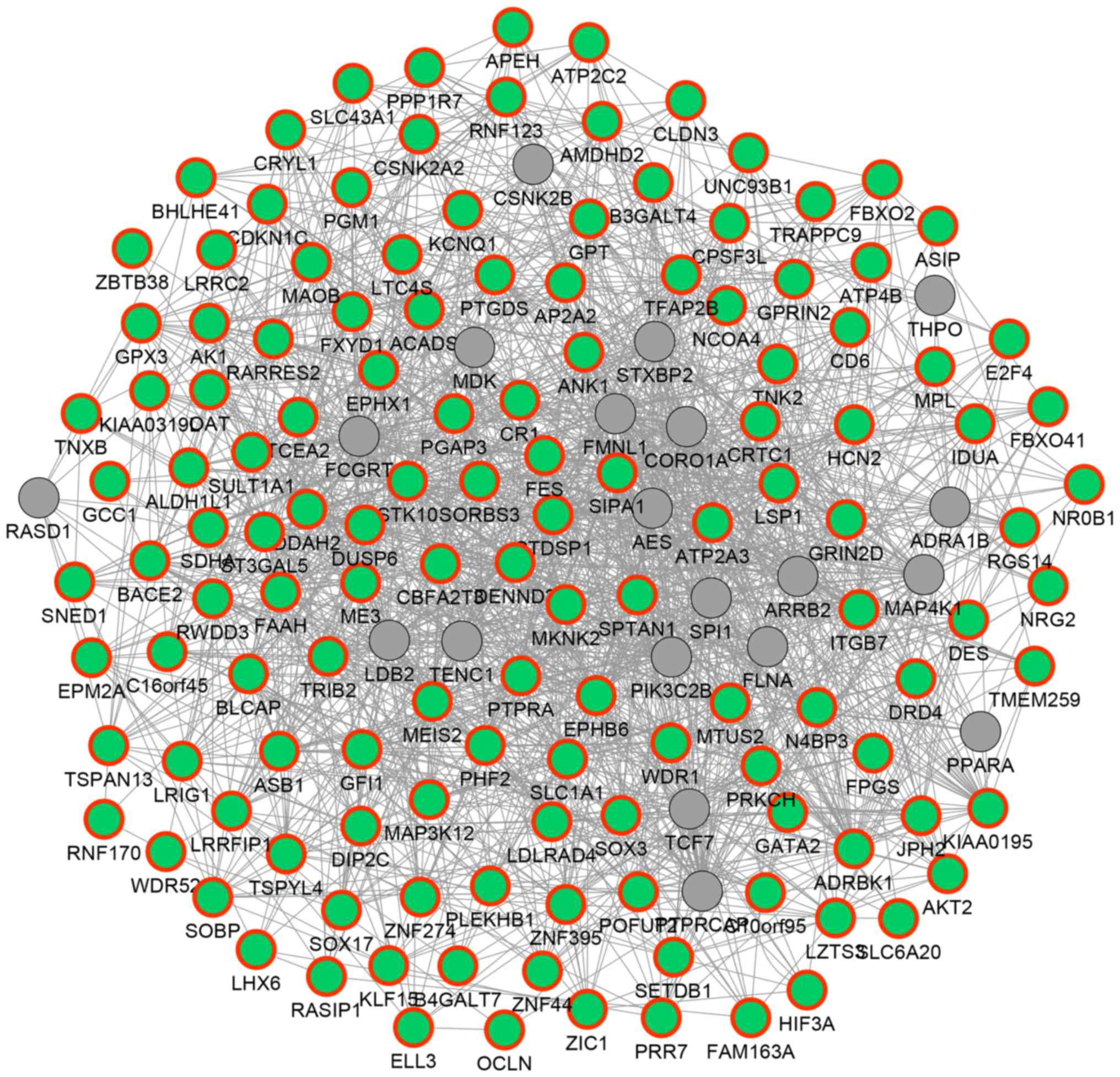
|
1
|
Hildesheim A and Wang CP: Genetic
predisposition factors and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk: A review
of epidemiological association studies, 2000–2011: Rosetta Stone
for NPC: Genetics, viral infection, and other environmental
factors. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:107–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang TJ, Riaz N, Cheng SK, Lu JJ and Lee
NY: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A review. J Radiat Oncol. 1:129–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Meissner A, Mikkelsen TS, Gu H, Wernig M,
Hanna J, Sivachenko A, Zhang X, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Jaffe DB,
et al: Genome-scale DNA methylation maps of pluripotent and
differentiated cells. Nature. 454:766–770. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Irizarry RA, Ladd-Acosta C, Wen B, Wu Z,
Montano C, Onyango P, Cui H, Gabo K, Rongione M, Webster M, et al:
The human colon cancer methylome shows similar hypo- and
hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores.
Nat Genet. 41:178–186. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai W, Cheung AK, Ko JM, Cheng Y, Zheng H,
Ngan RK, Ng WT, Lee AW, Yau CC, Lee VH and Lung ML: Comparative
methylome analysis in solid tumors reveals aberrant methylation at
chromosome 6p in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 4:1079–1090.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He D, Zeng Q, Ren G, Xiang T, Qian Y, Hu
Q, Zhu J, Hong S and Hu G: Protocadherin8 is a functional tumor
suppressor frequently inactivated by promoter methylation in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 21:569–575. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shu XS, Li L, Ji M, Cheng Y, Ying J, Fan
Y, Zhong L, Liu X, Tsao SW, Chan AT and Tao Q: FEZF2, a novel 3p14
tumor suppressor gene, represses oncogene EZH2 and MDM2 expression
and is frequently methylated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1984–1993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lan J, Tai HC, Lee SW, Chen TJ, Huang HY
and Li CF: Deficiency in expression and epigenetic DNA Methylation
of ASS1 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Negative prognostic
impact and therapeutic relevance. Tumour Biol. 35:161–169. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou W, Feng X, Ren C, Jiang X, Liu W,
Huang W, Liu Z, Li Z, Zeng L, Wang L, et al: Over-expression of
BCAT1, a c-Myc target gene, induces cell proliferation, migration
and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 12:532013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lian YF, Yuan J, Cui Q, Feng QS, Xu M, Bei
JX, Zeng YX and Feng L: Upregulation of KLHDC4 predicts a poor
prognosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One.
11:e01528202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton
MA, Dahl DB, Chen M, Cheng YJ, Westra WH, Chen CJ, Hildesheim A, et
al: Genome-wide expression profiling reveals EBV-associated
inhibition of MHC class I expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 66:7999–8006. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao YN, Cao X, Luo DH, Sun R, Peng LX,
Wang L, Yan YP, Zheng LS, Xie P, Cao Y, et al: Urokinase-type
plasminogen activator receptor signaling is critical in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth and metastasis. Cell Cycle.
13:1958–1969. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bose S, Yap LF, Fung M, Starzcynski J,
Saleh A, Morgan S, Dawson C, Chukwuma MB, Maina E, Buettner M, et
al: The ATM tumour suppressor gene is down-regulated in
EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol. 217:345–352.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Norfo R, Zini R, Pennucci V, Bianchi E,
Salati S, Guglielmelli P, Bogani C, Fanelli T, Mannarelli C, Rosti
V, et al: miRNA-mRNA integrative analysis in primary myelofibrosis
CD34+ cells: Role of miR-155/JARID2 axis in abnormal
megakaryopoiesis. Blood. 124:e21–e32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Teschendorff AE, Marabita F, Lechner M,
Bartlett T, Tegner J, Gomez-Cabrero D and Beck S: A beta-mixture
quantile normalization method for correcting probe design bias in
Illumina Infinium 450 k DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics.
29:189–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420.
2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Warden CD, Lee H, Tompkins JD, Li X, Wang
C, Riggs AD, Yu H, Jove R and Yuan YC: COHCAP: An integrative
genomic pipeline for single-nucleotide resolution DNA methylation
analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:e1172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi C, Hong L, Cheng Z and Yin Q:
Identification of metastasis-associated genes in colorectal cancer
using metaDE and survival analysis. Oncol Lett. 11:568–574.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O,
Zuberi K, Badrawi R, Chao P, Franz M, Grouios C, Kazi F, Lopes CT,
et al: The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network
integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:W214–W220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zuberi K, Franz M, Rodriguez H, Montojo J,
Lopes CT, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA prediction server 2013
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W115–W122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smith A, Price C, Cullen M, Muda M, King
A, Ozanne B, Arkinstall S and Ashworth A: Chromosomal localization
of three human dual specificity phosphatase genes (DUSP4, DUSP6 and
DUSP7). Genomics. 42:524–527. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jurek A, Amagasaki K, Gembarska A, Heldin
CH and Lennartsson J: Negative and positive regulation of MAPK
phosphatase 3 controls platelet-derived growth factor-induced Erk
activation. J Biol Chem. 284:4626–4634. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong VC, Chen H, Ko JM, Chan KW, Chan YP,
Law S, Chua D, Kwong DL, Lung HL, Srivastava G, et al: Tumor
suppressor dual-specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6) impairs cell
invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated
phenotype. Int J Cancer. 130:83–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Loeber G, Maurer-Fogy I and Schwendenwein
R: Purification, cDNA cloning and heterologous expression of the
human mitochondrial NADP(+)-dependent malic enzyme. Biochem J.
304:687–692. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wise DR and Thompson CB: Glutamine
addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci.
35:427–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ishii A, Ohta M, Watanabe Y, Matsuda K,
Ishiyama K, Sakoe K, Nakamura M, Inokuchi J, Sanai Y and Saito M:
Expression cloning and functional characterization of human cDNA
for ganglioside GM3 synthase. J Biol Chem. 273:31652–31655. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Liang Q, Cheung KF, Kang W, Lung
RW, Tong JH, To KF, Sung JJ and Yu J: Genome-wide identification of
Epstein-Barr virus-driven promoter methylation profiles of human
genes in gastric cancer cells. Cancer. 119:304–312. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shimizu H, Horii A, Sunamura M, Motoi F,
Egawa S, Unno M and Fukushige S: Identification of epigenetically
silenced genes in human pancreatic cancer by a novel method
‘microarray coupled with methyl-CpG targeted transcriptional
activation’ (MeTA-array). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:162–167.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chiovaro F, Chiquet-Ehrismann R and
Chiquet M: Transcriptional regulation of tenascin genes. Cell Adh
Migr. 9:34–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alcaraz LB, Exposito JY, Chuvin N, Pommier
RM, Cluzel C, Martel S, Sentis S, Bartholin L, Lethias C and
Valcourt U: Tenascin-X promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by activating latent TGF-β. J Cell Biol. 205:409–428.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan Y, Nymoen DA, Stavnes HT, Rosnes AK,
Bjørang O, Wu C, Nesland JM and Davidson B: Tenascin-X is a novel
diagnostic marker of malignant mesothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol.
33:1673–1682. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fox BP and Kandpal RP: DNA-based assay for
EPHB6 expression in breast carcinoma cells as a potential
diagnostic test for detecting tumor cells in circulation. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 7:9–16. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu J, Bulk E, Ji P, Hascher A, Tang M,
Metzger R, Marra A, Serve H, Berdel WE, Wiewroth R, et al: The
EPHB6 receptor tyrosine kinase is a metastasis suppressor that is
frequently silenced by promoter DNA hypermethylation in non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2275–2283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fox BP and Kandpal RP: EphB6 receptor
significantly alters invasiveness and other phenotypic
characteristics of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene.
28:1706–1713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He Y, Wang Y, Li P, Zhu S, Wang J and
Zhang S: Identification of GPX3 epigenetically silenced by CpG
methylation in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis
Sci. 56:681–688. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oleinik NV, Krupenko NI and Krupenko SA:
Epigenetic silencing of ALDH1L1, a metabolic regulator of cellular
proliferation, in cancers. Genes Cancer. 2:130–139. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|