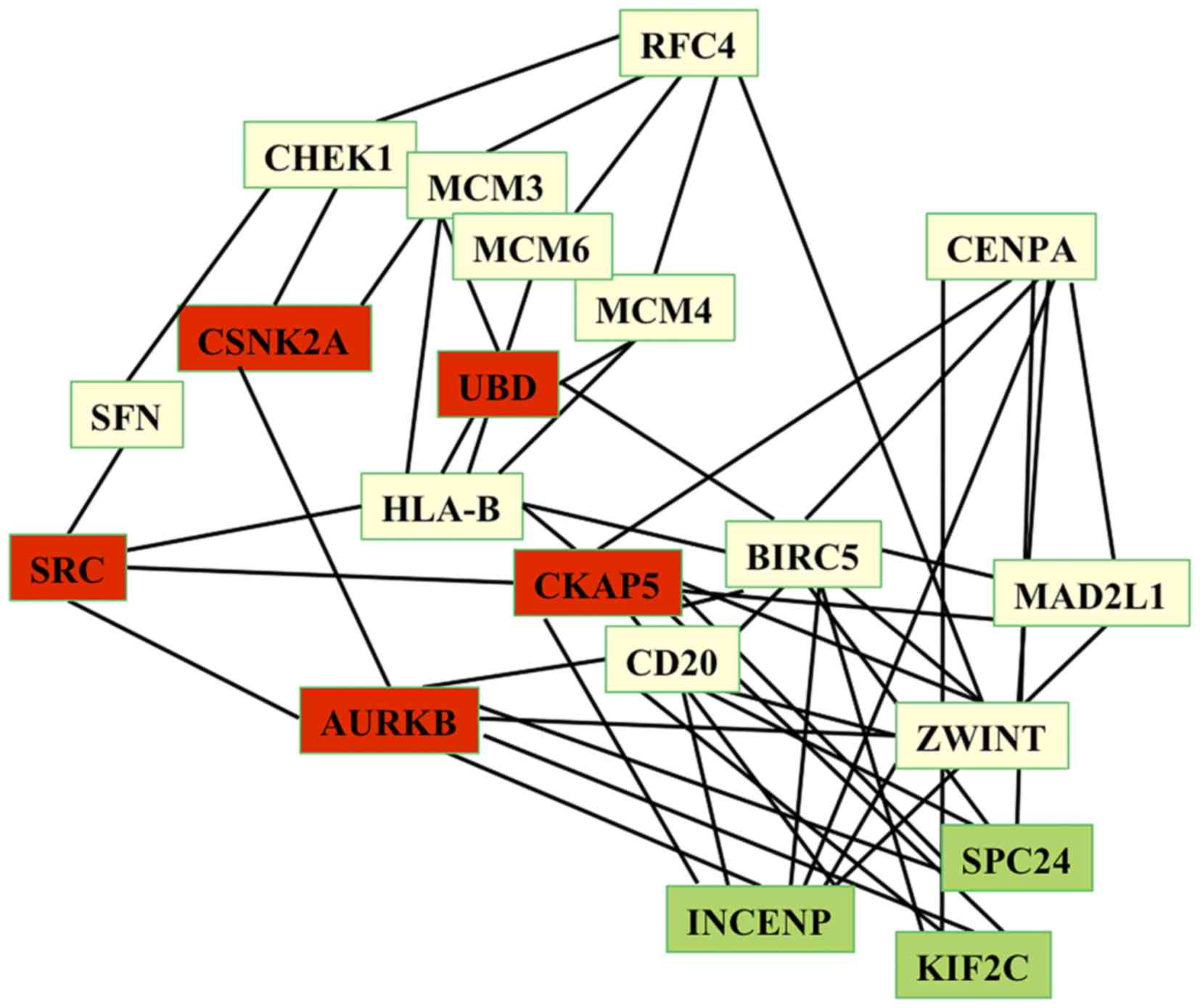
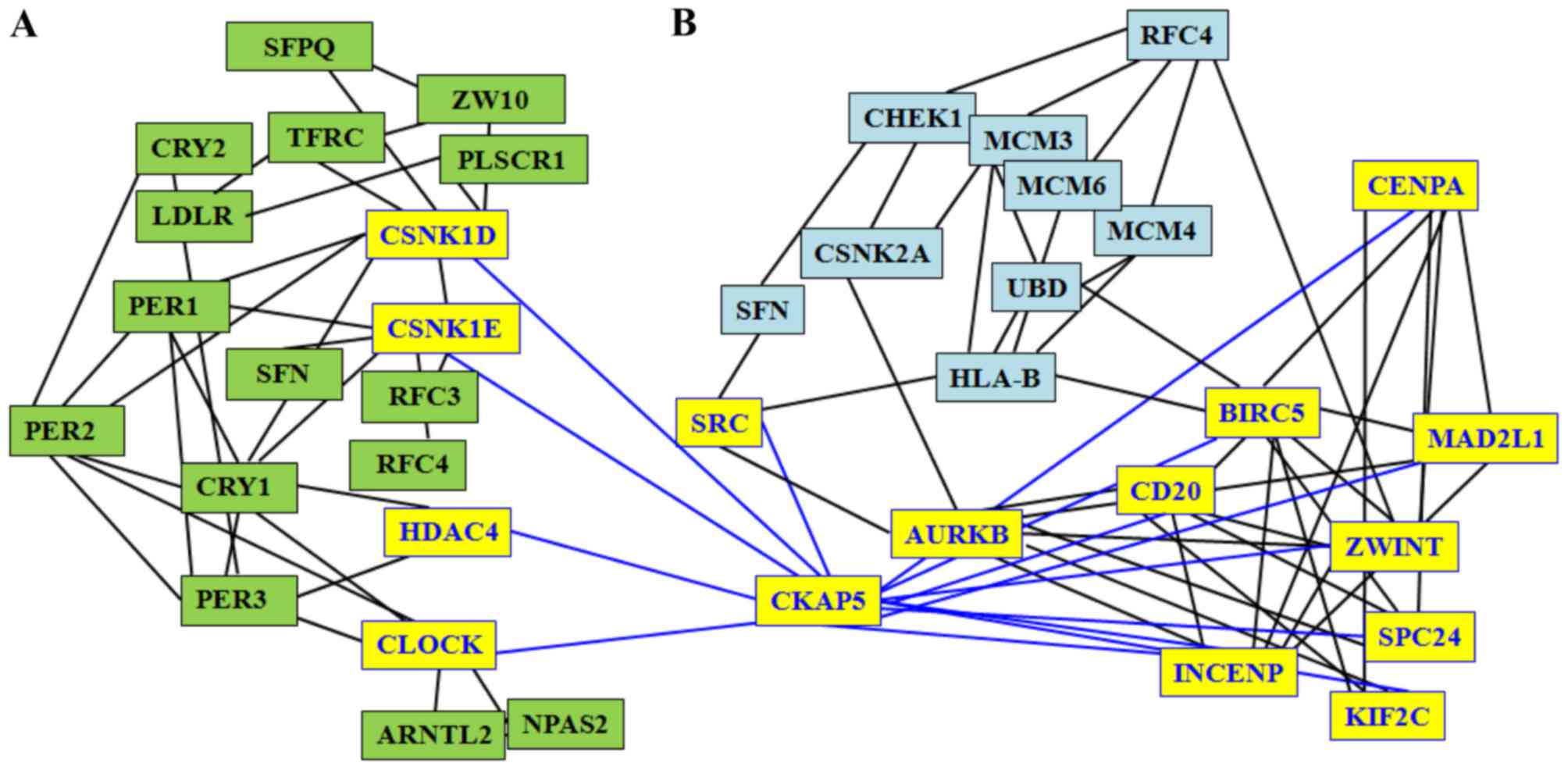
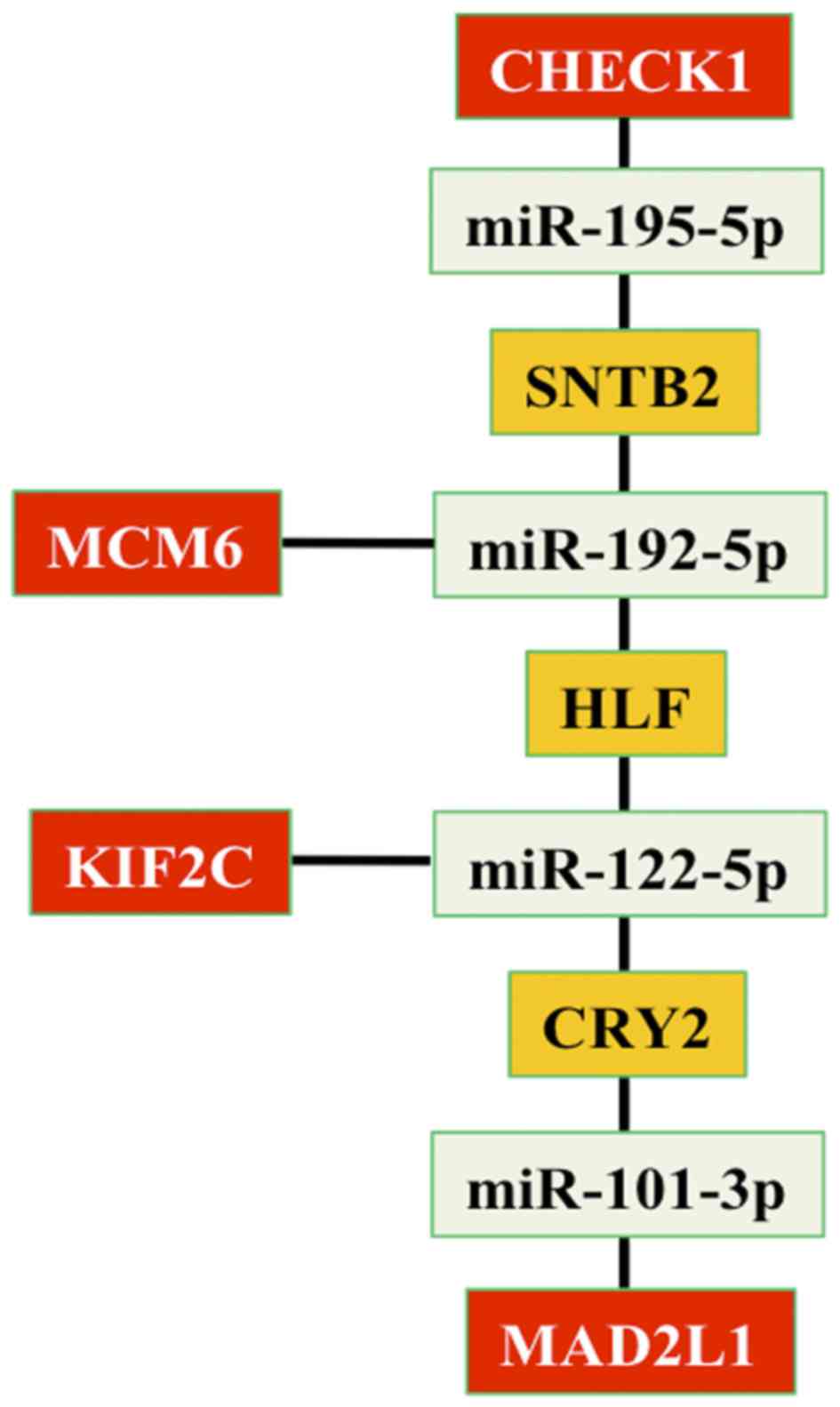
|
1
|
Czeisler CA and Klerman EB: Circadian and
sleep-dependent regulation of hormone release in humans. Recent
ProgHorm Res. 54:97–130. 1999.
|
|
2
|
Dibner C and Schibler U: Circadian timing
of metabolism in animal models and humans. J Intern Med.
277:513–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harfmann BD, Schroder EA and Esser KA:
Circadian rhythms the molecular clock and skeletal muscle. J Biol
Rhythms. 30:84–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
West AC and Bechtold DA: The cost of
circadian desynchrony: Evidence insights and open questions.
BioEssays. 37:777–788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fares S, Hermens DF, Naismith SL, White D,
Hickie IB and Robillard R: Clinical correlates of chronotypes in
young persons with mental disorders. Chronobiol Int. 32:1183–1191.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geoffroy PA, Etain B, Sportiche S and
Bellivier F: Circadian biomarkers in patients with bipolar
disorder: Promising putative predictors of lithium response. Int J
Bipolar Disord. 2:282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Geoffroy PA, Etain B, Franchi JA,
Bellivier F and Ritter P: Melatonin and melatonin agonists as
adjunctive treatments in bipolar disorders. Curr Pharm Des.
21:3352–3358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Benedetti F, Riccaboni R, Dallaspezia S,
Locatelli C, Smeraldi E and Colombo C: Effects of CLOCK gene
variants and early stress on hopelessness and suicide in bipolar
depression. Chronobiol Int. 32:1156–1161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Russo M, Mahon K, Shanahan M, Ramjas E,
Solon C, Purcell SM and Burdick KE: The relationship between sleep
quality and neurocognition in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord.
187:156–162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Challet E: Keeping circadian time with
hormones. Diabetes Obes Metab. 17:76–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anisimov VN, Vinogradova IA, Panchenko AV,
Popovich IG and Zabezhinski MA: Light-at-night-induced circadian
disruption cancer and aging. Curr Aging Sci. 5:170–177. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Belancio VP: LINE-1 activity as molecular
basis for genomic instability associated with light exposure at
night. Mob Genet Elements. 5:1–5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Savvidis C and Koutsilieris M: Circadian
rhythm disruption in cancer biology. Mol Med. 18:1249–1260. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uth K and Sleigh R: Deregulation of the
circadian clock constitutes a significant factor in tumorigenesis:
A clockwork cancer. Part II In vivo studies. Biotechnol Biotechnol
Equip. 28:379–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Michael AK, Harvey SL, Sammons PJ,
Anderson AP, Kopalle HM, Banham AH and Partch CL: Cancer/Testis
antigen PASD1 silences the circadian clock. Mol Cell. 58:743–754.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kiss Z and Ghosh PM: Woman in cancer
thematic review: Circadian rhythmicity and the influence of ‘clock’
genes on prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 23:T123–T134. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gutiérrez-Monreal MA, Villela L, Baltazar
S, Perfecto-Avalos Y, Cardineau GA and Scott SP: A PER3
polymorphism is associated with better overall survival in diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma in Mexican population. Cancer Biomark.
15:699–705. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Chen R, Ji M, Zou SL and Zhu LN:
Cisplatin-based chronotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung
cancer patients: A randomized controlled study and its
pharmacokinetworkics analysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
76:651–655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitchell MI and Engelbrecht AM: Circadian
rhythms and breast cancer: The role of Per2 in doxorubicin-induced
cell death. J Toxicol. 2015:3923602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poole EM, Schernhammer E, Mills L,
Hankinson SE and Tworoger SS: Urinary melatonin and risk of ovarian
cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 26:1501–1506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schmutz I, Albrecht U and Ripperger JA:
The role of clock genes and rhythmicity in the liver. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 349:38–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vollmers C, Gill S, DiTacchio L,
Pulivarthy SR, Le HD and Panda S: Time of feeding and the intrinsic
circadian clock drive rhythms in hepatic gene expression. ProcNatl
Acad Sci USA. 106:21453–21458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Elgohary N, Pellegrino R, Neumann O,
Elzawahry HM, Saber MM, Zeeneldin AA, Geffers R, Ehemann V,
Schemmer P, Schirmacher P and Longerich T: Protumorigenic role of
timeless in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 46:597–606.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu C, Yang SL, Fang X, Jiang JX, Sun CY
and Huang T: Hypoxia disrupts the expression levels of circadian
rhythm genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
11:4002–4008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li H, Lu YF, Chen H and Liu J:
Dysregulation of metallothionein and circadian genes in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronobiol Int. 20:192–202. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Yang SL, Yu C, Jiang JX, Liu LP, Fang X
and Wu C: Hepatitis B virus X protein disrupts the balance of the
expression of circadian rhythm genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 8:2715–2720. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turati F, Talamini R, Pelucchi C, Polesel
J, Franceschi S, Crispo A, Izzo F, La Vecchia C, Boffetta P and
Montella M: Metabolic syndrome and hepatocellular carcinoma risk.
Br J Cancer. 108:222–658. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Polesel J, Zucchetto A, Montella M, Dal
Maso L, Crispo A, La Vecchia C, Serraino D, Franceschi S and
Talamini R: The impact of obesity and diabetes mellitus on the risk
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 20:353–357. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shivappa N, Hébert JR, Polesel J,
Zucchetto A, Crispo A, Montella M, Franceschi S, Rossi M, La
Vecchia C and Serraino D: Inflammatory potential of diet and risk
for hepatocellular cancer in a case-control study from Italy. Br J
Nutr. 115:324–331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singh S, Colonna G, Di Bernardo G,
Bergantino F, Cammarota M, Castello G and Costantini S: The gene
expression profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma by a network
analysis approach shows a dominance of intrinsically disordered
proteins (IDPs) between hub nodes. Mol Biosyst. 11:2933–2945. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cerami EG, Gross BE, Demir E, Rodchenkov
I, Babur O, Anwar N, Schultz N, Bader GD and Sander C: Pathway
commons a web resource for biological pathway data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:(Database issue). D685–D690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher
L, Breitkreutz A and Tyers M: BioGRID: A general repository for
interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:(Database issue).
D535–D539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peri S, Navarro JD, Amanchy R, Kristiansen
TZ, Jonnalagadda CK, Surendranath V, Niranjan V, Muthusamy B,
Gandhi TK, Gronborg M, et al: Development of human protein
reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems
biology in humans. Genome Res. 13:2363–2371. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kamburov A, Wierling C, Lehrach H and
Herwig R: ConsensusPathDB-a database for integrating human
functional interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:(Database
issue). D623–D628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xenarios I, Salwinski L, Duan XJ, Higney
P, Kim SM and Eisenberg D: DIP, the database of interacting
proteins: A research tool for studying cellular networks of protein
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:303–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jayapandian M, Chapman A, Tarcea VG, Yu C,
Elkiss A, Ianni A, Liu B, Nandi A, Santos C, Andrews P, et al:
Michigan Molecular Interactions (MiMI): Putting the jigsaw puzzle
together. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:(Database issue). D566–D571. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E, Kuchinsky A,
Landys N, Workman C, Christmas R, Avila-Campilo I, Creech M, Gross
B, et al: Integration of biological networks and gene expression
data using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc. 2:2366–2382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3469.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yoon J, Blumer A and Lee K: An algorithm
for modularity analysis of directed and weighted biological
networks based on edge-betweenness centrality. Bioinformatics.
22:3106–3108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Newman MEJ: A measure of betweenness
centrality based on random walks. Soc Networks. 27:39–54. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Barabási AL, Gulbahce N and Loscalzo J:
Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat
Rev Genet. 12:56–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sharma A, Costantini S and Colonna G: The
protein-protein interaction network of the human Sirtuin family.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1834:1998–2009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu J, Tan Y, Deng H and Zhu D:
Relationship between degree-rank function and degree distribution
of protein-protein interaction networks. Comput Biol Chem. 32:1–4.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wu J, Tan YJ, Deng HZ and Zhu DZ: A new
measure of heterogeneity of complex networks based on degree
sequence. Unifying Themes in Complex Systems. 66–73. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Dong J and Horvath S: Understanding
network concepts in modules. BMC Syst Biol. 1:242007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Freeman LC: Centrality in social networks
conceptual clarification. Soc Networks. 1:215–239. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Estrada E: Quantifying network
heterogeneity. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys.
82:0661022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng K, Vucetic S, Radivojac P, Brown CJ,
Dunker AK and Obradovic Z: Optimizing long intrinsic disorder
predictors with protein evolutionary information. J Bioinform
Comput Biol. 3:35–60. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, Wang MY, Xie QH,
Tang F, Li PY, Song YH and Lin JS: MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in
hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 31:3357–3369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
3:e2642005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Costantini S, Di Bernardo G, Cammarota M,
Castello G and Colonna G: Gene expression signature of human HepG2
cell line. Gene. 518:335–345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nagase T, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Sazuka T,
Seki N, Sato S, Tabata S, Ishikawa K, Kawarabayasi Y, Kotani H, et
al: Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes.
III. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0081-KIAA0120)
deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1. DNA
Res. 2:37–43. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Charrasse S, Mazel M, Taviaux S, Berta P,
Chow T and Larroque C: Characterization of the cDNA and pattern of
expression of a new gene over-expressed in human hepatomas and
colonic tumors. Eur J Biochem. 234:406–413. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Takeshita N, Mania D, Herrero S, Ishitsuka
Y, Nienhaus GU, Podolski M, Howard J and Fischer R: The cell-end
marker TeaA and the microtubule polymerase AlpA contribute to
microtubule guidance at the hyphal tip cortex of Aspergillus
nidulans to provide polarity maintenance. J Cell Sci.
126:5400–5411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu Z, Chen Y, Yang T, Gao Q, Yuan M and Ma
L: Targeted ubiquitination and degradation of G-protein-coupled
receptor kinase 5 by the DDB1-CUL4 ubiquitin ligase complex. PLoS
One. 7:e439972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Golsteyn RM, Mundt KE, Fry AM and Nigg EA:
Cell cycle regulation of the activity and subcellular localization
of Plk1, a human protein kinase implicated in mitotic spindle
function. J Cell Biol. 129:1617–1628. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li JZ, Bunney BG, Meng F, Hagenauer MH,
Walsh DM, Vawter MP, Evans SJ, Choudary PV, Cartagena P, Barchas
JD, et al: Circadian patterns of gene expression in the human brain
and disruption in major depressive disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:pp. 9950–9955. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vinciguerra M, Mazzoccoli G, Piccoli C,
Tataranni T, Andriulli A and Pazienza V: Exploitation of host clock
gene machinery by hepatitis viruses B and C. World J Gastroenterol.
19:8902–8909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Masri S, Papagiannakopoulos T, Kinouchi K,
Liu Y, Cervantes M, Baldi P, Jacks T and Sassone-Corsi P: Lung
adenocarcinoma distally rewires hepatic circadian homeostasis.
Cell. 165:896–909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|