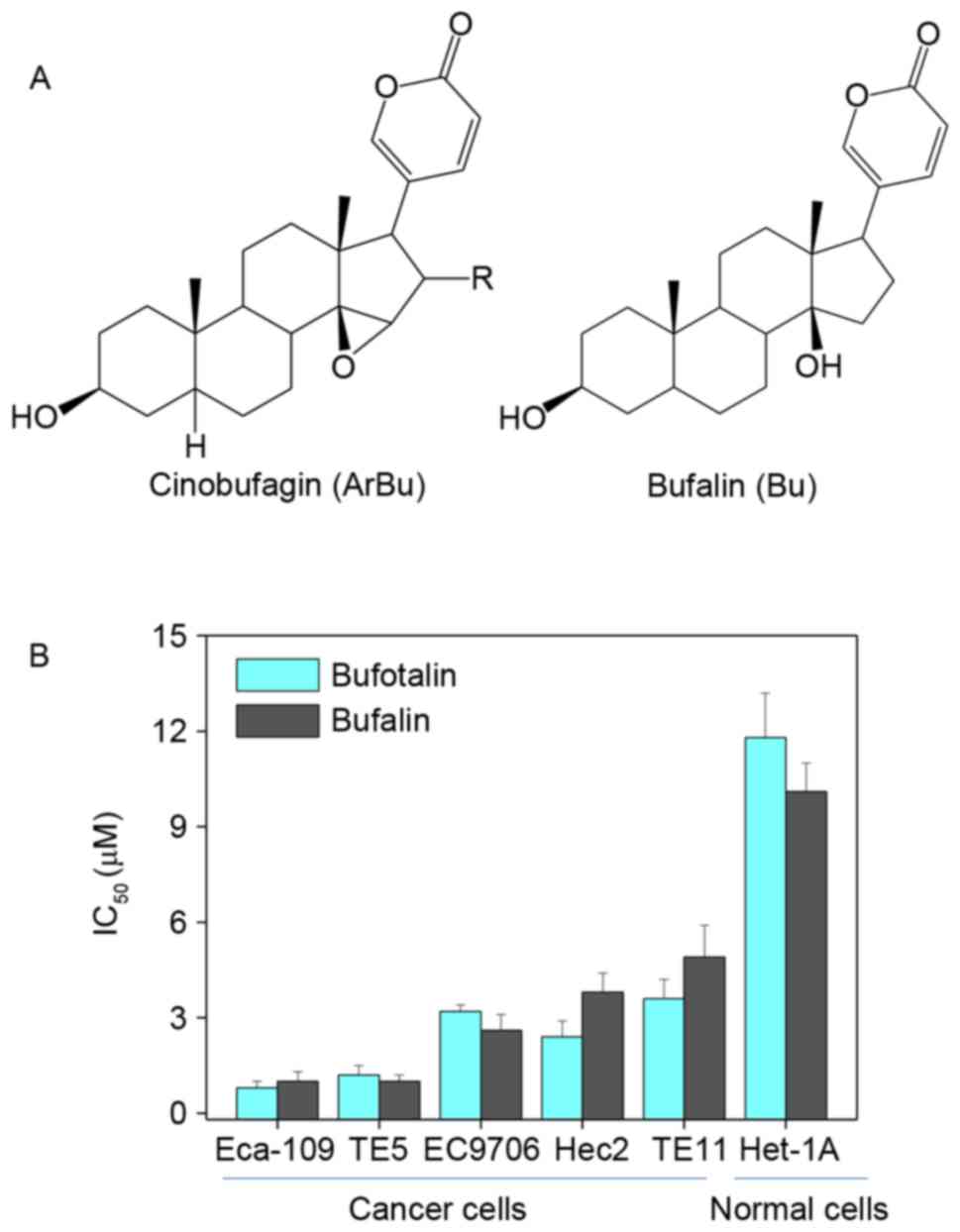
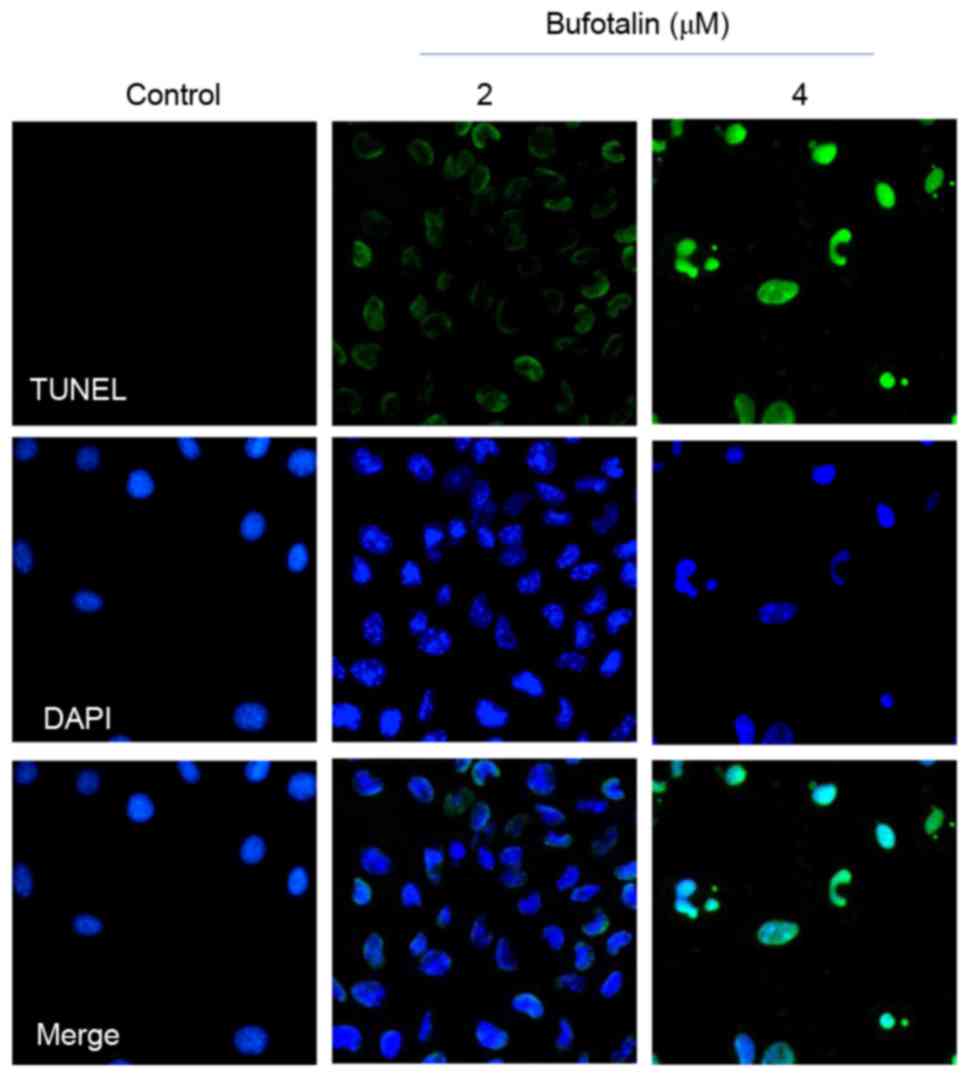
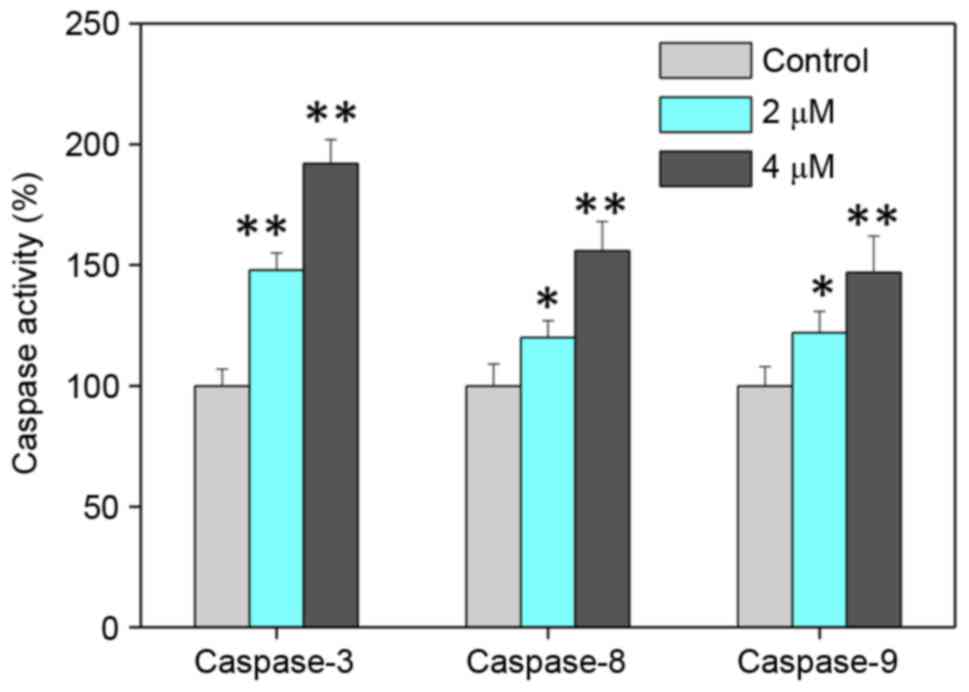
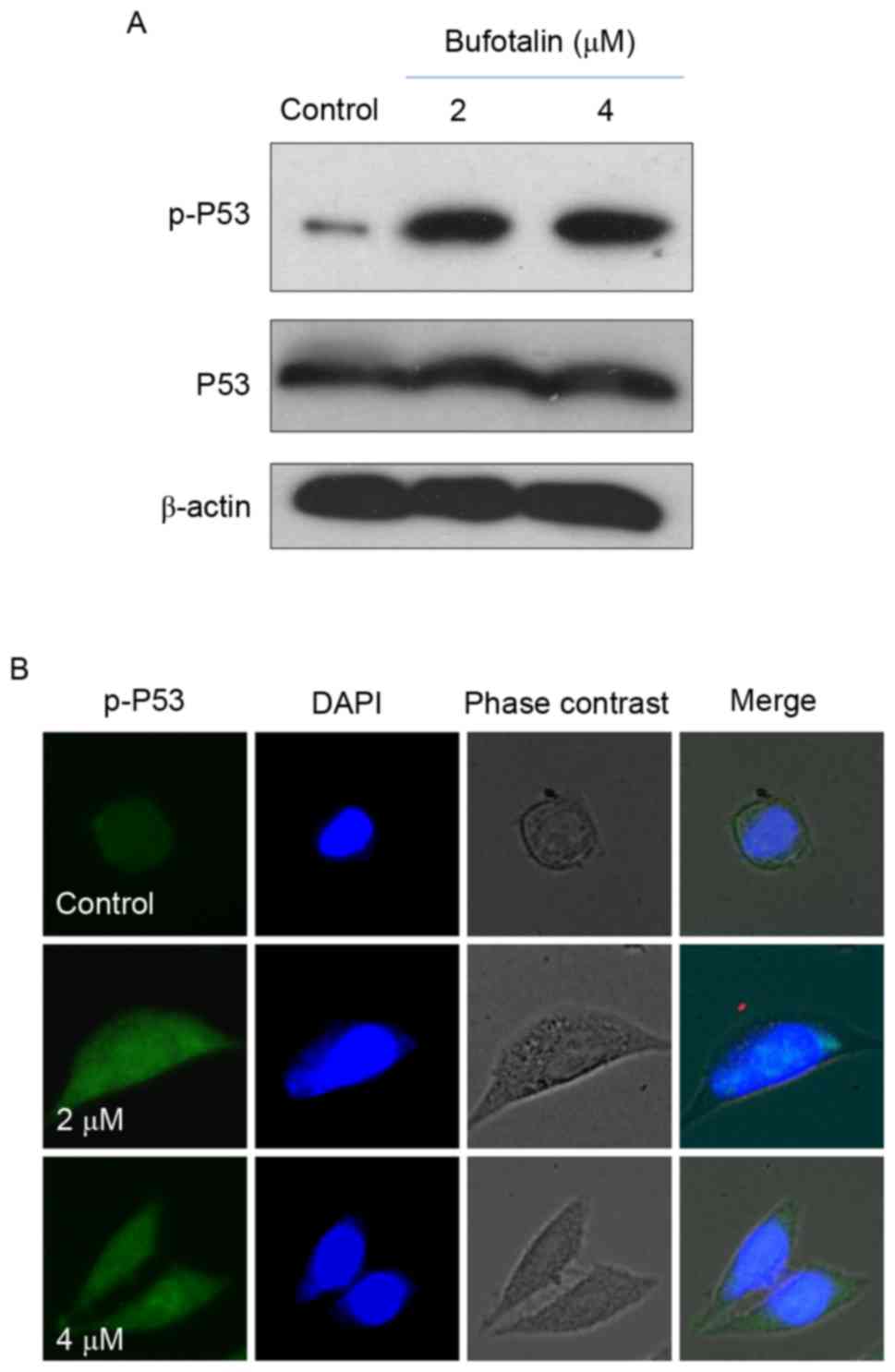
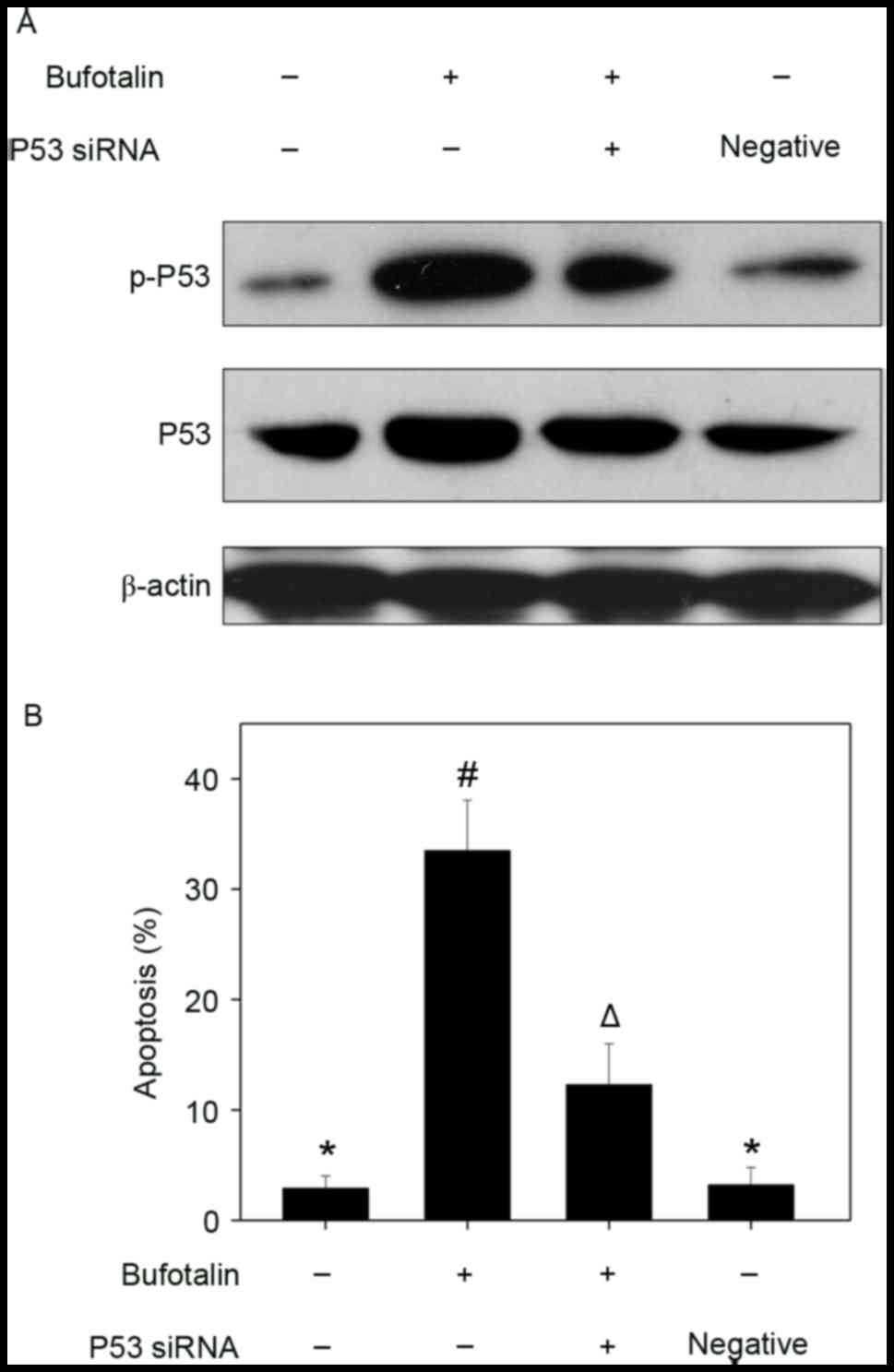
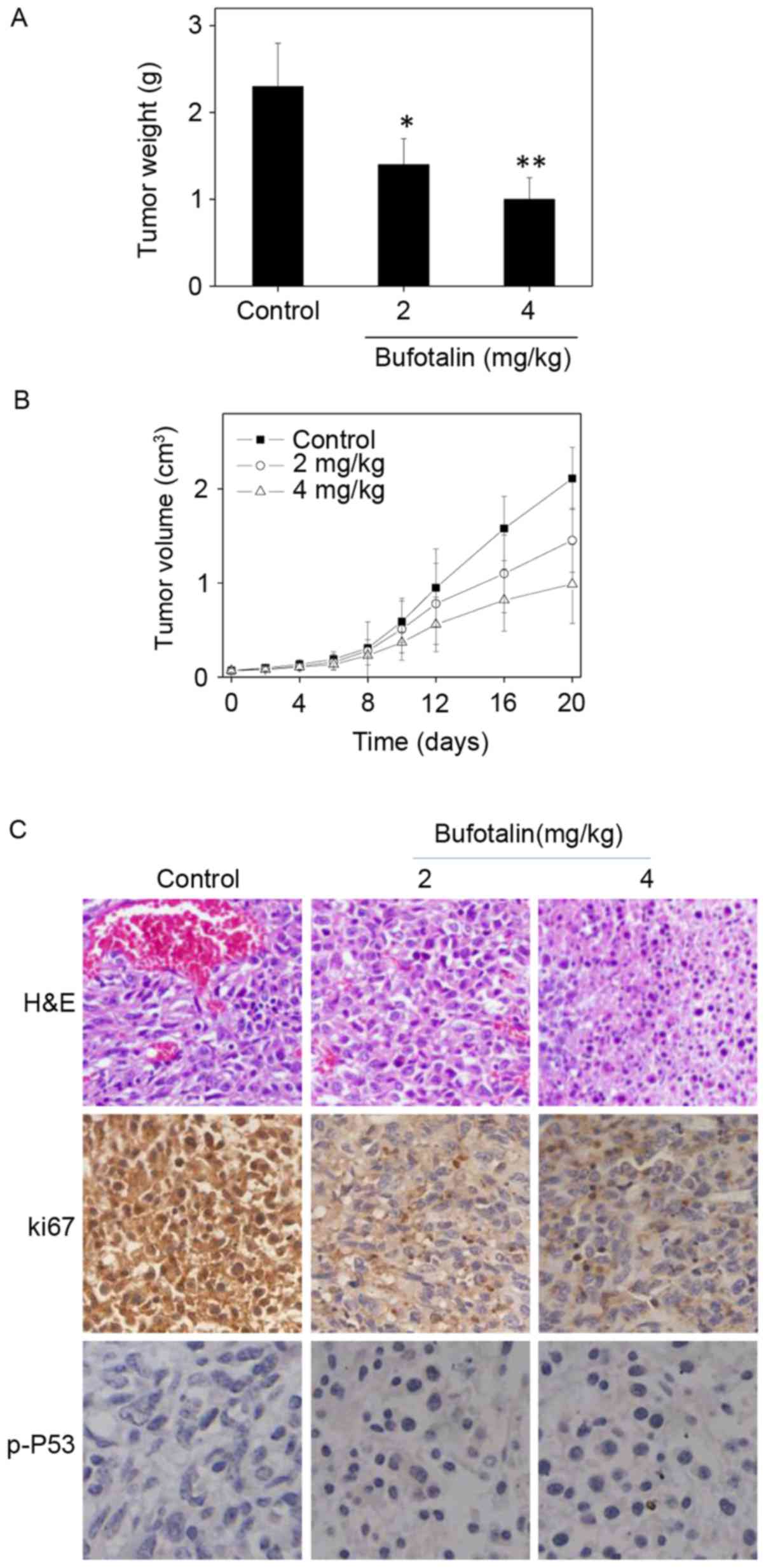
|
1
|
Song G, Cheng L, Chao Y, Yang K and Liu Z:
Emerging nanotechnology and advanced materials for cancer radiation
therapy. Adv Mater. 29:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers
C, Dandapani S and Lees JA: E2f3 is critical for normal cellular
proliferation. Genes Dev. 14:690–703. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang Y, He L, Li Z, Zeng L, Song Z, Li P,
Chan L, You Y, Yu XF, Chu PK and Chen T: Designing core-shell gold
and selenium nanocomposites for cancer radiochemotherapy. Acs Nano.
11:4848–4858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh SK, Banerjee S, Acosta EP, Lillard
JW and Singh R: Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
with docetaxel in prostate cancer cells via a p53/p21(WAF1/CIP1)
and p27(KIP1) pathway. Oncotarget. 8:17216–17228. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liong M, Lu J, Kovochich M, Xia T, Ruehm
SG, Nel AE, Tamanoi F and Zink JI: Multifunctional inorganic
nanoparticles for imaging, targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano.
2:889–896. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oelkrug C, Hartke M and Schubert A: Mode
of action of anticancer peptides (ACPs) from amphibian origin.
Anticancer Res. 35:635–643. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
apoptosis of A375 human melanoma cells by activating ROS-mediated
mitochondrial pathway and p53 phosphorylation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:2763–2775. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
caspase-independent apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells
with involvement of p53 phosphorylation and reactive oxygen species
generation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:666–676. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi FH, Li AY, Lv H, Zhao L, Li JJ, Gao B
and Tang W: Apoptosis-inducing effect of cinobufacini, Bufo bufo
gargarizans Cantor skin extract, on human hepatoma cell line
BEL-7402. Drug Discov Ther. 2:339–343. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Qiao L, Yu B, Li G, Liu C, Ji L
and Chao H: Mitochondria-specific phosphorescent imaging and
tracking in living cells with an AIPE-active iridium(III) complex.
Chem Commun (Camb). 49:11095–11097. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Wen J, Zhang J, Ye M and Guo D:
Simultaneous determination of four bufadienolides in human liver by
high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr.
18:318–322. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wen L, Huang Y, Xie X, Huang W, Yin J, Lin
W, Jia Q and Zeng W: Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive
activities of bufalin in rodents. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:1718392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang DL, Qi FH, Xu HL, Inagaki Y, Orihara
Y, Sekimizu K, Kokudo N, Wang FS and Tang W: Apoptosis-inducing
activity of compounds screened and characterized from cinobufacini
by bioassay-guided isolation. Mol Med Rep. 3:717–22.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu GX and Wang TT: Apoptosis of lens
epithelial cells induced by cinobufagin in vitro. Int J Ophthalmol.
3:128–131. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhai XF, Fang FF, Liu Q, Meng YB, Guo YY
and Chen Z: MiR-181a contributes to bufalin-induced apoptosis in
PC-3 prostate cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:3252013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang F, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Zheng D,
Hao L, Duan C, Jia L, Liu G and Liu Y: Synergistic effect of
folate-mediated targeting and verapamil-mediated P-gp inhibition
with paclitaxel-polymer micelles to overcome multi-drug resistance.
Biomaterials. 32:9444–9456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen YY, Lu HF, Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Chang SJ,
Lin JJ, Wu PP, Liu JY, Lee CH, Chung JG and Chang JB: Bufalin
inhibits migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma
SK-Hep1 cells through the inhibitions of NF-kB and matrix
metalloproteinase-2/−9-signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol.
30:74–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Shi A and Fan Z: Apoptosis of
T-47D cells induced by cinobufacini via a caspase-3-dependent
manner. Chem Res Chinese Univer. 30:108–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li M, Yu X, Guo H, Sun L, Wang A, Liu Q,
Wang X and Li J: Bufalin exerts antitumor effects by inducing cell
cycle arrest and triggering apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 35:2461–2471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang DM, Liu JS, Deng LJ, Chen MF, Yiu A,
Cao HH, Tian HY, Fung KP, Kurihara H, Pan JX and Ye WC:
Arenobufagin, a natural bufadienolide from toad venom, induces
apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Carcinogenesis.
34:1331–1342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo H, Wang F, Bai Y, Chen T and Zheng W:
Selenium nanoparticles inhibit the growth of HeLa and MDA-MB-231
cells through induction of S phase arrest. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 94:304–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang F, Tang Q, Zhong X, Bai Y, Chen T,
Zhang Y, Li Y and Zheng W: Surface decoration by Spirulina
polysaccharide enhances the cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy
of selenium nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:835–844.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Li X, Huang Z, Zheng W, Fan C and
Chen T: Enhancement of cell permeabilization apoptosis-inducing
activity of selenium nanoparticles by ATP surface decoration.
Nanomedicine. 9:74–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Wang S:
Targeting disease through novel pathways of apoptosis and
autophagy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:1203–1214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
apoptosis of A375 human melanoma cells by activating ROS-mediated
mitochondrial pathway and p53 phosphorylation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:2763–2775. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
caspase-independent apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells
with involvement of p53 phosphorylation and reactive oxygen species
generation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:666–676. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He L, Lai H and Chen T: Dual-function
nanosystem for synergetic cancer chemo-/radiotherapy through
ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Biomaterials. 51:30–42. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li M, Lai L, Zhao Z and Chen T: Aquation
is a crucial activation step for anticancer action of ruthenium(II)
polypyridyl complexes to trigger cancer cell apoptosis. Chem Asian
J. 11:310–320. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xie Q, Lan G, Zhou Y, Huang J, Liang Y,
Zheng W, Fu X, Fan C and Chen T: Strategy to enhance the anticancer
efficacy of X-ray radiotherapy in melanoma cells by platinum
complexes, the role of ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Cancer
Lett. 354:58–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fridman JS and Lowe SW: Control of
apoptosis by p53. Oncogene. 22:9030–9040. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He L, Huang Y, Zhu H, Pang G, Zheng W,
Wong YS and Chen T: Cancer-targeted monodisperse mesoporous silica
nanoparticles as carrier of ruthenium polypyridyl complexes to
enhance theranostic effects. Adv Funct Mater. 24:2754–2763. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|