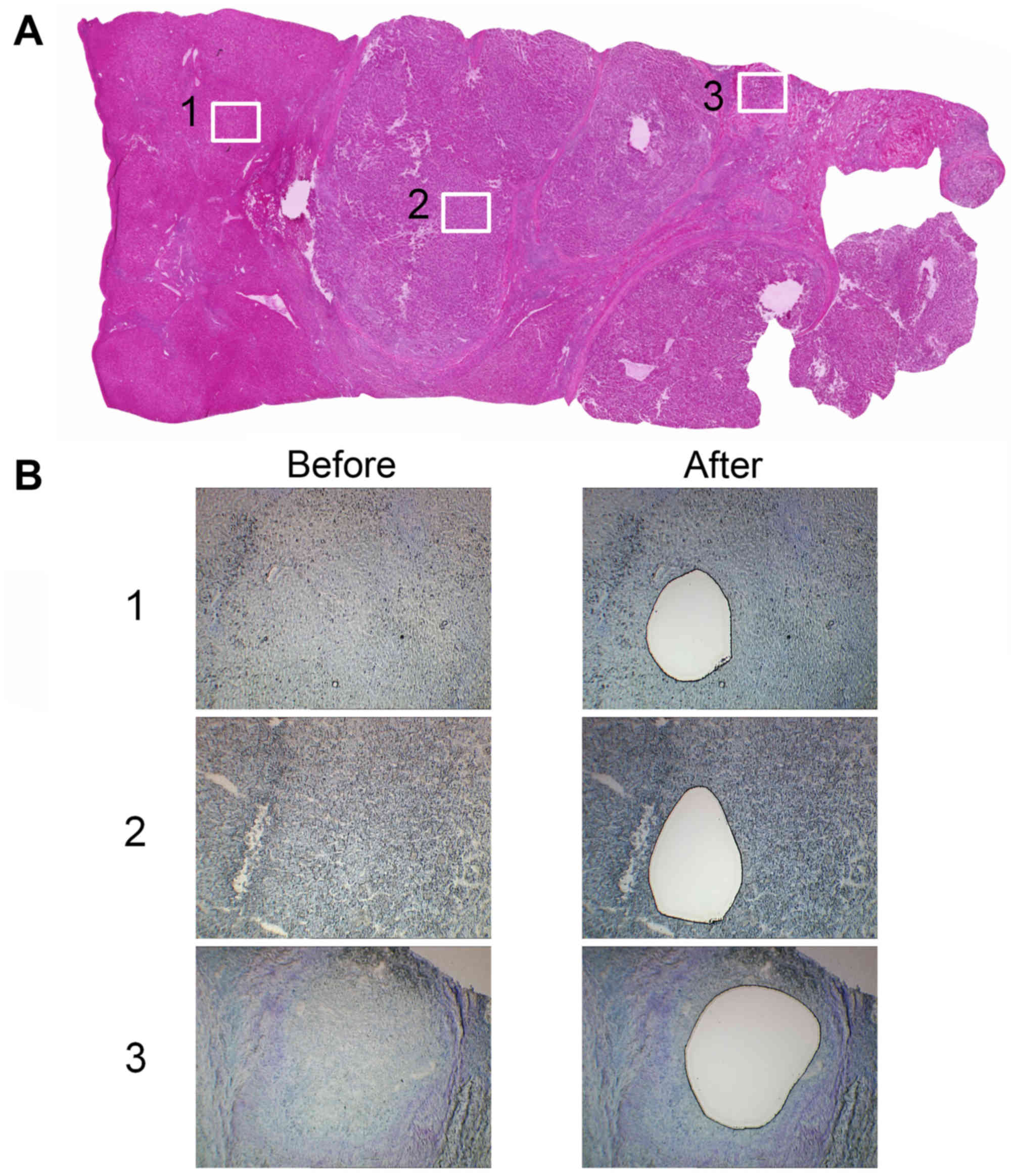
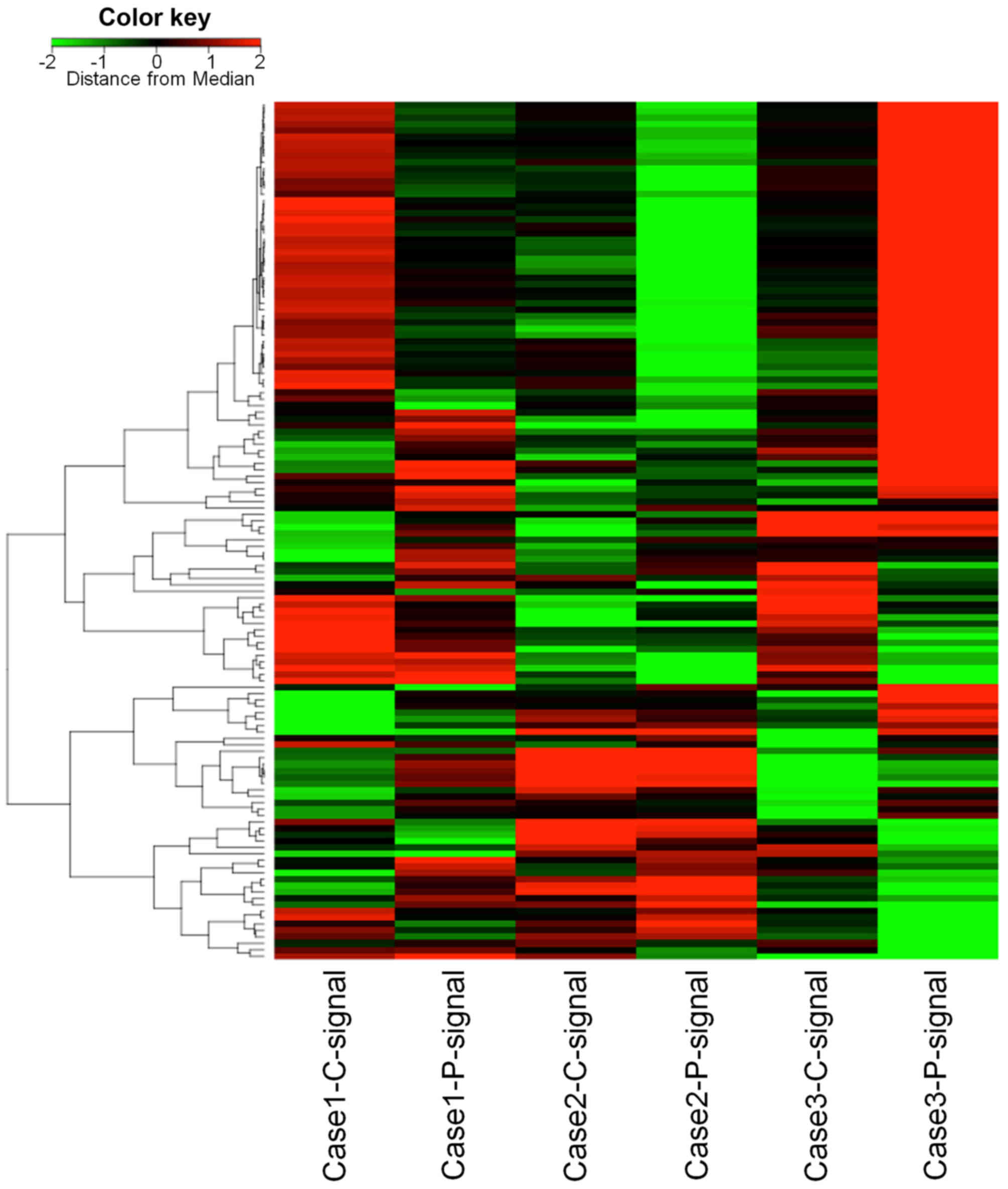
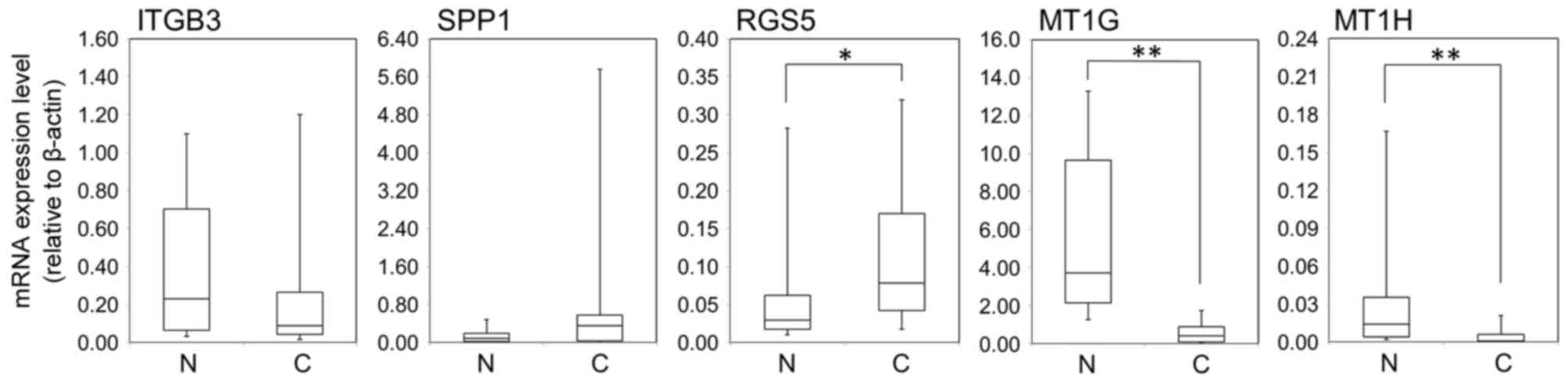
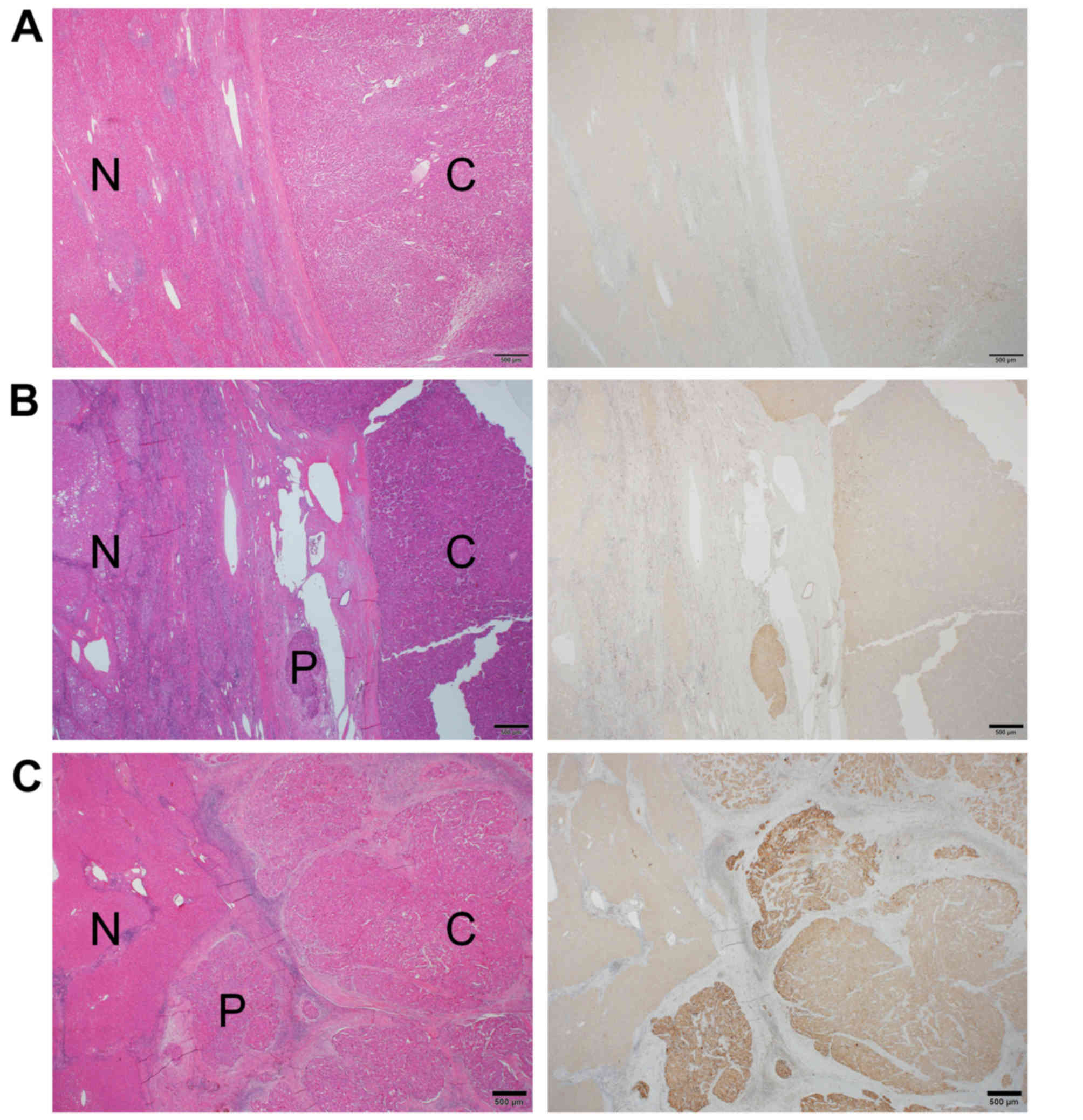
|
1
|
Koike Y, Shiratori Y, Sato S, Obi S,
Teratani T, Imamura M, Yoshida H, Shiina S and Omata M:
Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin as a useful predisposing factor for
the development of portal venous invasion in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective analysis of 227 patients.
Cancer. 91:561–569. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hui AM, Takayama T, Sano K, Kubota K,
Akahane M, Ohtomo K and Makuuchi M: Predictive value of gross
classification of hepatocellular carcinoma on recurrence and
survival after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 33:975–979. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murakata A, Tanaka S, Mogushi K, Yasen M,
Noguchi N, Irie T, Kudo A, Nakamura N, Tanaka H and Arii S: Gene
expression signature of the gross morphology in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg. 253:94–100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sumie S, Kuromatsu R, Okuda K, Ando E,
Takata A, Fukushima N, Watanabe Y, Kojiro M and Sata M:
Microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
and its predictable clinicopathological factors. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:1375–1382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ieta K, Ojima E, Tanaka F, Nakamura Y,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K, Inoue H, Kuwano H and Mori M: Identification
of overexpressed genes in hepatocellular carcinoma, with special
reference to ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C gene expression. Int
J Cancer. 121:33–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshitake K, Tanaka S, Mogushi K, Aihara
A, Murakata A, Matsumura S, Mitsunori Y, Yasen M, Ban D, Noguchi N,
et al: Importin-α1 as a novel prognostic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2093–2103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, Yang Y, Nie X and
Zhou RL: LAPTM4B-35 overexpression is a risk factor for tumor
recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 136:275–281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mayinuer A, Yasen M, Mogushi K, Obulhasim
G, Xieraili M, Aihara A, Tanaka S, Mizushima H, Tanaka H and Arii
S: Upregulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA member 3
(PTP4A3/PRL-3) is associated with tumor differentiation and a poor
prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
20:305–317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang Y, Zeng X, He F, Liao Y, Qian N and
Toi M: Caveolin-1 is related to invasion, survival and poor
prognosis in hepatocellular cancer. Med Oncol. 29:977–984. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad
B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, et al:
Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology
and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 5:R802004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quackenbush J: Microarray data
normalization and transformation. Nat Genet. 32 Suppl:S496–S501.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang
W, Bhagabati N, Braisted J, Klapa M, Currier T, Thiagarajan M, et
al: TM4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management
and analysis. Biotechniques. 34:374–378. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silini A, Ghilardi C, Figini S, Sangalli
F, Fruscio R, Dahse R, Pedley RB, Giavazzi R and Bani M: Regulator
of G-protein signaling 5 (RGS5) protein: A novel marker of cancer
vasculature elicited and sustained by the tumor's proangiogenic
microenvironment. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:1167–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen X, Higgins J, Cheung ST, Li R, Mason
V, Montgomery K, Fan ST, van de Rijn M and So S: Novel endothelial
cell markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 17:1198–1210.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hepler JR: Emerging roles for RGS proteins
in cell signalling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 20:376–382. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Siderovski DP, Strockbine B and Behe CI:
Whither goest the RGS proteins? Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol.
34:215–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng B, De Vries L and Gist Farquhar M:
Divergence of RGS proteins: Evidence for the existence of six
mammalian RGS subfamilies. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:411–414. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seki N, Sugano S, Suzuki Y, Nakagawara A,
Ohira M, Muramatsu M, Saito T and Hori T: Isolation, tissue
expression, and chromosomal assignment of human RGS5, a novel
G-protein signaling regulator gene. J Hum Genet. 43:202–205. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bondjers C, Kalen M, Hellstrom M, Scheidl
SJ, Abramsson A, Renner O, Lindahl P, Cho H, Kehrl J and Betsholtz
C: Transcription profiling of platelet-derived growth
factor-B-deficient mouse embryos identifies RGS5 as a novel marker
for pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol.
162:721–729. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang JH, Huang WS, Hu CR, Guan XX, Zhou HB
and Chen LB: Relationship between RGS5 expression and
differentiation and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:5642–5646. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu M, Chen X, Zhang J, Wang D, Fang X,
Wang X, Wang G, Chen G, Jiang X, Xia H, et al: Over-expression of
regulator of G protein signaling 5 promotes tumor metastasis by
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Surg Oncol. 108:192–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Furuya M, Nishiyama M, Kimura S, Suyama T,
Naya Y, Ito H, Nikaido T and Ishikura H: Expression of regulator of
G protein signalling protein 5 (RGS5) in the tumour vasculature of
human renal cell carcinoma. J Pathol. 203:551–558. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang G, Song H, Wang R, Han X and Chen L:
The relationship between RGS5 expression and cancer differentiation
and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol.
105:420–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|