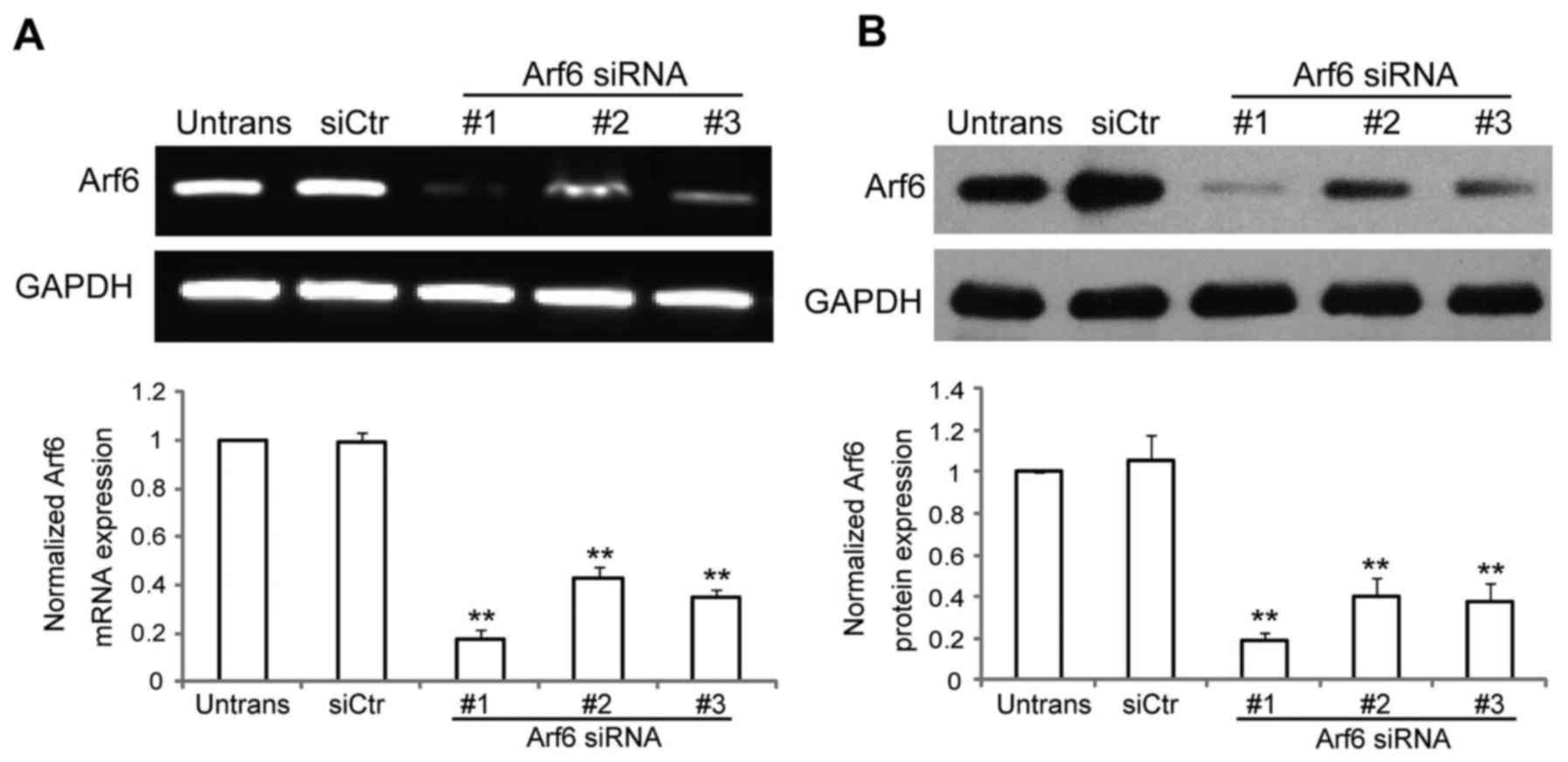
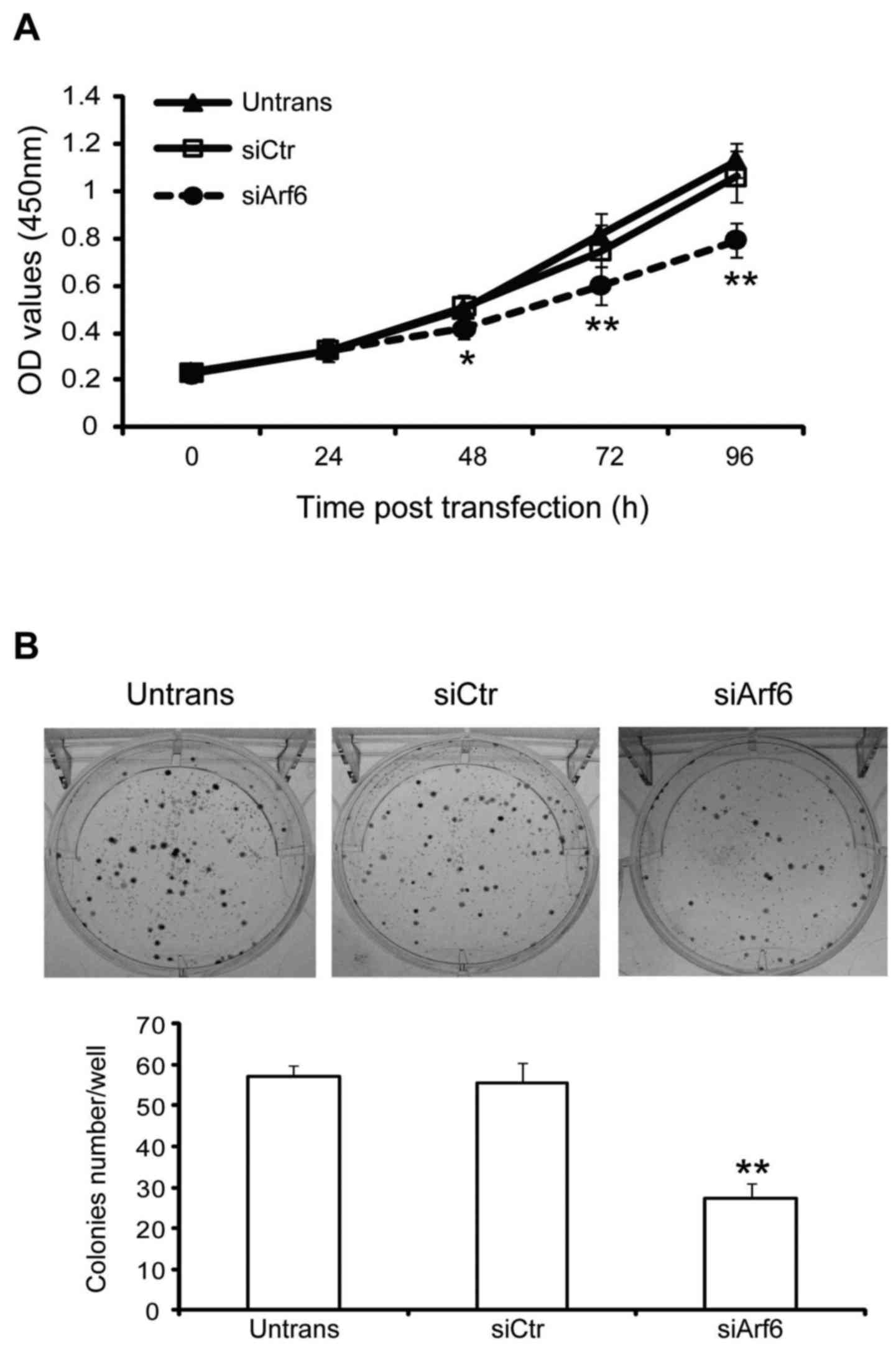
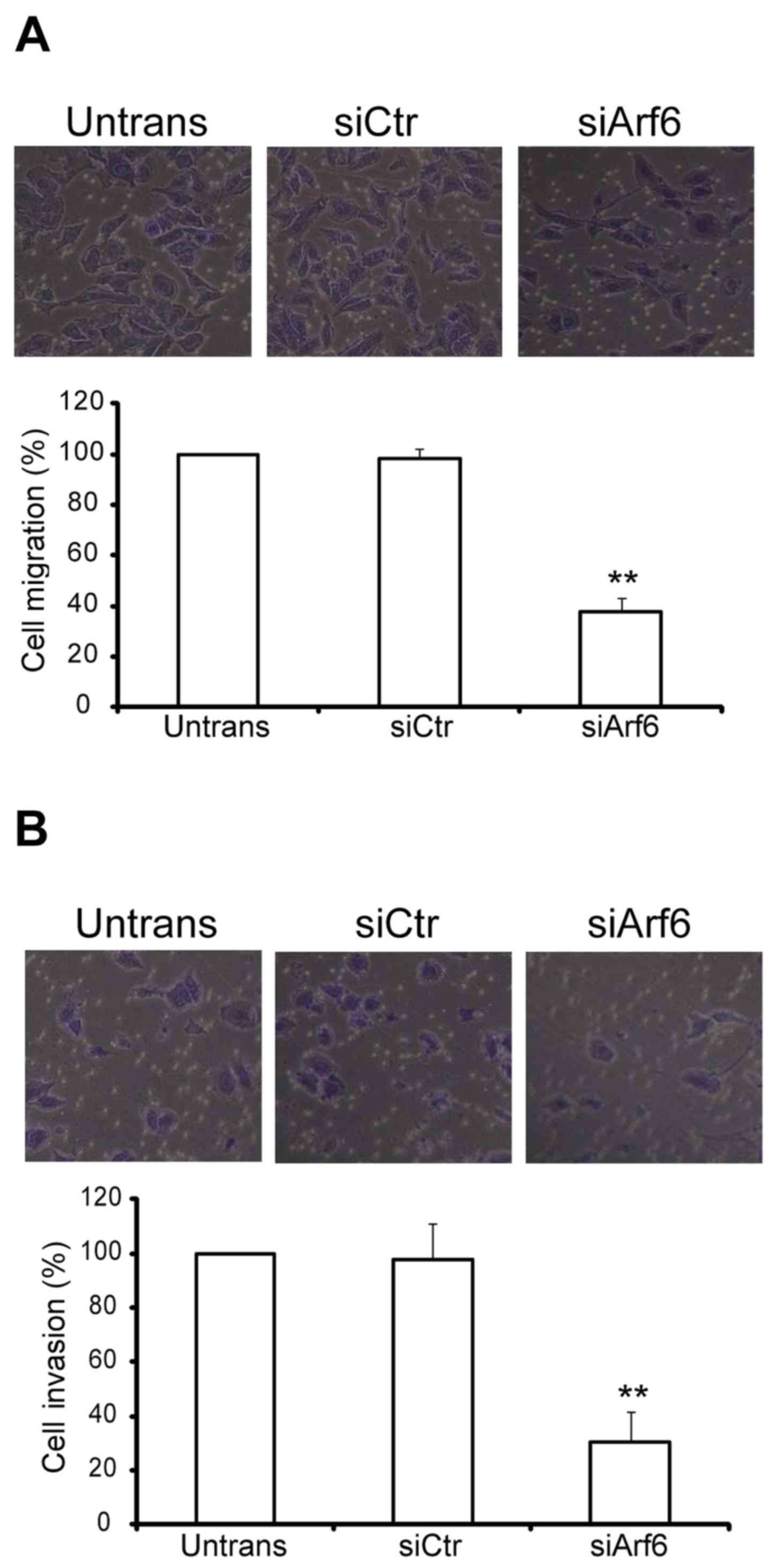
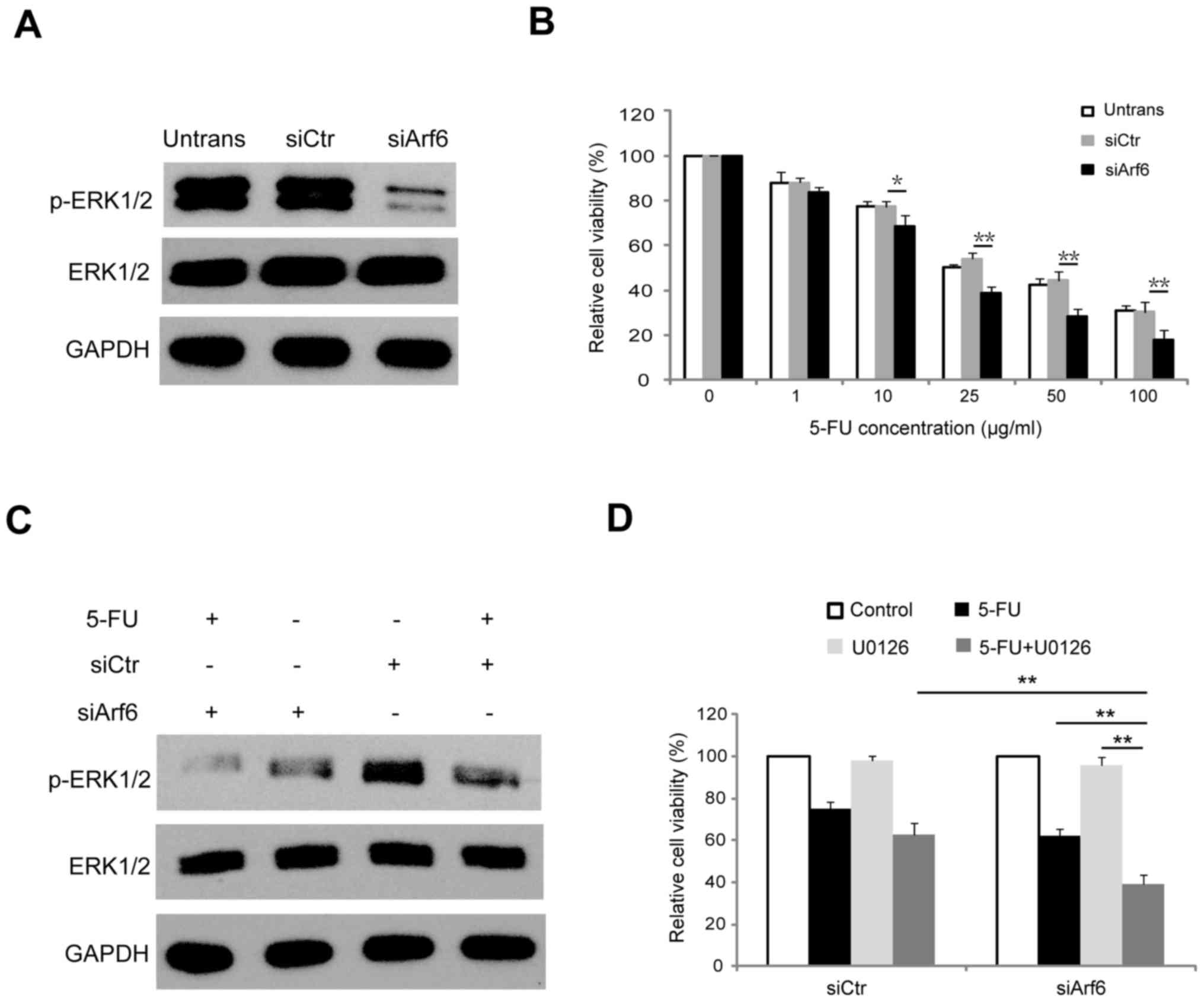
|
1
|
Piazuelo MB and Correa P: Gastric cáncer:
Overview. Colomb Med (Cali). 44:192–201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qi X, Liu Y, Wang W, Cai D, Li W, Hui J,
Liu C, Zhao Y and Li G: Management of advanced gastric cancer: An
overview of major findings from meta-analysis. Oncotarget.
7:78180–78205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akhavan-Niaki H and Samadani AA: Molecular
insight in gastric cancer induction: An overview of cancer stemness
genes. Cell Biochem Biophys. 68:463–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Flotow H: The use of high-throughput
screening in identifying chemotherapeutic agents for gastric
cancer. Future Med Chem. 6:2103–2112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mukhamedova N, Hoang A, Cui HL, Carmichael
I, Fu Y, Bukrinsky M and Sviridov D: Small GTPase ARF6 regulates
endocytic pathway leading to degradation of ATP-binding cassette
transporter A1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:2292–2303. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu X, Zhou T, Chen L, Zheng S, Chen S,
Zhang D, Li G and Wang Z: Arf6 controls endocytosis and polarity
during asexual development of Magnaporthe oryzae. FEMS Microbiol
Lett. 363:fnw2482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hashimoto S, Mikami S, Sugino H, Yoshikawa
A, Hashimoto A, Onodera Y, Furukawa S, Handa H, Oikawa T, Okada Y,
et al: Lysophosphatidic acid activates Arf6 to promote the
mesenchymal malignancy of renal cancer. Nat Commun. 7:106562016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hongu T, Yamauchi Y, Funakoshi Y, Katagiri
N, Ohbayashi N and Kanaho Y: Pathological functions of the small
GTPase Arf6 in cancer progression: Tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis. Small GTPases. 7:47–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang C, Qin Y, Zhang B, Ji S, Shi S, Xu
W, Liu J, Xiang J, Liang D, Hu Q, et al: ARF6, induced by mutant
Kras, promotes proliferation and Warburg effect in pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Lett. 388:303–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hashimoto S, Onodera Y, Hashimoto A,
Tanaka M, Hamaguchi M, Yamada A and Sabe H: Requirement for Arf6 in
breast cancer invasive activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp.
6647–6652. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morishige M, Hashimoto S, Ogawa E, Toda Y,
Kotani H, Hirose M, Wei S, Hashimoto A, Yamada A, Yano H, et al:
GEP100 links epidermal growth factor receptor signalling to Arf6
activation to induce breast cancer invasion. Nat Cell Biol.
10:85–92. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oka S, Uramoto H, Shimokawa H, Yamada S
and Tanaka F: Epidermal growth factor receptor-GEP100-Arf6 axis
affects the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncology. 86:263–270.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li M, Wang J, Ng SS, Chan CY, He ML, Yu F,
Lai L, Shi C, Chen Y, Yew DT, et al: Adenosine
diphosphate-ribosylation factor 6 is required for epidermal growth
factor-induced glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cancer.
115:4959–4972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hashimoto A, Hashimoto S, Ando R, Noda K,
Ogawa E, Kotani H, Hirose M, Menju T, Morishige M, Manabe T, et al:
GEP100-Arf6-AMAP1-cortactin pathway frequently used in cancer
invasion is activated by VEGFR2 to promote angiogenesis. PLoS One.
6:e233592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsumoto Y, Sakurai H, Kogashiwa Y,
Kimura T, Matsumoto Y, Shionome T, Asano M, Saito K and Kohno N:
Inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by cetuximab via
the EGFR-GEP100-Arf6-AMAP1 pathway in head and neck cancer. Head
Neck. 39:476–485. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dani N, Barbosa AJ, Del Rio A and Di
Girolamo M: ADP-ribosylated proteins as old and new drug targets
for anticancer therapy: The example of ARF6. Curr Pharm Des.
19:624–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hashimoto A, Hashimoto S, Sugino H,
Yoshikawa A, Onodera Y, Handa H, Oikawa T and Sabe H: ZEB1 induces
EPB41L5 in the cancer mesenchymal program that drives ARF6-based
invasion, metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogenesis. 5:e2592016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hashimoto A, Oikawa T, Hashimoto S, Sugino
H, Yoshikawa A, Otsuka Y, Handa H, Onodera Y, Nam JM, Oneyama C, et
al: P53- and mevalonate pathway-driven malignancies require Arf6
for metastasis and drug resistance. J Cell Biol. 213:81–95. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Du J, Zheng J, Liu J, Xu R, Shen
T, Zhu Y, Chang J, Wang H, Zhang Z, et al: EGF-reduced Wnt5a
transcription induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
Arf6-ERK signaling in gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget.
6:7244–7261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mitra A, Mishra L and Li S: EMT, CTCs and
CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget.
6:10697–10711. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ,
Ostell J and Sayers EW: GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D67–D72.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Z, Du J, Yang L, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Zheng
D, Someya A, Gu L and Lu X: GEP100/Arf6 is required for epidermal
growth factor-induced ERK/Rac1 signaling and cell migration in
human hepatoma HepG2 cells. PLoS One. 7:e387772012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu Z, Xu R, Liu J, Zhang Y, Du J, Li W,
Zhang W, Li Y, Zhu Y and Gu L: GEP100 regulates epidermal growth
factor-induced MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell invasion through the
activation of Arf6/ERK/uPAR signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res.
319:1932–1941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Davies JC, Tamaddon-Jahromi S, Jannoo R
and Kanamarlapudi V: Cytohesin 2/ARF6 regulates preadipocyte
migration through the activation of ERK1/2. Biochem Pharmacol.
92:651–660. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akter H, Park M, Kwon OS, Song EJ, Park WS
and Kang MJ: Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by
neurotensin promotes cell invasion and migration through ERK
pathway in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:6053–6062. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li P, Jia YF, Ma XL, Zheng Y, Kong Y,
Zhang Y, Zong S, Chen ZT and Wang YS: DEC2 suppresses tumor
proliferation and metastasis by regulating ERK/NF-κB pathway in
gastric cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1741–1757. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Teng H, Huang Q and Chen L: Inhibition of
cell proliferation and triggering of apoptosis by agrimonolide
through MAP kinase (ERK and p38) pathways in human gastric cancer
AGS cells. Food Funct. 7:4605–4613. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eva R, Crisp S, Marland JR, Norman JC,
Kanamarlapudi V, Ffrench-Constant C and Fawcett JW: ARF6 directs
axon transport and traffic of integrins and regulates axon growth
in adult DRG neurons. J Neurosci. 32:10352–10364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Torii T, Miyamoto Y, Yamamoto M, Ohbuchi
K, Tsumura H, Kawahara K, Tanoue A, Sakagami H and Yamauchi J: Arf6
mediates Schwann cell differentiation and myelination. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 465:450–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
George AA, Hayden S, Stanton GR and
Brockerhoff SE: Arf6 and the 5′phosphatase of Synaptojanin 1
regulate autophagy in cone photoreceptors. Inside Cell. 1:117–133.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grossmann AH, Zhao H, Jenkins N, Zhu W,
Richards JR, Yoo JH, Winter JM, Rich B, Mleynek TM, Li DY and
Odelberg SJ: The small GTPase ARF6 regulates protein trafficking to
control cellular function during development and in disease. Small
GTPases. 1–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen PW, Jian X, Yoon HY and Randazzo PA:
ARAP2 signals through Arf6 and Rac1 to control focal adhesion
morphology. J Biol Chem. 288:5849–5860. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hongu T, Funakoshi Y, Fukuhara S, Suzuki
T, Sakimoto S, Takakura N, Ema M, Takahashi S, Itoh S, Kato M, et
al: Arf6 regulates tumour angiogenesis and growth through
HGF-induced endothelial β1 integrin recycling. Nat Commun.
6:79252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bourmoum M, Charles R and Claing A: The
GTPase ARF6 controls ROS production to mediate angiotensin
II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. PLoS One.
11:e01480972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sabe H, Hashimoto S, Morishige M, Ogawa E,
Hashimoto A, Nam JM, Miura K, Yano H and Onodera Y: The
EGFR-GEP100-Arf6-AMAP1 signaling pathway specific to breast cancer
invasion and metastasis. Traffic. 10:982–993. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|