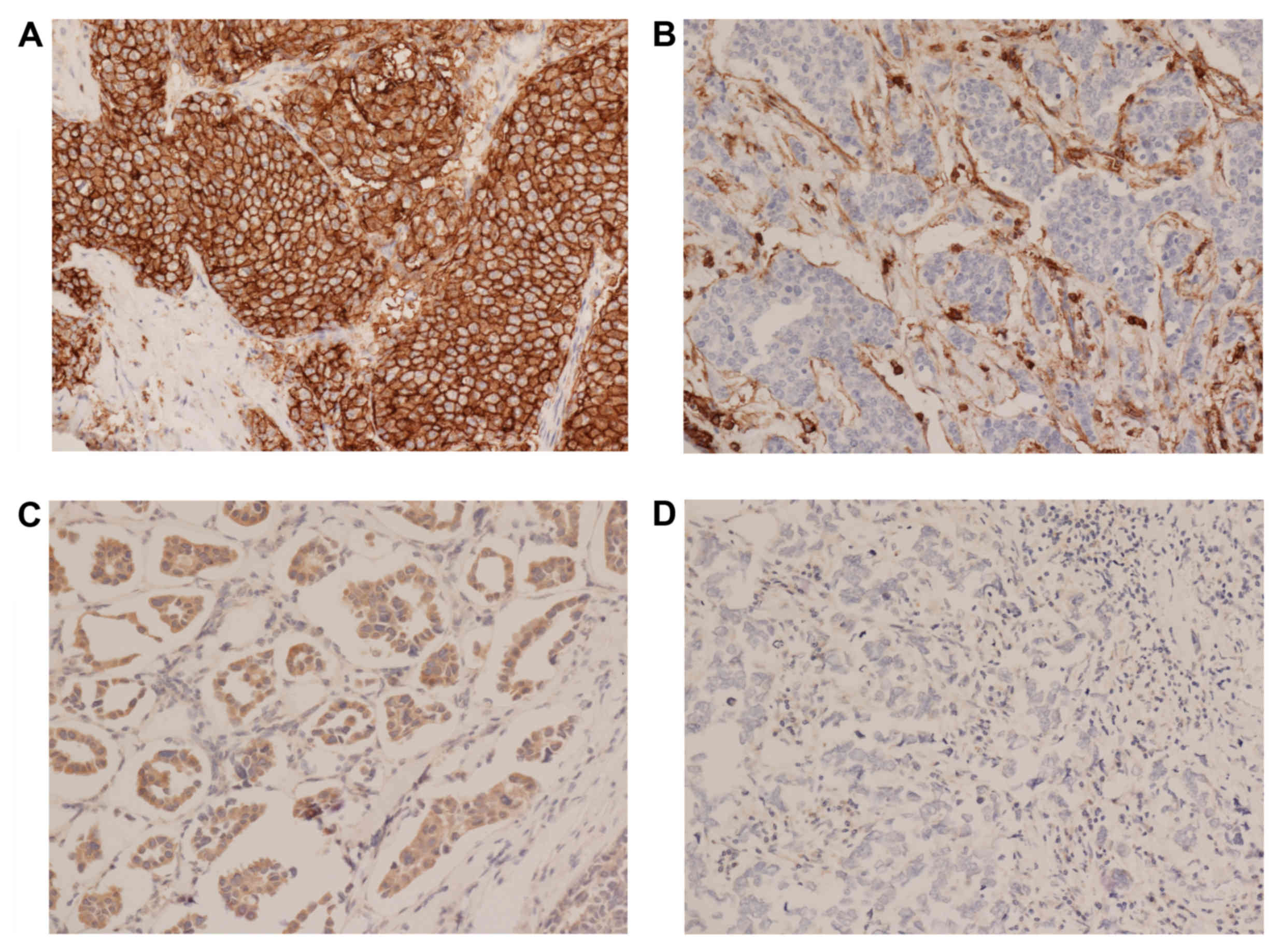
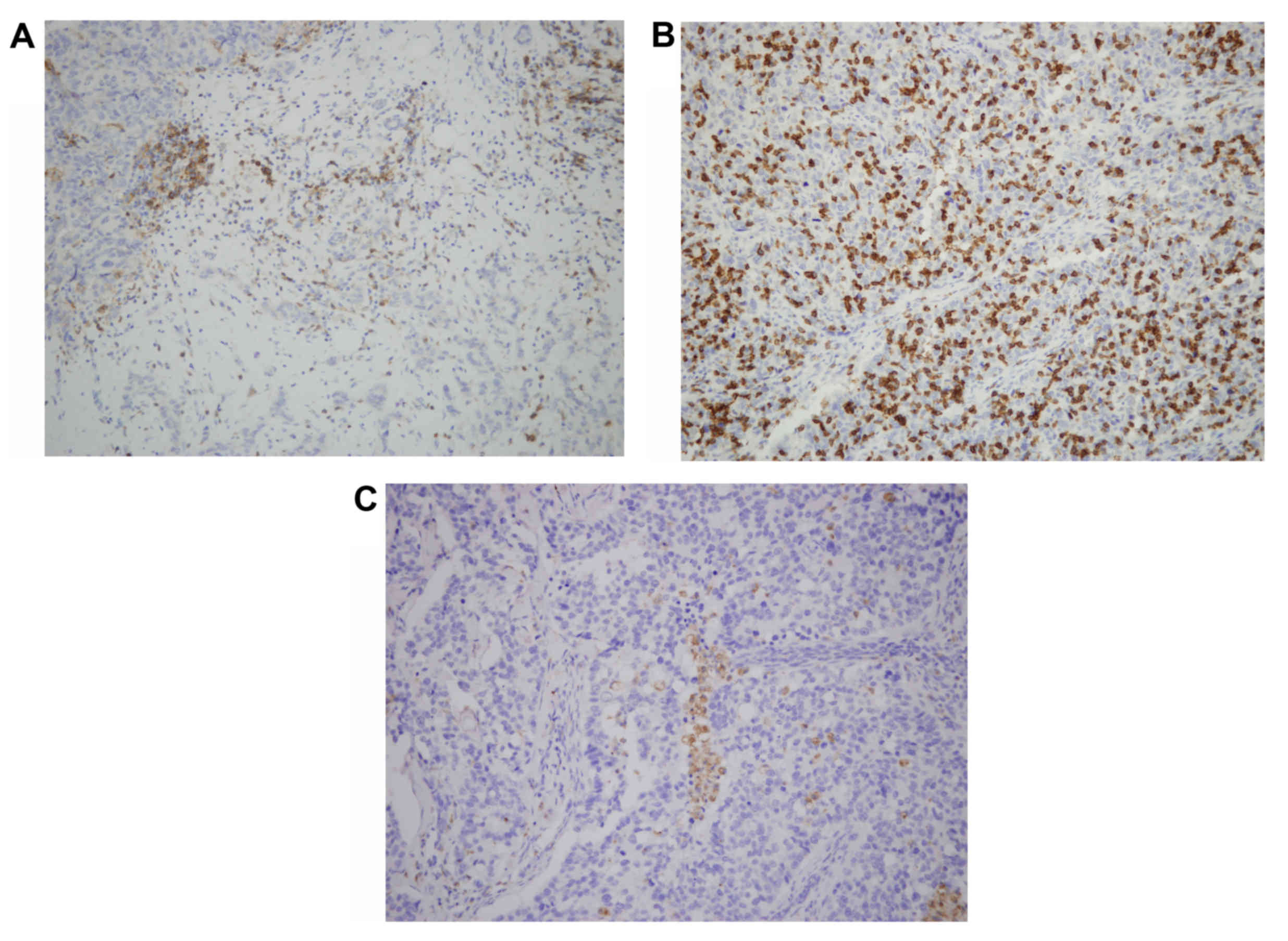
|
1
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arias JI, Aller MA and Arias J: Cancer
cell: Using inflammation to invade the host. Mol Cancer. 6:292007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Soria G, Ofri-Shahak M, Haas I,
Yaal-Hahoshen N, Leider-Trejo L, Leibovich-Rivkin T, Weitzenfeld P,
Meshel T, Shabtai E, Gutman M and Ben-Baruch A: Inflammatory
mediators in breast cancer: Coordinated expression of TNF-α &
IL-1β with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. BMC Cancer. 11:1302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lewis CE and Hughes R: Inflammation and
breast cancer. Microenvironmental factors regulating macrophage
function in breast tumours: Hypoxia and angiopoietin-2. Breast
Cancer Res. 9:2092007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin EY and Pollard JW: Tumor-associated
macrophages press the angiogenic switch in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:5064–5066. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soria G and Ben-Baruch A: The inflammatory
chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
267:271–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldberg JE and Schwertfeger KL:
Proinflammatory cytokines in breast cancer: Mechanisms of action
and potential targets for therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets.
11:1133–1146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Korkaya H, Kim GI, Davis A, Malik F, Henry
NL, Ithimakin S, Quraishi AA, Tawakkol N, D'Angelo R, Paulson AK,
et al: Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab
resistance in HER2+ breast cancer by expanding the
cancer stem cell population. Mol Cell. 47:570–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iqbal J, Chong PY and Tan PH: Breast
cancer stem cells: An update. J Clin Pathol. 66:485–490. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells-perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Boyle ST and Kochetkova M: Breast cancer
stem cells and the immune system: Promotion, evasion and therapy. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 19:203–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gammaitoni L, Leuci V, Mesiano G, Giraudo
L, Todorovic M, Carnevale-Schianca F, Agiletta M and Sangiolo D:
Immunotherapy of cancer stem cells in solid tumors: Initial
findings and future prospective. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
14:1259–1270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, . 7th edition.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL and Trotti FL:
Springer-Verlag; New York: pp. 347–377. 2010
|
|
14
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer I. The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jeong YJ, Jeong HY, Bong JG, Park SH and
Oh HK: Low methylation levels of the SFRP1 gene are associated with
the basal-like subtype of breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 29:1946–1954.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brabletz T: EMT and MET in metastasis:
Where are the cancer stem cells? Cancer Cell. 22:699–701. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shigdar S, Li Y, Bhattacharya S, O'Connor
M, Pu C, Lin J, Wang T, Xiang D, Kong L, Wei MQ, et al:
Inflammation and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 345:271–278. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vermeulen L, De Sousa Melo E, van der
Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M,
Merz C, Rodermond H, et al: Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem
cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol.
12:468–476. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Blaylock RL: Cancer microenvironment,
inflammation and cancer stem cells: A hypothesis for a paradigm
change and new targets in cancer control. Surg Neurol Int.
6:922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G and Struhl
K: Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their
dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1397–1402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F,
Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 induces
an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:2940–2947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri
T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P,
Marcu KB, et al: IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres
from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland. J Clin
Invest. 117:3988–4002. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katanov C, Lerrer S, Liubomirski Y,
Leider-Trejo L, Meshel T, Bar J, Feniger-Barish R, Kamer I,
Soria-Artzi G, Kahani H, et al: Regulation of the inflammatory
profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: Prominent roles
for TNF-α and the NF-κB pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:872015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
DeNardo DG and Coussens LM: Inflammation
and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: Crosstalk between
adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression.
Breast Cancer Res. 9:2122007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goto S, Sato M, Kaneko R, Itoh M, Sato S
and Takeuchi S: Analysis of Th1 and Th2 cytokine production by
peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a parameter of immunological
dysfunction in advanced cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
48:435–442. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Idowu MO, Kmieciak M, Dumur C, Burton RS,
Grimes MM, Powers CN and Manjili MH: CD44(+)/CD24(−/low) cancer
stem/progenitor cells are more abundant in triple-negative invasive
breast carcinoma phenotype and are associated with poor outcome.
Hum Pathol. 43:364–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim HJ, Kim MJ, Ahn SH, Son BH, Kim SB,
Ahn JH, Noh WC and Gong G: Different prognostic significance of
CD24 and CD44 expression in breast cancer according to hormone
receptor status. Breast. 20:78–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mylona E, Giannopoulou I, Fasomytakis E,
Nomikos A, Magkou C, Bakarakos P and Nakopoulou L: The
clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of
CD44(+)/CD24(−/low) and CD44−/CD24+ tumor
cells in invasive breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 39:1096–1102.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abraham BK, Fritz P, McClellan M,
Hauptvogel P, Athelogou M and Brauch H: Prevalence of
CD44+/CD24−/low cells in breast cancer may
not be associated with clinical outcome but may favor distant
metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1154–1159. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad USA. 100:3983–3988.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jiang X and Shapiro DJ: The immune system
and inflammation in breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:673–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tkach M, Coria L, Rosemblit C, Rivas MA,
Proietti CJ, Díaz Flaqué MC, Beguelin W, Frahm I, Charreau EH,
Cassataro J, et al: Targeting Stat3 induces senescence in tumor
cells and elicits prophylactic and therapeutic immune responses
against breast cancer growth mediated by NK cells and
CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 189:1162–1172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang B, Zaidi N, He LZ, Zhang L, Kuroiwa
JM, Keler T and Steinman RM: Targeting of the non-mutated tumor
antigen HER2/neu to mature dendritic cells induces an integrated
immune response that protects against breast cancer in mice. Breast
Cancer Res. 14:R392012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mamessier E, Sylvain A, Thibult ML,
Houvenaeghel G, Jacquemier J, Castellano R, Gonçalves A, André P,
Romagné F, Thibault G, et al: Human breast cancer cells enhance
self tolerance by promoting evasion from NK cell antitumor
immunity. J Clin Invest. 121:3609–3622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsukerman P, Stern-Ginossar N, Gur C,
Glasner A, Nachmani D, Bauman Y, Yamin R, Vitenshtein A, Stanietsky
N, Bar-Mag T, et al: MiR-10b downregulates the stress-induced cell
surface molecule MICB, a critical ligand for cancer cell
recognition by natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 72:5463–5472.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang X, Ellison SJ, Alarid ET and Shapiro
DJ: Interplay between the levels of estrogen and estrogen receptor
controls the level of the granzyme inhibitor, proteinase inhibitor
9 and susceptibility to immune surveillance by natural killer
cells. Oncogene. 26:4106–4114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bargou RC, Wagener C, Bommert K, Mapara
MY, Daniel PT, Arnold W, Dietel M, Guski H, Feller A, Royer HD and
Dorken B: Overexpression of the death-promoting gene bax-alpha
which is downregulated in breast cancer restores sensitivity to
different apoptotic stimuli and reduces tumor growth in SCID mice.
J Clin Invest. 97:2651–2659. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu S, Lachapelle J, Leung S, Gao D,
Foulkes WD and Nielsen TO: CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration
is an independent favorable prognostic indicator in basal-like
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mahmoud SM, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan
RD, Grainge MJ, Lee AH, Ellis IO and Green AR: Tumor-infiltrating
CD8+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:1949–1955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|