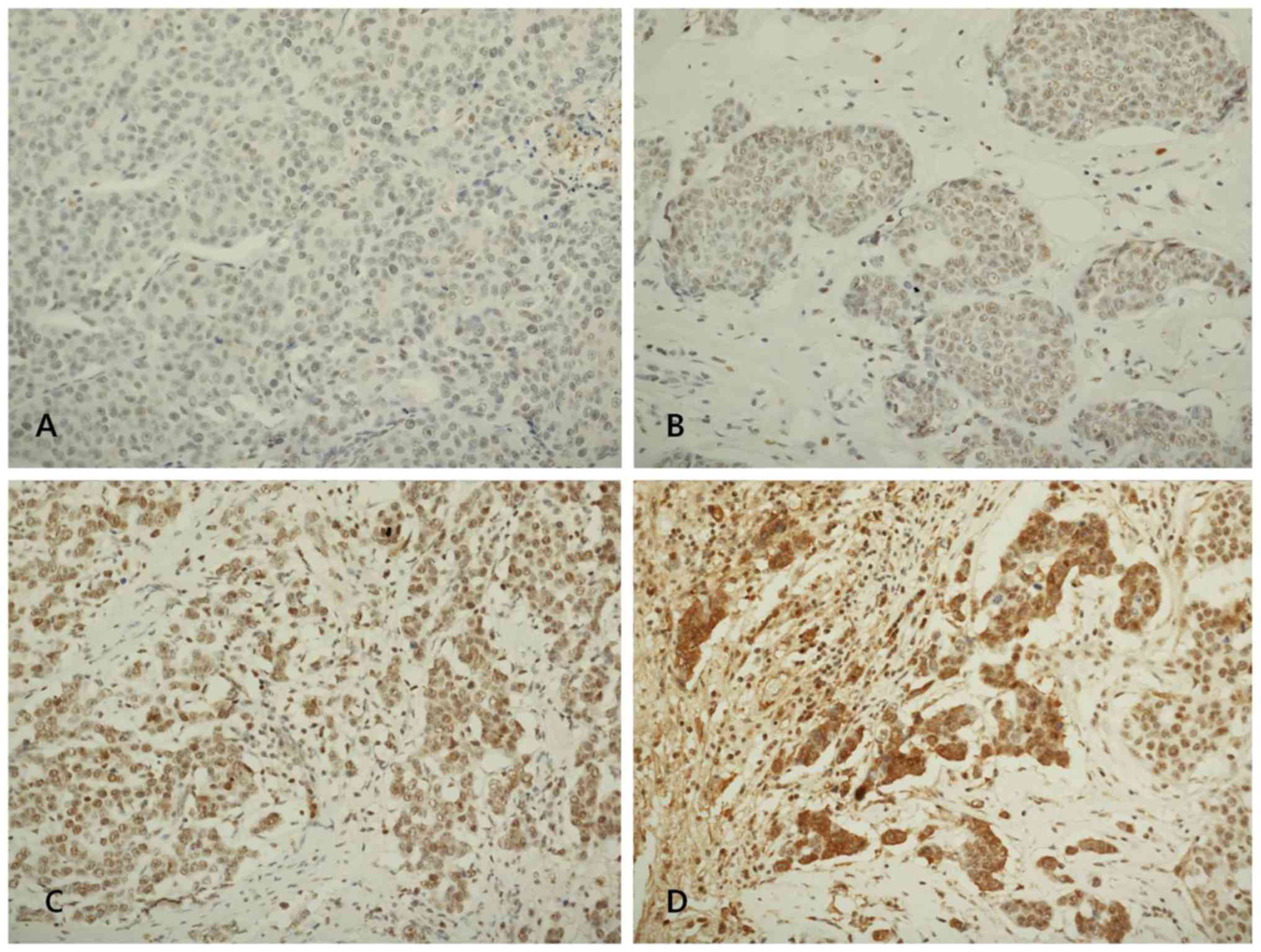
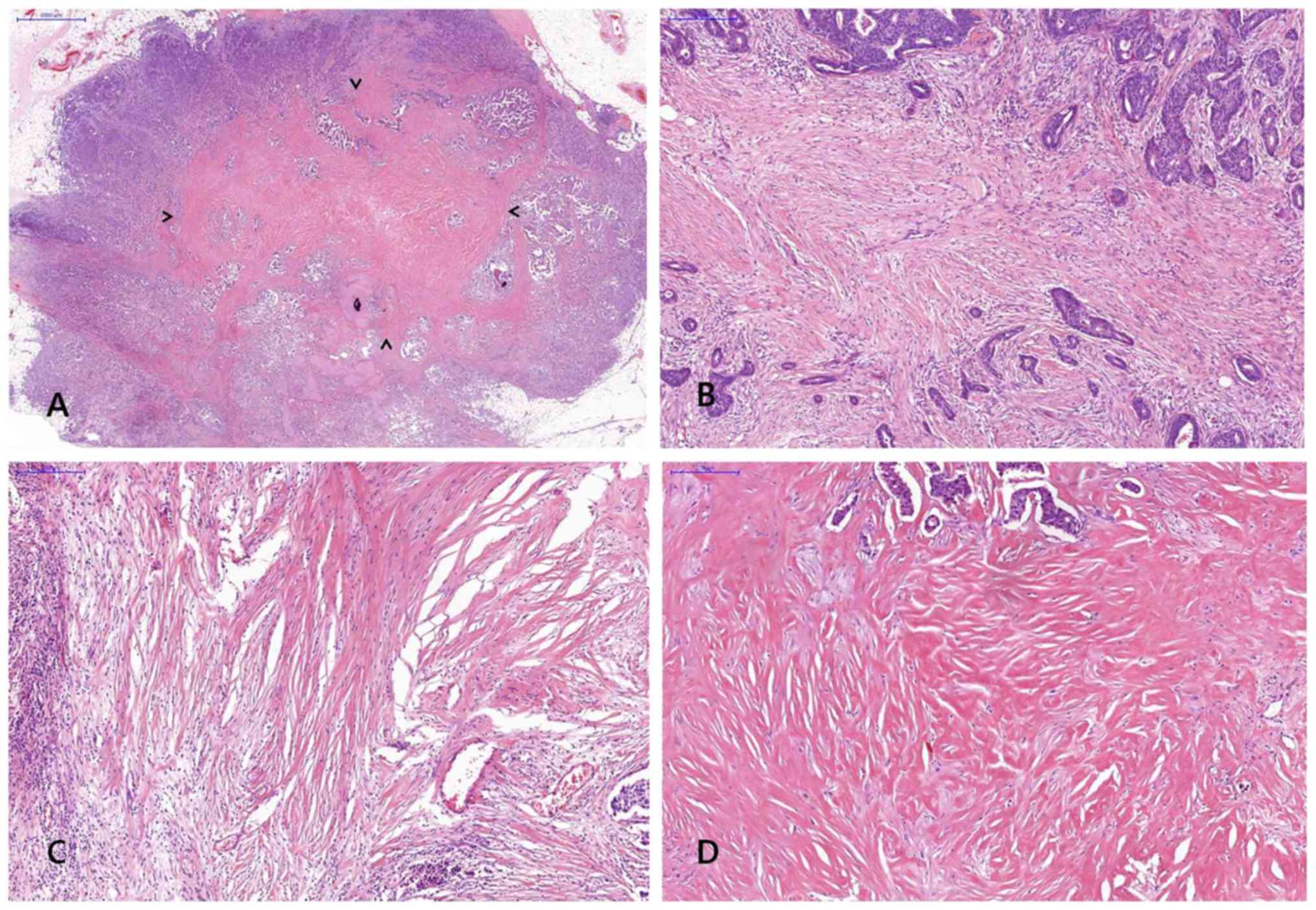
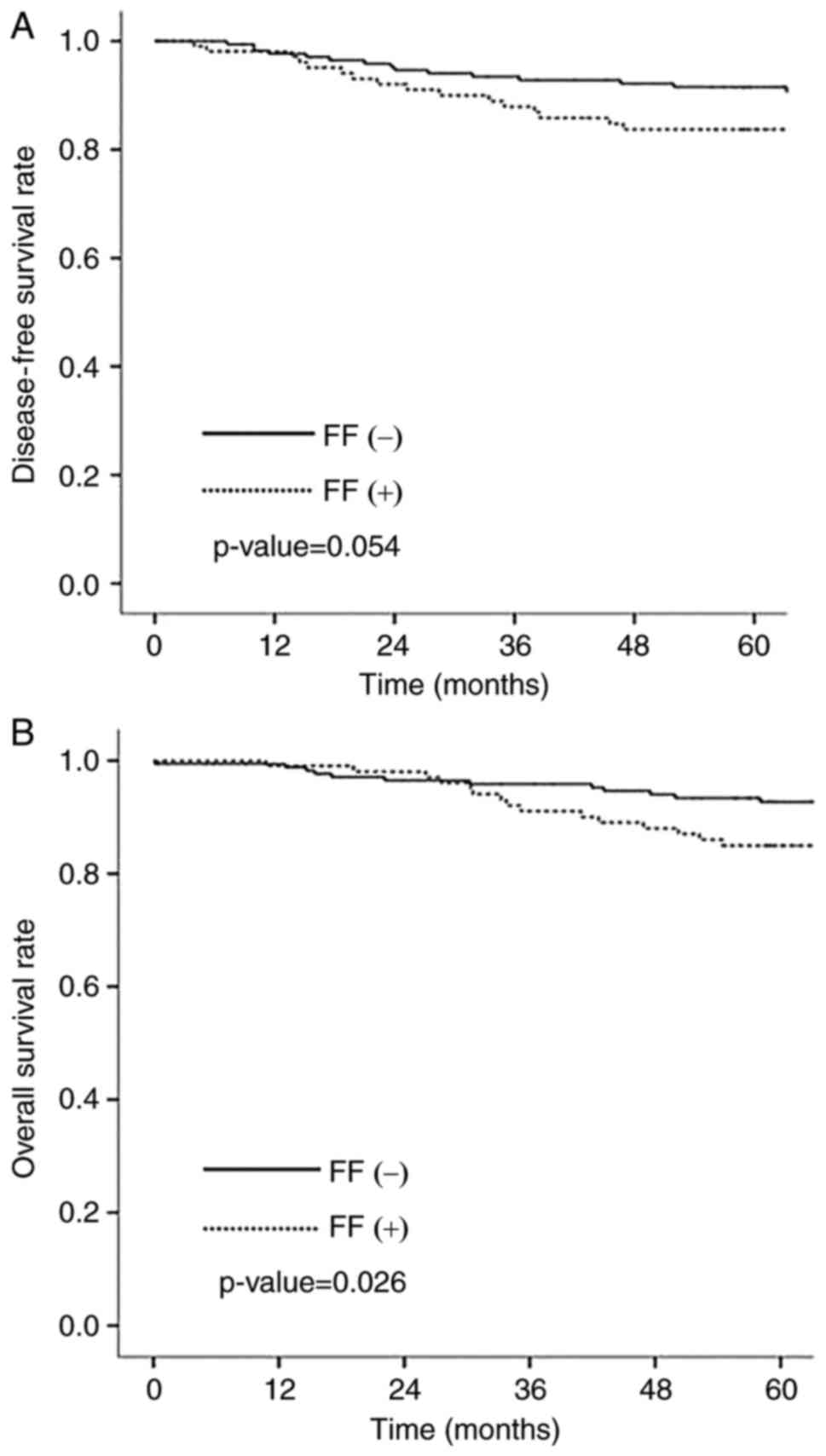
|
1
|
Pupa SM, Ménard S, Forti S and Tagliabue
E: New insights into the role of extracellular matrix during tumor
onset and progression. J Cell Physiol. 192:259–267. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins JN,
Egeblad M, Erler JT, Fong SFT, Csiszar K, Giaccia A, Weninger W, et
al: Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing
integrin signaling. Cell. 139:891–906. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL and Wirtz D: Hypoxia
and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:430–439. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Acerbi I, Cassereau L, Dean I, Shi Q, Au
A, Park C, Chen YY, Liphardt J, Hwang ES and Weaver VM: Human
breast cancer invasion and aggression correlates with ECM
stiffening and immune cell infiltration. Integr Biol (Camb).
7:1120–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cox TR, Bird D, Baker AM, Barker HE, Ho
MW, Lang G and Erler JT: LOX-mediated collagen crosslinking is
responsible for fibrosis-enhanced metastasis. Cancer Res.
73:1721–1732. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Csiszar K: Lysyl oxidase: A novel
multifunctional amine oxidase family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol
Biol. 70:1–32. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Payne SL, Hendrix MJC and Kirschmann DA:
Paradoxical roles for lysyl oxidases in cancer-a prospect. J Cell
Biochem. 101:1338–1354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith-Mungo LI and Kagan HM: Lysyl
oxidase: Properties, regulation and multiple functions in biology.
Matrix Biol. 16:387–398. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kagan HM and Li W: Lysyl oxidase:
Properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of
the cell. J Cell Biochem. 88:660–672. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Molnar J, Fong KSK, He QP, Hayashi K, Kim
Y, Fong SF, Fogelgren B, Szauter KM, Mink M and Csiszar K:
Structural and functional diversity of lysyl oxidase and the
LOX-like proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1647:220–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lucero HA and Kagan HM: Lysyl oxidase: An
oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life Sci.
63:2304–2316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baker AM, Cox TR, Bird D, Lang G, Murray
GI, Sun XF, Southall SM, Wilson JR and Erler JT: The role of lysyl
oxidase in SRC-dependent proliferation and metastasis of colorectal
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:407–424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M,
Dornhöfer N, Kong C, Le QT, Chi JT, Jeffrey SS and Giaccia AJ:
Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature.
440:1222–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barker HE, Chang J, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird
D, Nicolau M, Evans HR, Gartland A and Erler JT: LOXL2-mediated
matrix remodeling in metastasis and mammary gland involution.
Cancer Res. 71:1561–1572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cox TR and Erler JT: Remodeling and
homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: Implications for fibrotic
diseases and cancer. Dis Model Mech. 4:165–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hasebe T, Tsuda H, Hirohashi S, Shimosato
Y, Iwai M, Imoto S and Mukai K: Fibrotic focus in invasive ductal
carcinoma: An indicator of high tumor aggressiveness. Jpn J Cancer
Res. 87:385–394. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Van den Eynden GG, Colpaert CG, Couvelard
A, Pezzella F, Dirix LY, Vermeulen PB, Van Marck EA and Hasbe T: A
fibrotic focus is a prognostic factor and a surrogate marker for
hypoxia and (lymph)angiogenesis in breast cancer: Review of the
literature and proposal on the criteria of evaluation.
Histopathology. 51:440–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ueha S, Shand FH and Matsushima K:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of chronic
inflammation-associated organ fibrosis. Front Immunol. 3:712012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jeong YJ, Bong JG, Park SH, Choi JI and Oh
HK: Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, adiponectin, and
adiponectin receptor in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive
breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 14:96–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Radisky DC, Kenny PA and Bissell MJ:
Fibrosis and cancer: Do myofibroblasts come also from epithelial
cells via EMT? J Cell Biochem. 101:830–839. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ertz N: Cancer: Opening LOX to metastasis.
Nature. 522:41–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nishioka T, Eustace A and West C: Lysyl
oxidase: From basic science to future cancer treatment. Cell Struct
Funct. 37:75–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leight JL, Wozniak MA, Chen S, Lynch ML
and Chen CS: Matrix rigidity regulates a switch between TGF-β
1-induced apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Biol
Cell. 23:781–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wynn TA and Barron L: Macrophages: Master
regulators of inflammation and fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis.
30:245–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luzina IG, Todd NW, Iacono AT and Atamas
SP: Roles of T lymphocytes in pulmonary fibrosis. J Leuko Biol.
83:237–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meldrum KK, Metcalfe P, Leslie JA, Misseri
R, Hile KL and Meldrum DR: TNF-alpha neutralization decreases
nuclear factor-kappaB activation and apoptosis during renal
obstruction. J Surg Res. 131:181–188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tashiro K, Tamada S, Kuwabara N, Komiya T,
Takekida K, Asai T, Iwao H, Sugimura K, Matsumura Y, Takaoka M, et
al: Attenuation of renal fibrosis by proteasome inhibition in rat
obstructive nephropathy: Possible role of nuclear factor kappaB.
Int J Mol Med. 12:587–592. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB. Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure
J, Nelles L, van Roy F, Dargemont C, de Herreros AG, Bellacosa A
and Larue L: Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail
expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene.
26:7445–7456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim HJ, Litzenburger BC, Cui X, Delgado
DA, Grabiner BC, Lin X, Lewis MT, Gottardis MM, Wong TW, Attar RM,
et al: Constitutively active type I insulin-like growth factor
receptor causes transformation and xenograft growth of immortalized
mammary epithelial cells and is accompanied by an
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition mediated by NF-kappaB and
snail. Mol Cell Biol. 27:3165–3175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Denko NC, Fontana LA, Hudson KM, Sutphin
PD, Raychaudhuri S, Altman R and Giaccia AJ: Investigating hypoxic
tumor physiology through gene expression patterns. Oncogene.
22:5907–5914. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM,
Shrimanker N, Akai Y, Hohenstein B, Saito Y, Johnson RS, Kretzler
M, Cohen CD, et al: Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1
stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest.
117:3810–3820. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nagai S and Toi M: Interleukin-4 and
breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 7:181–186. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hasebe T, Sasaki S, Imoto S, Muki K,
Yokose T and Ochiai A: Prognostic significance of fibrotic focus in
invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: A prospective
observational study. Mod Pathol. 15:502–516. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hollosi P, Yakushiji JK, Fong KS, Csiszar
K and Fong SF: Lysyl oxidase-like 2 promotes migration in
noninvasive breast cancer cells no in normal breast epithelial
cells. Int J Cancer. 125:318–327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Fong SF, Nieva
DR, Sullivan CM, Edwards EM, Sommer P, Csiszar K and Hendrix MJ: A
molecular role for lysyl oxidase in breast cancer invasion. Cancer
Res. 62:4478–4483. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hellman J, Jansen MP, Ruigrok-Ritstier K,
van Staveren IL, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Sieuwerts AM, Klijn
JG, SleiJfer S, Foekens JA and Berns EM: Association of an
extracellular matrix gene cluster with breast cancer prognosis and
endocrine therapy response. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5555–5564. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Patani N, Jiang W, Newbold R and Mokbel K:
Prognostic implications of carboxyl-terminus of Hsc70 interacting
protein and lysyl-oxidase expression in human breast cancer. J
Carcinog. 9:92010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peinado H, Moreno-Bueno G, Hardisson D,
Pérez-Gómez E, Santos V, Mendiola M, de Diego JI, Nistal M,
Quintanilla M, Portillo F and Cano A: Lysyl oxidase-like 2 as a new
poor prognosis marker of squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res.
68:4541–4550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McSherry EA, McGoldrick A, Kay EW, Hopkins
AM, Gallagher WM and Dervan PA: Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
clinical tissues show spurious copy number changes in array-CGH
profiles. Clin Genet. 72:441–447. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|