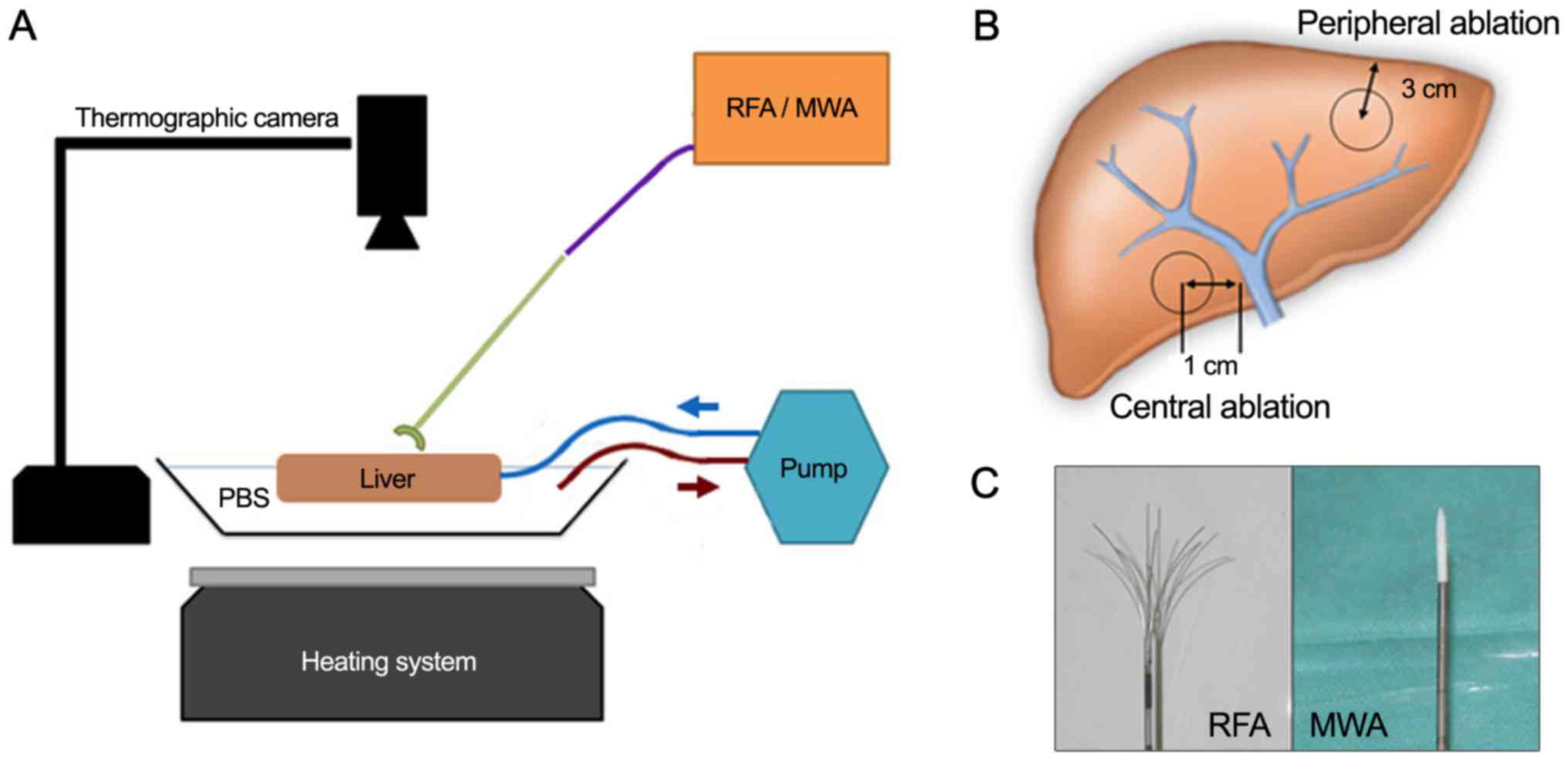
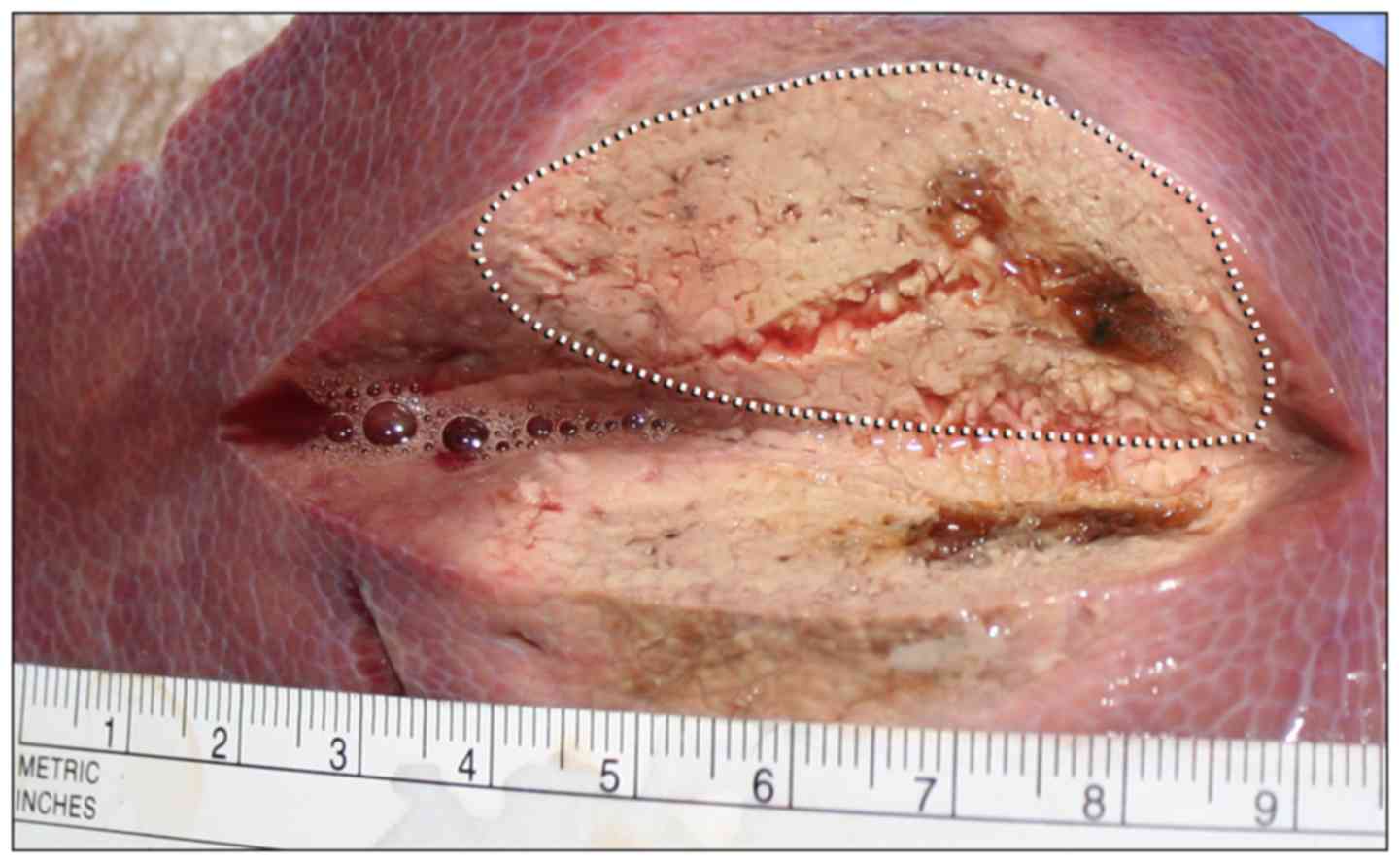
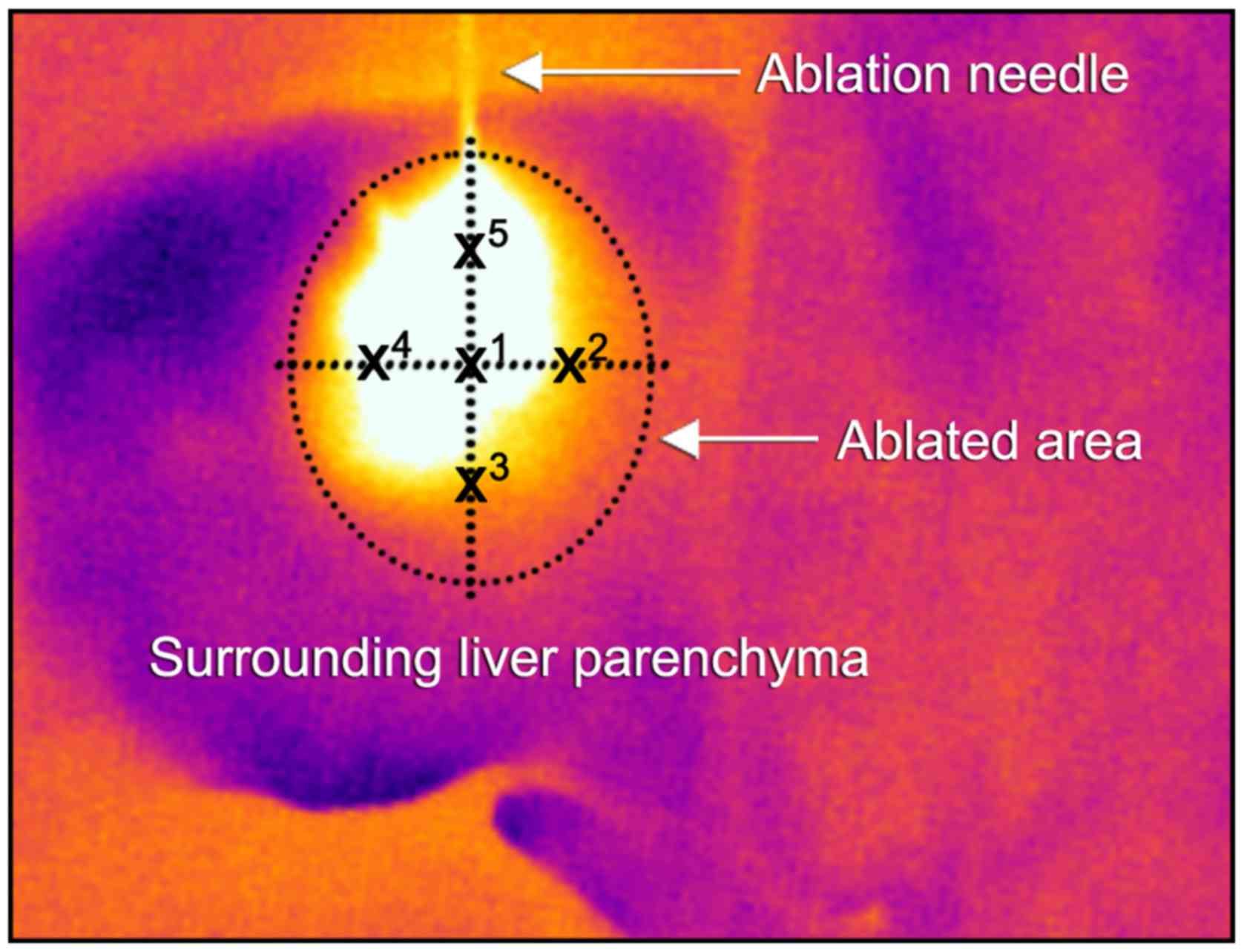
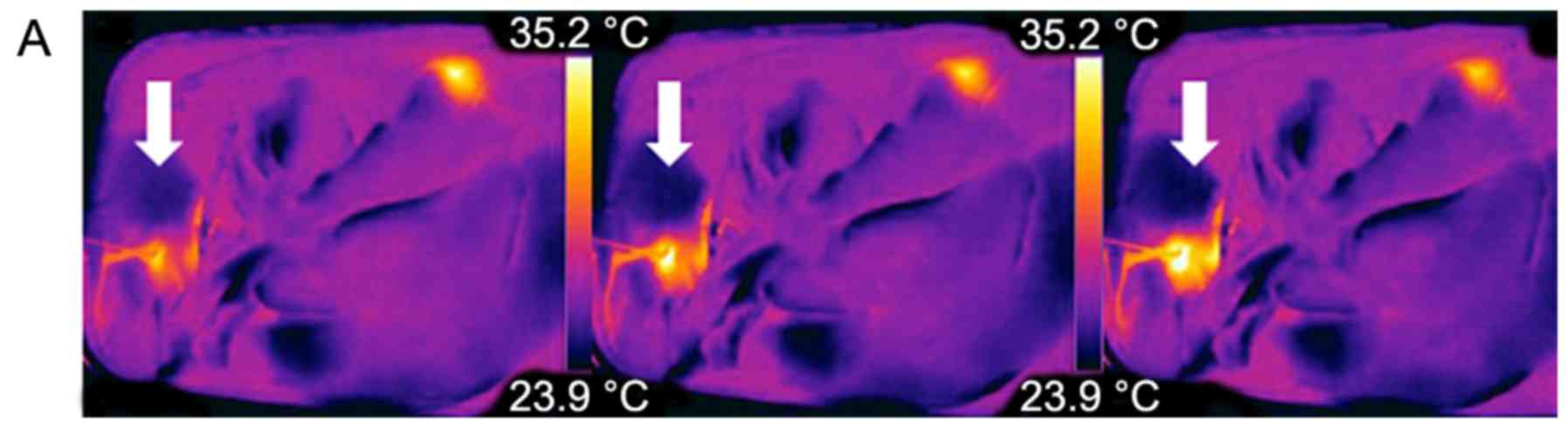
|
1
|
Evrard S, Poston G, Kissmeyer-Nielsen P,
Diallo A, Desolneux G, Brouste V, Lalet C, Mortensen F, Stättner S,
Fenwick S, et al: Combined ablation and resection (CARe) as an
effective parenchymal sparing treatment for extensive colorectal
liver metastases. PLoS One. 9:e1144042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Poulou LS, Botsa E, Thanou I, Ziakas PD
and Thanos L: Percutaneous microwave ablation vs radiofrequency
ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 7:1054–1063. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Molla N, AlMenieir N, Simoneau E, Aljiffry
M, Valenti D, Metrakos P, Boucher LM and Hassanain M: The role of
interventional radiology in the management of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Curr Oncol. 21:e480–e492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stättner S, Primavesi F, Yip VS, Jones RP,
Öfner D, Malik HZ, Fenwick SW and Poston GJ: Evolution of surgical
microwave ablation for the treatment of colorectal cancer liver
metastasis: Review of the literature and a single centre
experience. Surg Today. 45:407–415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS and Mueller PR:
Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: A unified approach
to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging
guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 174:323–331. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hänsler J, Neureiter D, Strobel D, Müller
W, Mutter D, Bernatik T, Hahn EG and Becker D: Cellular and
vascular reactions in the liver to radio-frequency thermo-ablation
with wet needle applicators. Study on juvenile domestic pigs. Eur
Surg Res. 34:357–363. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brace CL: Microwave tissue ablation:
Biophysics, technology, and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng.
38:65–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pillai K, Akhter J, Chua TC, Shehata M,
Alzahrani N, Al-Alem I and Morris DL: Heat sink effect on tumor
ablation characteristics as observed in monopolar radiofrequency,
bipolar radiofrequency, and microwave, using ex vivo calf liver
model. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e5802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL and Lee FT
Jr: Microwave tumor ablation: Mechanism of action, clinical
results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 21(8 Suppl): S192–S203.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dodd GD III, Dodd NA, Lanctot AC and
Glueck DA: Effect of variation of portal venous blood flow on
radiofrequency and microwave ablations in a blood-perfused bovine
liver model. Radiology. 267:129–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu H, Wilkins LR, Ziats NP, Haaga JR and
Exner AA: Real-time monitoring of radiofrequency ablation and
postablation assessment: Accuracy of contrast-enhanced US in
experimental rat liver model. Radiology. 270:107–116. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wiggermann P, Brünn K, Rennert J, Loss M,
Wobser H, Schreyer AG, Stroszczynski C and Jung EM: Monitoring
during hepatic radiofrequency ablation (RFA): Comparison of
real-time ultrasound elastography (RTE) and contrast-enhanced
ultrasound (CEUS): First clinical results of 25 patients.
Ultraschall Med. 34:590–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dewall RJ, Varghese T and Brace CL:
Visualizing ex vivo radiofrequency and microwave ablation zones
using electrode vibration elastography. Med Phys. 39:6692–6700.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ring EF and Ammer K: Infrared thermal
imaging in medicine. Physiol Meas. 33:R33–R46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ringe KI, Lutat C, Rieder C, Schenk A,
Wacker F and Raatschen HJ: Experimental evaluation of the heat sink
effect in hepatic microwave ablation. PLoS One. 10:e01343012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chinn SB, Lee FT Jr, Kennedy GD, Chinn C,
Johnson CD, Winter TC III, Warner TF and Mahvi DM: Effect of
vascular occlusion on radiofrequency ablation of the liver: Results
in a porcine model. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 176:789–795. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YS, Rhim H, Cho OK, Koh BH and Kim Y:
Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation
of hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of the pattern and risk
factors. Eur J Radiol. 59:432–441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Al-Alem I, Pillai K, Akhter J, Chua TC and
Morris DL: Heat sink phenomenon of bipolar and monopolar
radiofrequency ablation observed using polypropylene tubes for
vessel simulation. Surg Innov. 21:269–276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brannan JD and Ladtkow CM: Modeling
bimodal vessel effects on radio and microwave frequency ablation
zones. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009:pp. 5989–5992. 2009;
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF, Mahvi DM
and Lee FT Jr: Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a
hepatic porcine model. Radiology. 236:132–139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu NC, Raman SS, Kim YJ, Lassman C, Chang
X and Lu DS: Microwave liver ablation: Influence of hepatic vein
size on heat-sink effect in a porcine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol.
19:1087–1092. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhardwaj N, Strickland AD, Ahmad F,
El-Abassy M, Morgan B, Robertson GS and Lloyd DM: Microwave
ablation for unresectable hepatic tumours: Clinical results using a
novel microwave probe and generator. Eur J Surg Oncol. 36:264–268.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Awad MM, Devgan L, Kamel IR, Torbensen M
and Choti MA: Microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model:
Correlation of CT and histopathologic findings. HPB (Oxford).
9:357–362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bale R, Widmann G, Schullian P, Haidu M,
Pall G, Klaus A, Weiss H, Biebl M and Margreiter R: Percutaneous
stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver
metastases. Eur Radiol. 22:930–937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hori T, Nagata K, Hasuike S, Onaga M,
Motoda M, Moriuchi A, Iwakiri H, Uto H, Kato J, Ido A, et al: Risk
factors for the local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
a single session of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J
Gastroenterol. 38:977–981. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poon RT, Ng KK, Lam CM, Ai V, Yuen J and
Fan ST: Effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular
carcinomas larger than 3 cm in diameter. Arch Surg. 139:281–287.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Minami Y and Kudo M: Review of dynamic
contrast-enhanced ultrasound guidance in ablation therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4952–4959.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schutt DJ and Haemmerich D: Effects of
variation in perfusion rates and of perfusion models in
computational models of radio frequency tumor ablation. Med Phys.
35:3462–3470. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jakab F, Sugár I, Ráth Z, Nágy P and
Faller J: The relationship between portal venous and hepatic
arterial blood flow. I. Experimental liver transplantation. HPB
Surg. 10:21–26. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|