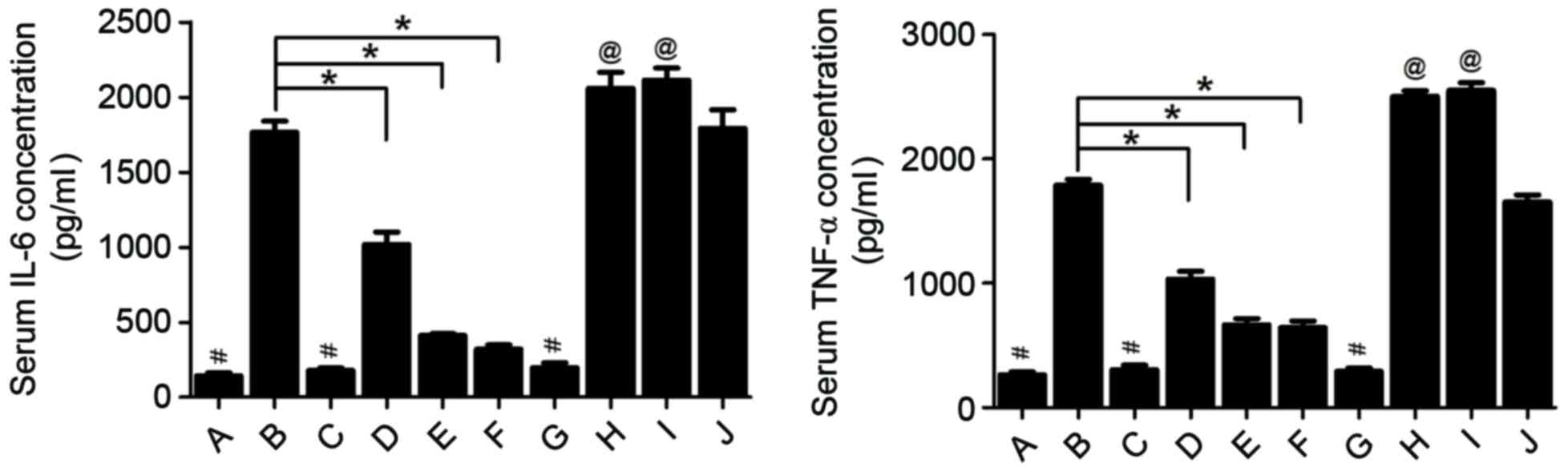
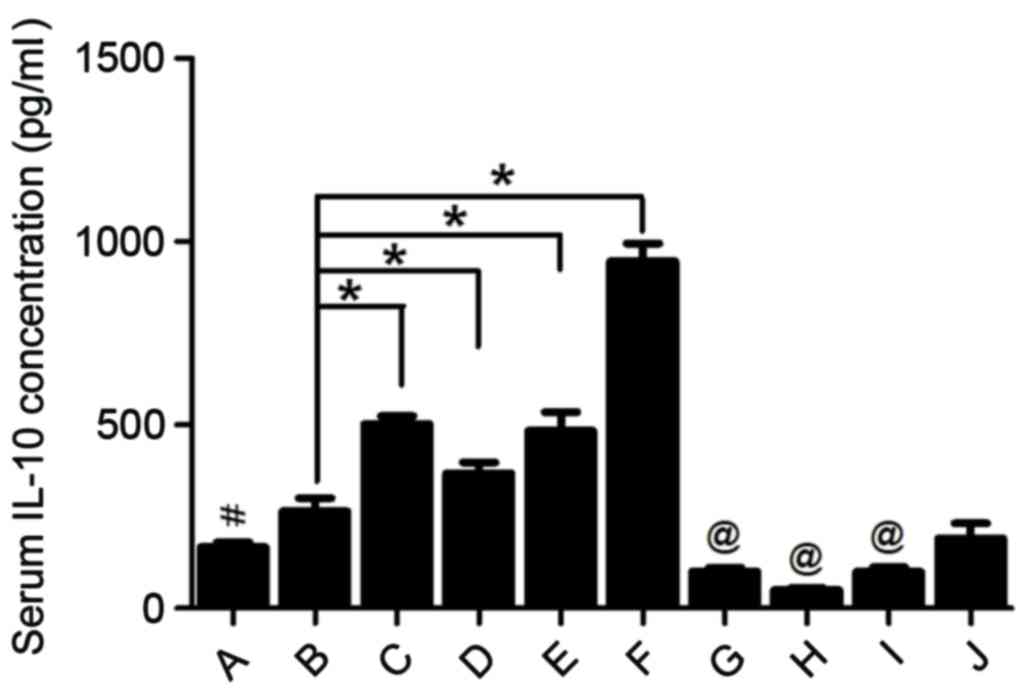
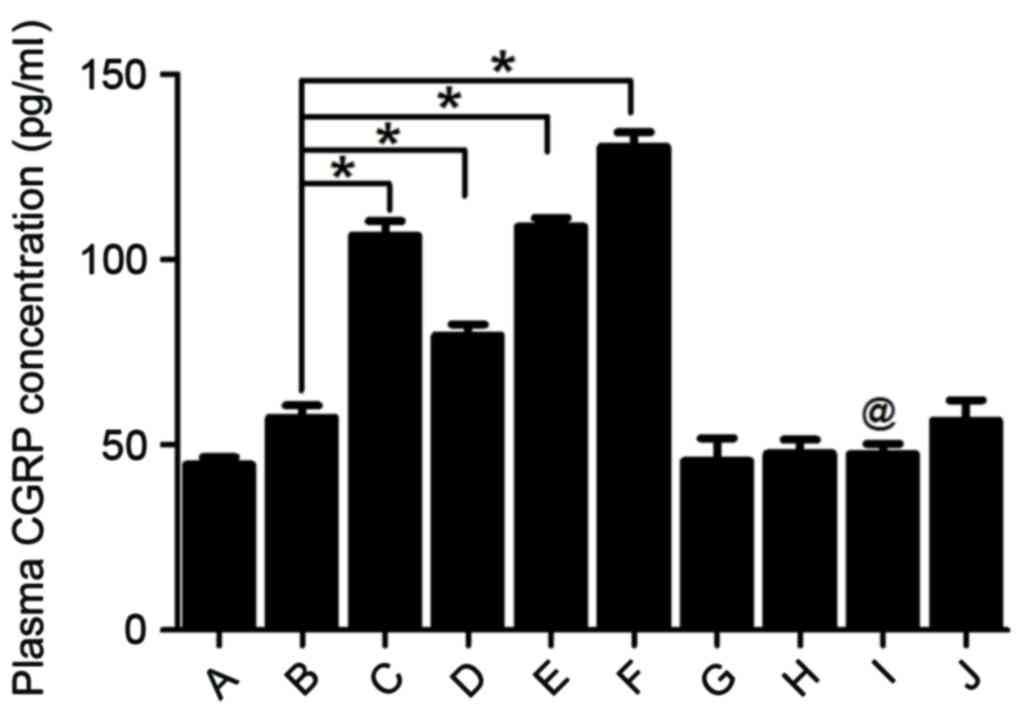
|
1
|
Maksimow M, Kyhälä L, Nieminen A, Kylänpää
L, Aalto K, Elima K, Mentula P, Lehti M, Puolakkainen P, Yegutkin
GG, et al: Early prediction of persistent organ failure by soluble
CD73 in patients with acute pancreatitis*. Crit Care Med.
42:2556–2564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yadav D and Lowenfels AB: The epidemiology
of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastrenterology.
144:1252–1261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang ZW, Meng XX and Xu P: Central role of
neutrophil in the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. J Cell
Mol Med. 19:2513–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dellinger EP, Forsmark CE, Layer P, Lévy
P, Maraví-Poma E, Petrov MS, Shimosegawa T, Siriwardena AK, Uomo G,
Whitcomb DC, et al: Determinant-based classification of acute
pancreatitis severity: An international multidisciplinary
consultation. Ann Surg. 256:875–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Forsmark CE and Toskes PP: Acute
pancreatitis. Medical management. Crit Care Clin. 11:295–309.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang XP, Li ZJ and Zhang J: Inflammatory
mediators and microcirculatory disturbance in acute pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 8:351–357. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klar E, Schratt W, Foitzik T, Buhr H,
Herfarth C and Messmer K: Impact of microcirculatory flow pattern
changes on the development of acute edematous and necrotizing
pancreatitis in rabbit pancreas. Dig Dis Sci. 39:2639–2644. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou ZG and Chen YD: Influencing factors
of pancreatic microcirculatory impairment in acute panceatitis.
World J Gastroenterol. 8:406–412. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gómez-Cambronero LG, Sabater L, Pereda J,
Cassinello N, Camps B, Viña J and Sastre J: Role of cytokines and
oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis:
Therapeutical implications. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy.
1:393–403. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiang H, Zhang Q, Qi B, Tao X, Xia S, Song
H, Qu J and Shang D: Chinese herbal medicines attenuate acute
pancreatitis: Pharmacological activities and mechanisms. Front
Pharmacol. 8:2162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Hu CP, Deng PY, Shen SS, Zhu HQ,
Ding JS, Tan GS and Li YJ: The protective effects of rutaecarpine
on gastric mucosa injury in rats. Planta Med. 71:416–419. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee SH, Son JK, Jeong BS, Jeong TC, Chang
HW, Lee ES and Jahng Y: Progress in the studies on rutaecarpine.
Molecules. 13:272–300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Tan GS, Deng PY, Xu KP, Hu CP and Li
YJ: Involvement of CGRP in the inhibitory effect of rutaecarpine on
vasoconstriction induced by anaphylaxis in guinea pig. Regul Pept.
125:93–97. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li JZ, Peng J, Xiao L, Zhang YS, Liao MC,
Li XH, Hu CP, Deng HW and Li YJ: Reversal of isoprenaline-induced
cardiac remodeling by rutaecarpine via stimulation of calcitonin
gene-related peptide production. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
88:949–959. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng PY, Ye F, Cai WJ, Tan GS, Hu CP, Deng
HW and Li YJ: Stimulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide
synthesis and release: Mechanisms for a novel antihypertensive
drug, rutaecarpine. J Hypertens. 22:1819–1829. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng J and Li YJ: The vanilloid receptor
TRPV1: Role in cardiovascular and gastrointestinal protection. Eur
J Pharmacol. 627:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Warzecha Z, Dembiński A, Jaworek J,
Ceranowicz P, Szlachcic A, Walocha J and Konturek SJ: Role of
sensory nerves in pancreatic secretion and caerulein-induced
pancreatitis. J PhysiolPharmacol. 48:43–58. 1997.
|
|
18
|
Warzecha Z, Dembiński A, Ceranowicz P,
Konturek PC, Stachura J, Konturek SJ and Niemiec J: Protective
effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide against caerulein-induced
pancreatitis in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 48:775–787.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dembiński A, Warzecha Z, Ceranowicz P,
Jaworek J, Sendur R, Knafel A, Dembiński M, Bilski J, Pawlik WW,
Tomaszewska R, et al: Stimulation of sensory nerves and CGRP
attenuate pancreatic damage in ischemia/reperfusion induced
pancreatitis. Med Sci Monit. 9:BR418–BR425. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van den Worm E, de Vires A, Nijkamp FP and
Engels F: Capsazepine, a vanilloid receptor antagonist, inhibits
allergen-induced tracheal contraction. Eur J Pharmacol. 518:77–78.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huan G, Jie P and Jixiang M: Experimental
study of therapeutic use of rutecarpin in severe acute
pancreatitis. Chin J Gen Surg. 23:2014.
|
|
22
|
Hu CP, Xiao L, Deng HW and Li YJ: The
cardioprotection of rutaecarpine is mediated by endogenous
calcitonin related-gene peptide through activation of vanilloid
receptors in guinea-pig hearts. Planta Med. 68:705–709. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sternini C, De Giorgio R and Furness JB:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide neurons innervating the canine
digestive system. Regul Pept. 42:15–26. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC:
1996, http://oacu.od.nih.gov/regs/guide/guide.pdf
|
|
25
|
Aho HJ and Nevalainen TJ: Experimental
pancreatitis in the rat. Ultrastructure of sodium
taurocholate-induced pancreatic lesions. Scand J Gastroenterol.
15:417–424. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yilmaz M, Topsakal S, Herek O, Ozmen O,
Sahinduran S, Buyukoglu T and Yonetci N: Effects of etanercept on
sodium taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Transl Res.
154:241–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Keceli M, Kucuk C, Sozuer E, Kerek M, Ince
O and Arar M: The effect of interleukin-10 on acute pancreatitis
induced by cerulein in a rat experimental model. J Invest Surg.
18:7–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Menger MD, Plusczyk T and Vollmar B:
Microcirculatory derangements in acute pancreatitis. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 8:187–194. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu CP, Xiao L, Deng HW and Li YJ: The
depressor and vasodilator effects of rutaecarpine are mediated by
calcitonin gene-related peptide. Planta Med. 69:125–129. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Caterina MJ and Julius D: The vanilloid
receptor: A molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 24:487–517. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wimalawansa SJ: Calcitonin gene-related
peptide and its receptors: Molecular genetics, physiology,
pathophysiology, and therapeutic potentials. Endocr Rev.
17:533–585. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pérez S, Pereda J, Sabater L and Sastre J:
Redox signaling in acute pancreatitis. Redox Biol. 5:1–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Monneret G, Pachot A, Laroche B, Picollet
J and Bienvenu J: Procalcitonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide
decrease LPS-induced tnf production by human circulating blood
cells. Cytokine. 12:762–764. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Granger J and Remick D: Acute
pancreatitis: Models, markers, and mediators. Shock. 24 Suppl
1:S45–S51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|