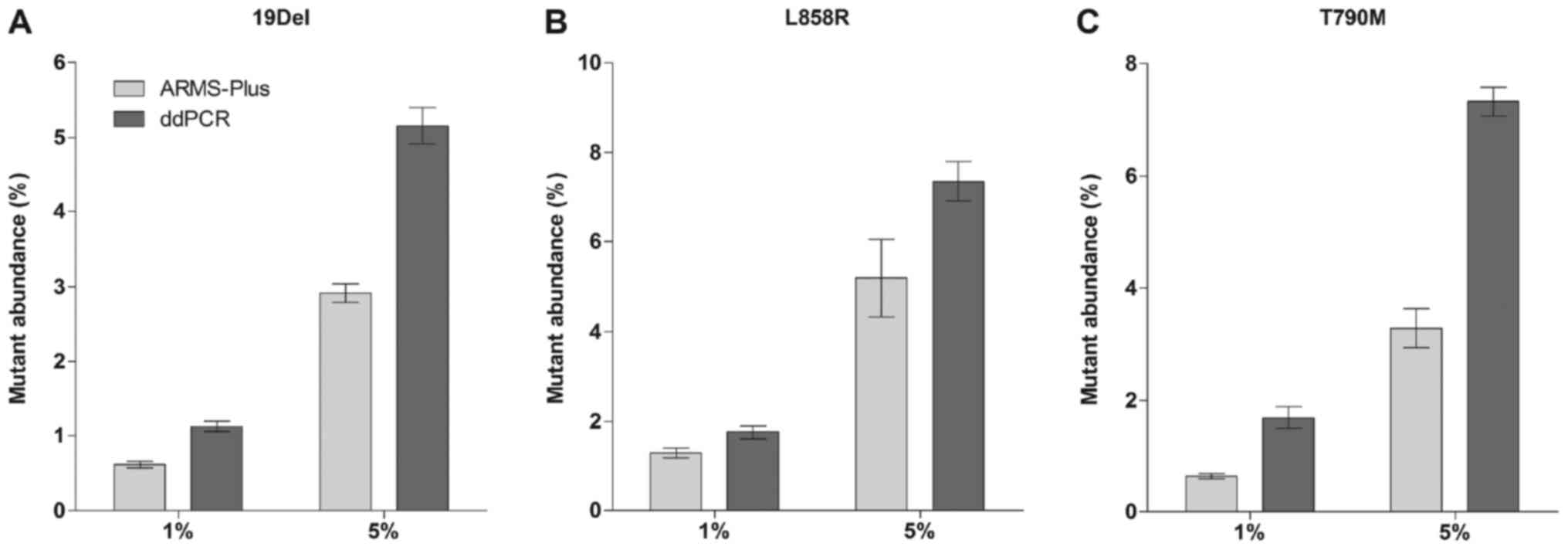
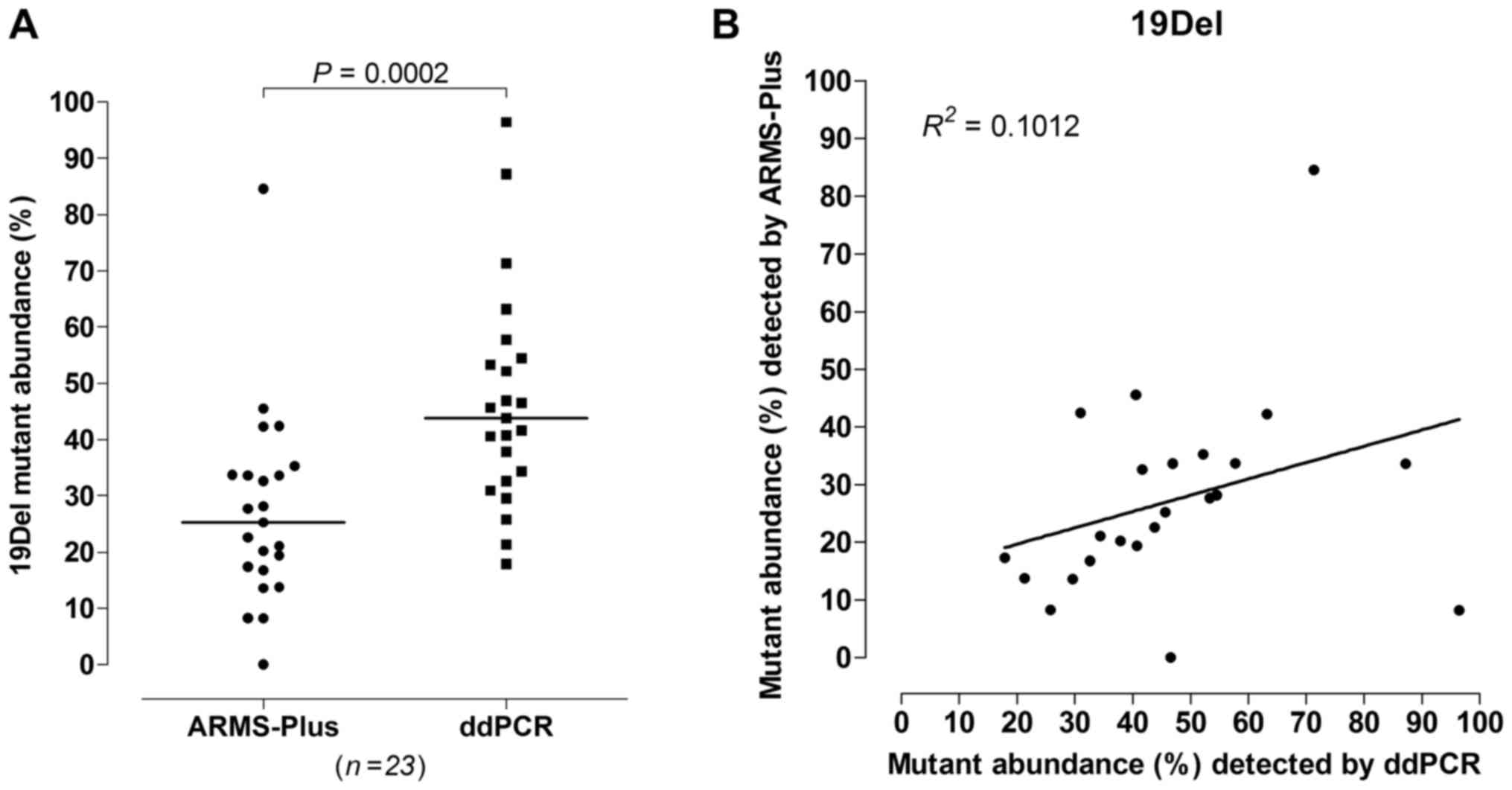
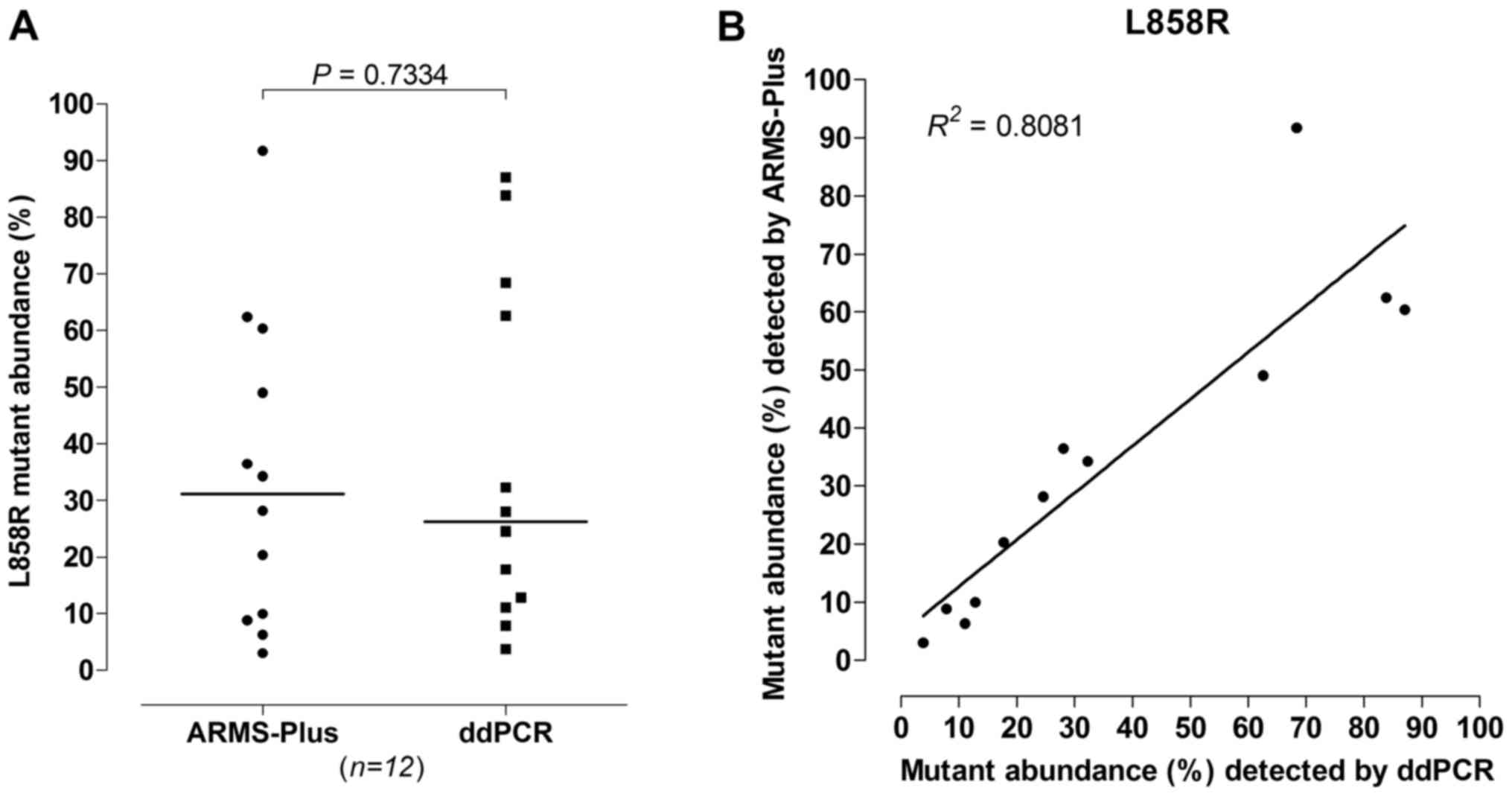
|
1
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
(NCCN), . Non-small cell lung cancer, Version 8.2017. NCCN Clinical
Practice Guidelines in Oncology. NCCN; Fort Washington, PA:
2017
|
|
2
|
Boch C, Kollmeier J, Roth A,
Stephan-Falkenau S, Misch D, Grüning W, Bauer TT and Mairinger T:
The frequency of EGFR and KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC): Routine screening data for central Europe from a
cohort study. BMJ Open. 3:pii: e0025602013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kayye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ,
et al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R,
Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R,
Pallares C, Sanchez JM, et al: Erlotinib versus standard
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 13:239–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne
K, Hirsh V, Mok T, Geater SL, Orlov S, Tsai CM, Boyer M, et al:
Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in
patients with metastastic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. J
Clin Oncol. 31:3327–3334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitsudomi T and Yatabe Y: Epidermal growth
factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and
cancer. FEBS J. 277:301–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T,
Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S,
Rischin D, et al: Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of
gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin
Oncol. 21:2237–2246. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ
Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H,
Sandler A, et al: Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic
patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized trial. JAMA.
290:2149–2158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Usuda K, Sagawa M, Motono N, Ueno M,
Tanaka M, Machida Y, Matoba M, Taniguchi M, Tonami H, Ueda Y and
Sakuma T: Relationships between EGFR mutation status of lung cancer
and preoperative factors-are they predictive? Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:657–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H,
Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T: Mutations of the epidermal growth
factor receptor gene in lung cancer: Biological and clinical
implications. Cancer Res. 64:8919–8923. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sutani A, Nagai Y, Udagawa K, Uchida Y,
Koyama N, Murayama Y, Tanaka T, Miyazawa H, Nagata M, Kanazawa M,
et al: Gefitinib for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with
epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations screened by peptide
nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Br J Cancer.
95:1483–1489. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inoue A, Suzuki T, Fukuhara T, Maemondo M,
Kimura Y, Morikawa N, Watanabe H, Saijo Y and Nukiwa T: Prospective
phase II study of gefitinib for chemotherapy-naive patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor
receptor gene mutations. J Clin Oncol. 24:3340–3346. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shih JY, Gow CH and Yang PC: EGFR mutation
conferring primary resistance to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:207–208. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su KY, Chen HY, Li KC, Kuo ML, Yang JC,
Chan WK, Ho BC, Chang GC, Shih JY, Yu SL and Yang PC: Pretreatment
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation predicts
shorter EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response duration in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:433–440.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou Q, Zhang XC, Chen ZH, Yin XL, Yang
JJ, Xu CR, Yan HH, Chen HJ, Su J, Zhong WZ, et al: Relative
abundance of EGFR mutations predicts benefit from gefitinib
treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
29:3316–3321. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao ZR, Wang JF, Lin YB, Wang F, Fu S,
Zhang SL, Su XD, Jiang L, Zhang YG, Shao JY and Long H: Mutation
abundance affects the efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
readministration in non-small-cell lung cancer with acquired
resistance. Med Oncol. 31:8102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ogino S, Kawasaki T, Brahmandam M, Yan L,
Cantor M, Namgyal C, Mino-Kenudson M, Lauwers GY, Loda M and Fuchs
CS: Sensitive sequencing method for KRAS mutation detection by
Pyrosequencing. J Mol Diagn. 7:413–421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cushman-Vokoun AM, Crowley AM, Rapp SA and
Greiner TC: Comparison study of the performance of the QIAGEN EGFR
RGQ and EGFR pyro assays for mutation analysis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 140:7–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shaozhang Z, Ming Z, Haiyan P, Aiping Z,
Qitao Y and Xiangqun S: Comparison of ARMS and direct sequencing
for detection of EGFR mutation and prediction of EGFR-TKI efficacy
between surgery and biopsy tumor tissues in NSCLC patients. Med
Oncol. 31:9262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ellison G, Donald E, McWalter G, Knight L,
Fletcher L, Sherwood J, Cantarini M, Orr M and Speake G: A
comparison of ARMS and DNA sequencing for mutation analysis in
clinical biopsy samples. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1322010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Q, Zhu Y, Bai Y, Wei X, Zheng X, Mao M
and Zheng G: Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation
in lung cancer by droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:1533–1541. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mok T, Wu YL, Lee JS, Yu CJ, Sriuranpong
V, Sandoval-Tan J, Ladrera G, Thongprasert S, Srimuninnimit V, Liao
M, et al: Detection and dynamic changes of EGFR mutations from
circulating tumor DNA as a predictor of survival outcomes in NSCLC
patients treated with first-line intercalated Erlotinib and
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3196–3203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tseng JS, Yang TY, Tsai CR, Chen KC, Hsu
KH, Tsai MH, Yu SL, Su KY, Chen JJ and Chang GC: Dynamic plasma
EGFR mutation status as a predictor of EGFR-TKI efficacy in
patients with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol.
10:603–610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lilenbaum RA and Horn LA: Management of
EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr
Canc Netw. 14(5 Suppl): S672–S674. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, Lee CK, Kurata T,
Kim DW, John T, Nogami N, Ohe Y, Mann H, Rukazenkov Y, et al:
Osimertinib as first-line tratment of EGFR mutation-positive
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. Aug
25–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang BO, Xu CW, Shao Y, Wang HT, Wu YF,
Song YY, Li XB, Zhang Z, Wang WJ, Li LQ and Cai CL: Comparison of
droplet digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring
EGFR gene mutation. Exp Ther Med. 9:1383–1388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu G, Ye X, Dong Z, Lu YC, Sun Y, Liu Y,
McCormack R, Gu Y and Liu X: Highly sensitive droplet digital PCR
method for detection of EGFR-activating mutations in plasma
cell-free DNA from patients with advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. J Mol Diagn. 17:265–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|