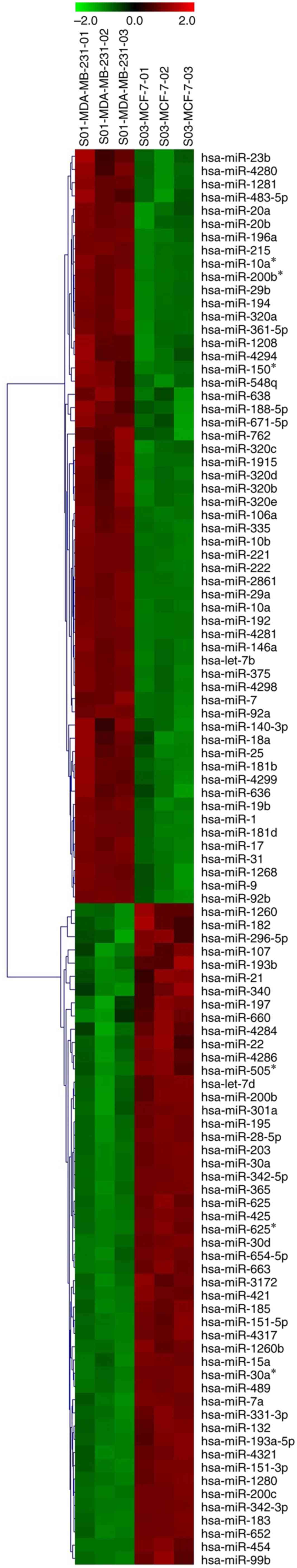
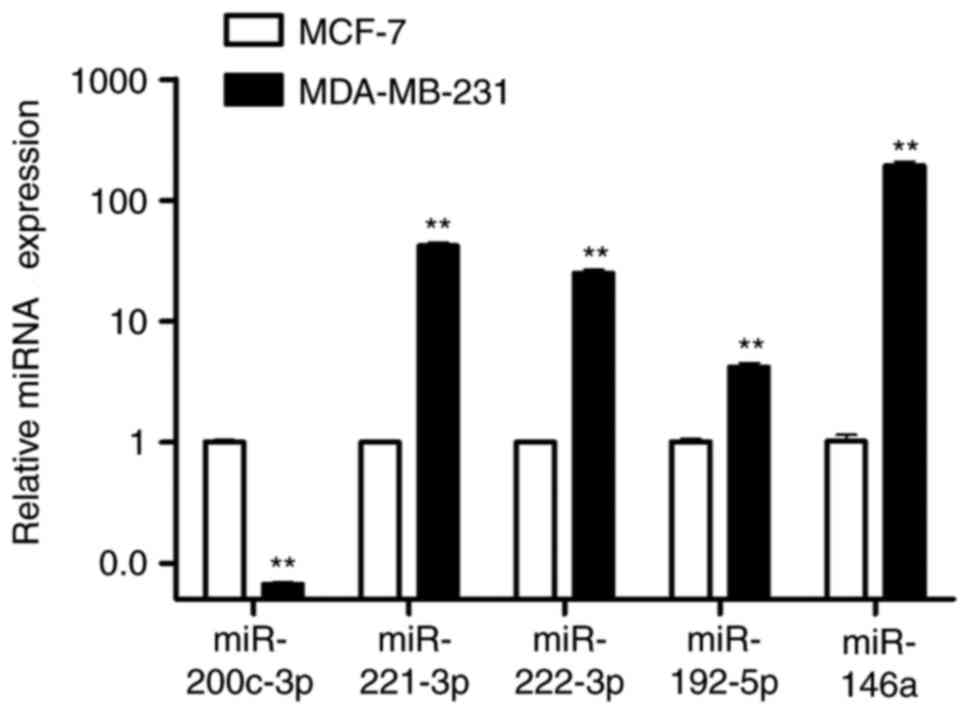
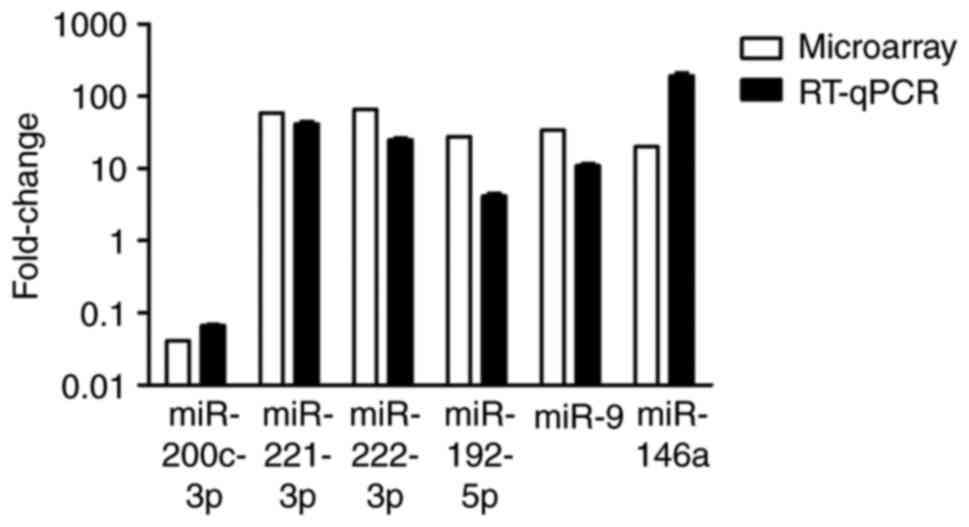
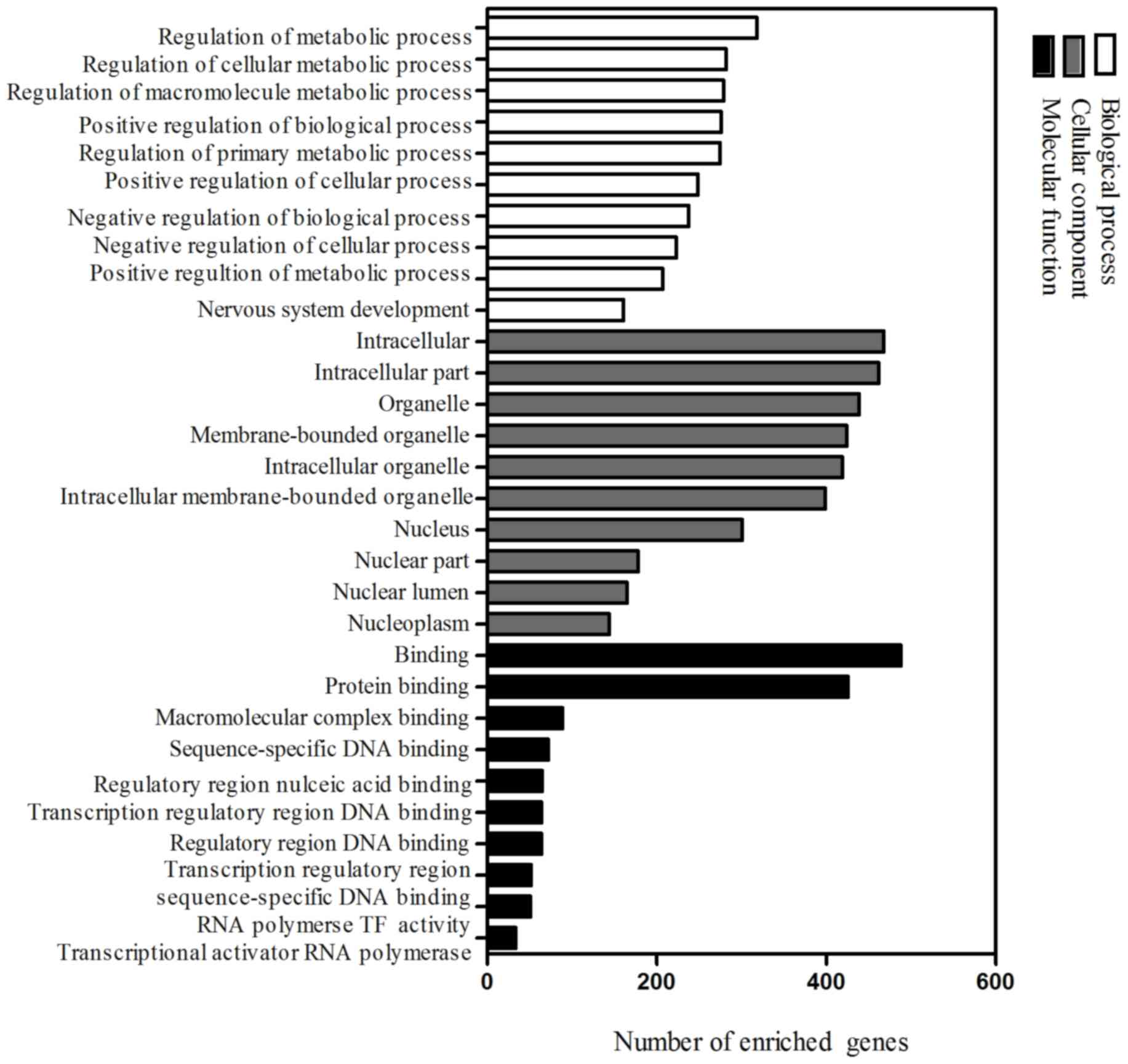
|
1
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnedos M, Bihan C, Delaloge S and Andre
F: Triple-negative breast cancer: Are we making headway at least.
Ther Adv Med Oncol. 4:195–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Izumiya M, Tsuchiya N, Okamoto K and
Nakagama H: Systematic exploration of cancer-associated microRNA
through functional screening assays. Cancer Sci. 102:1615–1621.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gwak JM, Kim HJ, Kim EJ, Chung YR, Yun S,
Seo AN, Lee HJ and Park SY: MicroRNA-9 is associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, breast cancer stem cell
phenotype, and tumor progression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 147:39–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eades G, Wolfson B, Zhang Y, Li Q, Yao Y
and Zhou Q.: lincRNA-RoR and miR-145 regulate invasion in
triple-negative breast cancer via targeting ARF6. Mol Cancer Res.
13:330–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Peng Y, Jin Z, Huang W, Cheng Y,
Liu Y, Feng X, Yang M, Huang Y, Zhao Z, et al: Integrated miRNA
profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal potential causative
miRNAs in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:32878–32889. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kleivi Sahlberg K, Bottai G, Naume B,
Burwinkel B, Calin GA, Børresen-Dale AL and Santarpia L: A serum
microRNA signature predicts tumor relapse and survival in
triple-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
21:1207–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Humphries B, Wang Z, Oom AL, Fisher T, Tan
D, Cui Y, Jiang Y and Yang C: MicroRNA-200b targets protein kinase
Cα and suppresses triple-negative breast cancer metastasis.
Carcinogenesis. 35:2254–2263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Terao M, Fratelli M, Kurosaki M, Zanetti
A, Guarnaccia V, Paroni G, Tsykin A, Lupi M, Gianni M, Goodall GJ
and Garattini E: Induction of miR-21 by retinoic acid in estrogen
receptor-positive breast carcinoma cells: Biological correlates and
molecular targets. J Biol Chem. 286:4027–4042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Smith E, Bert AG,
Wright JA, Roslan S, Morris M, Wyatt L, Farshid G and Lim YY: An
autocrine TGF-beta/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network regulates
establishment and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Mol Biol Cell. 22:1686–1698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Knezevic J, Pfefferle AD, Petrovic I,
Greene SB, Perou CM and Rosen JM: Expression of miR-200c in
claudin-low breast cancer alters stem cell functionality, enhances
chemosensitivity and reduces metastatic potential. Oncogene.
34:5997–6006. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ren Y, Han X, Yu K, Sun S, Zhen L, Li Z
and Wang S: microRNA-200c downregulates XIAP expression to suppress
proliferation and promote apoptosis of triple-negative breast
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:315–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Castilla MÁ, Díaz-Martín J, Sarrió D,
Romero-Pérez L, López-García MÁ, Vieites B, Biscuola M,
Ramiro-Fuentes S, Isacke CM and Palacios J: MicroRNA-200 family
modulation in distinct breast cancer phenotypes. PLoS One.
7:e477092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Tian W, Cai H, He H and Deng Y:
Down-regulation of microRNA-200c is associated with drug resistance
in human breast cancer. Med Oncol. 29:2527–2534. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Howe EN, Cochrane DR, Cittelly DM and
Richer JK: miR-200c targets a NF-κB up-regulated TrkB/NTF3
autocrine signaling loop to enhance anoikis sensitivity in triple
negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 7:e499872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Howe EN, Cochrane DR and Richer JK: The
miR-200 and miR-221/222 microRNA families: Opposing effects on
epithelial identity. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 17:65–77.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nassirpour R, Mehta PP, Baxi SM and Yin
MJ: miR-221 promotes tumorigenesis in human triple negative breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e621702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Søkilde R, Kaczkowski B, Podolska A,
Cirera S, Gorodkin J, Møller S and Litman T: Global microRNA
analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol Cancer Ther.
10:375–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Liang C, Ma H, Zhao Q, Lu Y, Xiang
Z, Li L, Qin J, Chen Y, Cho WC, et al: miR-221/222 promotes S-phase
entry and cellular migration in control of basal-like breast
cancer. Molecules. 19:7122–7137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garcia AI, Buisson M, Bertrand P, Rimokh
R, Rouleau E, Lopez BS, Lidereau R, Mikaélian I and Mazoyer S:
Down-regulation of BRCA1 expression by miR-146a and miR-146b-5p in
triple negative sporadic breast cancers. EMBO Mol Med. 3:279–290.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumaraswamy E, Wendt KL, Augustine LA,
Stecklein SR, Sibala EC, Li D, Gunewardena S and Jensen RA: BRCA1
regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in
human breast cancer cells involves microRNA-146a and is critical
for its tumor suppressor function. Oncogene. 34:4333–4346. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Giltnane JM and Balko JM: Rationale for
targeting the Ras/MAPK pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.
Discov Med. 17:275–283. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hashimoto K, Tsuda H, Koizumi F, Shimizu
C, Yonemori K, Ando M, Kodaira M, Yunokawa M, Fujiwara Y and Tamura
K: Activated PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways are potential good
prognostic markers in node-positive, triple-negative breast cancer.
Ann Oncol. 25:1973–1979. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bilir B, Kucuk O and Moreno CS: Wnt
signaling blockage inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and
induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Transl
Med. 11:2802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wahdan-Alaswad R, Harrell JC, Fan Z,
Edgerton SM, Liu B and Thor AD: Metformin attenuates transforming
growth factor beta (TGF-β) mediated oncogenesis in mesenchymal
stem-like/claudin-low triple negative breast cancer. Cell Cycle.
15:1046–1059. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|