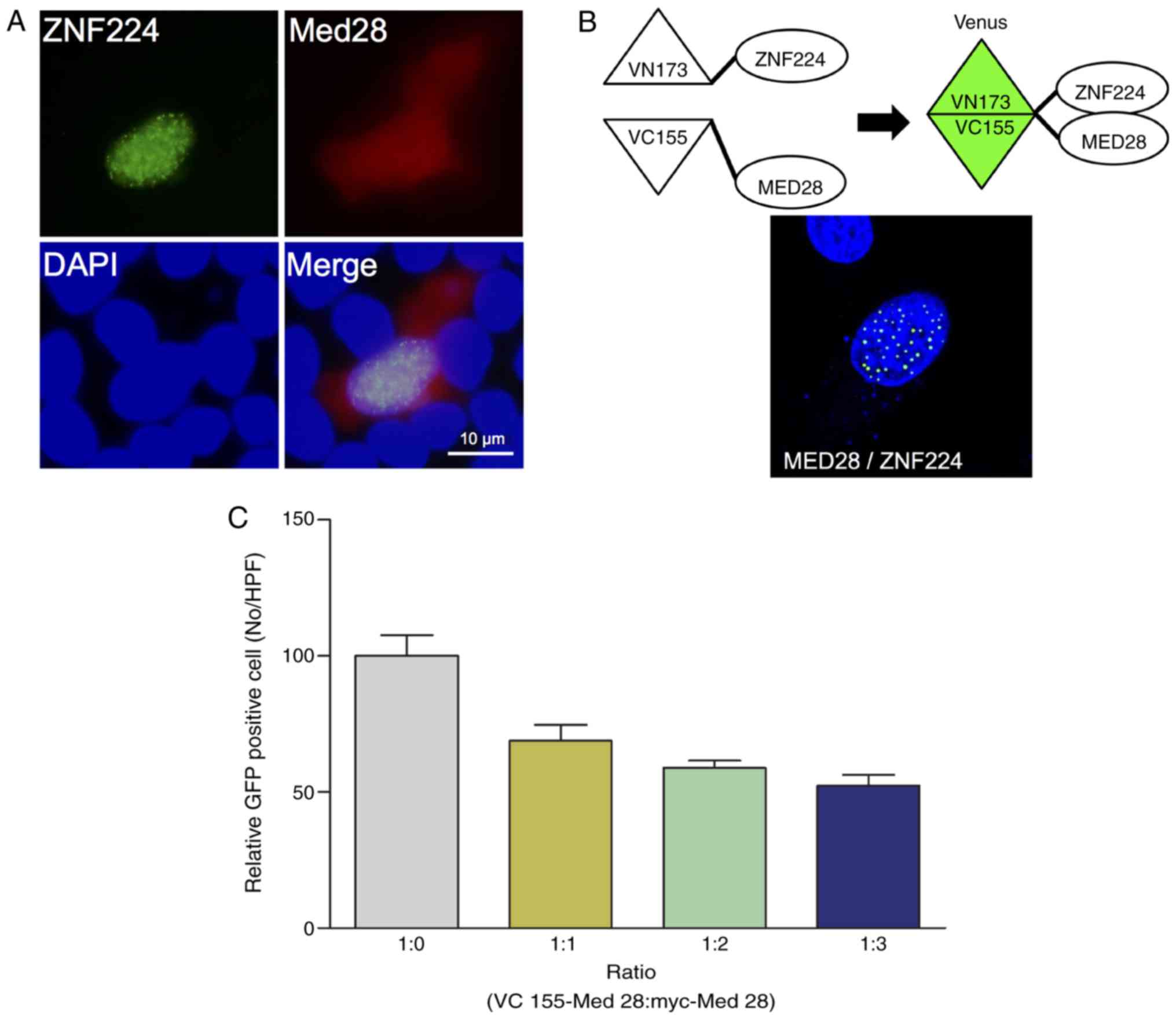
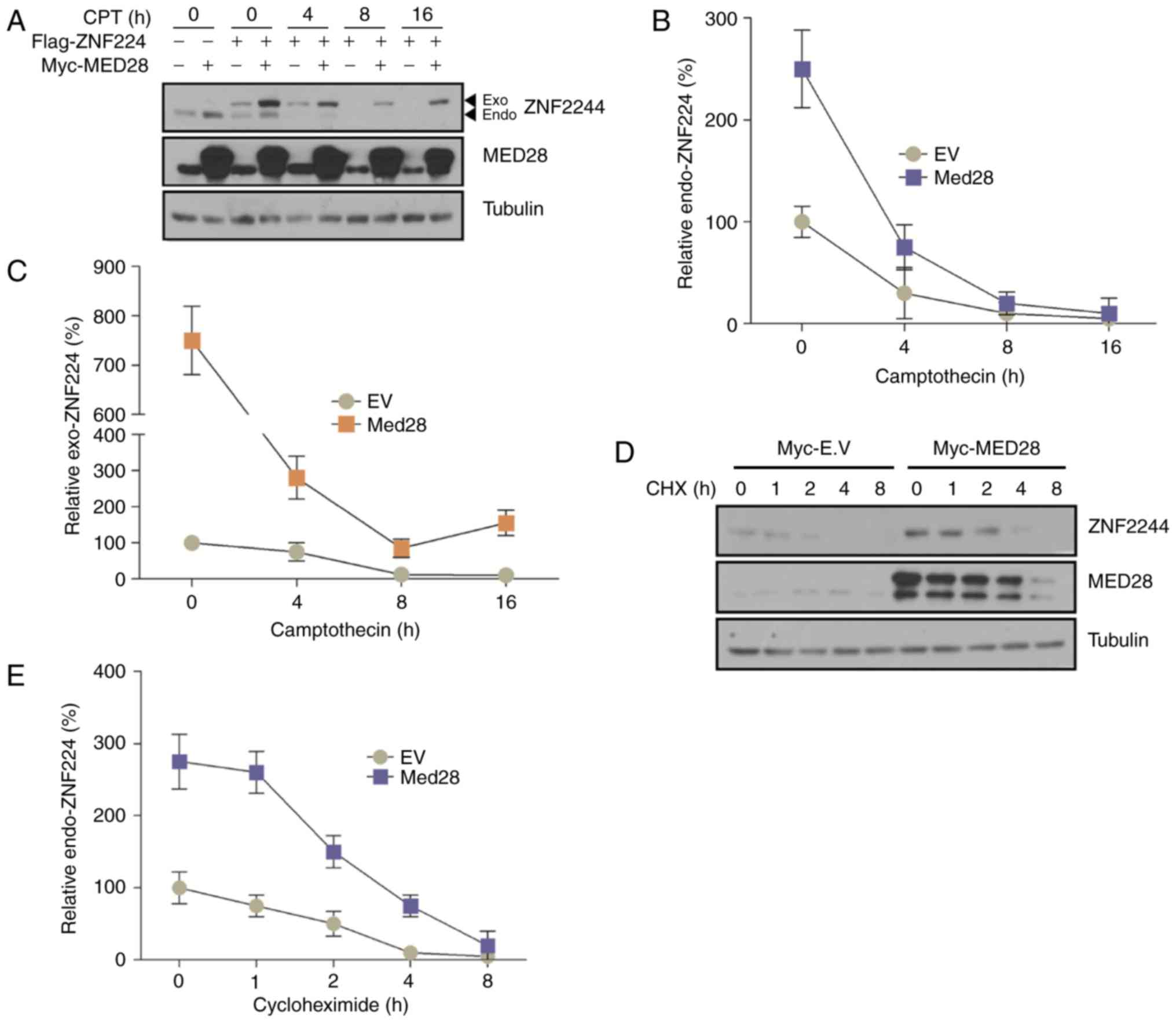
|
1
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: The DNA damage
response and cancer therapy. Nature. 481:287–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jackson SP and Bartek J: The DNA-damage
response in human biology and disease. Nature. 461:1071–1078. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weinert T: DNA damage and checkpoint
pathways: Molecular anatomy and interactions with repair. Cell.
94:555–558. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou BB and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: Putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 408:433–439.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roos WP, Thomas AD and Kaina B: DNA damage
and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:20–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Castedo M and
Kroemer G: Mitotic catastrophe: A mechanism for avoiding genomic
instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:385–392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Freed-Pastor W and Prives C: Targeting
mutant p53 through the mevalonate pathway. Nat Cell Biol.
18:1122–1124. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lane DP: Cancer. p53, guardian of the
genome. Nature. 358:15–16. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stracquadanio G, Wang X, Wallace MD,
Grawenda AM, Zhang P, Hewitt J, Zeron-Medina J, Castro-Giner F,
Tomlinson IP, Goding CR, et al: The importance of p53 pathway
genetics in inherited and somatic cancer genomes. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:251–265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Muller PA and Vousden KH: Mutant p53 in
cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell.
25:304–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menendez D, Inga A and Resnick MA: The
expanding universe of p53 targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:724–737. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho JG, Park S, Lim CH, Kim HS, Song SY,
Roh TY, Sung JH, Suh W, Ham SJ, Lim KH and Park SG: ZNF224, Krüppel
like zinc finger protein, induces cell growth and
apoptosis-resistance by down-regulation of p21 and p53 via
miR-663a. Oncotarget. 7:31177–31190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malik S and Roeder RG: The metazoan
mediator co-activator complex as an integrative hub for
transcriptional regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 11:761–772. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allen BL and Taatjes DJ: The mediator
complex: A central integrator of transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 16:155–166. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu M, Sartippour MR, Zhang L, Norris AJ
and Brooks MN: Targeted inhibition of EG-1 blocks breast tumor
growth. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:936–941. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee MF, Pan MH, Chiou YS, Cheng AC and
Huang H: Resveratrol modulates MED28 (Magicin/EG-1) expression and
inhibits epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced migration in
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
59:11853–11861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang CY, Chou YH, Hsieh NT, Chen HH and
Lee MF: MED28 regulates MEK1-dependent cellular migration in human
breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 227:3820–3827. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu MA, Cho JG, Kim KI, Jo YJ, Sung JH,
Yang HB and Park SG: Generation of med28 specific monoclonal
antibodies. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 34:30–35. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Florio F, Cesaro E, Montano G, Izzo P,
Miles C and Costanzo P: Biochemical and functional interaction
between ZNF224 and ZNF255, two members of the Kruppel-like
zinc-finger protein family and WT1 protein isoforms. Hum Mol Genet.
19:3544–3556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu M, Zhang L, Maul RS, Sartippour MR,
Norris A, Whitelegge J, Rao JY and Brooks MN: The novel gene EG-1
stimulates cellular proliferation. Cancer Res. 65:6159–6166. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lupo A, Cesaro E, Montano G, Zurlo D, Izzo
P and Costanzo P: KRAB-Zinc finger proteins: A repressor family
displaying multiple biological functions. Curr Genomics.
14:268–278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Myers LC and Kornberg RD: Mediator of
transcriptional regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:729–749. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Otto T and Sicinski P: Cell cycle proteins
as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:93–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sperka T, Wang J and Rudolph KL: DNA
damage checkpoints in stem cells, ageing and cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:579–590. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gokduman K: Strategies targeting DNA
topoisomerase i in cancer chemotherapy: Camptothecins, nanocarriers
for camptothecins, organic non-camptothecin compounds and metal
complexes. Curr Drug Targets. 17:1928–1939. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Medugno L, Florio F, De Cegli R, Grosso M,
Lupo A, Costanzo P and Izzo P: The Krüppel-like zinc-finger protein
ZNF224 represses aldolase A gene transcription by interacting with
the KAP-1 co-repressor protein. Gene. 359:35–43. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cesaro E, De Cegli R, Medugno L, Florio F,
Grosso M, Lupo A, Izzo P and Costanzo P: The Kruppel-like zinc
finger protein ZNF224 recruits the arginine methyltransferase PRMT5
on the transcriptional repressor complex of the aldolase A gene. J
Biol Chem. 284:32321–32330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Montano G, Ullmark T, Jernmark-Nilsson H,
Sodaro G, Drott K, Costanzo P, Vidovic K and Gullberg U: The
hematopoietic tumor suppressor interferon regulatory factor 8
(IRF8) is upregulated by the antimetabolite cytarabine in leukemic
cells involving the zinc finger protein ZNF224, acting as a
cofactor of the Wilms' tumor gene 1 (WT1) protein. Leuk Res.
40:60–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harada Y, Kanehira M, Fujisawa Y, Takata
R, Shuin T, Miki T, Fujioka T, Nakamura Y and Katagiri T:
Cell-permeable peptide DEPDC1-ZNF224 interferes with
transcriptional repression and oncogenicity in bladder cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 70:5829–5839. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee TH, Lwu S, Kim J and Pelletier J:
Inhibition of Wilms tumor 1 transactivation by bone marrow zinc
finger 2, a novel transcriptional repressor. J Biol Chem.
277:44826–44837. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moore M, Klug A and Choo Y: Improved DNA
binding specificity from polyzinc finger peptides by using strings
of two-finger units. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:pp. 1437–1441.
2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salmon SE: Human tumor colony assay and
chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Treat Rep. 68:117–125.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gur-Dedeoglu B, Konu O, Bozkurt B, Ergul
G, Seckin S and Yulug IG: Identification of endogenous reference
genes for qRT-PCR analysis in normal matched breast tumor tissues.
Oncol Res. 17:353–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Maul RS, Rao J, Apple S, Seligson
D, Sartippour M, Rubio R and Brooks MN: Expression pattern of the
novel gene EG-1 in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3504–3508. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|