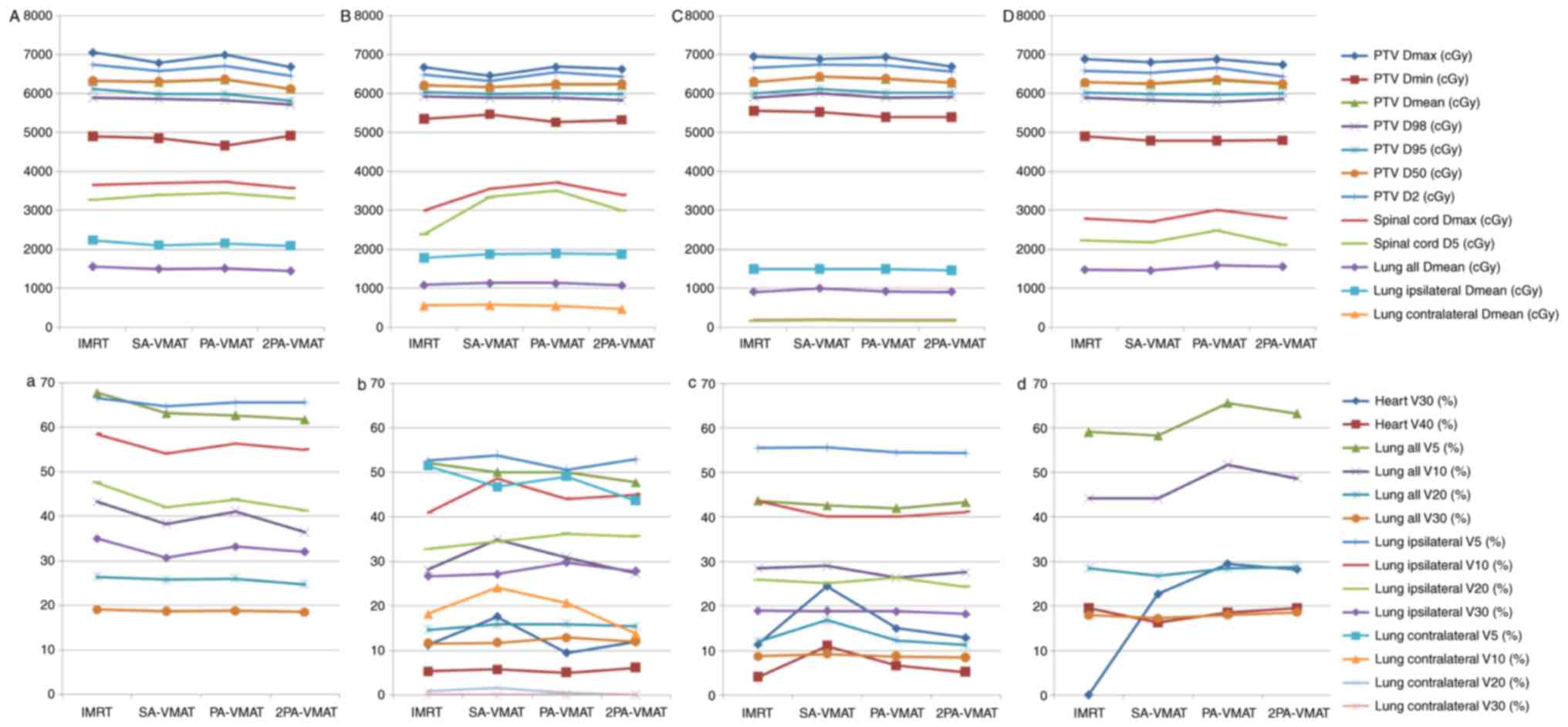
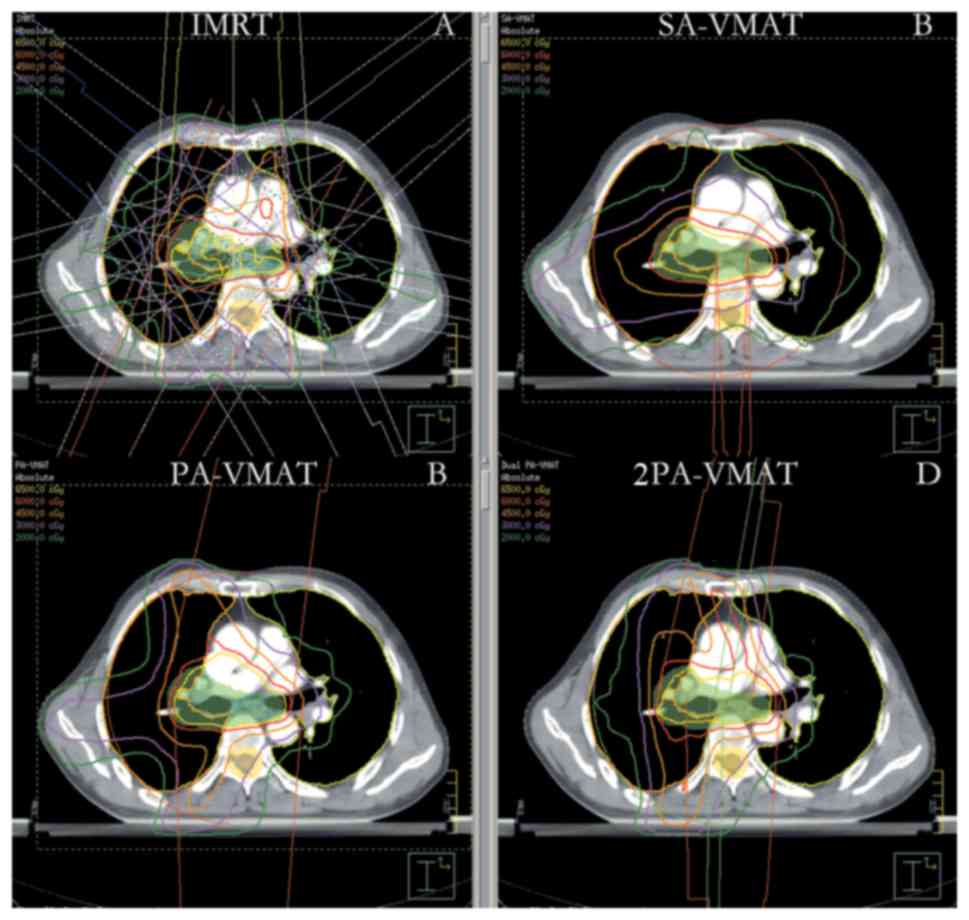
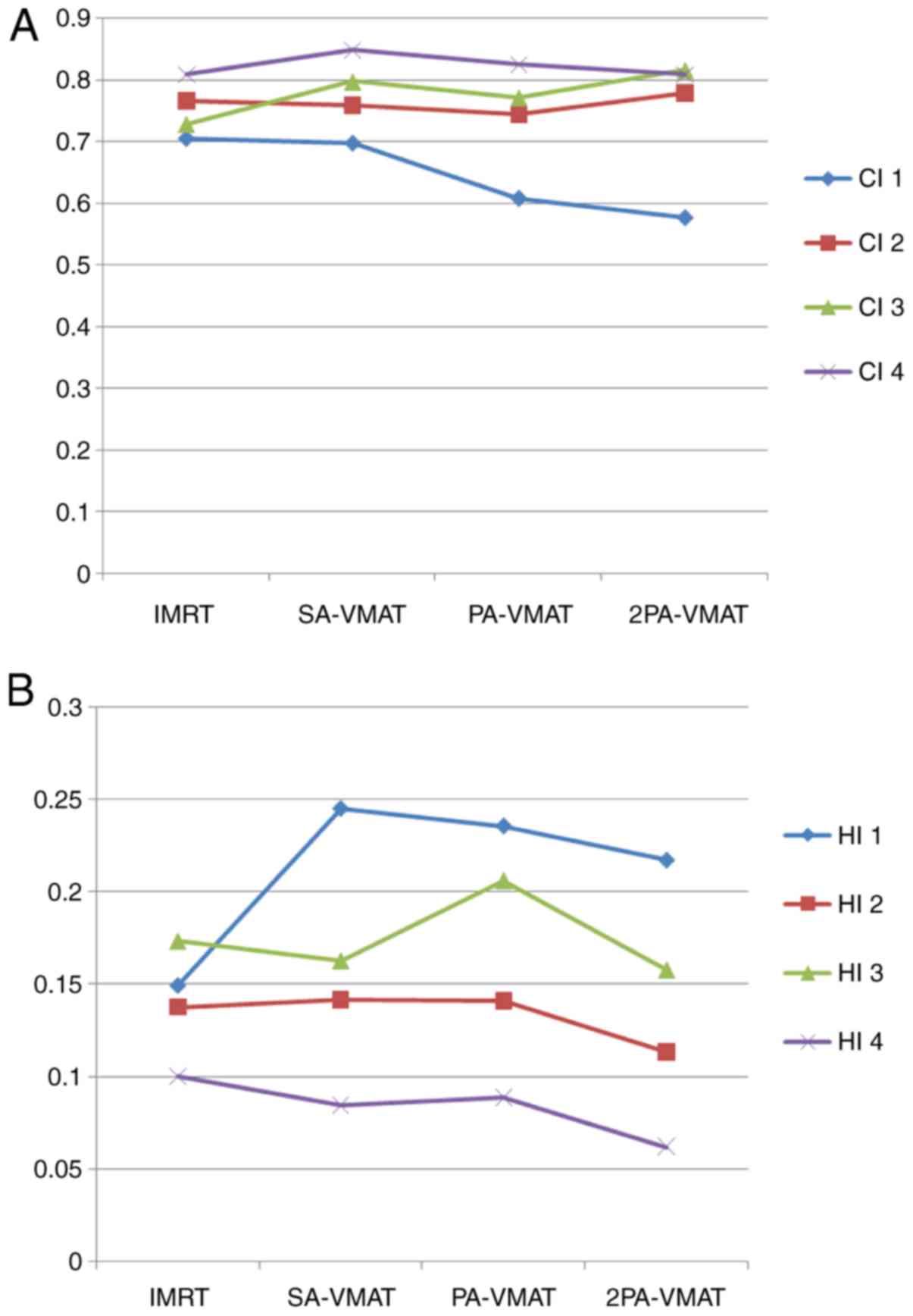
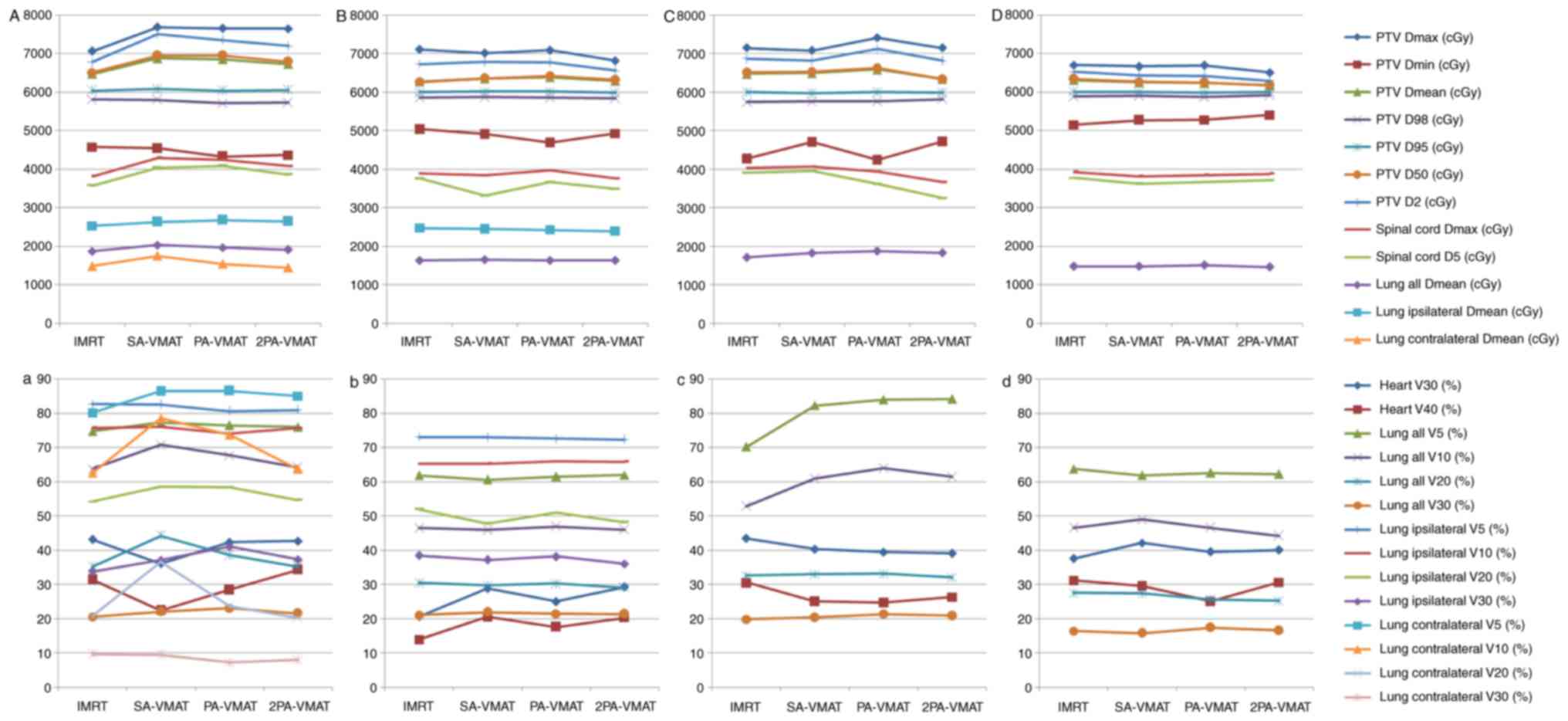
|
1
|
Peeters ST, Heemsbergen WD, Van Putten WL,
Slot A, Tabak H, Mens JW, Lebesque JV and Koper PC: Acute and late
complications after radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Results of a
multicenter randomized trial comparing 68 to 78 Gy. Int J Radiat
Oncol. 61:1019–1034. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pollack A, Zagars GK, Smith LG, Lee JJ,
von Eschenbach AC, Antolak JA, Starkschall G and Rosen I:
Preliminary results of a randomized radiotherapy dose-escalation
study comparing 70 Gy with 78 Gy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol.
18:3904–3911. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kupelian PA, Ciezki J, Reddy CA, Klein EA
and Mahadevan A: Effect of increasing radiation doses on local and
distant failures in patients with localized prostate cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 71:16–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolff D, Stieler F, Welzel G, Lorenz F,
Abo-Madyan Y, Mai S, Herskind C, Polednik M, Steil V, Wenz F and
Lohr F: Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) vs. serial
tomotherapy, step-and-shoot IMRT and 3D-conformal RT for treatment
of prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 93:226–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brahme A, Roos JE and Lax I: Solution of
an integral-equation encountered in rotation therapy. Phys Med
Biol. 27:1221–1229. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bratengeier K: 2-Step IMAT and 2-Step IMRT
in three dimensions. Med Phys. 32:3849–3861. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Otto K: Volumetric modulated arc therapy:
IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 35:310–317. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu CX: Intensity-modulated arc therapy
with dynamic multileaf collimation: An alternative to tomotherapy.
Phys Med Biol. 40:1435–1449. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Palma D, Vollans E, James K, Nakano S,
Moiseenko V, Shaffer R, Mckenzie M, Morris J and Otto K: Volumetric
modulated arc therapy for delivery of prostate radiotherapy:
Comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapy and
three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 72:996–1001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cozzi L, Dinshaw KA, Shrivastava SK,
Mahantshetty U, Engineer R, Deshpande DD, Jamema SV, Vanetti E,
Clivio A, Nicolini G and Fogliata A: A treatment planning study
comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field
IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 89:180–191.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoo S, Wu QJ, Lee WR and Yin FF:
Radiotherapy treatment plans with RapidArc for prostate cancer
involving seminal vesicles and lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 76:935–942. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Popescu CC, Olivotto IA, Beckham WA,
Ansbacher W, Zavgorodni S, Shaffer R, Wai ES and Otto K: Volumetric
modulated arc therapy improves dosimetry and reduces treatment time
compared to conventional intensity-modulated radiotherapy for
locoregional radiotherapy of left-sided breast cancer and internal
mammary nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:287–295. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clivio A, Fogliata A, Franzetti-Pellanda
A, Nicolini G, Vanetti E, Wyttenbach R and Cozzi L:
Volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anal
canal: A treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT.
Radiother Oncol. 92:118–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rao M, Yang WS, Chen F, Sheng K, Ye JS,
Mehta V, Shepard D and Cao DL: Comparison of Elekta VMAT with
helical tomotherapy and fixed field IMRT: Plan quality, delivery
efficiency and accuracy. Med Phys. 37:1350–1359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scorsetti M, Bignardi M, Clivio A, Cozzi
L, Fogliata A, Lattuada P, Mancosu P, Navarria P, Nicolini G, Urso
G, et al: Volumetric modulation arc radiotherapy compared with
static gantry intensity-modulated radiotherapy for malignant
pleural mesothelioma tumor: A feasibility study. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 77:942–949. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang P, Happersett L, Hunt M, Jackson A,
Zelefsky M and Mageras G: Volumetric modulated arc therapy:
Planning and evaluation for prostate cancer cases. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 76:1456–1462. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu QJ, Yoo S, Kirkpatrick JP, Thongphiew D
and Yin FF: Volumetric arc intensity-modulated therapy for spine
body radiotherapy: Comparison with static intensity-modulated
treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:1596–1604. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zacarias AS, Brown MF and Mills MD:
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) treatment planning for
superficial tumors. Med Dosim. 35:226–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Verbakel WF, Cuijpers JP, Hoffmans D,
Bieker M, Slotman BJ and Senan S: Volumetric intensity-modulated
arc therapy vs. conventional IMRT in head-and-neck cancer: A
comparative planning and dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 74:252–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lagerwaard FJ, Meijer OW, van der Hoorn
EA, Verbakel WF, Slotman BJ and Senan S: Volumetric modulated arc
radiotherapy for vestibular schwannomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 74:610–615. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lagerwaard FJ, van der Hoorn EA, Verbakel
WF, Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ and Senan S: Whole-brain radiotherapy
with simultaneous integrated boost to multiple brain metastases
using volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 75:253–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Verbakel WF, Senan S, Cuijpers JP, Slotman
BJ and Lagerwaard FJ: Rapid delivery of stereotactic radiotherapy
for peripheral lung tumors using volumetric intensity-modulated
arcs. Radiother Oncol. 93:122–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ong CL, Verbakel WF, Cuijpers JP, Slotman
BJ, Lagerwaard FJ and Senan S: Stereotactic radiotherapy for
peripheral lung tumors: A comparison of volumetric modulated arc
therapy with 3 other delivery techniques. Radiother Oncol.
97:437–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matuszak MM, Yan D, Grills I and Martinez
A: Clinical applications of volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:608–616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Quan EM, Chang JY, Liao Z, Xia T, Yuan Z,
Liu H, Li X, Wages CA, Mohan R and Zhang X: Automated volumetric
modulated Arc therapy treatment planning for stage III lung cancer:
How does it compare with intensity-modulated radio therapy? Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 84:e69–e76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van't Riet A, Mak AC, Moerland MA, Elders
LH and van der Zee W: A conformation number to quantify the degree
of conformality in brachytherapy and external beam irradiation:
Application to the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
37:731–736. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scorsetti M, Navarria P, Mancosu P, Alongi
F, Castiglioni S, Cavina R, Cozzi L, Fogliata A, Pentimalli S,
Tozzi A and Santoro A: Large volume unresectable locally advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: Acute toxicity and initial outcome
results with rapid arc. Radiat Oncol. 5:942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang X, Li T, Liu Y, Zhou L, Xu Y, Zhou X
and Gong Y: Planning analysis for locally advanced lung cancer:
Dosimetric and efficiency comparisons between intensity-modulated
radiotherapy (IMRT), single-arc/partial-arc volumetric modulated
arc therapy (SA/PA-VMAT). Radiat Oncol. 6:1402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McGrath SD, Matuszak MM, Yan D, Kestin LL,
Martinez AA and Grills IS: Volumetric modulated arc therapy for
delivery of hypofractionated stereotactic lung radiotherapy: A
dosimetric and treatment efficiency analysis. Radiother Oncol.
95:153–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Holt A, van Vliet-Vroegindeweij C, Mans A,
Belderbos JS and Damen EM: Volumetric-modulated arc therapy for
stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung tumors: A comparison with
intensity-modulated radiotherapy techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 81:1560–1567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bertelsen A, Hansen CR, Johansen J and
Brink C: Single Arc volumetric modulated Arc therapy of head and
neck cancer. Radiother Oncol. 95:142–148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guckenberger M, Richter A, Krieger T,
Wilbert J, Baier K and Flentje M: Is a single arc sufficient in
volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for complex-shaped target
volumes? Radiother Oncol. 93:259–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shaffer R, Morris WJ, Moiseenko V, Welsh
M, Crumley C, Nakano S, Schmuland M, Pickles T and Otto K:
Volumetric modulated Arc therapy and conventional
intensity-modulated radiotherapy for simultaneous maximal
intraprostatic boost: A planning comparison study. Clin Oncol (R
Coll Radiol). 21:401–407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hernando ML, Marks LB, Bentel GC, Zhou SM,
Hollis D, Das SK, Fan M, Munley MT, Shafman TD, Anscher MS and Lind
PA: Radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity: A dose-volume histogram
analysis in 201 patients with lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 51:650–659. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Claude L, Pérol D, Ginestet C, Falchero L,
Arpin D, Vincent M, Martel I, Hominal S, Cordier JF and Carrie C: A
prospective study on radiation pneumonitis following conformal
radiation therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: Clinical and
dosimetric factors analysis. Radiother Oncol. 71:175–181. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rancati T, Ceresoli GL, Gagliardi G,
Schipani S and Cattaneo GM: Factors predicting radiation
pneumonitis in lung cancer patients: A retrospective study.
Radiother Oncol. 67:275–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Graham MV, Purdy JA, Emami B, Harms W,
Bosch W, Lockett MA and Perez CA: Clinical dose-volume histogram
analysis for pneumonitis after 3D treatment for non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 45:323–329. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schallenkamp JM, Miller RC, Brinkmann DH,
Foote T and Garces YI: Incidence of radiation pneumonitis after
thoracic irradiation: Dose-volume correlates. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 67:410–416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang S, Liao Z, Wei X, Liu HH, Tucker SL,
Hu CS, Mohan R, Cox JD and Komaki R: Analysis of clinical and
dosimetric factors associated with treatment-related pneumonitis
(TRP) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated
with concurrent chemotherapy and three-dimensional conformal
radiotherapy (3D-CRT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 66:1399–1407.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chung HT, Lee B, Park E, Lu JJ and Xia P:
Can all centers plan intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT)
effectively? An external audit of dosimetric comparisons between
three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and IMRT for adjuvant
chemoradiation for gastric cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
71:1167–1174. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|