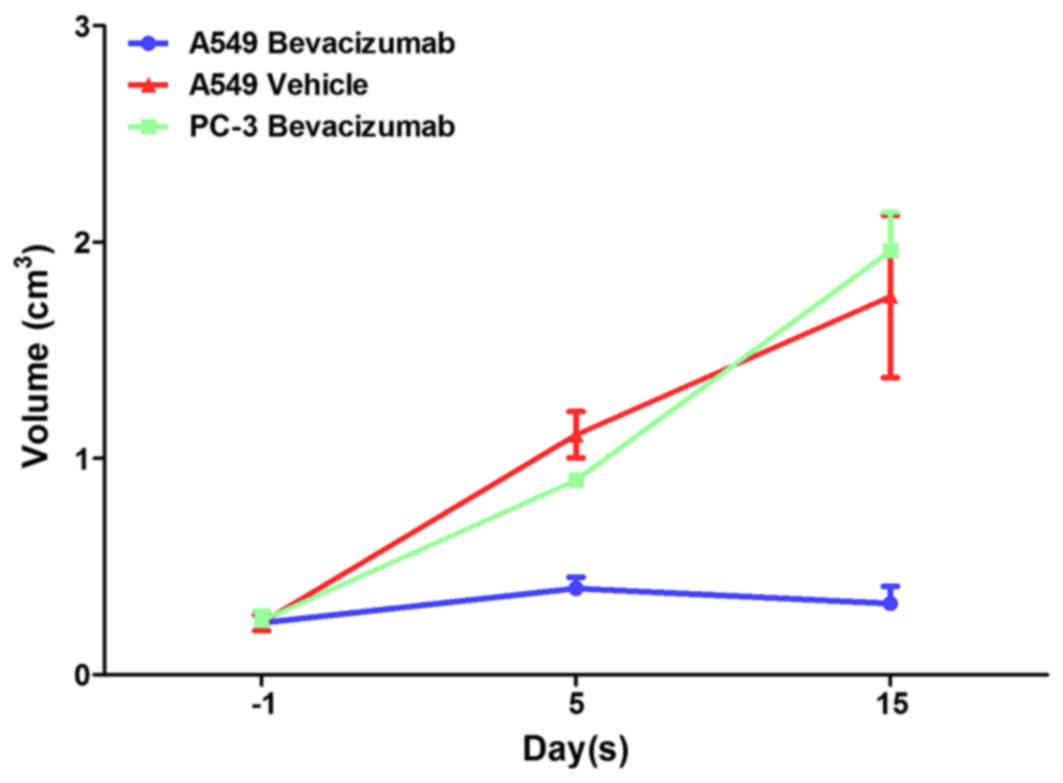
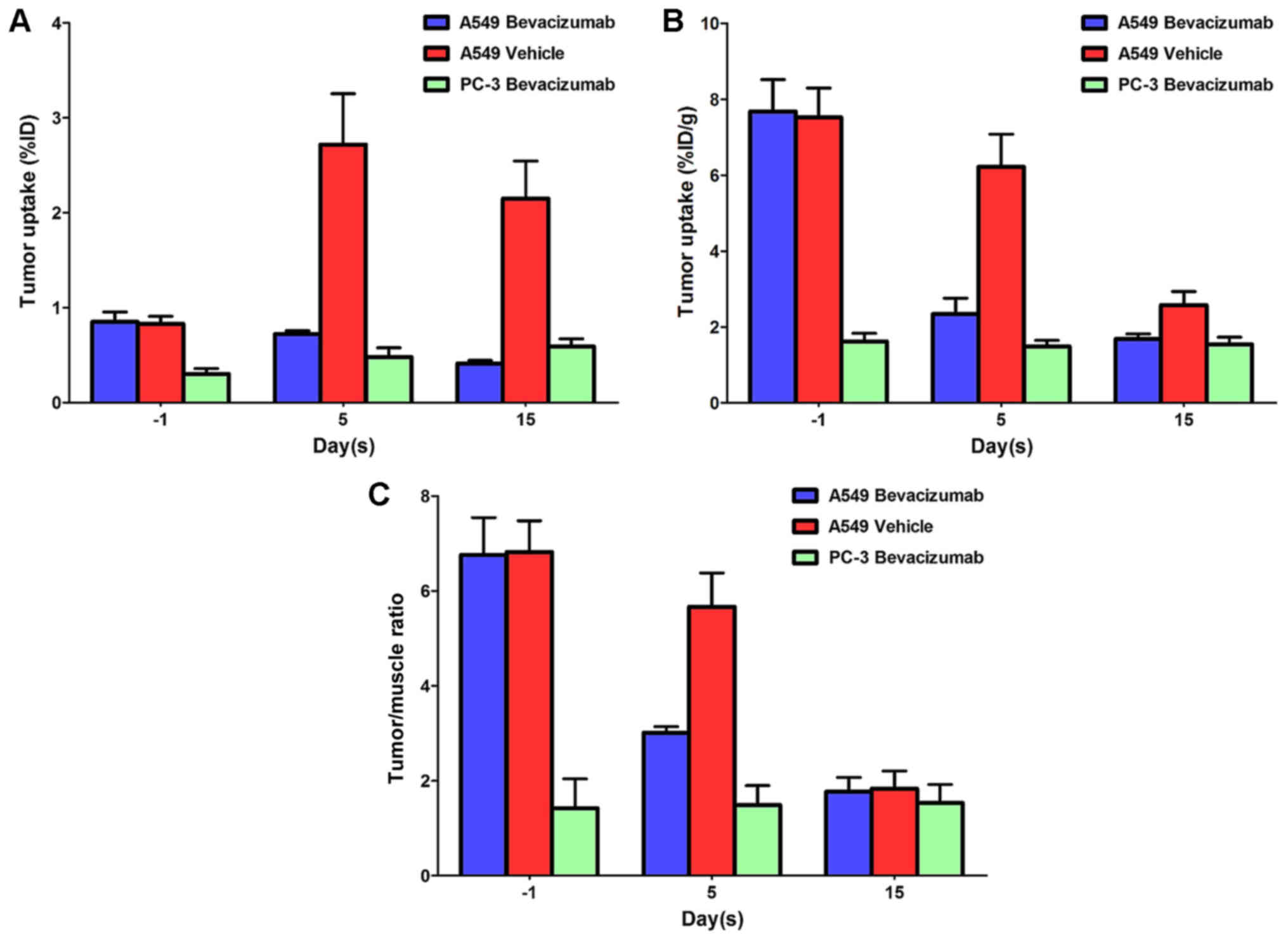
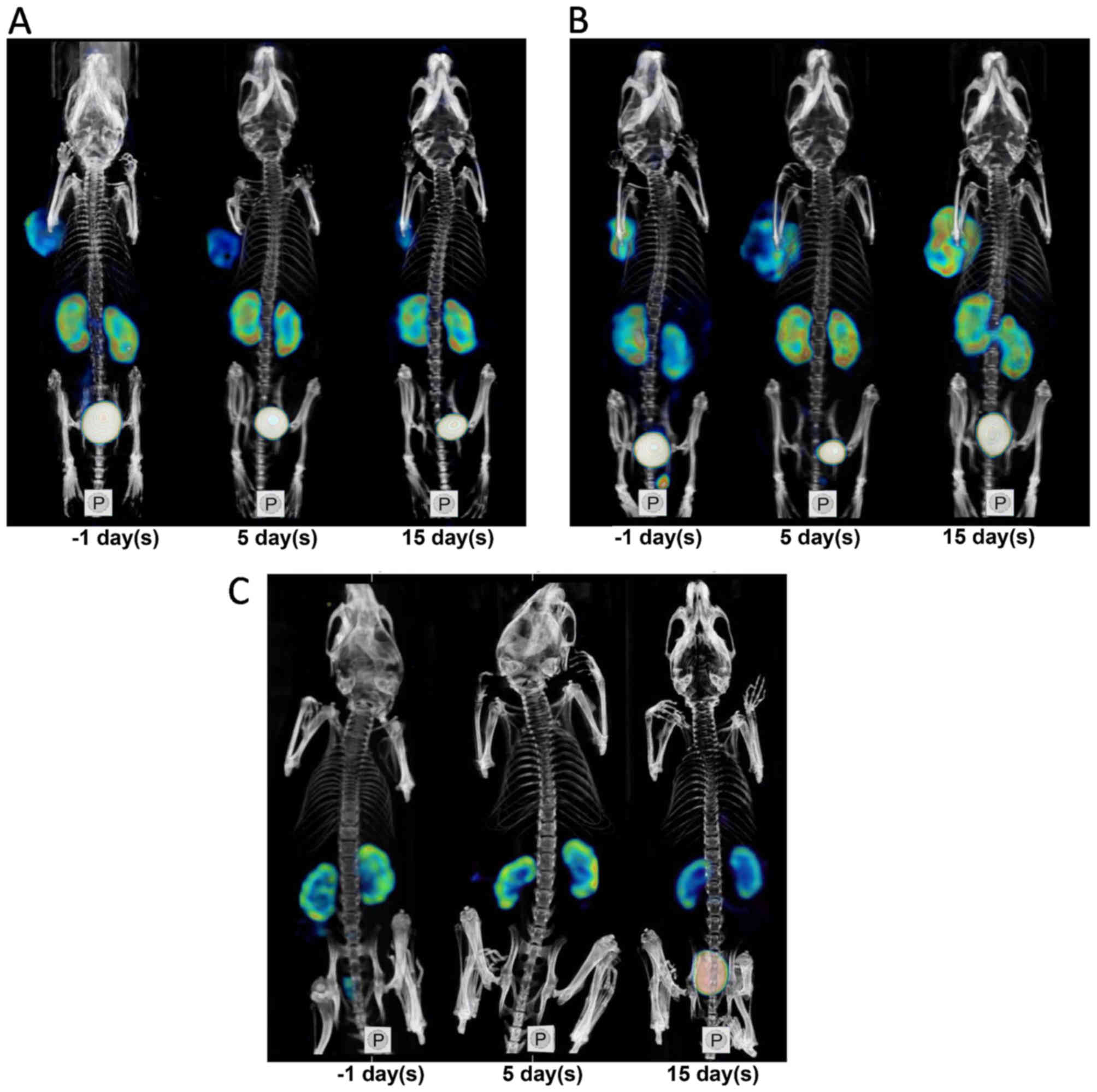
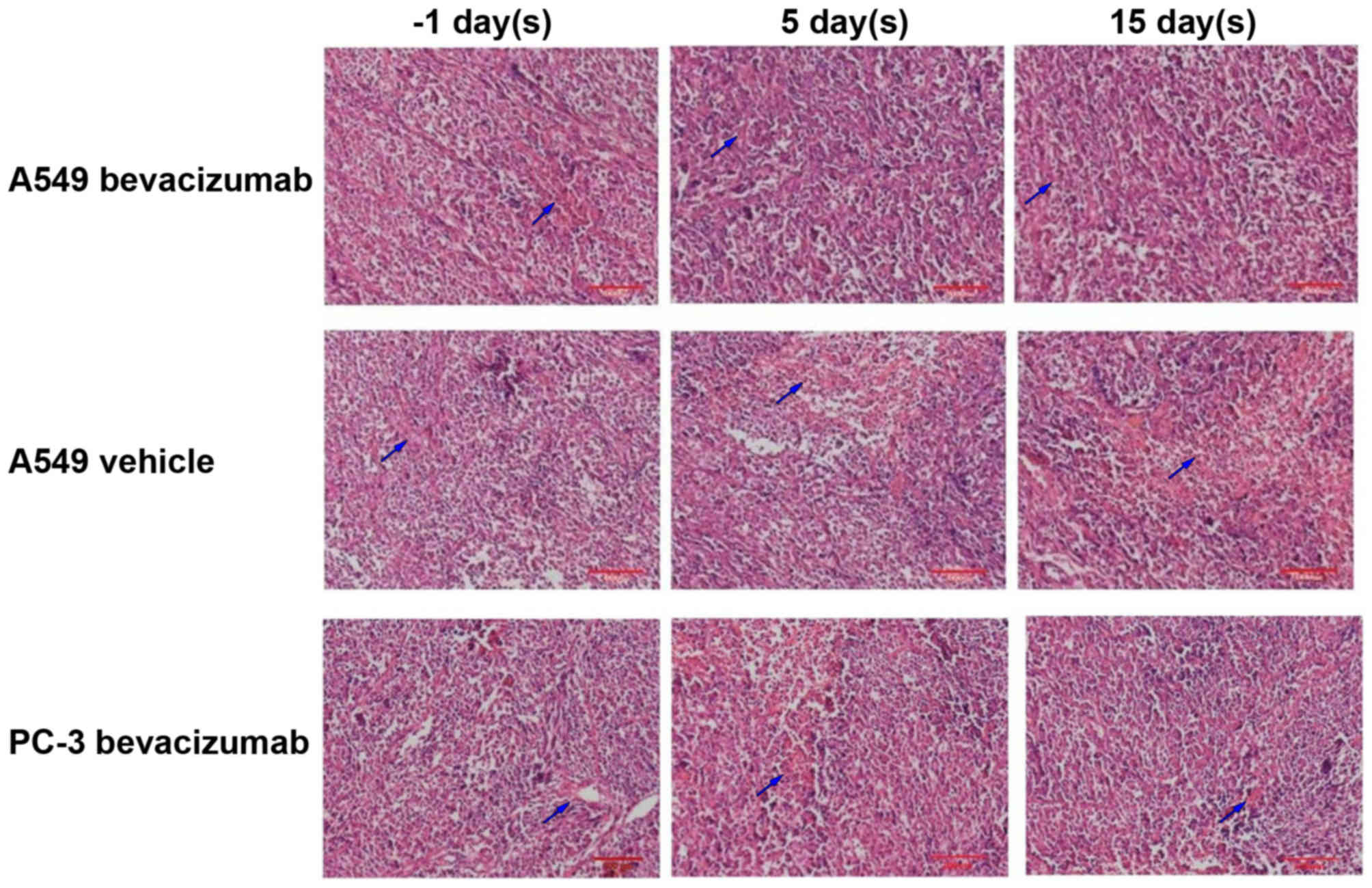
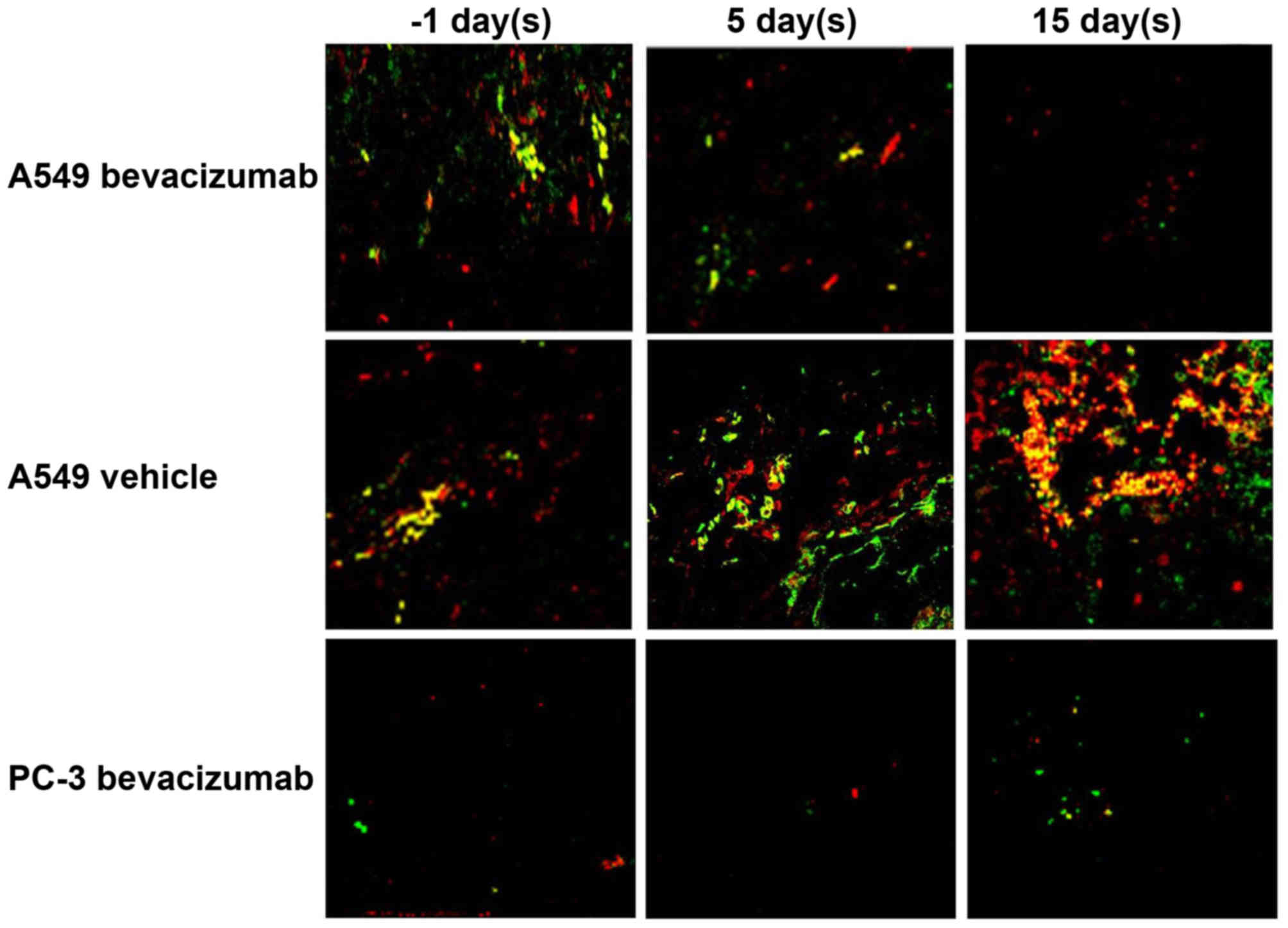
|
1
|
Rayson D, Vantyghem SA and Chambers AF:
Angiogenesis as a target for breast cancer therapy. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 4:415–423. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rodgers M, Soares M, Epstein D, Yang H,
Fox D and Eastwood A: Bevacizumab in combination with a taxane for
the first-line treatment of her2-negative metastatic breast cancer.
Health Technol Assess. 15 Suppl 1:S1–S12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sheng J, Yang YP, Yang BJ, Zhao YY, Ma YX,
Hong SD, Zhang YX, Zhao HY, Huang Y and Zhang L: Efficacy of
addition of antiangiogenic agents to taxanes-containing
chemotherapy in advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
and systemic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e12822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee SM, BAAS P and Wakelee H:
Anti-angiogenesis drugs in lung cancer. Respirology. 15:387–392.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lange A, Prenzler A, Frank M, Golpon H,
Welte T and von der Schulenburg JM: A systematic review of the
cost-effectiveness of targeted therapies for metastatic non-small
cell lung cancer (nsclc). BMC Pulm Med. 14:1922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schreuder SM, Lensing R, Stoker J and
Bipat S: Monitoring treatment response in patients undergoing
chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced uterine cervical cancer by
additional diffusion-weighted imaging: A systematic review. J Magn
Reson Imaging. 42:572–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lei L, Wang X and Chen Z: PET/CT imaging
for monitoring recurrence and evaluating response to treatment in
breast cancer. Adv Clin Exp Med. 25:377–382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ji B, Chen B, Wang T, Song Y, Chen M, Ji
T, Wang X, Gao S and Ma Q: 99mTc-3PRGD2 SPECT
to monitor early response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in stage II
and III breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 42:1362–1370.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma Q, Min K, Wang T, Chen B, Wen Q, Wang
F, Ji T and Gao S: (99m)Tc-3PRGD 2 SPECT/CT predicts the outcome of
advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer receiving
chemoradiotherapy plus bevacizumab. Ann Nucl Med. 29:519–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jia B, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Shi J, Jin X, Zhao H,
Li F, Liu S and Wang F: Blood clearance kinetics, biodistribution,
and radiation dosimetry of a kit-formulated integrin αvβ3-selective
radiotracer 99mTc-3PRGD2 in non-human primates. Mol Imaging Biol.
13:730–736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niu G and Chen X: Why integrin as a
primary target for imaging and therapy. Theranostics. 1:30–47.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Shi J, Kim YS, Zhai S, Jia B, Zhao
H, Liu Z, Wang F, Chen X and Liu S: Improving tumor-targeting
capability and pharmacokinetics of (99m)Tc-labeled cyclic RGD
dimers with PEG(4) linkers. Mol Pharm. 6:231–245. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou Y, Kim YS, Chakraborty S, Shi J, Gao
H and Liu S: 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD peptides for noninvasive
monitoring of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression.
Mol Imaging. 10:386–397. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M,
Gay RE, Gay S and Distler O: Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in
the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 47:149–161.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wong CI, Koh TS, Soo R, Hartono S, Thng
CH, McKeegan E, Yong WP, Chen CS, Lee SC, Wong J, et al: Phase I
and biomarker study of ABT-869, a multiple receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. J Clin
Oncol. 27:4718–4726. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang F, Albert DH, Luo Y, Tapang P, Zhang
K, Davidsen SK, Fox GB, Lesniewski R and McKeegan EM: ABT-869, a
multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, reduces tumor
microvascularity and improves vascular wall integrity in
preclinical tumor models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:134–142. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tannir NM, Wong YN, Kollmannsberger CK,
Ernstoff MS, Perry DJ, Appleman LJ, Posadas EM, Cho D, Choueiri TK,
Coates A, et al: Phase 2 trial of linifanib (ABT-869) in patients
with advanced renal cell cancer after sunitinib failure. Eur J
Cancer. 47:2706–2714. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gullino PM: Angiogenesis and neoplasia. N
Engl J Med. 305:884–885. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis
E and Fezoulidis I: Cancer vascularization: Implications in
radiotherapy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 48:545–553. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morrison MS, Ricketts SA, Barnett J,
Cuthbertson A, Tessier J and Wedge SR: Use of a novel Arg-Gly-Asp
radioligand, 18F-AH111585, to determine changes in tumor
vascularity after antitumor therapy. J Nucl Med. 50:116–122. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Battle MR, Goggi JL, Allen L, Barnett J
and Morrison MS: Monitoring tumor response to antiangiogenic
sunitinib therapy with 18F-fluciclatide, an 18F-labeled
αVbeta3-integrin and αVbeta5-integrin imaging agent. J Nucl Med.
52:424–430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun X, Yan Y, Liu S, Cao Q, Yang M,
Neamati N, Shen B, Niu G and Chen X: 18F-FPPRGD2 and 18F-FDG PET of
response to Abraxane therapy. J Nucl Med. 52:140–146. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Kim YS, Lu X and Liu S: Evaluation
of 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD dimers: Impact of cyclic RGD peptides
and 99mTc chelates on biological properties. Bioconjug Chem.
23:586–595. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|