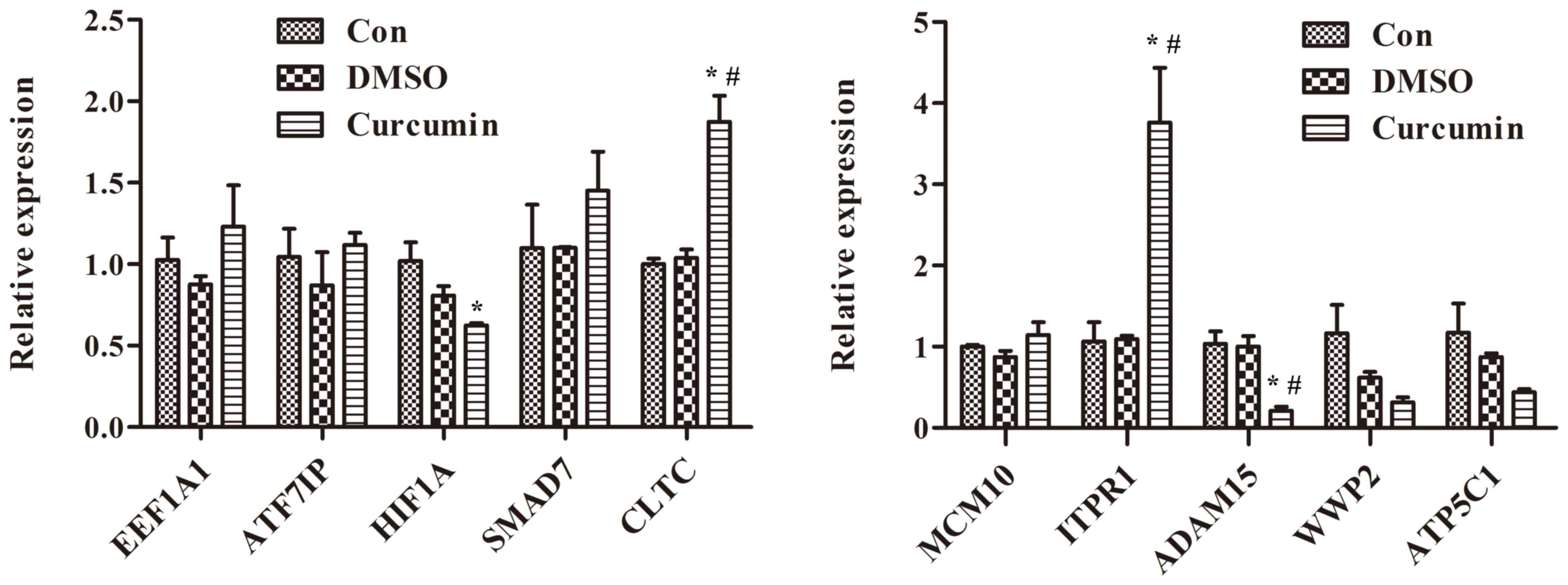
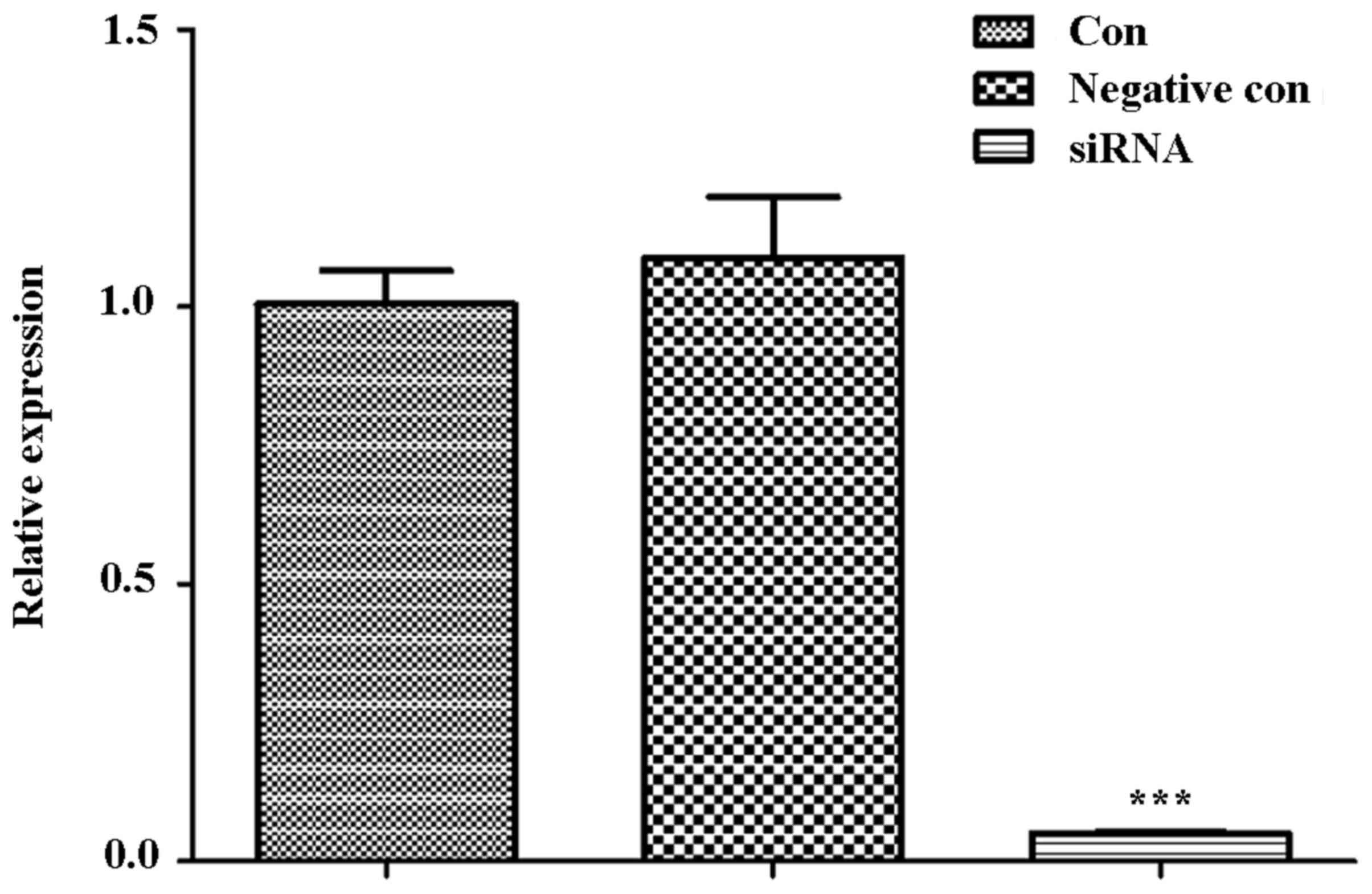
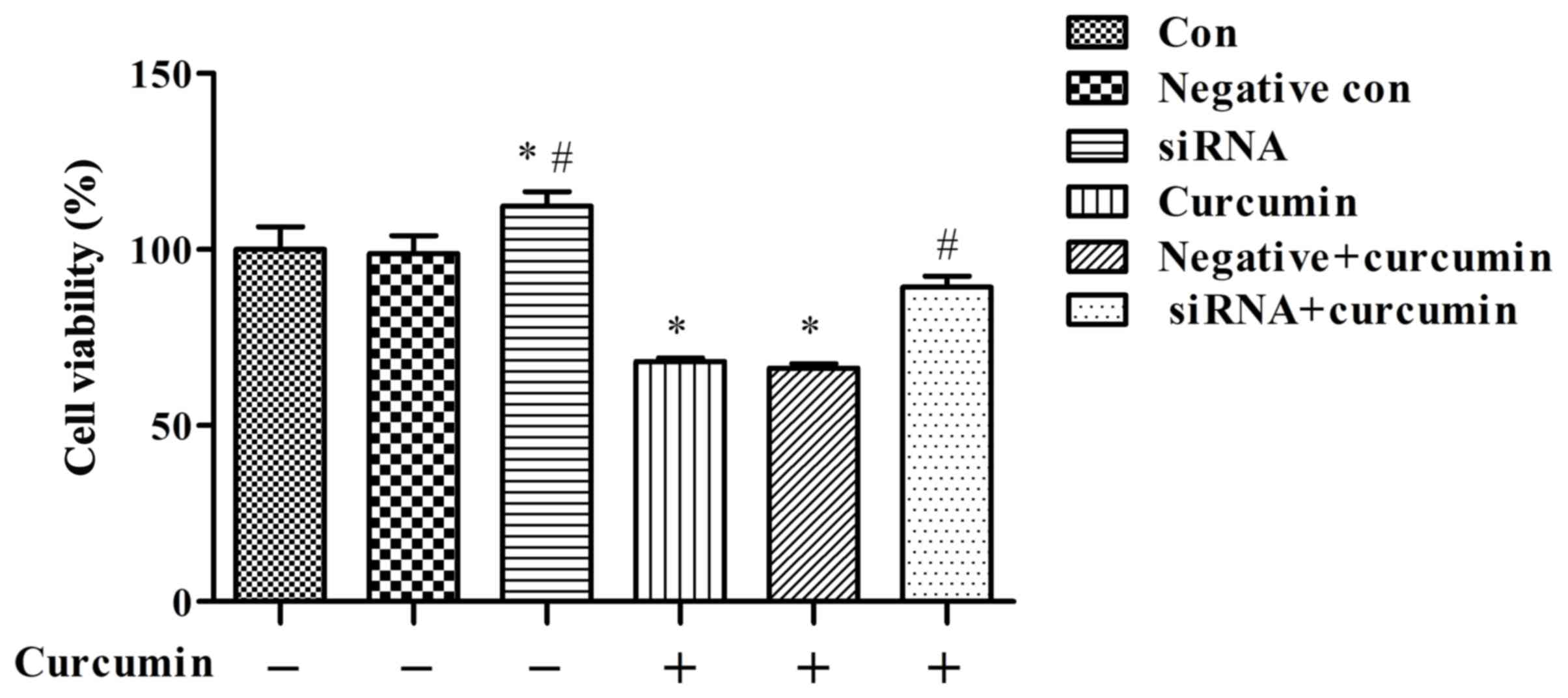
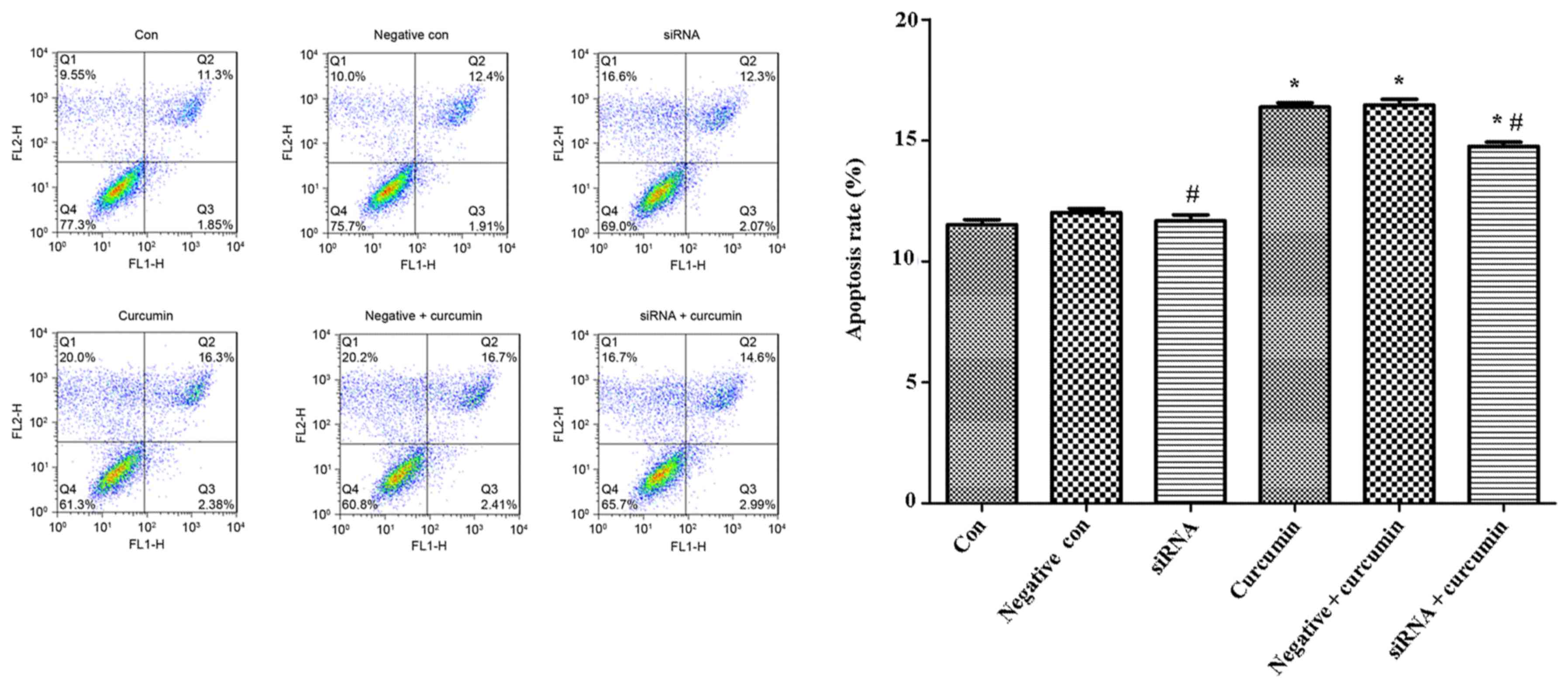
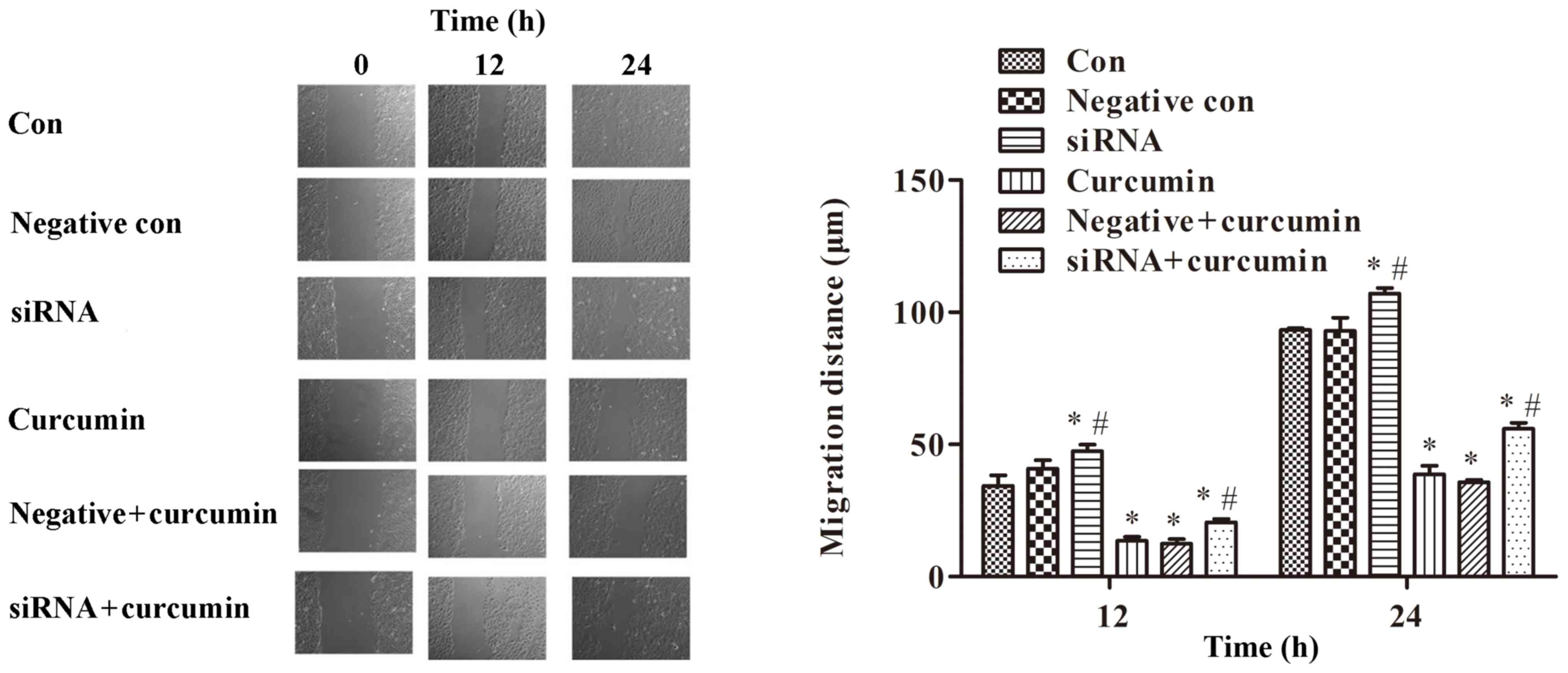
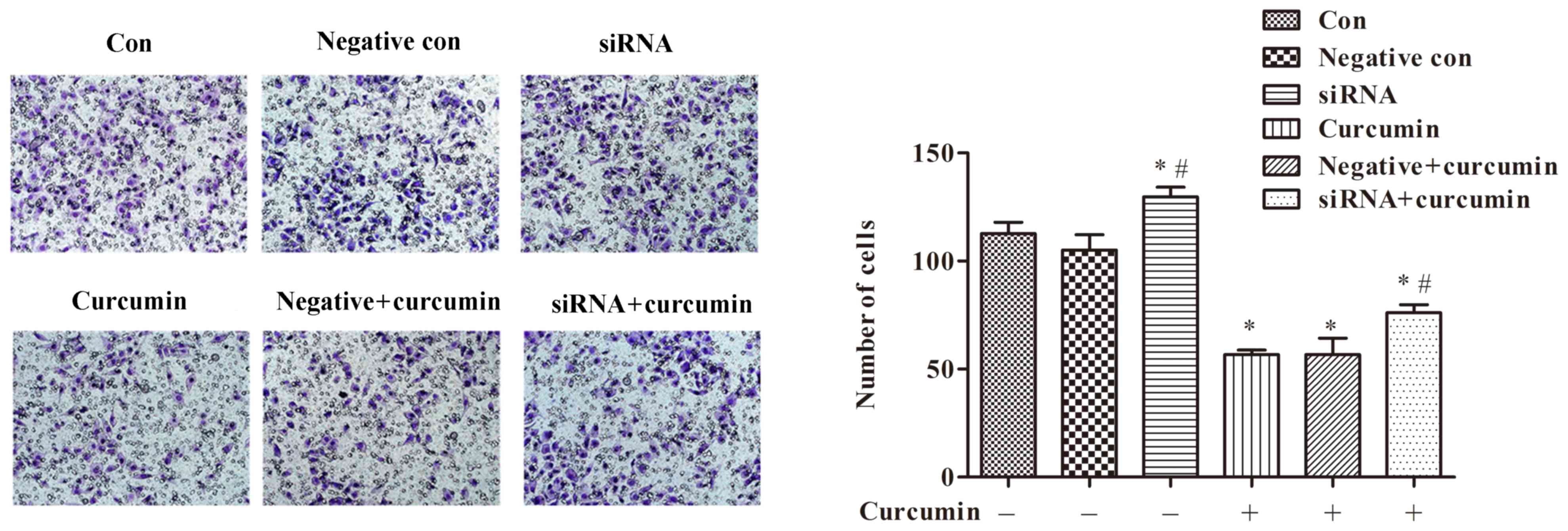
|
1
|
Broadhead ML, Clark J, Myers DE, Dass CR
and Choong PF: The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A
review. Sarcoma. 2011:9592482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma = Pediatric and adolescent osteosarcoma. Springer;
pp. 3–13. 2010
|
|
3
|
He JP, Hao Y, Wang XL, Yang XJ, Shao JF,
Guo FJ and Feng JX: Review of the molecular pathogenesis of
osteosarcoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5967–5976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng BY, Hua YQ and Cai ZD: Establishing
an osteosarcoma associated protein-protein interaction network to
explore the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. Eur J Med Res. 18:572013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Liu WH, Chen BL, Fan L, Han Y,
Wang G, Hu DL, Tan ZR, Zhou G, Cao S and Zhou HH: Plant polyphenol
curcumin significantly affects CYP1A2 and CYP2A6 activity in
healthy, male Chinese volunteers. Ann Pharmacother. 44:1038–1045.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rattigan Y and Maitra A: Metabolomic
profiling of curcumin effects on pancreatic cancer: Insights into
anti-tumor activity. Pancreatology. 13:e682013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Motterlini R, Foresti R, Bassi R and Green
CJ: Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces
heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative
stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 28:1303–1312. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chattopadhyay I, Biswas K, Bandyopadhyay U
and Banerjee RK: Turmeric and curcumin: Biological actions and
medicinal applications. Curr Sci. 87:44–53. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Qiong L and Ran X: Pharmacological effects
of curcumin and bladder cancer treatment research progress.
Zhongyaoyao li yulinchuang. 3:0502012.
|
|
10
|
Walters DK, Muff R, Langsam B, Born W and
Fuchs B: Cytotoxic effects of curcumin on osteosarcoma cell lines.
Invest New Drugs. 26:289–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bao B, Ali S, Kong D, Sarkar SH, Wang Z,
Banerjee S, Aboukameel A, Padhye S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH:
Anti-tumor activity of a novel compound-CDF is mediated by
regulating miR-21, miR-200, and PTEN in pancreatic cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e178502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaiswal AS, Marlow BP, Gupta N and Narayan
S: Beta-catenin-mediated transactivation and cell-cell adhesion
pathways are important in curcumin (diferuylmethane)-induced growth
arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 21:8414–8427.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fossey SL, Bear MD, Lin J, Li C, Schwartz
EB, Li PK, Fuchs JR, Fenger J, Kisseberth WC and London CA: The
novel curcumin analog FLLL32 decreases STAT3 DNA binding activity
and expression and induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma cell lines.
BMC Cancer. 11:1122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang Z, Xing J and Yu X: Curcumin induces
osteosarcoma MG63 cells apoptosis via ROS/Cyto-C/Caspase-3 pathway.
Tumour Biol. 35:753–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leow PC, Tian Q, Ong ZY, Yang Z and Ee PL:
Antitumor activity of natural compounds, curcumin and PKF118-310,
as Wnt/β-catenin antagonists against human osteosarcoma cells.
Invest New Drugs. 28:766–782. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Gerstein M and Snyder M: RNA-Seq:
A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 10:57–63.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ozsolak F and Milos PM: RNA sequencing:
Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet. 12:87–98.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Langmead B: Aligning short sequencing
reads with Bowtie. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. Dec;2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS,
Karolchik D, Cline MS, Goldman M, Barber GP, Clawson H, Coelho A,
et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2011. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database Issue): D876–D882. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Trapnell C, Hendrickson DG, Sauvageau M,
Goff L, Rinn JL and Pachter L: Differential analysis of gene
regulation at transcript resolution with RNA-seq. Nat Biotechnol.
31:46–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Database
Issue): D322–D326. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database Issue): D480–D484.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
26
|
Keshava Prasad TS, Goel R, Kandasamy K,
Keerthikumar S, Kumar S, Mathivanan S, Telikicherla D, Raju R,
Shafreen B, Venugopal A, et al: Human protein reference
database-2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database Issue):
D767–D772. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chau NM, Rogers P, Aherne W, Carroll V,
Collins I, McDonald E, Workman P and Ashcroft M: Identification of
novel small molecule inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 that
differentially block hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induction in response to hypoxic
stress and growth factors. Cancer Res. 65:4918–4928. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu Q, Yang SH, Ye SN and Wang RY:
Therapeutic effects of RNA interference targeting HIF-1 alpha gene
on human osteosarcoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 85:409–413. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
El Naggar A, Clarkson P, Zhang F, Mathers
J, Tognon C and Sorensen PH: Expression and stability of hypoxia
inducible factor 1α in osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
59:1215–1222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen WL, Feng HJ and Li HG: Expression and
significance of hypoxemia-inducible factor-1alpha in osteosarcoma
of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
106:254–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Selga E, Oleaga C, Ramírez S, de Almagro
MC, Noé V and Ciudad CJ: Networking of differentially expressed
genes in human cancer cells resistant to methotrexate. Genome Med.
1:832009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ruest LB, Marcotte R and Wang E: Peptide
elongation factor eEF1A-2/S1 expression in cultured differentiated
myotubes and its protective effect against caspase-3-mediated
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:5418–5425. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Blanch A, Robinson F, Watson IR, Cheng LS
and Irwin MS: Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1-alpha 1
inhibits p53 and p73 dependent apoptosis and chemotherapy
sensitivity. PLoS One. 8:e664362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kastan MB, Canman CE and Leonard CJ: P53,
cell cycle control and apoptosis: Implications for cancer. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 14:3–15. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillett E,
Fleming MD, Dötsch V, Andrews NC, Caput D and McKeon F: p63, a p53
homolog at 3q27-29, encodes multiple products with transactivating,
death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell.
2:305–316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Eliseev RA, Schwarz EM, Zuscik MJ, O'Keefe
RJ, Drissi H and Rosier RN: Smad7 mediates inhibition of Saos2
osteosarcoma cell differentiation by NFkappaB. Exp Cell Res.
312:40–50. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lamora A, Talbot J, Bougras G, Amiaud J,
Leduc M, Chesneau J, Taurelle J, Stresing V, Le Deley MC, Heymann
MF, et al: Overexpression of smad7 blocks primary tumor growth and
lung metastasis development in osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5097–5112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Won KY, Kim YW and Park YK: Expression of
Smad and its signalling cascade in osteosarcoma. Pathology.
42:242–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee DS, Lee MK and Kim JH: Curcumin
induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma (HOS)
cells. Anticancer Res. 29:5039–5044. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jin S, Xu HG, Shen JN, Chen XW, Wang H and
Zhou JG: Apoptotic effects of curcumin on human osteosarcoma U2OS
cells. Orhop Surg. 1:144–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Ma D, Zhang L, Si M, Yin H
and Li J: Curcumin inhibits proliferation and invasion of
osteosarcoma cells through inactivation of Notch-1 signaling. FEBS
J. 279:2247–2259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li C, Wang X, Vais H, Thompson CB, Foskett
JK and White C: Apoptosis regulation by Bcl-x(L) modulation of
mammalian inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor channel isoform
gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 12565–12570. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B and Nicotera P:
Regulation of cell death: The calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:552–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Boehning D, Patterson RL and Snyder SH:
Apoptosis and calcium: New roles for cytochrome c and inositol
1,4,5-trisphosphate. Cell Cycle. 3:250–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bradford PG, Maglich JM and Kirkwood KL:
IL-1 beta increases type 1 inositol trisphosphate receptor
expression and IL-6 secretory capacity in osteoblastic cell
cultures. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 3:73–75. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|