Introduction
The lymphatic system forms an extensive network of
low shear force vessels that penetrates almost all organs of the
human body. It plays a key role in the maintenance of tissue-fluid
homeostasis and is essential for the immune system functioning
(1). Lymphatic vasculature has long
been considered one of the main routes of solid tumors metastatic
dissemination to distant organs (2,3).
Highly-permeable and comparatively wide lymphatic capillaries seem
to be well accommodated to tumor cell transport from the primary
tumor mass into the blood circulation. Sentinel lymph nodes that
directly drain primary tumors are usually the first sites of
detectable metastases. Histological examination of these and nearby
lymph nodes is routinely used for determining the stage of disease
progression and for prediction of patients' survival (4). Moreover, it has become clear that
lymphatics profoundly affects cancer progression (5). Growing evidence indicates that direct
modulation of immune cell functions by lymphatic endothelial cells
(LECs) may be essential for both antitumor immune response at early
stages of tumor progression and subsequent cancer-induced
immunosuppression (6). Based on these
assumptions, it has been proposed that tumors may stimulate
formation of new lymphatic vessel via process of lymphangiogenesis
in a manner analogous to tumor angiogenesis, thereby promoting both
tumorigenesis and lymphagenous metastasis (3,5,7).
Evidence for ongoing lymphangiogenesis inside
growing tumors was initially provided from animal studies. In
experimental models of cancer, forced formation of intratumor
lymphatic vasculature increased tumor aggressiveness and
facilitated metastatic spread (8–11), while
inhibition of the lymphangiogenesis prevented lymph node and
distant metastases without significantly affecting primary tumor
growth (12,13). In agreement with these data, numerous
clinical studies demonstrated an association between tumor
expression of lymphatic-specific growth factors or lymph vessel
density and tumor progression or poor patient survival (14–16).
However, a lack of the correlation as well as an absence of
proliferating LECs in the primary tumors were reported by others
(17,18). Moreover, detailed histological
analyses of various solid tumors frequently failed to reveal
lymphatic vessels throughout tumor masses except the periphery of
these tumors (19–21), suggesting a lack of ongoing
lymphangiogenesis. Besides, growing evidence suggests that
lymphatics suppression might be favorable for tumor growth at early
stages of cancer progression due to anti-tumor immune response
weakening (22).
Thus, formation of new lymphatic vessels in growing
human tumors remains an unresolved question. In order to evaluate a
probability of lymphangiogenesis induction in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC), we performed a comprehensive analysis of the
transcriptional activity of 15 genes encoding lymphatics regulators
or markers (23–26). Using a comparative quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) method we examined the expression
at mRNA level of the vascular endothelial growth factors: VEGFA,
VEGFC, and VEGFD/FIFG, their receptors: VEGFR1/FLT1, FEGFR2/KDR,
and VEGFR3/FLT4 and co-receptors neuropilin 2 (NRP2) and integrin
a9 subunit (ITG9), basic fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2),
transcription factors: prospero-related homeobox domain 1 (PROX1)
and Forkhead box C2 (FOXC2), lymphatic-specific membrane proteins:
lymphatic vessel hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1) and glomerular
podocyte mucoprotein podoplanin (PDPN), spleen protein kinase (SYK)
and key component of desmosomal plaque proteins: desmoplakin (DSP).
A brief characteristics of the analyzed factors is presented in
Table I. Transcript levels were
evaluated by comparison to those in non-malignant lung tissue and
analyzed in terms of patients' clinicopathological
characteristics.
 | Table I.Brief characteristics of the analysed
genes. |
Table I.
Brief characteristics of the analysed
genes.
| Gene
symbola | Brief
characteristics of the encoded protein role in lymphatic system
development and functioning | Assay ID | (Refs.) |
|---|
| VEGFC | Vascular
endothelial growth factor C, a VEGF family member, is the most
potent inducer of lymphatic endothelial cell migration and
sprouting, is a ligand for the receptor tyrosine kinases VEGFR2 and
VEGFR3 | Hs01099203_m1 | (5,25) |
|
VEGFD/FIGF | Vascular
endothelial growth factor D, a VEGF family member, is an inducer of
lymphatic sprouting | Hs01128657_m1 | (5,25) |
| VEGFA | Vascular
endothelial growth factor A, a founder of VEGF family, a key
regulator of tumor angiogenesis, but also essential for lymphatic
vessel formation | Hs00900055_m1 | (23,33) |
|
VEGFR3/FLT4 | Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 3, fms-like tyrosine kinase 4,
the main receptor for VEGFC, also binds VEGFD, is expressed by
lymphatic endothelial cells, on some blood vessels and stem
cells | Hs01047677_m1 | (5,25) |
|
VEGFR2/KDR | Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2, is found in blood vessels and
in a subset of lymphatic vessels, binds vascular growth factors
VEGFA and VEGFC | Hs00911700_m1 | (23,33) |
|
VEGFR1/FLT1 | Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 1, fms-like tyrosine kinase 1,
VEGFA receptor | Hs01052961_m1 | (23,33) |
| NRP2 | Neuropilin-2-VEGFR3
co-receptor is found on lymphatic vessels, binds the
lymphangiogenic growth factors VEGFC and VEGFD, also expressed on
veins | Hs00187290_m1 | (60,61) |
| ITGA9 | Integrin a9,
cell-matrix adhesion receptor, is critical for lymphatic valve
maturation | Hs00979865_m1 | (59) |
| LYVE1 | Lymphatic vessel
hyaluronan receptor, is strongly expressed on the surface of
lymphatic endothelial cells of growing vessels during
lymphangiogenesis, and also on some blood vessels and macrophages;
participates in cell migration and differentiation | Hs00272659_m1 | (35,36) |
| PDPN |
Podoplanin-glomerular podocyte
mucoprotein, is expressed on lymphatic but not on blood vessel
endothelium, osteoblasts, renal podocytes, lung alveolar cells;
participates in cell motility | Hs00366766_m1 | (38,54) |
| PROX1 | Prospero-related
homeobox domain 1 transcription factor, plays a key role for
lymphatic endothelial cell differentiation and maintenance of their
identity | Hs00896293_m1 | (40,41) |
| FOXC2 | Forkhead box C2
transcription factor, is essential for the normal development of
the lymphatic system | Hs00270951_s1 | (37) |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast growth
factor 2, is important for tumor angiogenesis but also promotes
lymphangiogenesis via an indirect mechanism involving VEGFC/VEGFR3
signaling | Hs00266645_m1 | (55) |
| SYK | Spleen tyrosine
kinase, possible indirect role through inhibition of cell motility
and enhancement of cell-cell interactions | Hs00895377_m1 | (58) |
| DSP | Desmoplakin, a key
component of desmosomal plague proteins, may contribute to vessel
formation | Hs00950591_m1 | (56,57) |
Materials and methods
Patients and samples
The study was performed on 140 pairs of tumor and
matched unaffected lung tissue specimens obtained from I–IIIA stage
NSCLC patients who underwent a curative surgery at the Bialystok
Medical University Hospital between 2000 and 2010. Disease staging
was performed according to the seventh edition of the
tumor-nodes-metastasis system (TNM) for lung cancer (27). None of the patients received chemo- or
radiotherapy before the surgery. All of them gave the written
informed consent for specimen collection and clinicopathological
data processing. The study design was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the University.
Tissue samples were collected intraoperatively and
processed immediately after surgical removal according to the
systematic biobanking quality (28).
After the macroscopic visual assessment, the tumors were divided
into two sections. One of them was fixed in formalin followed by
paraffin embedding, and the other was divided into small pieces
(approximately 0.5 cm in diameter) and frozen in liquid nitrogen
followed by storage at −80°C. Unaffected lung parenchyma specimens
were dissected from the same lobe or lung of the patient at an area
at least 5 cm distant from the tumor and processed similarly to
tumor specimens. Prior to RNA extraction, the cross-sections of
frozen tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin-eozyn and
evaluated by an experienced pathologist (L.C.) to confirm the
suitability of cell content. Namely, tumor specimens with the
highest percentage of the malignant cells (but at least 60% of
tumor cells on a microscopic section) and normal lung epithelium
without metaplasia or dysplasia were used for further
processing.
RNA extraction
Total RNA was isolated from tissue specimens by
magnetic extraction method on EasyMag machine (bioMerieux, Marcy
l'Étoile, France) according to the producer's protocol. The
resulting RNA was transcripted into cDNA in a reaction with High
Capacity RNA-to-cDNA Master Mix (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) according to the producer's
recommendations.
mRNA expression level
For an mRNA level evaluation a TaqMan Low Density
Array analysis was used: For each sample, amplification of all the
analyzed transcripts was performed simultaneously in the MicroFluid
Cards (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) that
contained manufactory loaded and dried commercially available
primers/probe sets for gene expression examination
(Assays-on-Demand; Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). Gene symbols and Assay-on-Demand accession numbers are
summarized in Table I. Ribosomal 18S
RNA (18SrRNA) gene with a relatively low level of expression
variability in lung cancer cell lines and clinical specimens
(29) was used to normalize for the
differences in the input cDNA concentration. Each channel of a card
was loaded with 100 µl of the reaction mixture containing 50 µl 2X
TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix (Applied Biosystems; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 20 µl of a cDNA solution
(corresponding to 100 ng of total RNA). The amplification was
performed with ABI PRISM 7900HT Sequence Detection System equipped
with the SDS v.2.4 software for baseline and Cq
calculations. The cycling conditions were as follows: 50°C for 2
min followed by 95°C for 10 min hold, 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec
and 60°C for 60 sec. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. The
raw Cq data for each mRNA (Cq) was normalized as follows:
ΔCq=Cq-Cq ref, where
Cq ref equaled the Ct value of the
reference 18SrRNA gene. Tumor-associated fold-changes (FC) in gene
activities (relative expression) were calculated as follows:
FC=2−ΔΔCq, where ΔΔCq equaled the differences
between normalized expressions of the analyzed gene in tumor
(ΔCqT) and nonmalignant lung tissue (ΔCqN)
from the same patient
(ΔΔCq=ΔCqT-ΔCqN) (30). To examine possible associations
between gene activity and patients' clinicopathological
characteristics or survival, log2FC values were used.
For survival analysis a median log2FC for each gene was
used as a cutoff and the expression was categorized as high (equal
or higher than the median) or low (lower than the median).
Statistical analysis
The differences in mRNA expression levels between
the tumor and unaffected lung tissues were analyzed with paired
Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The Wilcoxon rank-sum or Kruskal-Wallis
rank tests were used to analyze the associations between
clinicopathological characteristics and mRNA expression levels. OS
was calculated and plotted with Kaplan-Meier method with the
log-rank test for comparison between the groups. Cox proportional
hazards method was used to evaluate the effect of
clinicopathological and molecular variables on OS. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All
the statistical analyses in this study were performed using
STATA/SE 11.1 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX,
USA.
Results
Patient characteristics
A total of 140 NSCLC patients, aged from 39 to 79
years (mean 62, standard deviation 8.0 years), were included in the
study. The majority of the patients (117 out of 140, 84%) were
males. Among the patients, 57 (41.4%) had lung adenocarcinoma
(ADC), 66 (47.1%) had squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and the
remaining 17 (11.4%) had large cell lung carcinoma (LCC).
Forty-five tumors were recognized as highly differentiated (grade 1
or 2), and fifty-five were lowly differentiated ones (grade 3 or
4). Lymph node metastasis was detected in 60 (42.9%) patients.
Fifty-seven (40.8%) patients had TNM stage I disease, 66 (47.1%)
had stage II disease, and 17 patients (12.1%) had stage III
disease.
Differential gene expression between
tumor and non-tumor lung tissues
Ten out of 15 analyzed genes (VEGFC, VEGFD,
VEGFR3, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, FGF2, SYK, LYVE1, ITGA, and
FOXC2) showed a significantly lower mRNA level in tumors
compared with non-tumor tissues. Four genes (PROX1, PDPN,
NRP2, and VEGFA) had similar expression levels in the
tumors and in the normal samples, and only for one gene
(DSP) an increase in expression in tumors was observed
(Table II).
 | Table II.Gene expression at mRNA level in
tumor and non-tumor lung tissue [log2(ΔCq)] and the
difference in the log-FC between the paired tissues
[log2(FC)]. |
Table II.
Gene expression at mRNA level in
tumor and non-tumor lung tissue [log2(ΔCq)] and the
difference in the log-FC between the paired tissues
[log2(FC)].
|
|
| mRNA level
[log2(ΔCq)] |
|
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Gene symbol | N | Tumor tissue Me
(25–75%) | Normal lung tissue
Me (25–75%) | P-value | Difference in mRNA
level between tumor and normal lung tissues [log2(FC)]
Me (25–75%) |
|---|
| VEGFC | 136 | 17.67
(16.33–18.54) | 16.58
(15.39–17.84) | <0.0001 | −0.92
(−1.88–0.06) |
| VEGFD | 136 | 18.75
(16.37–21.74) | 15.57
(14.27–16.55) | <0.0001 | −2.72
-(5.92–0.61) |
| VEGFR3 | 136 | 18.72
(17.65–19.53) | 17.39
(16.79–18.27) | <0.0001 | −0.89
-(1.95–0.16) |
| LYVE1 | 136 | 18.91
(17.15–20.23) | 16.69
(15.31–17.68) | <0.0001 | −2.08
-(3.37–0.48) |
| ITGA9 | 136 | 16.06
(15.16–17.34) | 15.43
(14.45–16.22) | <0.0001 | −1.02
(−1.86–0.14) |
| PDPN | 136 | 15.71
(14.45–16.96) | 15.75
(14.50–16.81) | 0.640 | −0.13
(−1.15–1.30) |
| DSP | 137 | 13.81
(11.93–15.59) | 16.66
(15.12–17.52) | <0.0001 | 2.58
(0.44–4.39) |
| PROX1 | 136 | 20.53
(18.27–21.80) | 20.47
(18.95–22.09) | 0.611 | 0.17
(−1.21–1.70) |
| FOXC1 | 136 | 15.27
(14.04–16.44) | 13.96
(13.06–15.03) | 0.0003 | −1.45
(−2.29–0.41) |
| NRP2 | 136 | 14.16
(12.78–15.29) | 13.97
(12.61–14.99) | 0.021 | −0.16
(−1.12–0.55) |
| VEGFA | 136 | 13.34
(11.86–14.77) | 13.37
(11.97–14.76) | 0.861 | 0.03
(−0.81–0.80) |
| FGF2 | 137 | 19.57
(17.46–20.50) | 18.05
(16.86–19.05) | 0.0002 | −1.10
(−2.41–0.24) |
| VEGFR1 | 136 | 16.99
(15.48–18.40) | 16.83
(14.73–17.42) | 0.0002 | −0.92
-(1.78–0.15) |
| VEGFR2 | 136 | 16.13
(14.65–17.85) | 15.11
(13.63–16.56) | <0.0001 | −1.16
(−2.18–0.10) |
| SYK | 138 | 16.27
(15.28–17.40) | 16.16
(15.02–17.50) | 0.387 | −0.30
(−1.11–1.61) |
Associations between transcript level
and clinicopathological characteristics
The analysis of the effect of patients'
clinicopathological features on gene expression revealed a
relatively limited and differentiated influence on the fold-change
values. In particular, tumor-associated downregulation of the
expression for VEGFC (P=0.049), VEGFR3 (P=0.107),
VEGFR2 (P=0.028), and ITGA (P=0.011) genes was higher
in SCC than in ADC or LCC, and two genes (PROX1 and
VEGFA) were downregulated in SCC but not in non-squamous
histological types (P=0.005 and P=0.012 for PROX1 and
VEGFA, respectively) (Fig.
1A-F). In larger tumors, suppression of VEGFR3 and
LYVE1 activity was more significant than those in smaller
ones (P=0.034 and P=0.50 for VEGFR3 and LYVE1,
respectively), whereas the opposite relation was revealed for
PDPN and NRP2 genes (P=0.019 and P=0.019,
respectively) (Fig. 2A-D). However,
we failed to find associations between the analyzed mRNA levels and
lymph node metastases or disease stage. PDPN (P=0.049),
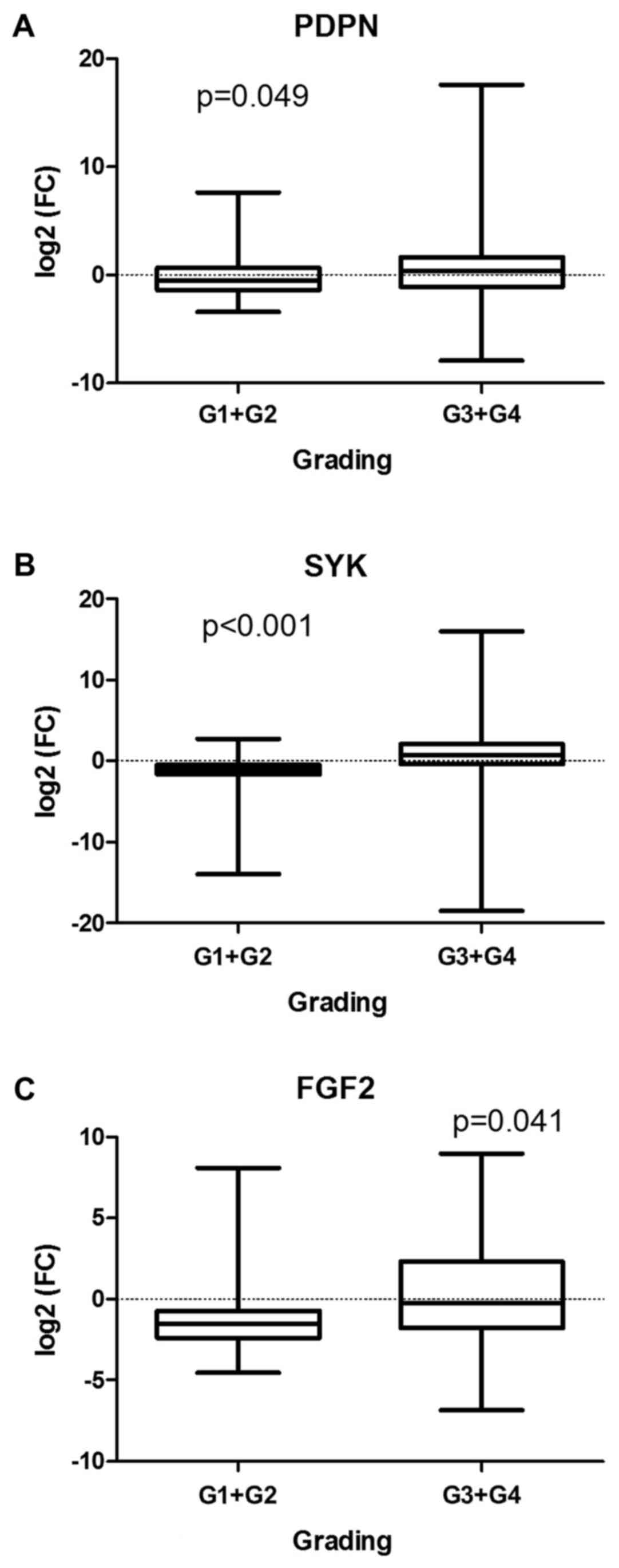
SYK (P<0.001) and FGF2 (P=0.041) transcriptional
downregulation was more significant in high-graded tumors (G3 or
G4) compared with low-graded ones (G1 or G2) (Fig. 3A-C). Although unchanged in the whole
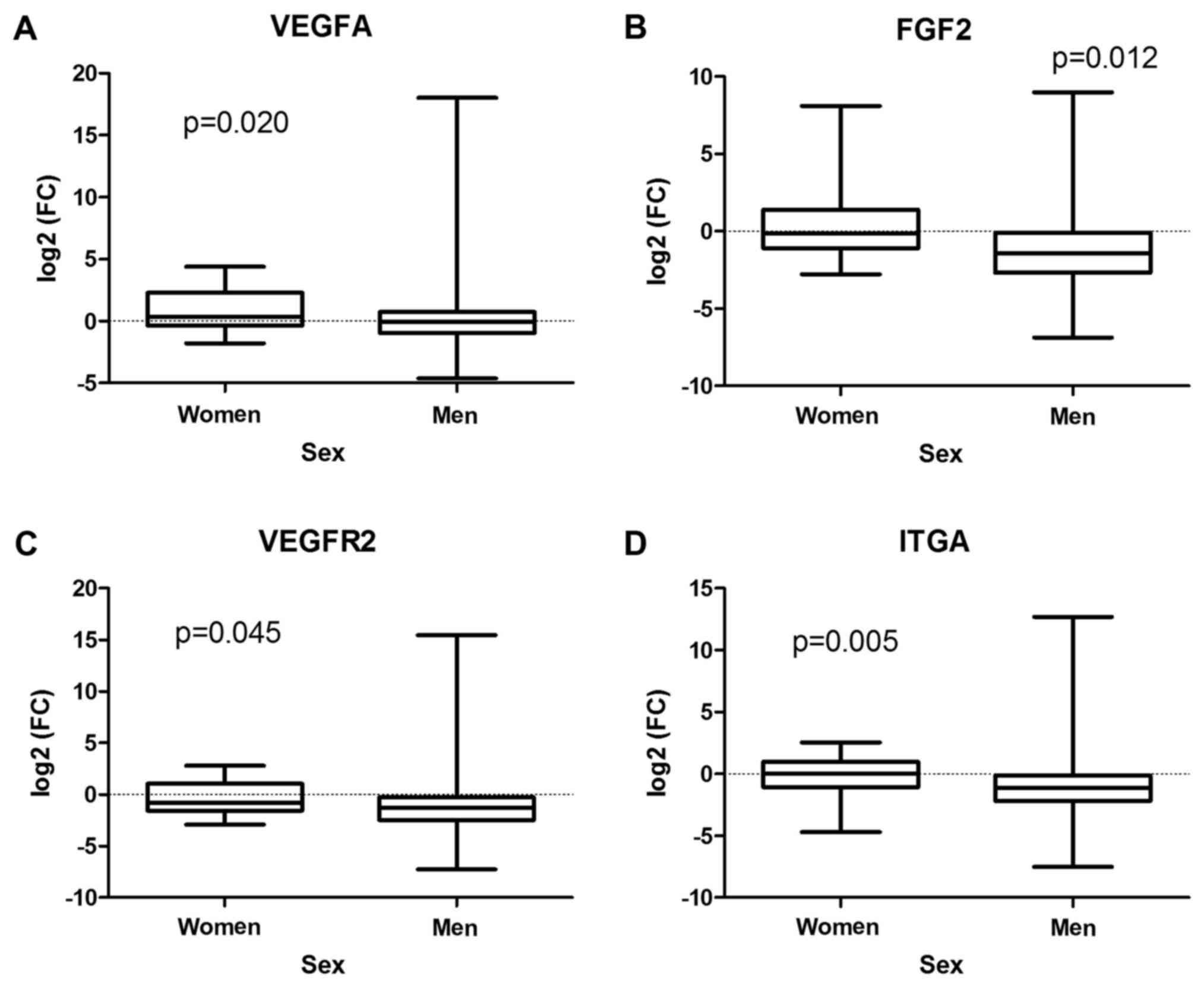
cohort of our patients or in men, VEGFA expression was
upregulated in tumors derived from women (P=0.020) (Fig. 4A). In addition, more significant
suppression of FGF2 (P=0.012), VEGFR2 (P=0.045), and
ITGA (P=0.005) transcription was observed in men compared to
women (Fig. 4B-D).
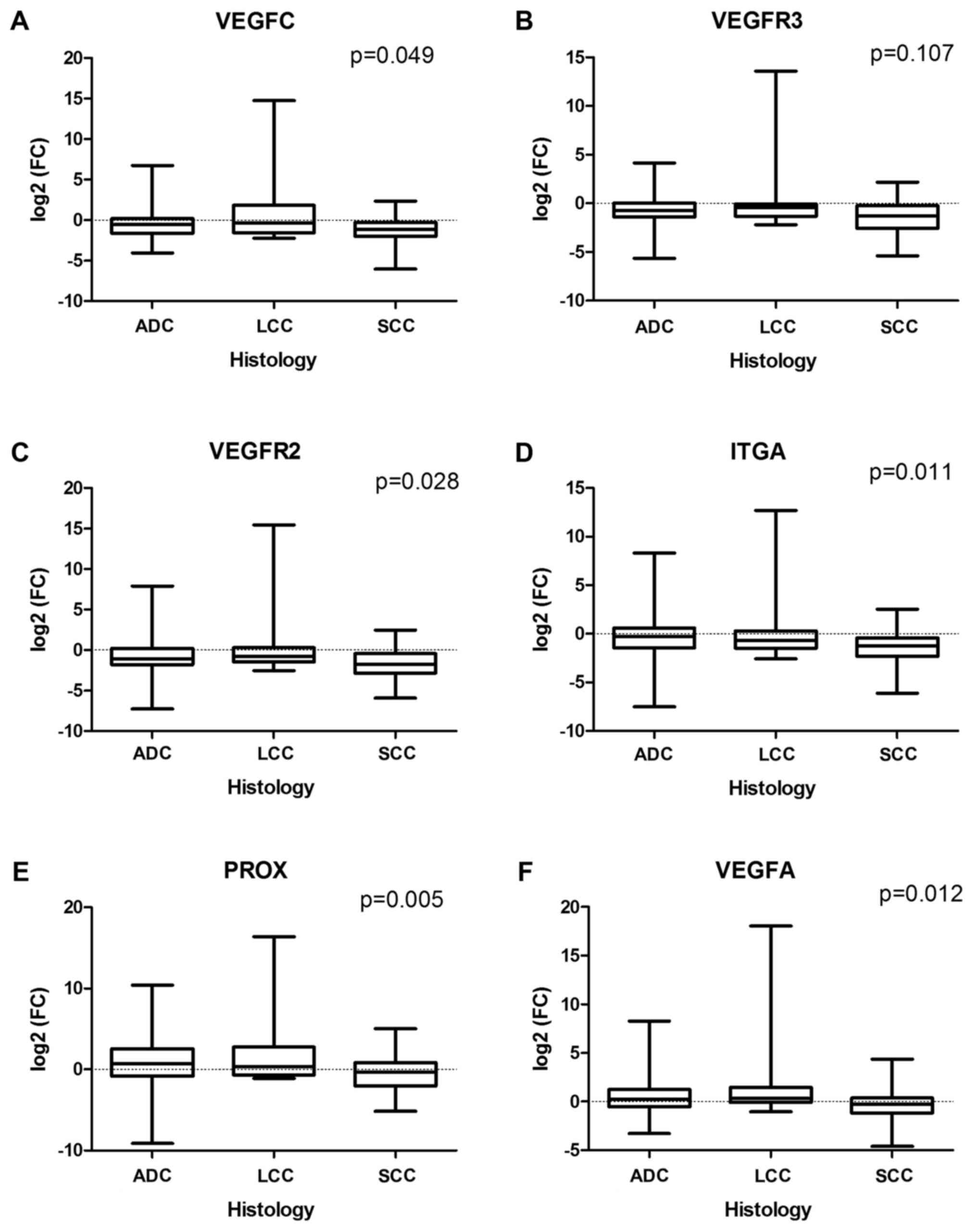 | Figure 1.Associations between NSCLC
histological type and (A) VEGFC, (B) VEGFR3, (C)
VEGFR2, (D) ITGA, (E) PROX1 and (F)
VEGFA mRNA expression level, defined as log2(FC).
NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; VEGF, vascular endothelial
growth factor; ITGA9, integrin a9; PROX1, prospero-related homeobox
domain 1; ADC, adenocarcinoma; LCC, large cell carcinoma; SCC,
squamous cell carcinoma; FC, fold-change difference in mRNA
level. |
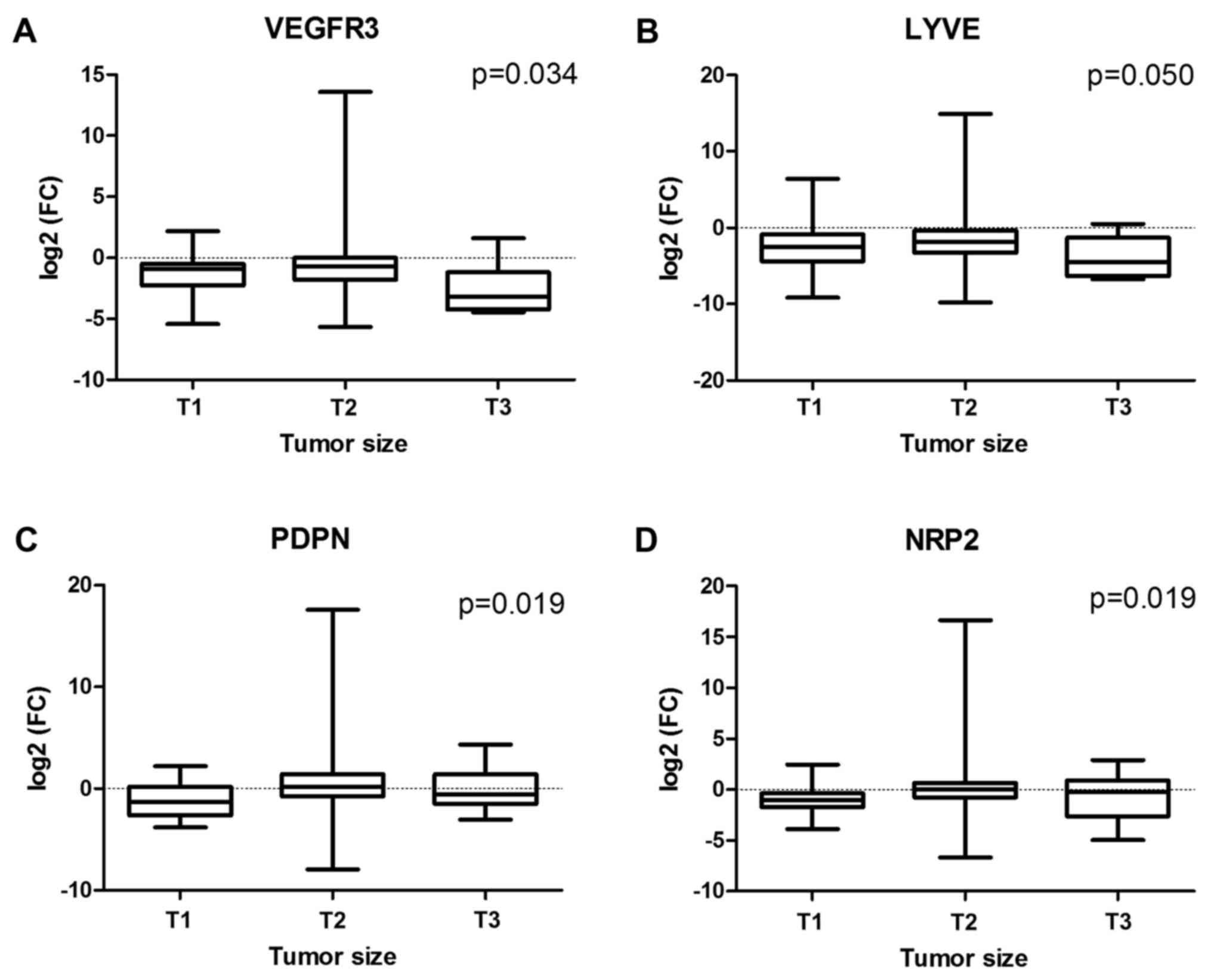 | Figure 2.Associations between NSCLC tumor size
and (A) VEGFR3, (B) LYVE1, (C) PDPN and (D)
NRP2 mRNA expression level, defined as log2(FC)
NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; VEGF, vascular endothelial
growth factor; LYVE1, lymphatic vessel hyaluronan receptor 1; PDPN,
podoplanin; NRP2, neuropilin 2; FC, fold-change, difference in mRNA
level between tumor and normal lung tissues. |
The effects of gene expression level
on patients' survival
The median follow-up time was equal to 54.6 months
(ranged from 2 to 86 months). During the follow-up, 64 (45.6%)
patients had disease recurrence and all of them had died. In the
Kaplan-Meier curve analysis, none of the analyzed parameters
influenced OS, except VEGFR1 expression. The OS rate of the
patients with low VEGFR1 expression was significantly
shorter than that of the patients with high expression level
(P=0.045). In multivariate analysis by Cox's proportional hazards
method, low VEGFR1 expression was an independent prognostic
factor for a poor OS time (HR 2.103; 95% CI: 1.005–4.401; P=0.049)
(Table III).
 | Table III.Univariate and multivariable analysis
of the prognostic effect of patients' clinicopathological
characteristics and gene mRNA level [defined as
log2(fold-change) difference between NSCLC and non-tumor
lung tissues] on overall survival (Cox proportional hazards
model). |
Table III.
Univariate and multivariable analysis
of the prognostic effect of patients' clinicopathological
characteristics and gene mRNA level [defined as
log2(fold-change) difference between NSCLC and non-tumor
lung tissues] on overall survival (Cox proportional hazards
model).
|
| Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variable | Hazard ratio | P-value | 95% confidence
interval | Hazard ratio | P-value | 95% confidence
interval |
|---|
| Age | 1.448 | 0.138 | 0.888–2.361 |
|
|
|
| Sex | 1.570 | 0.234 | 0.747–3.297 |
|
|
|
| Histology | 0.979 | 0.873 | 0.759–1.263 |
|
|
|
| Grading | 1.169 | 0.587 | 0.665–2.054 |
|
|
|
| Tumor size | 1.749 | 0.036 | 1.037–2.948 | 1.264 | 0.435 | 0.701–2.280 |
| Lymph node
metastasis | 2.258 | 0.001 | 1.376–3.704 | 0.836 | 0.642 | 0.392–1.780 |
| TNM | 2.414 | <0.001 | 1.713–3.402 | 2.542 | 0.001 | 1.486–4.346 |
| VEGFC | 0.824 | 0.445 | 0.502–1.353 | 0.557 | 0.259 | 0.201–1.539 |
|
VEGFD/FIGF | 0.967 | 0.893 | 0.592–1.578 | 1.480 | 0.481 | 0.498–4.401 |
| VEGFA | 1.322 | 0.275 | 0.800–2.184 | 1.143 | 0.810 | 0.382–3.428 |
|
VEGFR1/FLT1 | 2.110 | 0.046 | 1.012–4.392 | 2.103 | 0.049 | 1.005–4.401 |
|
VEGFR2/KDR | 0.874 | 0.553 | 0.533–1.435 | 0.805 | 0.684 | 0.284–2.285 |
|
VEGFR3/FLT4 | 0.970 | 0.905 | 0.590–1.595 | 1.179 | 0.761 | 0.409–3.411 |
| NRP2 | 1.084 | 0.754 | 0.656–1.791 | 1.156 | 0.800 | 0.376–3.553 |
| ITGA9 | 1.052 | 0.839 | 0.642–3.663 | 0.924 | 0.868 | 0.364–2.347 |
| FGF2 | 1.845 | 0.080 | 0.929–3.663 | 2.161 | 0.094 | 0.878–5.334 |
| PROX1 | 0.806 | 0.394 | 0.491–1.323 | 0.829 | 0.686 | 0.335–2.052 |
| FOXC2 | 0.599 | 0.155 | 0.297–1.212 | 0.569 | 0.222 | 0.230–1.406 |
| LYVE1 | 0.934 | 0.806 | 0.572–1.544 | 1.277 | 0.663 | 0.425–3.837 |
| PDPN | 1.156 | 0.569 | 0.703–1.901 | 1.952 | 0.261 | 0.608–6.267 |
| SYK | 1.345 | 0.397 | 0.677–2.671 | 1.297 | 0.605 | 0.843–3.481 |
| DSP | 0.855 | 0.530 | 0.525–1.393 | 0.458 | 0.068 | 0.197–1.060 |
Discussion
NSCLC remains one of the most life-threatening human
malignances (31), mostly due to
early metastasis occurrence (32).
Although lymphatic system has long been considered one of the main
routes of cancer cell dissemination to distant organs (2,3), an issue
of new lymphatic vessel formation in solid tumors, including lung
cancer, remains unresolved (33). The
aim of the present study was to examine a possible impact of lung
cancer cells on lymphangiogenesis induction within lung tumor mass.
To do that we, firstly, analyzed mRNA expression level of
well-established lymphangiogenesis inductors and markers (namely,
VEGFC, VEGFD, VEGFR3, LYVE1, PDPN) and also of a number of
pleiotrophic factors with reported contribution to the process
(VEGFA, FGF2, NRP2, PROX1 and others). Secondly, although we did
not perform tissue microdissection to exclude the influence of
nonmalignant stromal cells on the analyzed parameters, we used lung
cancer tissue specimens enriched in malignant cells (a median
cancer cell content was 80%, ranged from 60 to 100%). Thirdly, we
compared the expression level of the examined genes in tumors with
that in the nonmalignant lung tissue derived from the same patient.
We assumed that transcriptional activation (an increase in
transcript level in tumors compared with paired unaffected lung
tissues) of the genes essential for lymphatic vessel formation,
reorganization and maintenance had to be observed in
lymphangiogenesis-inducing tumors.
Despite expectations, none of the analyzed genes,
except DSP, was activated in tumor tissue. Moreover, in
malignant tissues, a statistically significant decrease in
transcript level was observed for growth factors VEGFC and VEGFD
and their receptor VEGFR3 that are thought to be the most potent
inductors of lymphatic vessel formation (10,34,35), and
transcripts for lymphatics-specific markers LYVE1 (36,37) and
FOXC2 (38). The expression levels of
other well-estimated lymphatic molecules PDPN (39,40) and
PROX1 (41,42) were similar to those in nonmalignant
tissue. Moreover, neither lymph node status, nor disease stage
influenced transcript level for these genes, while more significant
suppression of gene activity seemed to occur in SCC, compared to
ADC or LCC. Also, no impact of aforementioned genes on patients'
survival was observed. Thus, our results do not confirm a
hypothesis of lymphangiogenesis induction in NSCLC, but instead
seem to indicate a possible transcriptional suppression of the
process.
Similar results were recently published by Sanmartín
et al (43), who analyzed the
mRNA expression of all the VEGF family members, their receptors and
co-receptors NRP1 and NRP2 in early-stage NSCLCs. The authors
applied a similar methodological approach for mRNA evaluation and
indicated significantly lower levels of VEGFD, VEGFR2, and
VEGFR3 mRNA in tumors, especially remarkable in the case of
VEGFD transcripts. Unfortunately, no information about the
remaining analyzed genes has been reported by authors (43). Lower VEGFC and similar
VEGFR3 mRNA expression levels in NSCLC tissues compared with
normal lung tissues were also indicated by Takizawa et al
(44). However, in another study, a
differentiated VEGFC and VEGFD expression across
tumor mass was indicated. In this analysis, a significantly reduced
VEGFC and VEGFD mRNA expression was indicated in
central tumor regions compared with the corresponding non-tumor
lung tissues. However, in external tumor marginal regions, the mRNA
level was found to be similar (for VEGFC transcripts) or
even higher (for VEGFD transcripts) than those in
non-tumoral tissues. Immunohistochemical examination confirmed
these data. Moreover, the number of D2-40-immunostained lymphatic
vessels was much higher at tumor periphery than in the central
zone, and correlated with VEGFC and VEGFD mRNA levels
(45). These results suggest that
formation of new lymphatic vessels in NSCLC may be restricted to
the peripheral tumor zones. In the present study, we did not
analyze separately internal and external tumor zones. Instead,
specimens of bulk tumor mass enriched in malignant cells were used
for transcript evaluation. In our opinion, our results do not
confirm an induction of new lymphatic vessels formation in
NSCLC.
We also failed to indicate associations between
VEGFC, VEGFD or VEGFR3 mRNA expression and lymph node
metastasis or patients' prognosis. Our data are partially
consistent with previously reported observations, although in terms
of the expression at mRNA level, limited and opposite data have
also been reported. Thus, no associations between VEGFC and
VEGFR3 expression and lymph node status or patients'
survival were indicated by Maekawa et al (46), whereas Takizawa et al (44) and Li et al (47) reported similar data for VEGFC
and VEGFR3 expression, respectively. In contrast, Takizawa
et al (44) indicated
significantly lower VEGFR3 mRNA levels in the node-positive
group and an inverse relation in terms of VEGFC/VEGFR3 expression
ratios. In respect to VEGFD, a negative correlation was found
between VEGFD mRNA under-expression in NSCLC and lymph node
metastasis (43,46). In contrast, Feng et al
(45) indicated a positive
correlation between VEGFC or VEGFD mRNA expression and lymph node
metastases, but only in terms of the invasive marginal tumor
regions.
Although studies on VEGFC, VEGFD, and VEGFR3
expression at mRNA level are limited, protein expression in NSCLC
cells has been examined extensively by immunohistochemistry. A
number of recent meta-analyses that summarize the results of these
clinical investigations preferentially indicate positive VEGFC/D
and VEGFR3 immunostaining in tumor cells and a positive correlation
between the expression level and lymph node involvement or disease
progression (48,49). Similar data were obtained for breast,
colorectal and esophageal cancer patients (50–52).
However, in all the reports, significant discrepancies across
particular studies have been highlighted. In our opinion,
currently, there is no data to clearly support or oppose new
lymphatic vessel formation in NSCLC.
In terms of the remaining genes examined in the
present study, it is difficult to compare our results to previously
reported data. Protein products of these genes have been
demonstrated to be implicated in lymphatic system development,
reorganization and maintenance in both physiological and
pathological conditions (24–26,34) and
are widely used as markers for microscopic imaging of lymphatic
vessels (40,53). However, in addition to lymphatics,
these protein are expressed in various cell types and contribute to
multiple molecular processes, including those in malignancies, as
it has been demonstrated in a number of recent comprehensive
reviews (54–62). This may provide an explanation for
inconsistent data on the expression of analyzed proteins in cancer
and their impact on tumor progression and clinical outcome
(63–77).
For one of the genes, namely DSP, encoded for
desmoplakin, an increase in mRNA level in NSCLC has been
demonstrated. Desmoplakin is one of the main components of
desmosomes that confer strong cell-cell adhesion and tissue
resistance against mechanical stress but are also involved in cell
proliferation, differentiation migration, morphogenesis and
apoptosis (57,58). A body of evidence indicates that
desmosomal proteins are deregulated in various cancers and the
deregulation contributes to cancerogenesis (58). Although a tumor-suppressive function
of desmosomal proteins has mainly been postulated, discrepant data
in the literature indicate that differential changes in their
expression in tumor tissue may occur and possibly have different
consequences (58).
Among the genes we examined here, there were those
for growth factor VEGF and their receptors VEGFR1 and VEGFR2.
VEGFA/VEGFR1-2 signaling is considered a key inductor of
physiological and tumor-associated angiogenesis (78). Recently, VEGFA and VEGFR2 have also
been implicated in tumor lymphangiogenesis (3,5,33,34). Of
interest, a number of clinical NSCLC studies demonstrated a
positive correlation between high tumor cell VEGFA expression and
lymph node metastasis (79,80) and an inverse association in terms of
stromal cell VEGFA expression (80).
In our study, we failed to demonstrate VEGFAVEGFR1-2 signaling
up-regulation in NSCLC, and these data seem to be discordant with a
widely accepted view on angiogenesis induction in cancers (81). However, a gross of other factors have
been found to stimulate new blood vessel formation, and tumors with
VEGFA-independent angiogenesis (82,83) or
those co-opting preexisting vessels have been frequently indicated
(84,85).
In our study, VEGFR1 mRNA expression level
seemed to be linked to patients' survival (P=0,049). However,
further investigations on larger patients cohort are needed to
confirm this possibility. VEGFR1 is an alternative VEGFA receptor
which also binds VEGFB and placental growth factor PIGF (78,86). The
prognostic value of this receptor expression in NSCLC remains
controversial. In several recent studies, an unfavorable effect of
high VEGFR1 expression on NSCLC patient' survival has been
demonstrated (87,49), whereas others found no correlation
between the expression and the prognosis of the disease (88). To resolve discrepancies in the results
further investigations are needed.
An important conclusion raising from our analysis
reveals possible differences between NSCLC histological types in
lymphangiogenesis regulation which are known to exist regarding new
blood vessel formation and are taken into account in targeted
antivascular therapy. We indicated a significantly lower VEGFC,
VEGFR2, VEGFR3, and PROX1 mRNA expression in SCC compared with
non-squamous NSCLC histological types, that suggests a more
profound suppression of lymphangiogenesis in SCC and is in line
with Takizawa et al data according to VEGFC and
VEGFR3 mRNA levels (44).
In summary, our results demonstrate that the
expression of the lymphangiogenesis-promoting factors in NSCLC
cells seem to be suppressed at mRNA level early in cancer
progression and more profoundly in SCC compared with ADC or LCC.
These findings are in accordance with a recent hypothesis of
absence of ongoing lymphangiogenesis inside a growing tumor mass,
but do not exclude a possibility of lymphangiogenesis in narrow
marginal tumor regions and a contribution of this lymphatics to
lymph node metastasis. On the other hand, in the light of current
knowledge on crosstalk between lymphatic and immune cells, our data
may suggest a possibility of repression of active lymphatic
function by tumor cells in order to reduce anti-tumor immunity. Of
course, the some factors we had analyzed in the present study, are
not limited only to lymphatic system development and functioning,
but may play other multiple roles in both tumor and stromal cells,
and alterations in their expression may depend on tumor biological
characteristics and progression stage.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Polish Ministry of
Science and Higher Education (funds for 2010–2014) grant no. N N
403577938 and conducted with the use of equipment purchased by
Medical University of Bialystok as part of the OP DEP 2007–2013,
Priority Axis I.3, contract no. POPW.01.03.00-20-022/09. The
authors wish to thank Joanna Kisluk, PhD and Anna
Michalska-Falkowska, PhD for editing and preparing the manuscript
for publication.
References
|
1
|
Schulte-Merker S, Sabine A and Petrova TV:
Lymphatic vascular morphogenesis in development, physiology, and
disease. J Cell Biol. 193:607–618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alitalo K, Tammela T and Petrova TV:
Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature.
438:946–953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Achen MG, McColl BK and Stacker SA: Focus
on lymphangiogenesis in tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell. 7:121–127.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alitalo A and Detmar M: Interaction of
tumor cells and lymphatic vessels in cancer progression. Oncogene.
31:4499–4508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stachura J, Wachowska M, Kilarski WW, Güç
E, Golab J and Muchowicz A: The dual role of tumor lymphatic
vessels in dissemination of metastases and immune response
development. Oncoimmunology. 5:e11822782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shields JD: Lymphatics: At the interface
of immunity, tolerance, and tumor metastasis. Microcirculation.
18:517–531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M,
Compagni A, Baetens D, Prevo R, Banerji S, Huarte J, Montesano R,
Jackson DG, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated
lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 20:672–682.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo
R, Janes L, Velasco P, Riccardi L, Alitalo K, Claffey K and Detmar
M: Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast
cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 7:192–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stacker SA, Caesar C, Baldwin ME, Thornton
GE, Williams RA, Prevo R, Jackson DG, Nishikawa S, Kubo H and Achen
MG: VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the
lymphatics. Nat Med. 7:186–191. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hoshida T, Isaka N, Hagendoorn J, di
Tomaso E, Chen YL, Pytowski B, Fukumura D, Padera TP and Jain RK:
Imaging steps of lymphatic metastasis reveals that vascular
endothelial growth factor-C increases metastasis by increasing
delivery of cancer cells to lymph nodes: Therapeutic implications.
Cancer Res. 66:8065–8075. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K,
Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T and Alitalo K: Suppression of tumor
lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst.
94:819–825. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Z, Varney ML, Backora MW, Cowan K,
Solheim JC, Talmadge JE and Singh RK: Down-regulation of vascular
endothelial cell growth factor-C expression using small interfering
RNA vectors in mammary tumors inhibits tumor lymphangiogenesis and
spontaneous metastasis and enhances survival. Cancer Res.
65:9004–9011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Renyi-Vamos F, Tovari J, Fillinger J,
Timar J, Paku S, Kenessey I, Ostoros G, Agocs L, Soltesz I and Dome
B: Lymphangiogenesis correlates with lymph node metastasis,
prognosis, and angiogenic phenotype in human non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7344–7353. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miyahara M, Tanuma J, Sugihara K and Semba
I: Tumor lymphangiogenesis correlates with lymph node metastasis
and clinicopathologic parameters in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer. 110:1287–1294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Imabun
S, Nakahara M, Nakao K, Nakamura M, Mori I and Kakudo K: Lymph
vessel density correlates with nodal status, VEGF-C expression, and
prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 91:125–132.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Agarwal B, Saxena R, Morimiya A, Mehrotra
S and Badve S: Lymphangiogenesis does not occur in breast cancer.
Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1449–1455. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Van der Schaft DW, Pauwels P, Hulsmans S,
Zimmermann M, van de Poll-Franse LV and Griffioen AW: Absence of
lymphangiogenesis in ductal breast cancer at the primary tumor
site. Cancer Lett. 254:128–136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Williams CS, Leek RD, Robson AM, Banerji
S, Prevo R, Harris AL and Jackson DG: Absence of lymphangiogenesis
and intratumoural lymph vessels in human metastatic breast cancer.
J Pathol. 200:195–206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trojan L, Michel MS, Rensch F, Jackson DG,
Alken P and Grobholz R: Lymph and blood vessel architecture in
benign and malignant prostatic tissue: Lack of lymphangiogenesis in
prostate carcinoma assessed with novel lymphatic marker lymphatic
vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor (LYVE-1). J Urol.
172:103–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis
E, Simopoulos C, Gatter KC, Harris AL and Jackson DG: LYVE-1
immunohistochemical assessment of lymphangiogenesis in endometrial
and lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 58:202–206. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steinskog ES, Sagstad SJ, Wagner M,
Karlsen TV, Yang N, Markhus CE, Yndestad S, Wiig H and Eikesdal HP:
Impaired lymphatic function accelerates cancer growth. Oncotarget.
7:45789–45802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Achen MG and Stacker SA: Molecular control
of lymphatic metastasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1131:225–234. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirakawa S: Regulation of pathological
lymphangiogenesis requires factors distinct from those governing
physiological lymphangiogenesis. J Dermatol Sci. 61:85–93. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng W, Aspelund A and Alitalo K:
Lymphangiogenic factors, mechanisms, and applications. J Clin
Invest. 124:878–887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yoshimatsu Y, Miyazaki H and Watabe T:
Roles of signaling and transcriptional networks in pathological
lymphangiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:161–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sobin LH and Compton CC: TNM seventh
edition: What's new, what's changed: Communication from the
international union against cancer and the American joint committee
on cancer. Cancer. 116:5336–5339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Niklinski J, Kretowski A, Moniuszko M,
Reszec J, Michalska-Falkowska A, Niemira M, Ciborowski M,
Charkiewicz R, Jurgilewicz D, Kozlowski M, et al: Systematic
biobanking, novel imaging techniques, and advanced molecular
analysis for precise tumor diagnosis and therapy: The Polish MOBIT
project. Adv Med Sci. 62:405–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Endoh H, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Konishi H,
Osada H, Tajima K, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T:
Prognostic model of pulmonary adenocarcinoma by expression
profiling of eight genes as determined by quantitative real-time
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Oncol.
22:811–819. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
Cancer Statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Detterbeck FC, Postmus PE and Tanoue LT:
The stage classification of lung cancer: Diagnosis and management
of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American college of chest physicians
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 143 5
Suppl:e191S–e210S. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Albrecht I and Christofori G: Molecular
mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in development and cancer. Int J
Dev Biol. 55:483–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gomes FG, Nedel F, Alves AM, Nör JE and
Tarquinio SB: Tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis:
Tumor/endothelial crosstalk and cellular/microenvironmental
signaling mechanisms. Life Sci. 92:101–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Regan E, Sibley RC, Cenik BK, Silva A,
Girard L, Minna JD and Dellinger MT: Identification of gene
expression differences between lymphangiogenic and
non-lymphangiogenic non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. PLoS
One. 11:e01509632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jackson DG: Biology of the lymphatic
marker LYVE-1 and applications in research into lymphatic
trafficking and lymphangiogenesis. APMIS. 112:526–538. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu M, Du Y, Liu Y, He Y, Yang C, Wang W
and Gao F: Low molecular weight hyaluronan induces
lymphangiogenesis through LYVE-1-mediated signaling pathways. PLoS
One. 9:e928572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu X and Liu NF: FOXC2 transcription
factor: A novel regulator of lymphangiogenesis. Lymphology.
44:35–41. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan Y and Xia L: Emerging roles of
podoplanin in vascular development and homeostasis. Front Med.
9:421–430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baluk P and McDonald DM: Markers for
microscopic imaging of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1131:1–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Elsir T, Smits A, Lindström MS and Nistér
M: Transcription factor PROX1: Its role in development and cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:793–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Watabe T: Roles of transcriptional network
during the formation of lymphatic vessels. J Biochem. 152:213–220.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sanmartín E, Sirera R, Usó M, Blasco A,
Gallach S, Figueroa S, Martínez N, Hernando C, Honguero A,
Martorell M, et al: A gene signature combining the tissue
expression of three angiogenic factors is a prognostic marker in
early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:612–620.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Takizawa H, Kondo K, Fujino H, Kenzaki K,
Miyoshi T, Sakiyama S and Tangoku A: The balance of VEGF-C and
VEGFR-3 mRNA is a predictor of lymph node metastasis in non-small
cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 95:75–79. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Feng Y, Wang W, Hu J, Ma J, Zhang Y and
Zhang J: Expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D as significant markers for
assessment of lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 293:802–812. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Maekawa S, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Enatsu
S, Kawakami T and Kuroki M and Kuroki M: Correlation between lymph
node metastasis and the expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in
T1 lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 27:3735–3741.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li J, Yi H, Liu Z, Zhang H, Zhang D, Yue
W, Jia H, Xu S and Li B: Association between VEGFR-3 expression and
lymph node metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med.
9:389–394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kilvaer TK, Paulsen EE, Hald SM, Wilsgaard
T, Bremnes RM, Busund LT and Donnem T: Lymphangiogenic markers and
their impact on nodal metastasis and survival in non-small cell
lung cancer-a structured review with meta analysis. PLoS One.
10:e01324812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng CL, Qiu C, Shen MX, Qu X, Zhang TH,
Zhang JH and Du JJ: Prognostic impact of elevation of vascular
endothelial growth factor family expression in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:1881–1895. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang Z, Luo G, Tang H, Cheng C and Wang
P: Prognostic significance of high VEGF-C expression for patients
with breast cancer: An update meta analysis. PLoS One.
11:e01657252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zong S, Li H, Shi Q, Liu S, Li W and Hou
F: Prognostic significance of VEGF-C immunohistochemical expression
in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 458:106–114.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xia H, Shen J, Chen S, Huang H, Xu Y and
Ma H: Overexpression of VEGF-C correlates with a poor prognosis in
esophageal cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 17:165–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kato S, Shimoda H, Ji RC and Miura M:
Lymphangiogenesis and expression of specific molecules as lymphatic
endothelial cell markers. Anat Sci Int. 81:71–83. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jackson DG: Immunological functions of
hyaluronan and its receptors in the lymphatics. Immunol Rev.
230:216–231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ugorski M, Dziegiel P and Suchanski J:
Podoplanin-a small glycoprotein with many faces. Am J Cancer Res.
6:370–386. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Akl MR, Nagpal P, Ayoub NM, Tai B, Prabhu
SA, Capac CM, Gliksman M, Goy A and Suh KS: Molecular and clinical
significance of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2/bFGF) in
malignancies of solid and hematological cancers for personalized
therapies. Oncotarget. 7:44735–44762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kowalczyk AP and Green KJ: Structure,
function, and regulation of desmosomes. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
116:95–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huber O and Petersen I: 150th anniversary
series: Desmosomes and the hallmarks of cancer. Cell Commun Adhes.
22:15–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Krisenko MO and Geahlen RL: Calling in
SYK: SYK's dual role as a tumor promoter and tumor suppressor in
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:254–263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bazigou E, Xie S, Chen C, Weston A, Miura
N, Sorokin L, Adams R, Muro AF, Sheppard D and Makinen T:
Integrin-alpha9 is required for fibronectin matrix assembly during
lymphatic valve morphogenesis. Dev Cell. 17:175–186. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Rizzolio S and Tamagnone L: Multifaceted
role of neuropilins in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 18:3563–3575. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zachary I: Neuropilins: Role in
signalling, angiogenesis and disease. Chem Immunol Allergy.
99:37–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sasahira T, Ueda N, Yamamoto K, Kurihara
M, Matsushima S, Bhawal UK, Kirita T and Kuniyasu H: Prox1 and
FOXC2 act as regulators of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e925342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Prud'homme GJ and Glinka Y: Neuropilins
are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation,
growth, metastasis and immunity. Oncotarget. 3:921–939. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jiang W, Fan H, Qian C, Ding J, Wang Q and
Pang X: Prognostic value of high FoxC2 expression in resectable
non-small cell lung cancer, alone or in combination with E-cadherin
expression. BMC Cancer. 16:162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhu JL, Song YX, Wang ZN, Gao P, Wang MX,
Dong YL, Xing CZ and Xu HM: The clinical significance of mesenchyme
forkhead 1 (FoxC2) in gastric carcinoma. Histopathology.
62:1038–1048. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nishida N, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Sudo T,
Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y and Mori M: FOXC2 is a novel
prognostic factor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Surg Oncol. 18:535–542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Skog M, Bono P, Lundin M, Lundin J,
Louhimo J, Linder N, Petrova TV, Andersson LC, Joensuu H, Alitalo K
and Haglund CH: Expression and prognostic value of transcription
factor PROX1 in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 105:1346–1351.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Versmold B, Felsberg J, Mikeska T,
Ehrentraut D, Köhler J, Hampl JA, Röhn G, Niederacher D, Betz B,
Hellmich M, et al: Epigenetic silencing of the candidate tumor
suppressor gene PROX1 in sporadic breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
121:547–554. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Schneider M, Büchler P, Giese N, Giese T,
Wilting J, Büchler MW and Friess H: Role of lymphangiogenesis and
lymphangiogenic factors during pancreatic cancer progression and
lymphatic spread. Int J Oncol. 28:883–890. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Juchniewicz A, Niklińska W, Kowalczuk O,
Laudański W, Sulewska A, Dziegielewski P, Milewski R, Naumnik W,
Kozłowski M and Nikliński J: Prognostic value of vascular
endothelial growth factor-C and podoplanin mRNA expression in
esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:3668–3674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kadota K, Huang CL, Liu D, Nakashima N,
Yokomise H, Ueno M and Haba R: The clinical significance of the
tumor cell D2-40 immunoreactivity in non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 70:88–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Shimada Y, Ishii G, Nagai K, Atsumi N,
Fujii S, Yamada A, Yamane Y, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Yoshida J, et
al: Expression of podoplanin, CD44, and p63 in squamous cell
carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Sci. 100:2054–2059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ito T, Ishii G, Nagai K, Nagano T, Kojika
M, Murata Y, Atsumi N, Nishiwaki Y, Miyazaki E, Kumamoto T and
Ochiai A: Low podoplanin expression of tumor cells predicts poor
prognosis in pathological stage IB squamous cell carcinoma of the
lung, tissue microarray analysis of 136 patients using 24
antibodies. Lung Cancer. 63:418–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ikoma Y, Kijima H, Masuda R, Tanaka M,
Inokuchi S and Iwazaki M: Podoplanin expression is correlated with
the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res.
36:393–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Suzuki H, Onimaru M, Yonemitsu Y, Maehara
Y, Nakamura S and Sueishi K: Podoplanin in cancer cells is
experimentally able to attenuate prolymphangiogenic and
lymphogenous metastatic potentials of lung squamoid cancer cells.
Mol Cancer. 9:2872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kawakami T, Tokunaga T, Hatanaka H, Kijima
H, Yamazaki H, Abe Y, Osamura Y, Inoue H, Ueyama Y and Nakamura M:
Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly
correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in
nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 95:2196–2201. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K,
Delghandi MP, Persson M, Nilsen MN, Busund LT and Bremnes RM:
Inverse prognostic impact of angiogenic marker expression in tumor
cells versus stromal cells in non small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:6649–6657. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Donnem T, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S,
Delghandi MP, Busund LT and Bremnes RM: VEGF-A and VEGFR-3
correlate with nodal status in operable non-small cell lung cancer:
Inverse correlation between expression in tumor and stromal cells.
Lung Cancer. 63:277–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shahneh FZ, Baradaran B, Zamani F and
Aghebati-Maleki L: Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic
therapies. Hum Antibodies. 22:15–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ferrara N: Role of myeloid cells in
vascular endothelial growth factor-independent tumor angiogenesis.
Curr Opin Hematol. 17:219–224. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao Y and Adjei A: Targeting angiogenesis
in cancer therapy: Moving beyond vascular endothelial growth
factor. Oncologist. 20:660–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Donnem T, Hu J, Ferguson M, Adighibe O,
Snell C, Harris AL, Gatter KC and Pezzella F: Vessel co-option in
primary human tumors and metastases: An obstacle to effective
anti-angiogenic treatment? Cancer Med. 2:427–436. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bridgeman VL, Vermeulen PB, Foo S, Bilecz
A, Daley F, Kostaras E, Nathan MR, Wan E, Frentzas S, Schweiger T,
et al: Vessel co-option is common in human lung metastases and
mediates resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy in preclinical lung
metastasis models. J Pathol. 241:362–374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Vieira JM, Ruhrberg C and Schwarz Q: VEGF
receptor signaling in vertebrate development. Organogenesis.
6:97–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang SD, McCrudden CM and Kwok HF:
Prognostic significance of combining VEGFA, FLT1 and KDR mRNA
expression in lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:1893–1901. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pajares MJ, Agorreta J, Larrayoz M, Vesin
A, Ezponda T, Zudaire I, Torre W, Lozano MD, Brambilla E, Brambilla
C, et al: Expression of tumor-derived vascular endothelial growth
factor and its receptors is associated with outcome in early
squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J Clin Oncol. 30:1129–1136.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|