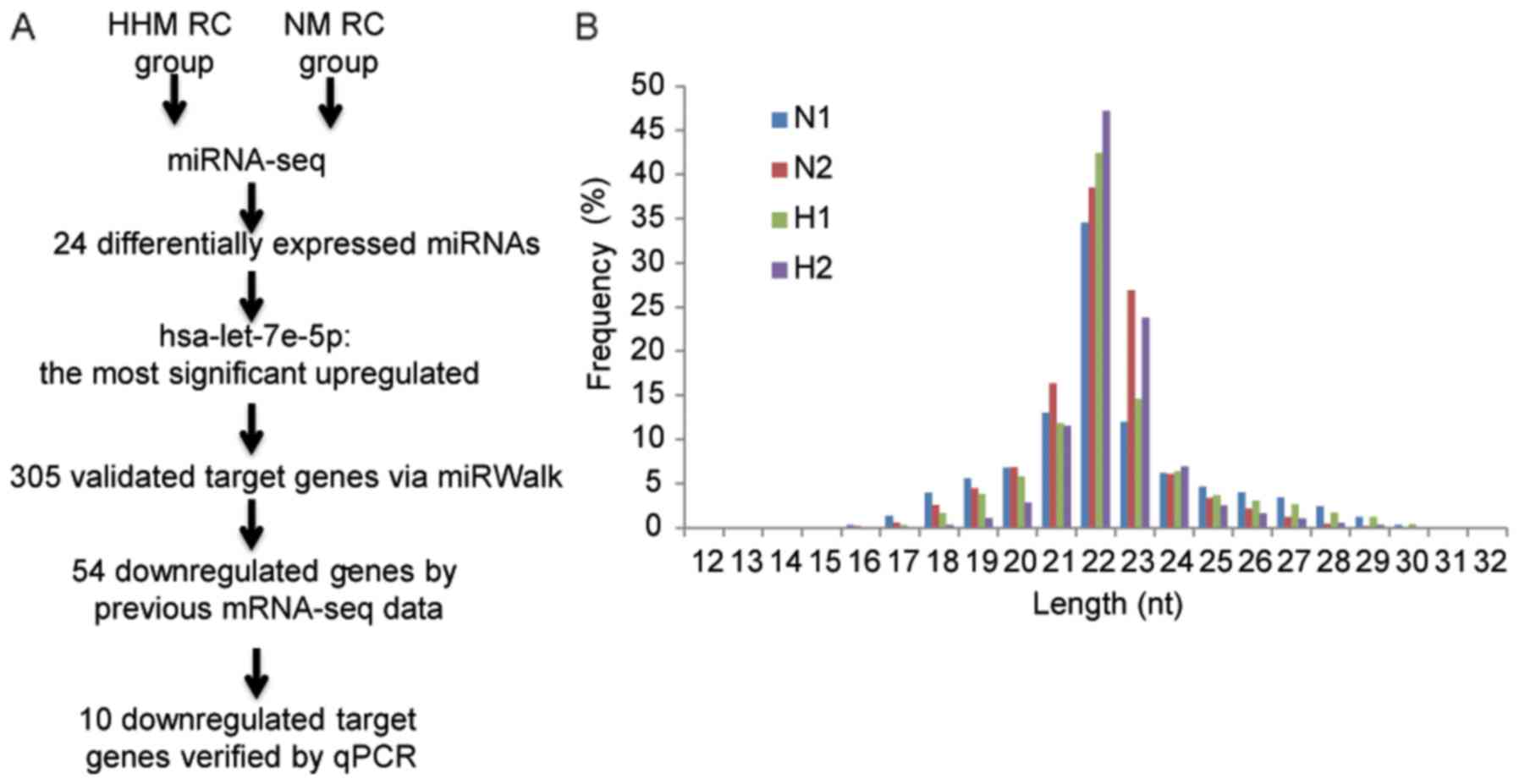
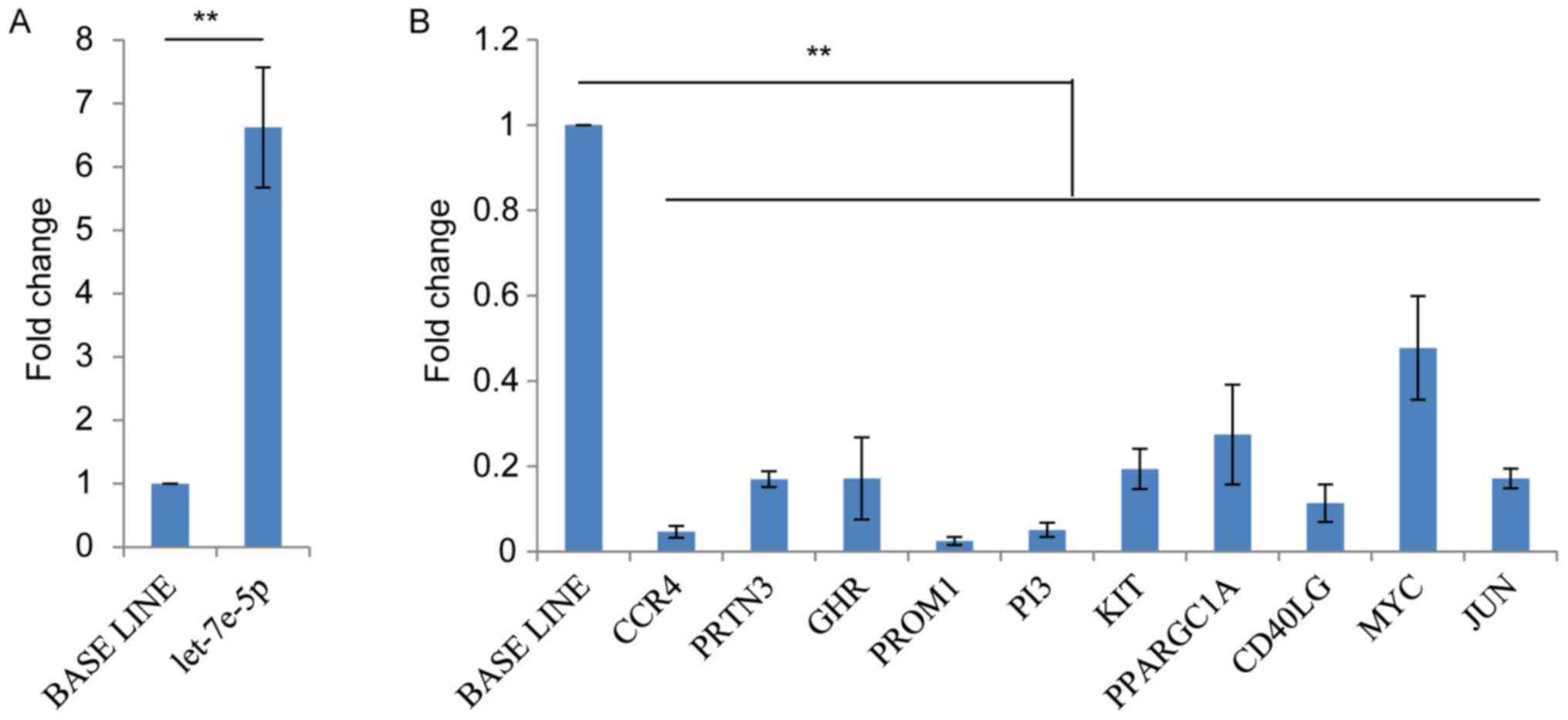
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Charnley RM
and Scheele J: Factors influencing the natural history of
colorectal liver metastases. Lancet. 343:1405–1410. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Geramizadeh B and Robertson S: Serrated
polyps of colon and rectum: A clinicopathologic review. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 48:291–298. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ji D, Chen Z, Li M, Zhan T, Yao Y, Zhang
Z, Xi J, Yan L and Gu J: MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and
liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor
suppressor WIF-1. Mol Cancer. 13:862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, Coatmeur O,
Faivre J and Bouvier AM: Epidemiology and management of liver
metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 244:254–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sobhani I, Tap J, Roudot-Thoraval F,
Roperch JP, Letulle S, Langella P, Corthier G, Van Nhieu Tran J and
Furet JP: Microbial dysbiosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
PLoS One. 6:e163932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu T, Weng S, Tang W, Xue R, Chen S, Cai
G, Cai Y, Shen X, Zhang S and Dong L: Overexpression of BIRC6 is a
predictor of prognosis for colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01252812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du T and Zamore PD: microPrimer: The
biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 132:4645–4652.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lai EC: Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′
UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional
regulation. Nat Genet. 30:363–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Du L, Wen Z, Yang Y, Li J, Wang L,
Zhang X, Liu Y, Dong Z, Li W, et al: Up-regulation of miR-182
expression in colorectal cancer tissues and its prognostic value.
Int J Colorectal Dis. 28:697–703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shivapurkar N, Mikhail S, Navarro R, Bai
W, Marshall J, Hwang J, Pishvaian M, Wellstein A and He AR:
Decrease in blood miR-296 predicts chemotherapy resistance and poor
clinical outcome in patients receiving systemic chemotherapy for
metastatic colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 28:8872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou T, Zhang G, Liu Z, Xia S and Tian H:
Overexpression of miR-92a correlates with tumor metastasis and poor
prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis.
28:19–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rotelli MT, Di Lena M, Cavallini A,
Lippolis C, Bonfrate L, Chetta N, Portincasa P and Altomare DF:
Fecal microRNA profile in patients with colorectal carcinoma before
and after curative surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 30:891–898. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jr CMT, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM and Mattox
KL: Sabiston Textbook of Surgery: The Biological Basis of Modern
Surgical Practice. 18th edition. Saunders; 2008
|
|
17
|
Benson AB III, Venook AP, Bekaii-Saab T,
Chan E, Chen YJ, Cooper HS, Engstrom PF, Enzinger PC, Fenton MJ,
Grem JL, et al: Rectal cancer, version 2.2015. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 13:719–728. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou YJ, Xie YT, Gu J, Yan L, Guan GX and
Liu X: Overexpression of cyclin E isoforms correlates with poor
prognosis in rectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 37:1078–1084. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The american joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tapan U, Ozbayrak M and Tatli S: MRI in
local staging of rectal cancer: An update. Diagn Interv Radiol.
20:390–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai X, Liu G, Lu Y and Yin W: Accuracy of
endoscopic ultrasound in the preoperative staging and the guidance
of transanal endoscopic microsurgery for rectal cancer. Zhonghua
Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 18:487–490. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwak Y, Lee HE, Kim WH, Kim DW, Kang SB
and Lee HS: The clinical implication of cancer-associated
microvasculature and fibroblast in advanced colorectal cancer
patients with synchronous or metachronous metastases. PLoS One.
9:e918112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Engstrom PF, Arnoletti JP, Benson AB III,
Chen YJ, Choti MA, Cooper HS, Covey A, Dilawari RA, Early DS,
Enzinger PC, et al: NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology:
Rectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 7:838–881. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fuchs RT, Sun Z, Zhuang F and Robb GB:
Bias in ligation-based small RNA sequencing library construction is
determined by adaptor and RNA structure. PLoS One. 10:e01260492015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu F, Peng W, Li Z, Li W, Li L, Pan J,
Zhang S, Miao Y, Chen S and Su S: Next-generation small RNA
sequencing for microRNAs profiling in Apis mellifera: Comparison
between nurses and foragers. Insect Mol Biol. 21:297–303. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, Lam TW, Yiu SM,
Kristiansen K and Wang J: SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for
short read alignment. Bioinformatics. 25:1966–1967. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Audic S and Claverie JM: The significance
of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 7:986–995. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye J, Fang L, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Chen J,
Zhang Z and Wang J, Li S, Li R, Bolund L and Wang J: WEGO: A web
tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:(Web Server
Issue). W293–W297. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:(Database Issue). D480–D484.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking‘ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dweep H, Gretz N and Sticht C: miRWalk
database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1182:289–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu H, Radisky DC, Yang D, Xu R, Radisky
ES, Bissell MJ and Bishop JM: MYC suppresses cancer metastasis by
direct transcriptional silencing of αv and β3 integrin subunits.
Nat Cell Biol. 14:567–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gavert N, Shvab A, Sheffer M, Ben-Shmuel
A, Haase G, Bakos E, Domany E and Ben-Ze'ev A: c-Kit is suppressed
in human colon cancer tissue and contributes to L1-mediated
metastasis. Cancer Res. 73:5754–5763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Kinkade CW,
Lefebvre C, Lei M, Phelan V, LeKaye HC, Koutcher JA, Cardiff RD,
Califano A, et al: ETV4 promotes metastasis in response to
activation of PI3-kinase and Ras signaling in a mouse model of
advanced prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E3506–E3515.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Pu X, Shi M, Chen L, Song Y, Qian
L, Yuan G, Zhang H, Yu M, Hu M, et al: Critical role of c-Jun
overexpression in liver metastasis of human breast cancer xenograft
model. BMC Cancer. 7:1452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ness TL, Ewing JL, Hogaboam CM and Kunkel
SL: CCR4 is a key modulator of innate immune responses. J Immunol.
177:7531–7539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Elgueta R, Benson MJ, de Vries VC, Wasiuk
A, Guo Y and Noelle RJ: Molecular mechanism and function of
CD40/CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol Rev.
229:152–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang H and Ward WF: PGC-1alpha: A key
regulator of energy metabolism. Adv Physiol Educ. 30:145–151. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Lee KD, Bae YK, Sung KW,
Nam SJ and Chun KH: MicroRNA let-7a suppresses breast cancer cell
migration and invasion through downregulation of C-C chemokine
receptor type 7. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liang S, He L, Zhao X, Miao Y, Gu Y, Guo
C, Xue Z, Dou W, Hu F, Wu K, et al: MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor
invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer.
PLoS One. 6:e184092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu X, Guo J, Zheng L, Li C, Zheng TM,
Tanyi JL, Liang S, Benedetto C, Mitidieri M, Katsaros D, et al: The
heterochronic microRNA let-7 inhibits cell motility by regulating
the genes in the actin cytoskeleton pathway in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 11:240–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ohshima K, Inoue K, Fujiwara A, Hatakeyama
K, Kanto K, Watanabe Y, Muramatsu K, Fukuda Y, Ogura S, Yamaguchi K
and Mochizuki T: Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into
the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric
cancer cell line. PLoS One. 5:e132472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yun J, Frankenberger CA, Kuo WL, Boelens
MC, Eves EM, Cheng N, Liang H, Li WH, Ishwaran H, Minn AJ and
Rosner MR: Signalling pathway for RKIP and Let-7 regulates and
predicts metastatic breast cancer. EMBO J. 30:4500–4514. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meyer N and Penn LZ: Reflecting on 25
years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:976–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM and Prochownik EV:
MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 18:3004–3016.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liao DJ and Dickson RB: c-Myc in breast
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 7:143–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Adhikary S and Eilers M: Transcriptional
regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 6:635–645. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fang Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Meng Y, Zhu J, Jin
H, Li J, Zhang D, Yu Y, Wu XR and Huang C: A new tumour suppression
mechanism by p27Kip1: EGFR down-regulation mediated by JNK/c-Jun
pathway inhibition. Biochem J. 463:383–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
LeBleu VS, O'Connell JT, Herrera Gonzalez
KN, Wikman H, Pantel K, Haigis MC, de Carvalho FM, Damascena A,
Chinen Domingos LT, Rocha RM, et al: PGC-1α mediates mitochondrial
biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells to promote
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 16(992–1003): 1–15. 2014.
|