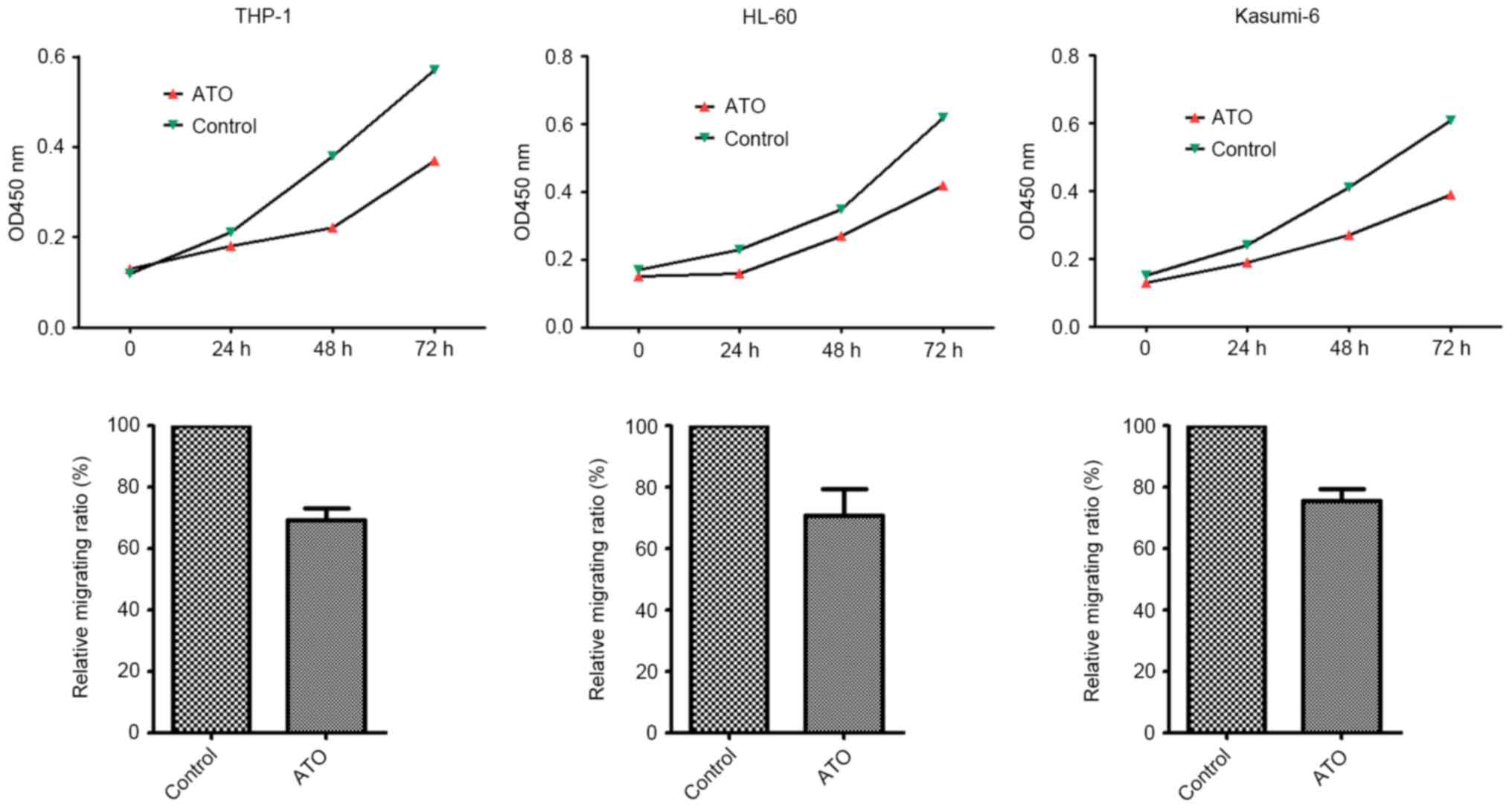
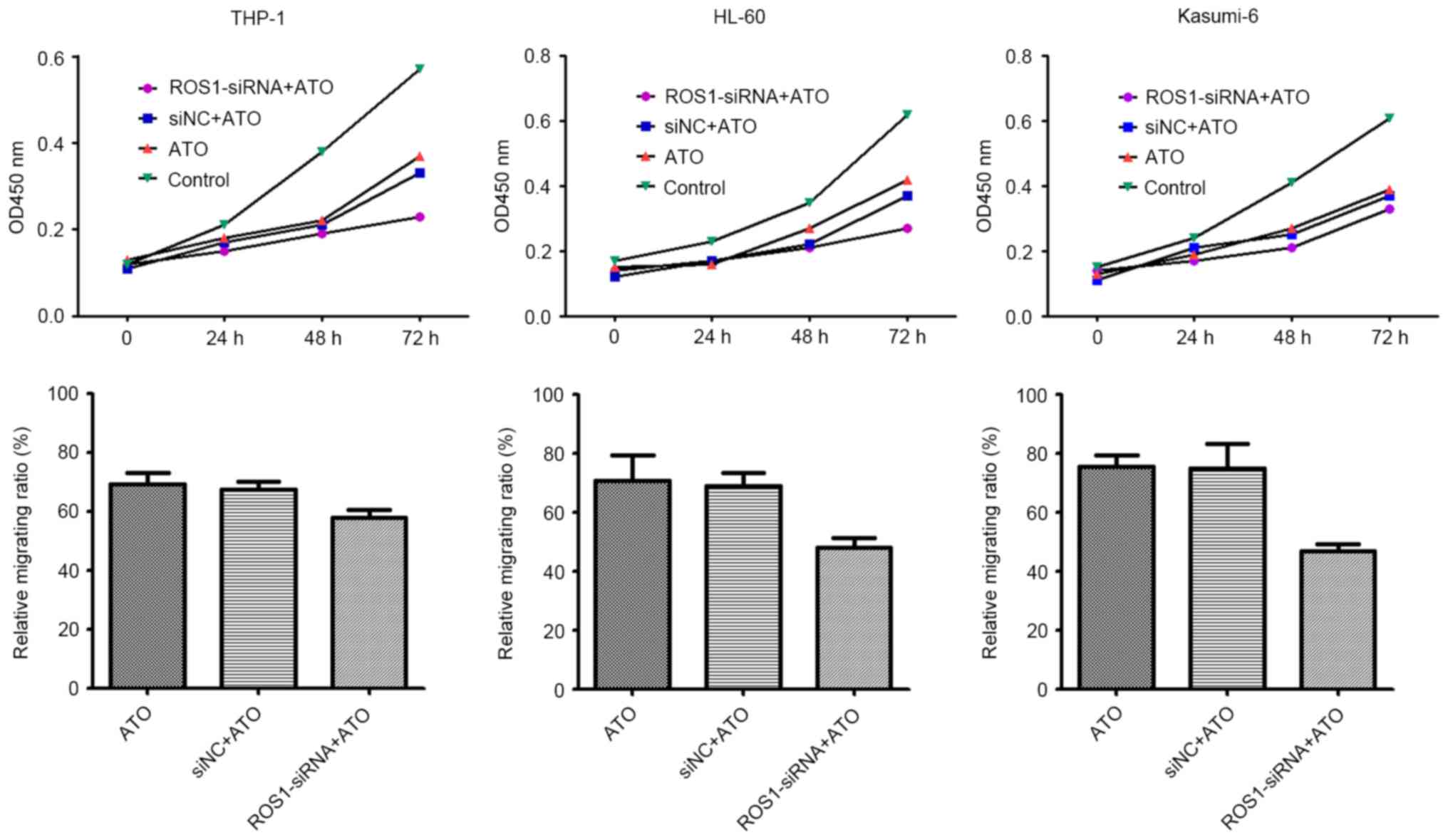
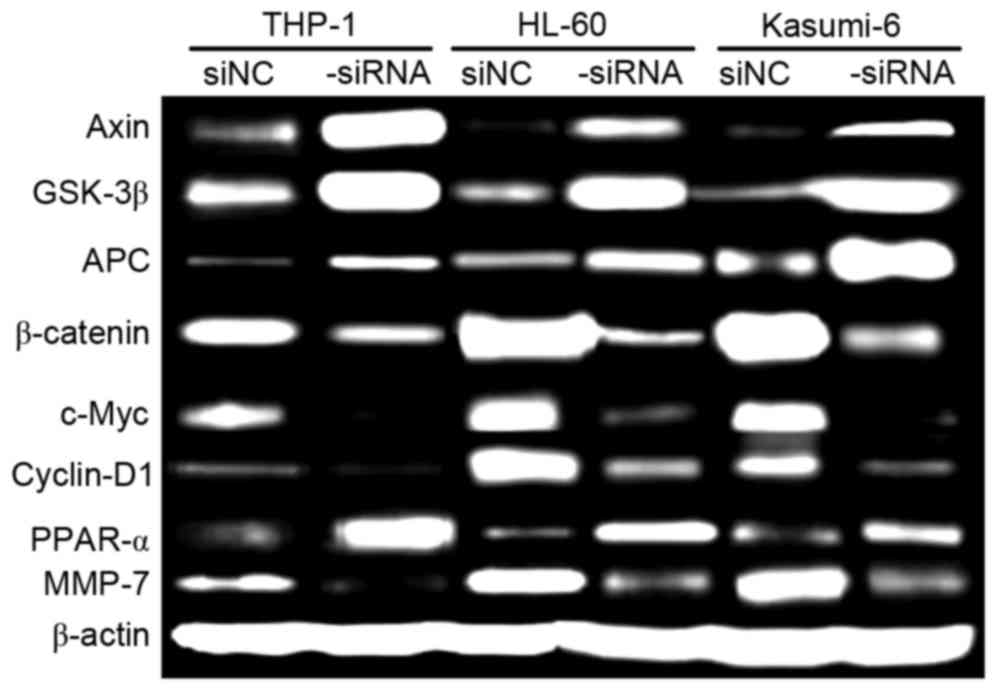
|
1
|
Estey E and Döhner H: Acute myeloid
leukaemia. Lancet. 368:1894–1907. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Estey EH: Acute myeloid leukemia: 2013
update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol.
88:318–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coombs CC, Tavakkoli M and Tallman MS:
Acute promyelocytic leukemia: Where did we start, where are we now,
and the future. Blood Cancer J. 5:e3042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cicconi L and Lo-Coco F: Current
management of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann
Oncol. 27:1474–1481. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lo-Coco F, Cicconi L and Breccia M:
Current standard treatment of adult acute promyelocytic leukaemia.
Br J Haematol. 172:841–854. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanz MA and Lo-Coco F: Modern approaches
to treating acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 29:495–503.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu J, Chen Z, Lallemand-Breitenbach V and
de Thé H: How acute promyelocytic leukaemia revived arsenic. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:705–713. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Thé H and Chen Z: Acute promyelocytic
leukaemia: Novel insights into the mechanisms of cure. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:775–783. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takahashi S: Combination therapy with
arsenic trioxide for hematological malignancies. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 10:504–510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shaw AT, Hsu PP, Awad MM and Engelman JA:
Tyrosine kinase gene rearrangements in epithelial malignancies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:772–787. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Deeb IM, Yoo KH and Lee SH: ROS
receptor tyrosine kinase: A new potential target for anticancer
drugs. Med Res Rev. 31:794–818. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye M, Zhang X, Li N, Zhang Y, Jing P,
Chang N, Wu J, Ren X and Zhang J: ALK and ROS1 as targeted therapy
paradigms and clinical implications to overcome crizotinib
resistance. Oncotarget. 7:12289–12304. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arnaoutakis K: Crizotinib in
ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
372:6832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gold KA: ROS1-targeting the one percent in
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 371:2030–2031. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lambros L, Guibourg B and Uguen A:
ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers with concomitant
oncogenic driver alterations: About some rare therapeutic dilemmas.
Clin Lung Cancer. 19:e73–e74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murgo AJ: Clinical trials of arsenic
trioxide in hematologic and solid tumors: Overview of the national
cancer institute cooperative research and development studies.
Oncologist. 6 Suppl 2:S22–S28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tallman MS: What is the role of arsenic in
newly diagnosed APL? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 21:659–666.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Berenson JR and Yeh HS: Arsenic compounds
in the treatment of multiple myeloma: A new role for a historical
remedy. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 7:192–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Evens AM, Tallman MS and Gartenhaus RB:
The potential of arsenic trioxide in the treatment of malignant
disease: Past, present, and future. Leuk Res. 28:891–900. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baj G, Arnulfo A, Deaglio S, Mallone R,
Vigone A, De Cesaris MG, Surico N, Malavasi F and Ferrero E:
Arsenic trioxide and breast cancer: Analysis of the apoptotic,
differentiative and immunomodulatory effects. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 73:61–73. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Z, Chen GQ, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Tong JH,
Wang ZY and Chen SJ: Expanding the use of arsenic trioxide:
Leukemias and beyond. Semin Hematol. 39 2 Suppl 1:S22–S26. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dilda PJ and Hogg PJ: Arsenical-based
cancer drugs. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:542–564. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Verstovsek S, Giles F, Quintás-Cardama A,
Perez N, Ravandi-Kashani F, Beran M, Freireich E and Kantarjian H:
Arsenic derivatives in hematologic malignancies: A role beyond
acute promyelocytic leukemia? Hematol Oncol. 24:181–188. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eaves CJ and Humphries RK: Acute myeloid
leukemia and the Wnt pathway. N Engl J Med. 362:2326–2327. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caye A, Strullu M, Guidez F, Cassinat B,
Gazal S, Fenneteau O, Lainey E, Nouri K, Nakhaei-Rad S, Dvorsky R,
et al: Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia displays mutations in
components of the RAS pathway and the PRC2 network. Nat Genet.
47:1334–1340. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang H, Peng C, Hu Y, Li H, Sheng Z, Chen
Y, Sullivan C, Cerny J, Hutchinson L, Higgins A, et al: The Blk
pathway functions as a tumor suppressor in chronic myeloid leukemia
stem cells. Nat Genet. 44:861–871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kühnl A, Valk PJ, Sanders MA, Ivey A,
Hills RK, Mills KI, Gale RE, Kaiser MF, Dillon R, Joannides M, et
al: Downregulation of the Wnt inhibitor CXXC5 predicts a better
prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 125:2985–2994. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, North TE,
Goessling W, Feng Z, Zon LI and Armstrong SA: The Wnt/beta-catenin
pathway is required for the development of leukemia stem cells in
AML. Science. 327:1650–1653. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heidel FH, Bullinger L, Feng Z, Wang Z,
Neff TA, Stein L, Kalaitzidis D, Lane SW and Armstrong SA: Genetic
and pharmacologic inhibition of β-catenin targets
imatinib-resistant leukemia stem cells in CML. Cell Stem Cell.
10:412–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kleppe M and Levine RL: Targeting
β-catenin in CML: Leukemia stem cells beware! Cell Stem Cell.
10:351–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hoffmeyer K, Raggioli A, Rudloff S, Anton
R, Hierholzer A, Del Valle I, Hein K, Vogt R and Kemler R:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates telomerase in stem cells and
cancer cells. Science. 336:1549–1554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morikawa T, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M,
Meyerhardt JA, Shima K, Nosho K, Chan AT, Giovannucci E, Fuchs CS
and Ogino S: Association of CTNNB1 (beta-catenin) alterations, body
mass index, and physical activity with survival in patients with
colorectal cancer. JAMA. 305:1685–1694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang K, Li N, Yeung CH, Cooper TG, Liu XX,
Liu J, Wang WT, Li Y, Shi H and Liu FJ: Comparison of gene
expression of the oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
components in the mouse and human epididymis. Asian J Androl.
17:1006–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|