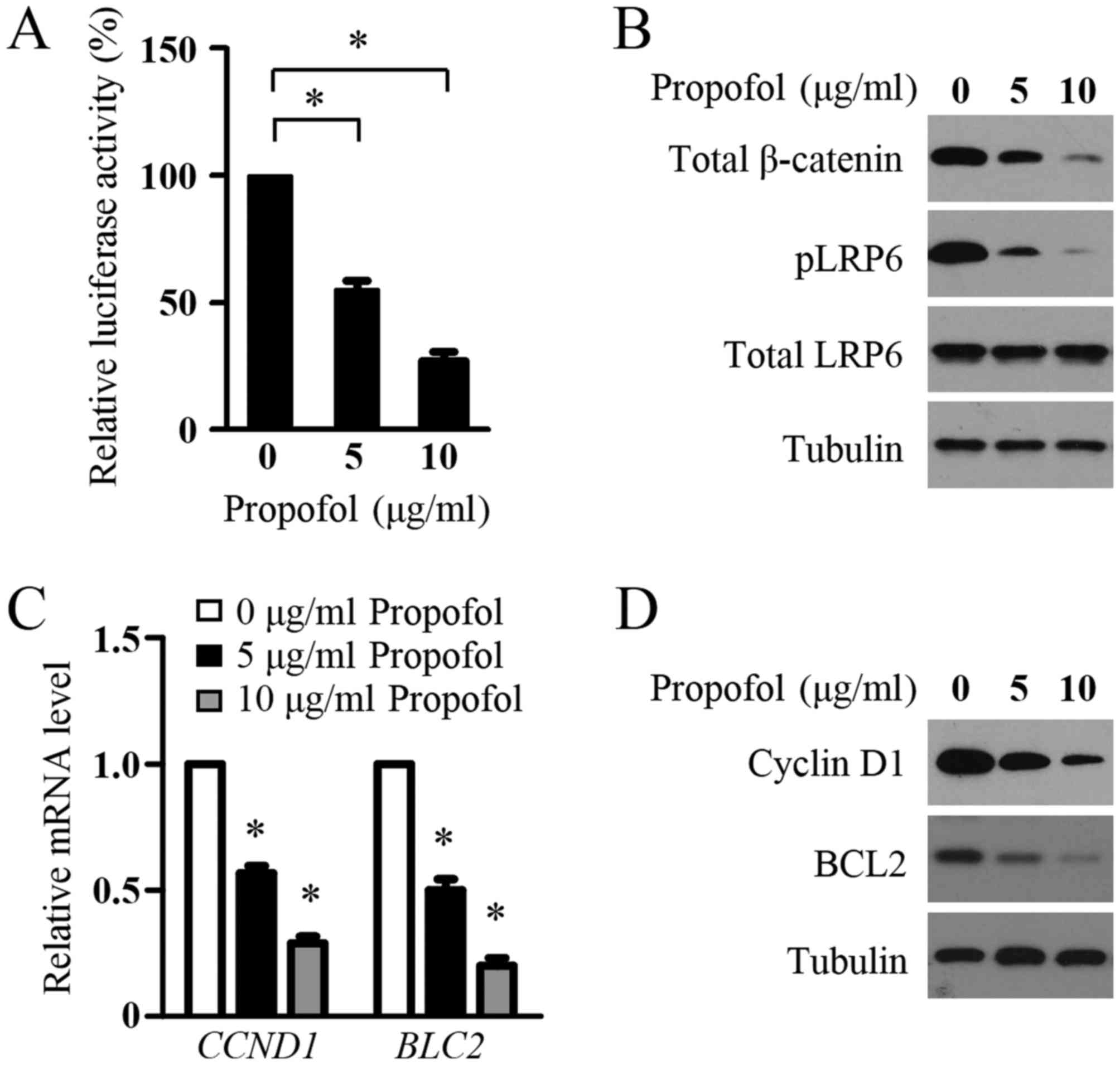
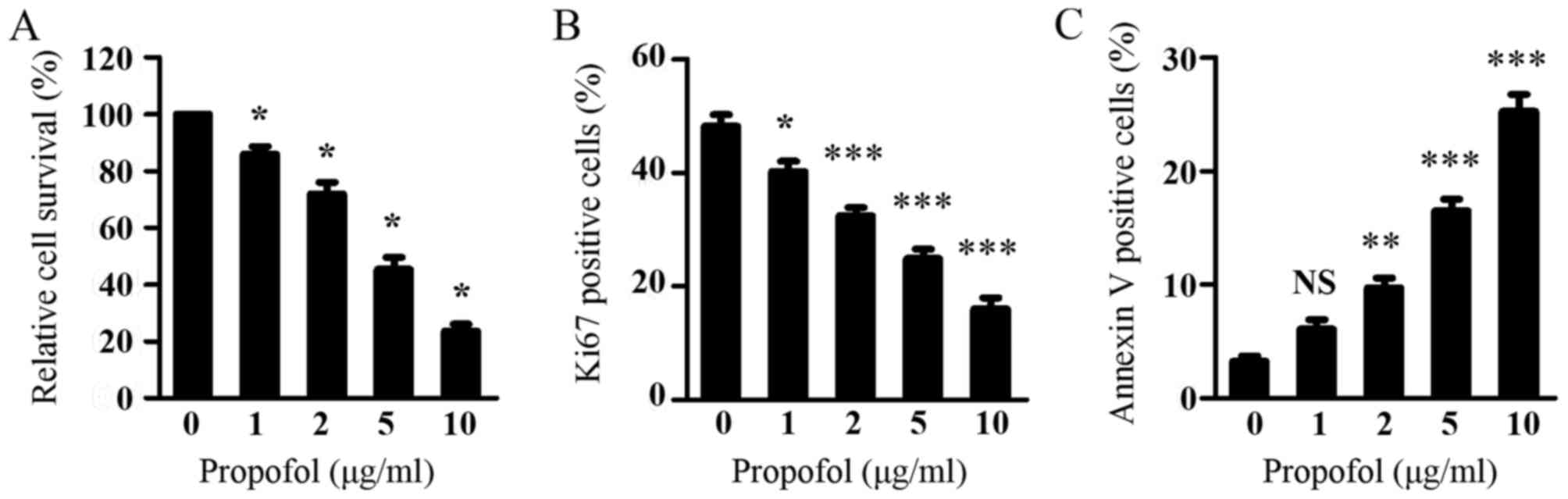
|
1
|
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Tischfield M, Williams J,
Smallwood PM, Rattner A, Taketo MM and Nathans J: Canonical WNT
signaling components in vascular development and barrier formation.
J Clin Invest. 124:3825–3846. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiurillo MA: Role of the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer: An in-depth literature review. World J
Exp Med. 5:84–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kahn M: Can we safely target the WNT
pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:513–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou L and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signalling
and podocyte dysfunction in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 11:535–545. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inestrosa NC and Varela-Nallar L: Wnt
signalling in neuronal differentiation and development. Cell Tissue
Res. 359:215–223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Louis DN: Molecular pathology of malignant
gliomas. Ann Rev Pathol. 1:97–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee Y, Lee JK, Ahn SH, Lee J and Nam DH:
WNT signaling in glioblastoma and therapeutic opportunities. Lab
Invest. 96:137–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang K, Zhang J, Han L, Pu P and Kang C:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in glioma. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
7:740–749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Tu Y, Sun X, Jiang J, Jin X, Bo X,
Li Z, Bian A, Wang X, Liu D, et al: Wnt/beta-Catenin pathway in
human glioma: Expression pattern and clinical/prognostic
correlations. Clin Exp Med. 11:105–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Augustin I, Goidts V, Bongers A, Kerr G,
Vollert G, Radlwimmer B, Hartmann C, Herold-Mende C, Reifenberger
G, von Deimling A and Boutros M: The Wnt secretion protein
Evi/Gpr177 promotes glioma tumourigenesis. EMBO Mol Med. 4:38–51.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sareddy GR, Panigrahi M, Challa S,
Mahadevan A and Babu PP: Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf
signaling pathway in human astrocytomas. Neurochem Int. 55:307–317.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT,
Colman H, Huang H, Xue J, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: FoxM1 promotes
β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene
expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 20:427–442. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Huang K, Shi Z, Zou J, Wang Y,
Jia Z, Zhang A, Han L, Yue X, Liu N, et al: High β-catenin/Tcf-4
activity confers glioma progression via direct regulation of AKT2
gene expression. Neuro Oncol. 13:600–609. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Foltz G, Yoon JG, Lee H, Ma L, Tian Q,
Hood L and Madan A: Epigenetic regulation of wnt pathway
antagonists in human glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Cancer.
1:81–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mizobuchi Y, Matsuzaki K, Kuwayama K,
Kitazato K, Mure H, Kageji T and Nagahiro S: REIC/Dkk-3 induces
cell death in human malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 10:244–253.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marik PE: Propofol: Therapeutic
indications and side-effects. Curr Pharm Des. 10:3639–3649. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen X, Lu P, Chen L, Yang SJ, Shen HY, Yu
DD, Zhang XH, Zhong SL, Zhao JH and Tang JH: Perioperative
propofol-paravertebral anesthesia decreases the metastasis and
progression of breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:8259–8266. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui WY, Liu Y, Zhu YQ, Song T and Wang QS:
Propofol induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis in
lung cancer cell H460. Tumour Biol. 35:5213–5217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miao Y, Zhang Y, Wan H, Chen L and Wang F:
GABA-receptor agonist, propofol inhibits invasion of colon
carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 64:583–588. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang D, Zhou XH, Zhang J, Zhou YX, Ying
J, Wu GQ and Qian JH: Propofol promotes cell apoptosis via
inhibiting HOTAIR mediated mTOR pathway in cervical cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 468:561–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Wu Q, You L, Chen S, Zhu M and
Miao C: Propofol attenuates pancreatic cancer malignant potential
via inhibition of NMDA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 795:150–159.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang C, Gao J, Yan N, Wu B, Ren Y, Li H
and Liang J: Propofol inhibits the growth and survival of gastric
cancer cells in vitro through the upregulation of ING3. Oncol Rep.
37:587–593. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Willert K, Shibamoto S and Nusse R:
Wnt-induced dephosphorylation of axin releases beta-catenin from
the axin complex. Genes Dev. 13:1768–1773. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roberts KP, Ensrud KM and Hamilton DW: A
comparative analysis of expression and processing of the rat
epididymal fluid and sperm-bound forms of proteins D and E. Biol
Reprod. 67:525–533. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Li B, Zhou L, Yu S, Su Z, Song J,
Sun Q, Sha O, Wang X, Jiang W, et al: Prodigiosin inhibits
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exerts anticancer activity in breast
cancer cells. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 113:13150–13155. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen H, Khemtong C, Yang X, Chang X and
Gao J: Nanonization strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs. Drug
Discov Today. 16:354–360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang H, Benzonana LL, Zhao H, Watts HR,
Perry NJ, Bevan C, Brown R and Ma D: Prostate cancer cell
malignancy via modulation of HIF-1α pathway with isoflurane and
propofol alone and in combination. Br J Cancer. 111:1338–1349.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Q, Zhang L, Han Y, Jiang Z and Wang Q:
Propofol reduces MMPs expression by inhibiting NF-κB activity in
human MDA-MB-231 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:52–56. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu X, Wang L, Zhao S, Ji X, Luo Y and
Ling F: β-Catenin overexpression in malignant glioma and its role
in proliferation and apoptosis in glioblastma cells. Med Oncol.
28:608–614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pu P, Zhang Z, Kang C, Jiang R, Jia Z,
Wang G and Jiang H: Downregulation of Wnt2 and beta-catenin by
siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:351–361. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sareddy GR, Kesanakurti D, Kirti PB and
Babu PP: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac and
celecoxib attenuates Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway in human
glioblastoma cells. Neurochem Res. 38:2313–2322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paul I, Bhattacharya S, Chatterjee A and
Ghosh MK: Current understanding on EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin signaling
in glioma and their possible crosstalk. Genes Cancer. 4:427–446.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|