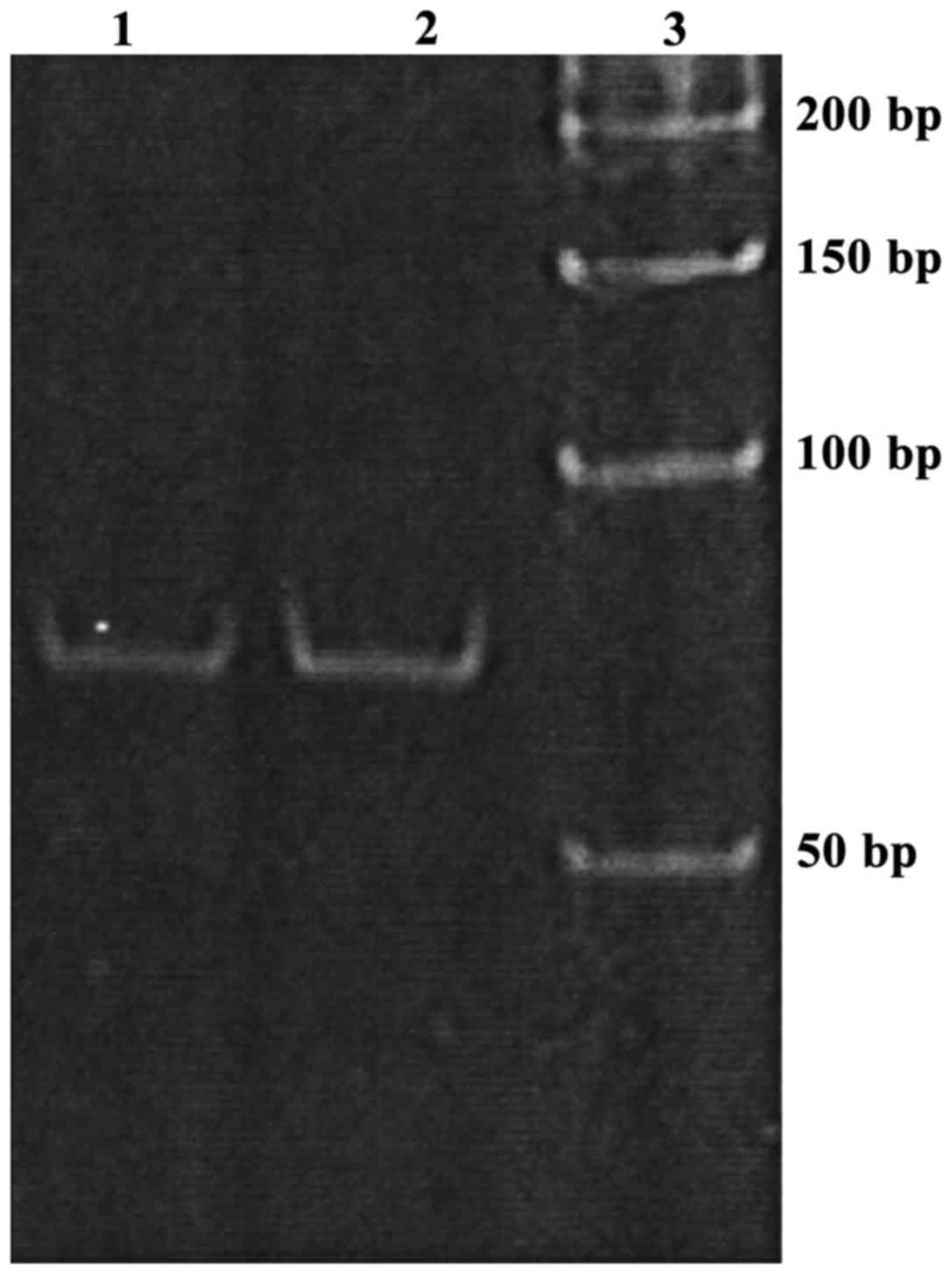
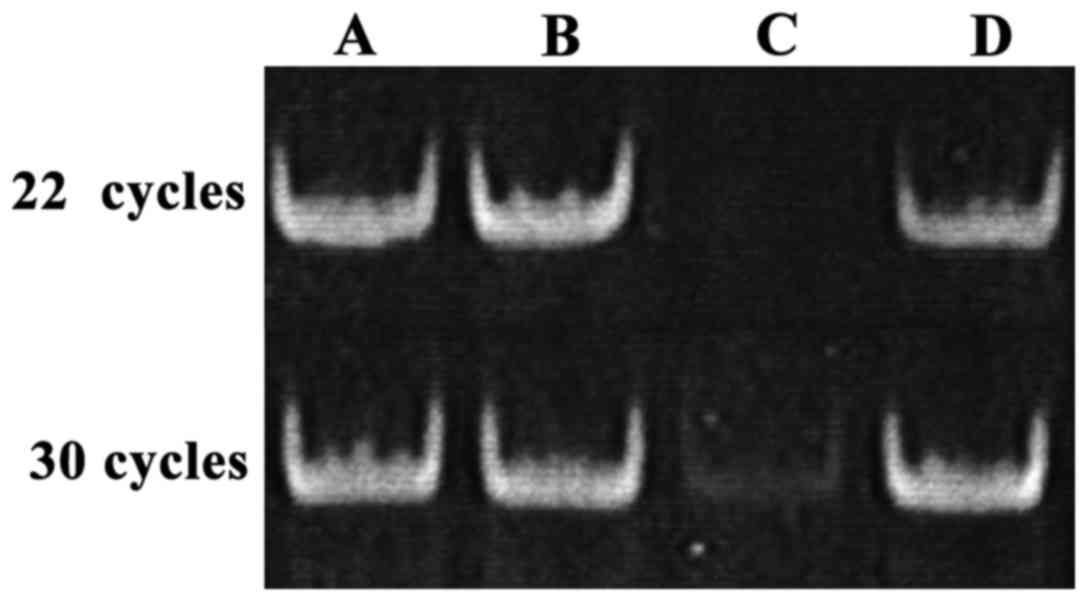
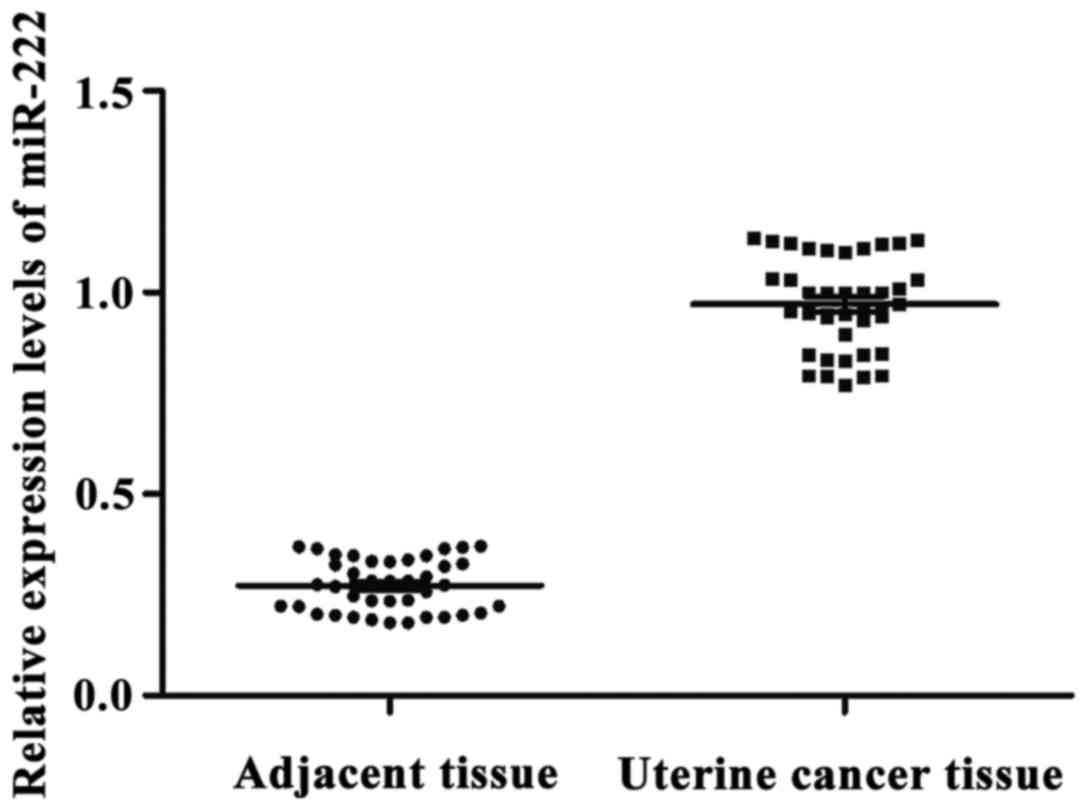
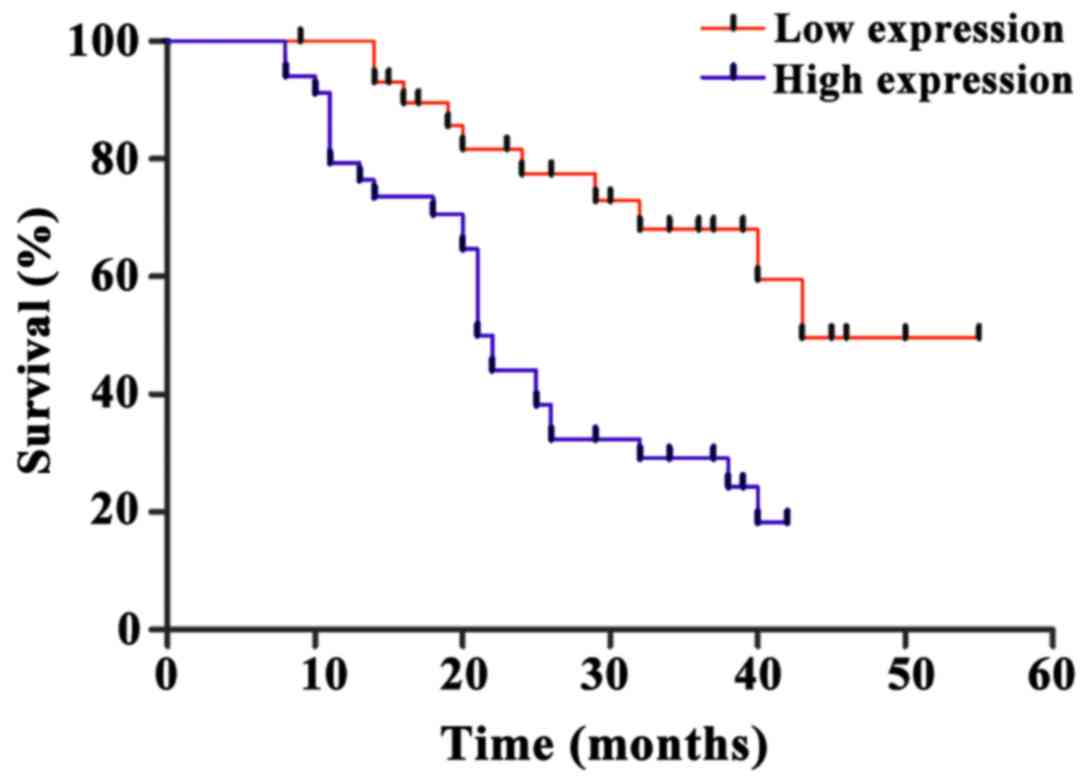
|
1
|
Kowalewska M, Bakula-Zalewska E,
Chechlinska M, Goryca K, Nasierowska-Guttmejer A, Danska-Bidzinska
A and Bidzinski M: MicroRNAs in uterine sarcomas and mixed
epithelial-mesenchymal uterine tumors: A preliminary report. Tumour
Biol. 34:2153–2160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Deas J, Meneses-Acosta
A, de la O-Gómez F, Fernández-Tilapa G, Gómez-Cerón C,
Benítez-Boijseauneau O, Burguete-García A, Torres-Poveda K,
Bermúdez-Morales VH, et al: Relevance of miR-21 in regulation of
tumor suppressor gene PTEN in human cervical cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 16:2152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fang H, Shuang D, Yi Z, Sheng H and Liu Y:
Up-regulated microRNA-155 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in cervical cancer patients. Biomed Pharmacother.
83:64–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pang H and Yue X: MiR-205 serves as a
prognostic factor and suppresses proliferation and invasion by
targeting insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 in human cervical
cancer. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177013082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun Y, Zhang B, Cheng J, Wu Y, Xing F,
Wang Y, Wang Q and Qiu J: MicroRNA-222 promotes the proliferation
and migration of cervical cancer cells. Clin Invest Med.
37:E1312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun L, Jiang R, Li J, Wang B, Ma C, Lv Y
and Mu N: MicoRNA-425-5p is a potential prognostic biomarker for
cervical cancer. Ann Clin Biochem. 54:127–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu P, Sun M, Jiang W, Zhao J, Liang C and
Zhang H: Identification of targets of miRNA-221 and miRNA-222 in
fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:3882–3888.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang DQ, Zhou CK, Jiang XW, Chen J and
Shi BK: Increased expression of miR-222 is associated with poor
prognosis in bladder cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:2412014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahmed FE, Amed NC, Vos PW, Bonnerup C,
Atkins JN, Casey M, Nuovo GJ, Naziri W, Wiley JE and Allison RR:
Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon
cancer in blood. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:179–192.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lorimer IA: Regulation of p27Kip1 by miRNA
221/222 in glioblastoma. Cell Cycle. 8:26852009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu J, Song Y, Cao
Y, Chen X, Yang W, Wang F, Gao J, et al: MicroRNA-222 controls
human pancreatic cancer cell line capan-2 proliferation by p57
targeting. J Cancer. 6:1230–1235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peltier HJ and Latham GJ: Normalization of
microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays:
Identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and
cancerous human solid tissues. RNA. 14:844–852. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong Y, Si JW, Li WT, Liang L, Zhao J,
Zhou M, Li D and Li T: miR-200a/miR-141 and miR-205 upregulation
might be associated with hormone receptor status and prognosis in
endometrial carcinomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2864–2875.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tseng JH, Bisogna M, Hoang LN, Olvera N,
Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Levine DA and
Jelinic P: miR-200c-driven mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition is
a therapeutic target in uterine carcinosarcomas. Sci Rep.
7:36142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun H, Xin J, Lu Z, Wang N, Liu N and Guo
Q: Potential molecular mechanisms for improved prognosis and
outcome with neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to laparoscopical
radical hysterectomy for patients with cervical cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1528–1540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiong X, Cheng J, Liu X, Tang S and Luo X:
Correlation analysis between miR-124 rs531564 polymorphisms and
susceptibility to cervical cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
34:210–213. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He Z, Xu H, Meng Y and Kuang Y: miR-944
acts as a prognostic marker and promotes the tumor progression in
endometrial cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:902–910. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu B, Che Q, Qiu H, Bao W, Chen X, Lu W,
Li B and Wan X: Elevated MiR-222-3p promotes proliferation and
invasion of endometrial carcinoma via targeting ERα. PLoS One.
9:e875632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yue Z, Yun-Shan Z and Feng-Xia X: miR-205
mediates the inhibition of cervical cancer cell proliferation using
olmesartan. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.
17:14703203166633272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang T, Zou P, Wang T, Xiang J, Cheng J,
Chen D and Zhou J: Down-regulation of miR-320 associated with
cancer progression and cell apoptosis via targeting Mcl-1 in
cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:8931–8940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yin ZL, Wang YL, Ge SF, Guo TT, Wang L,
Zheng XM and Liu J: Reduced expression of miR-503 is associated
with poor prognosis in cervical cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:4081–4085. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Liang J, Zhang Z, Lou H, Zhao L, Xu
Y and Ou R: MicroRNA-329-3p targets MAPK1 to suppress cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer. Oncol
Rep. 37:2743–2750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Dong Y, Ti H, Zhao J, Wang Y, Li
T and Zhang B: Down-regulation of miR-145 and miR-143 might be
associated with DNA methyltransferase 3B overexpression and worse
prognosis in endometrioid carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 44:2571–2580.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun J, Chu H, Ji J, Huo G, Song Q and
Zhang X: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates HLA-G expression by
absorbing miR-148a in human cervical cancer. Int J Oncol.
49:943–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen SN, Wang LF, Jia YF, Hao YQ, Zhang L
and Wang H: Upregulation of microRNA-224 is associated with
aggressive progression and poor prognosis in human cervical cancer.
Diagn Pathol. 8:692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Azizmohammadi S, Safari A, Azizmohammadi
S, Kaghazian M, Sadrkhanlo M, Yahaghi E, Farshgar R and
Seifoleslami M: Molecular identification of miR-145 and miR-9
expression level as prognostic biomarkers for early-stage cervical
cancer detection. QJM. 110:11–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chun-Zhi Z, Lei H, An-Ling Z, Yan-Chao F,
Xiao Y, Guang-Xiu W, Zhi-Fan J, Pei-Yu P, Qing-Yu Z and Chun-Sheng
K: MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell
proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer.
10:3672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Zeng J, Pan J, Geng X, Liu Y, Wu
J, Song P, Wang Y, Jia J and Wang L: MicroRNA-200c is involved in
proliferation of gastric cancer by directly repressing p27Kip1.
Biochem Biophys Rep. 8:227–233. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang E, He X, Yin D, Han L, Qiu M, Xu T,
Xia R, Xu L, Yin R and De W: Increased expression of long noncoding
RNA TUG1 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and regulates
cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p57. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e21092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu L, Cheng X, Shi J, Jiacheng L, Chen G,
Jin H, Liu AB, Pyo H, Ye J, Zhu Y, et al: Crosstalk between bone
marrow-derived myofibroblasts and gastric cancer cells regulates
cancer stemness and promotes tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 35:5388–5399.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|