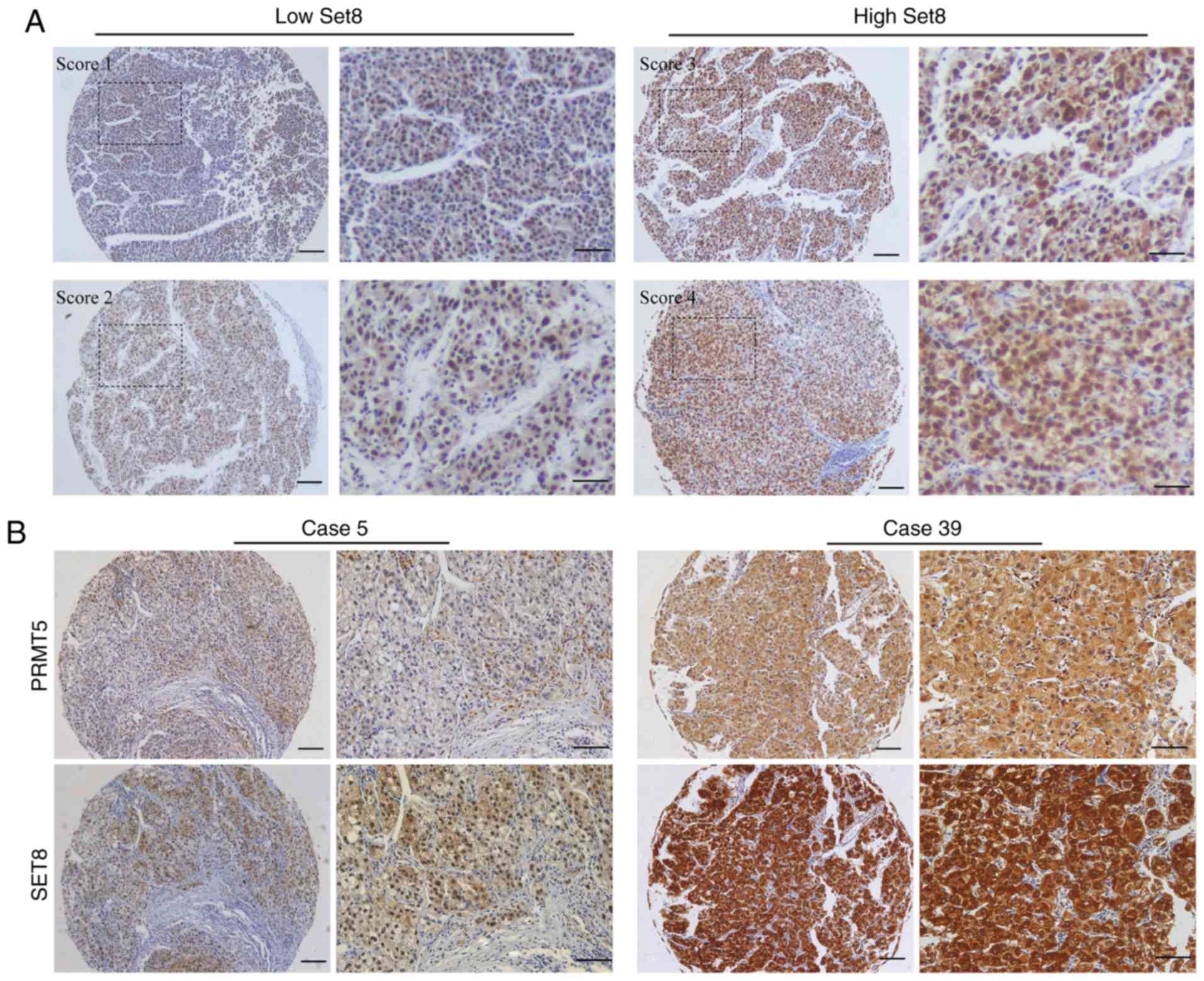
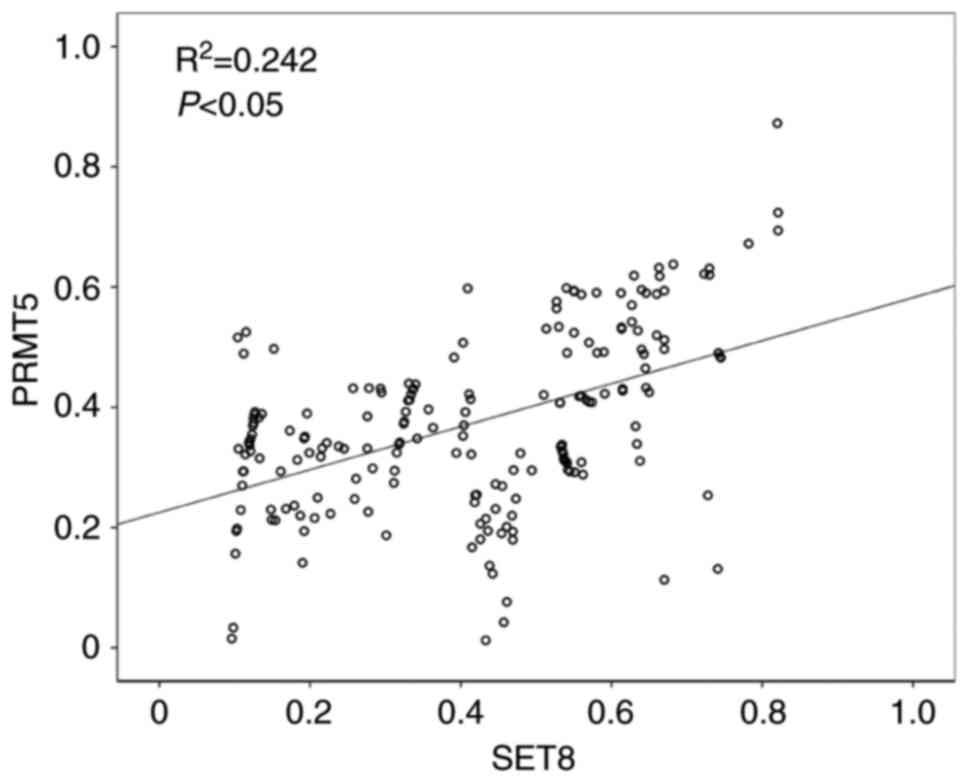
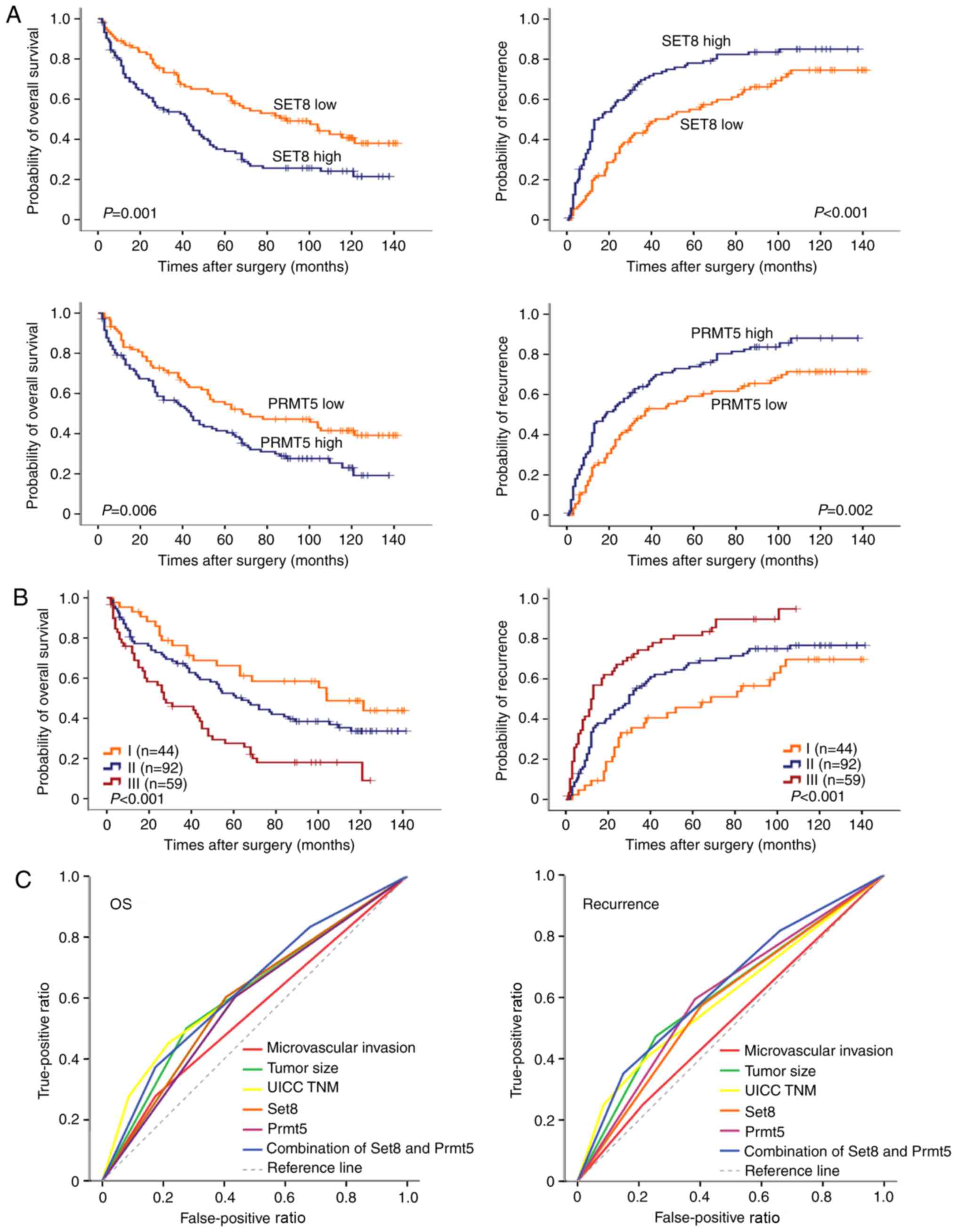
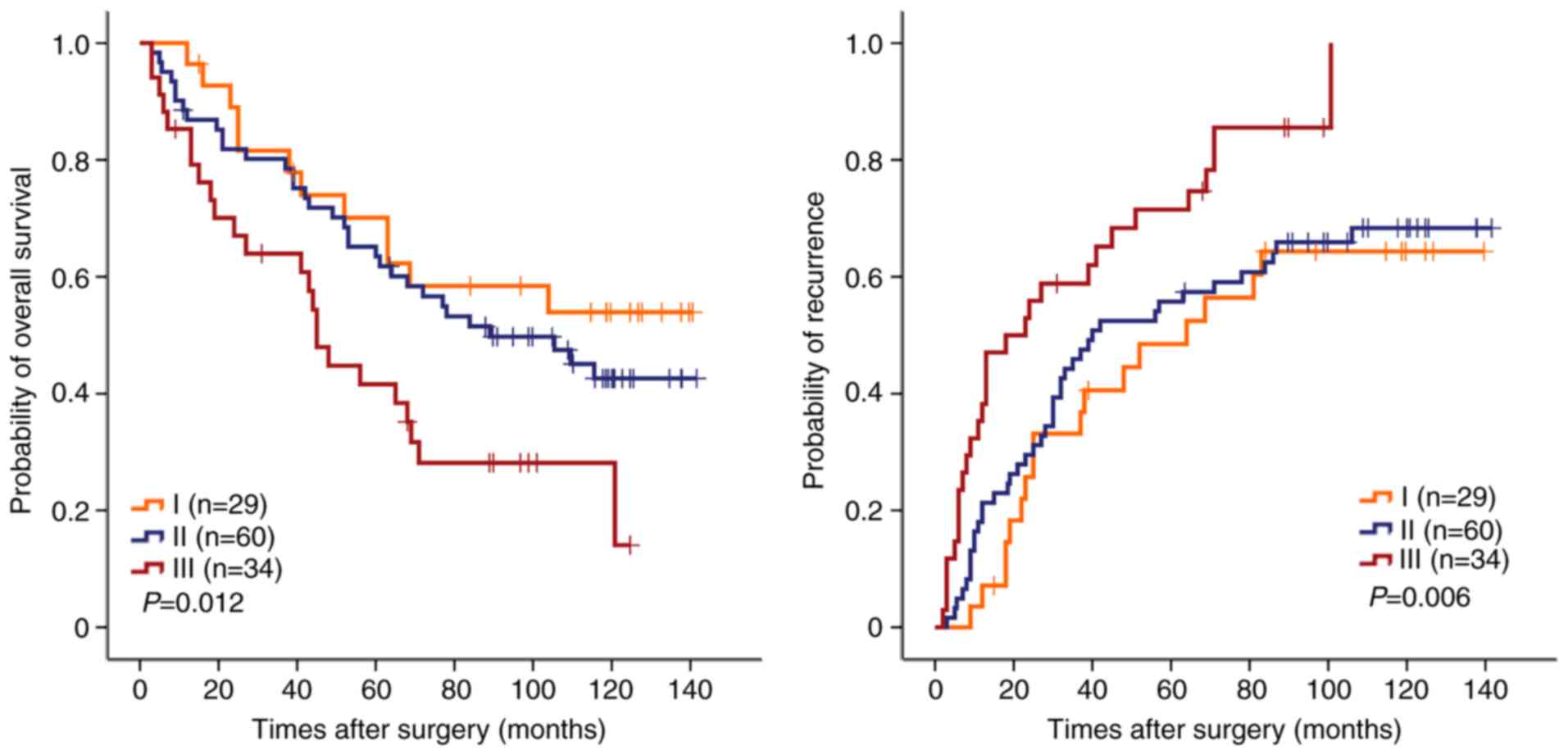
|
1
|
Liu M, Jiang L and Guan XY: The genetic
and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A
recent update. Protein Cell. 5:673–691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma L, Chua MS, Andrisani O and So S:
Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update and future
therapy perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 20:333–345. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herath NI, Leggett BA and MacDonald GA:
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:15–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wahid B, Ali A, Rafique S and Idrees M:
New insights into the epigenetics of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:16095752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pogribny IP and Rusyn I: Role of
epigenetic aberrations in the development and progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 342:223–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang J, Feng Q, Ketel CS, Wang H, Cao R,
Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Simon JA and Zhang Y:
Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal
histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr Biol.
12:1086–1099. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao B, Jing C, Kelly G, Walker PA,
Muskett FW, Frenkiel TA, Martin SR, Sarma K, Reinberg D, Gamblin SJ
and Wilson JR: Specificity and mechanism of the histone
methyltransferase Pr-Set7. Genes Dev. 19:1444–1454. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishioka K, Rice JC, Sarma K,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Werner J, Wang Y, Chuikov S, Valenzuela P,
Tempst P, Steward R, et al: PR-Set7 is a nucleosome-specific
methyltransferase that modifies lysine 20 of histone H4 and is
associated with silent chromatin. Mol Cell. 9:1201–1213. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Houston SI, McManus KJ, Adams MM, Sims JK,
Carpenter PB, Hendzel MJ and Rice JC: Catalytic function of the
PR-Set7 histone H4 lysine 20 monomethyltransferase is essential for
mitotic entry and genomic stability. J Biol Chem. 283:19478–19488.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oda H, Okamoto I, Murphy N, Chu J, Price
SM, Shen MM, Torres-Padilla ME, Heard E and Reinberg D:
Monomethylation of histone H4-lysine 20 is involved in chromosome
structure and stability and is essential for mouse development. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:2278–2295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Nie F, Wang S and Li L: Histone H4
Lys 20 monomethylation by histone methylase SET8 mediates Wnt
target gene activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:3116–3123.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu S, Wang W, Kong X, Congdon LM, Yokomori
K, Kirschner MW and Rice JC: Dynamic regulation of the PR-Set7
histone methyltransferase is required for normal cell cycle
progression. Genes Dev. 24:2531–2542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jørgensen S, Elvers I, Trelle MB, Menzel
T, Eskildsen M, Jensen ON, Helleday T, Helin K and Sørensen CS: The
histone methyltransferase SET8 is required for S-phase progression.
J Cell Biol. 179:1337–1345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Congdon LM, Houston SI, Veerappan CS,
Spektor TM and Rice JC: PR-Set7-mediated monomethylation of histone
H4 lysine 20 at specific genomic regions induces transcriptional
repression. J Cell Biochem. 110:609–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abbas T, Shibata E, Park J, Jha S, Karnani
N and Dutta A: CRL4(Cdt2) regulates cell proliferation and histone
gene expression by targeting PR-Set7/Set8 for degradation. Mol
Cell. 40:9–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stopa N, Krebs JE and Shechter D: The
PRMT5 arginine methyltransferase: Many roles in development, cancer
and beyond. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:2041–2059. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Y and Bedford MT: Protein arginine
methyltransferases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:37–50. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pal S, Vishwanath SN, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Tempst P and Sif S: Human SWI/SNF-associated PRMT5 methylates
histone H3 arginine 8 and negatively regulates expression of ST7
and NM23 tumor suppressor genes. Mol Cell Biol. 24:9630–9645. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pal S, Baiocchi RA, Byrd JC, Grever MR,
Jacob ST and Sif S: Low levels of miR-92b/96 induce PRMT5
translation and H3R8/H4R3 methylation in mantle cell lymphoma. EMBO
J. 26:3558–3569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karkhanis V, Hu YJ, Baiocchi RA, Imbalzano
AN and Sif S: Versatility of PRMT5-induced methylation in growth
control and development. Trends Biochem Sci. 36:633–641. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei TY, Juan CC, Hisa JY, Su LJ, Lee YC,
Chou HY, Chen JM, Wu YC, Chiu SC, Hsu CP, et al: Protein arginine
methyltransferase 5 is a potential oncoprotein that upregulates G1
cyclins/cyclin-dependent kinases and the phosphoinositide
3-kinase/AKT signaling cascade. Cancer Sci. 103:1640–1650. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bernstein BE, Meissner A and Lander ES:
The mammalian epigenome. Cell. 128:669–681. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y and Reinberg D: Transcription
regulation by histone methylation: Interplay between different
covalent modifications of the core histone tails. Genes Dev.
15:2343–2360. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qian YB, Zhang JB, Wu WZ, Fang HB, Jia WD,
Zhuang PY, Zhang BH, Pan Q, Xu Y, Wang L, et al: P48 is a
predictive marker for outcome of postoperative interferon-alpha
treatment in patients with hepatitis B virus infection-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 107:1562–1569. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: Practice Guidelines
Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases:
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 42:1208–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo
T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T,
Kawasaki S and Makuuchi M: Risk factors contributing to early and
late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma
after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 38:200–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Jia HL, He P,
Zanetti KA, Kammula US, Chen Y, Qin LX, Tang ZY and Wang XW:
Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response
signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 10:99–111.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Seligson DB, Horvath S, Shi T, Yu H, Tze
S, Grunstein M and Kurdistani SK: Global histone modification
patterns predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Nature.
435:1262–1266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jenuwein T and Allis CD: Translating the
histone code. Science. 293:1074–1080. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheng D, Yadav N, King RW, Swanson MS,
Weinstein EJ and Bedford MT: Small molecule regulators of protein
arginine methyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 279:23892–23899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang B, Dong S, Li Z, Lu L, Zhang S, Chen
X, Cen X and Wu Y: Targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5
inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma growth via the
downregulation of beta-catenin. J Transl Med. 13:3492015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|