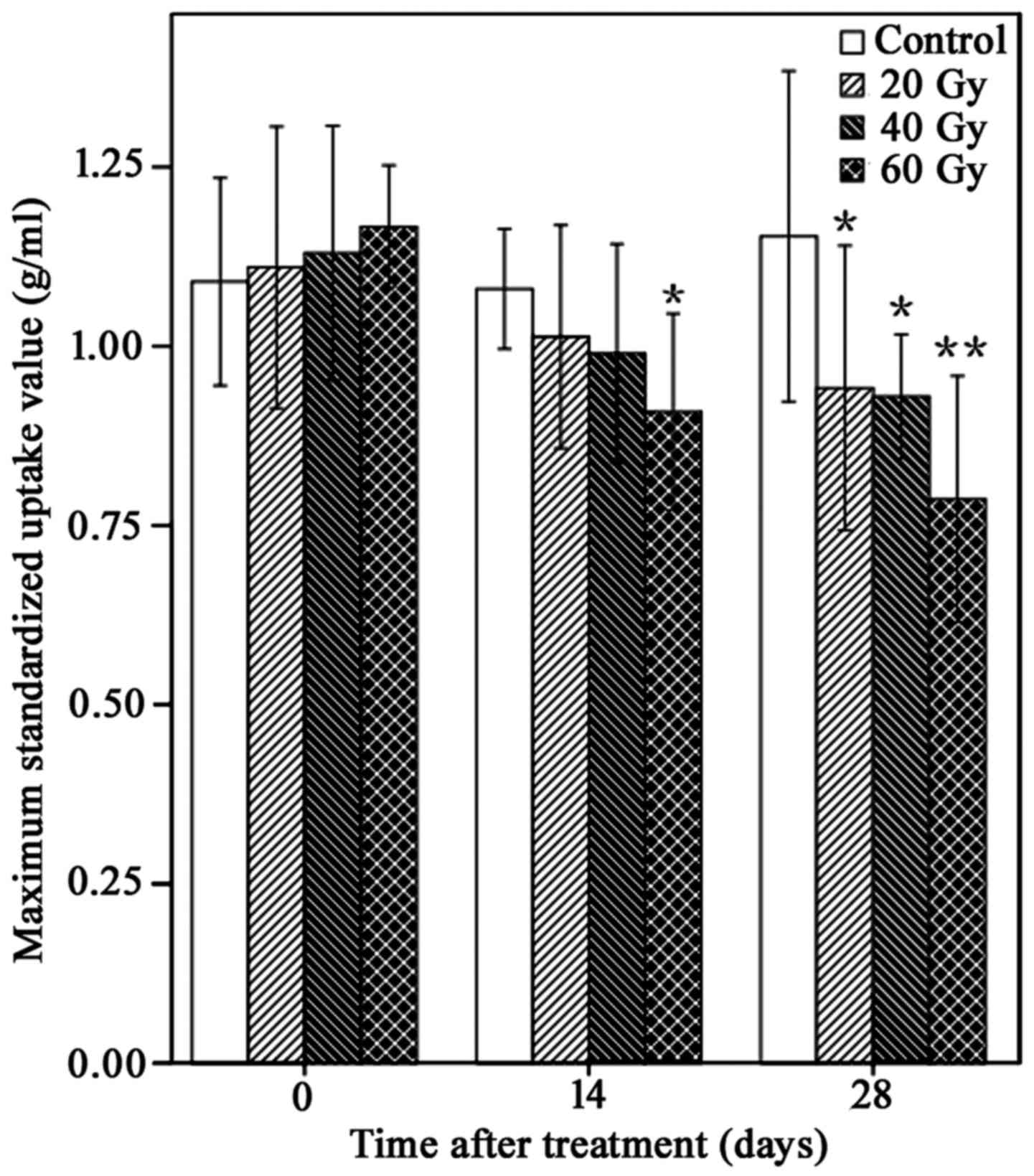
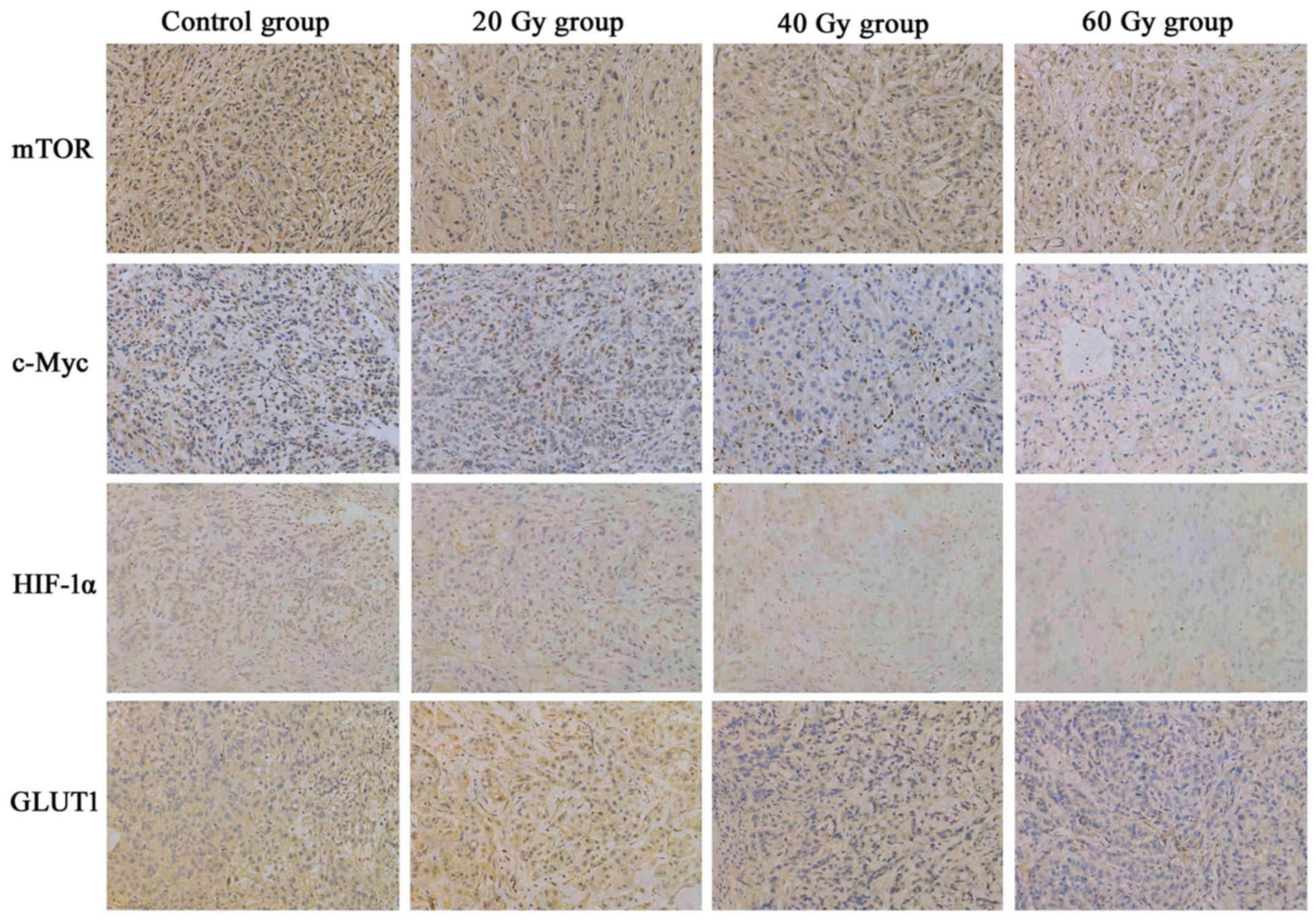
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huo X, Wang H, Yang J, Li X, Yan W, Huo B,
Zheng G, Chai S, Wang J, Guan Z and Yu Z: Effectiveness and safety
of CT-guided (125)I seed brachytherapy for postoperative
locoregional recurrence in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Brachytherapy. 15:370–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li W, Guan J, Yang L, Zheng X, Yu Y and
Jiang J: Iodine-125 brachytherapy improved overall survival of
patients with inoperable stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer
versus the conventional radiotherapy. Med Oncol. 32:3952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu X, Li J, Zhong X and He J: Combination
of Iodine-125 brachytherapy and chemotherapy for locally recurrent
stage III non-small cell lung cancer after concurrent
chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 15:6562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li W, Dan G, Jiang J, Zheng Y, Zheng X and
Deng D: Repeated iodine-125 seed implantations combined with
external beam radiotherapy for the treatment of locally recurrent
or metastatic stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer: A
retrospective study. Radiat Oncol. 11:1192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen HH, Jia RF, Yu L, Zhao MJ, Shao CL
and Cheng WY: Bystander effects induced by continuous low-dose-rate
125I seeds potentiate the killing action of irradiation on human
lung cancer cells in vitro. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
72:1560–1566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu A, Wang H, Li J, Wang J, Liu J, Hou Y,
Huang L and Zhao Y: Biological effects of (125)i seeds radiation on
A549 lung cancer cells: G2/M arrest and enhanced cell death. Cancer
Invest. 32:209–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Zhao Z, Lu J, Chen Z, Mao A, Teng
G and Liu F: A comparison of the biological effects of 125I seeds
continuous low-dose-rate radiation and 60Co high-dose-rate gamma
radiation on non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
10:e1337282015.
|
|
10
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M and Prasad PD:
Nutrient transporters in cancer: Relevance to Warburg hypothesis
and beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 121:29–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu J, Dong M, Sun X, Li W, Xing L and Yu
J: Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in surgical non-small cell
lung cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 11:e1461952016.
|
|
13
|
Madsen PH, Holdgaard PC, Christensen JB
and Høilund-Carlsen PF: Clinical utility of F-18 FDG PET-CT in the
initial evaluation of lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
43:2084–2097. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ruilong Z, Daohai X, Li G, Xiaohong W,
Chunjie W and Lei T: Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG-PET/CT for the
evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Nucl Med Commun. 38:67–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sheikhbahaei S, Mena E, Yanamadala A,
Reddy S, Solnes LB, Wachsmann J and Subramaniam RM: The value of
FDG PET/CT in treatment response assessment, follow-up, and
surveillance of lung cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 208:420–433.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cremonesi M, Gilardi L, Ferrari ME,
Piperno G, Travaini LL, Timmerman R, Botta F, Baroni G, Grana CM,
Ronchi S, et al: Role of interim 18F-FDG-PET/CT for the
early prediction of clinical outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) during radiotherapy or chemo-radiotherapy. A systematic
review. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 44:1915–1927. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allen KT, Chin-Sinex H, DeLuca T,
Pomerening JR, Sherer J, Watkins JR, Foley J, Jesseph JM and
Mendonca MS: Dichloroacetate alters Warburg metabolism, inhibits
cell growth, and increases the X-ray sensitivity of human A549 and
H1299 NSC lung cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 89:263–273. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lv XB, Liu L, Cheng C, Yu B, Xiong L, Hu
K, Tang J, Zeng L and Sang Y: SUN2 exerts tumor suppressor
functions by suppressing the Warburg effect in lung cancer. Sci
Rep. 5:179402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu T and Yin H: PDK1 promotes tumor cell
proliferation and migration by enhancing the Warburg effect in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:193–200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma JX, Jin ZD, Si PR, Liu Y, Lu Z, Wu HY,
Pan X, Wang LW, Gong YF, Gao J and Zhao-shen L: Continuous and
low-energy 125I seed irradiation changes DNA methyltransferases
expression patterns and inhibits pancreatic cancer tumor growth. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jian L, Zhongmin W, Kemin C, Yunfeng Z and
Gang H: MicroPET-CT evaluation of interstitial brachytherapy in
pancreatic carcinoma xenografts. Acta Radiol. 54:800–804. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Subocz E, Hałka J and Dziuk M: The role of
FDG-PET in Hodgkin lymphoma. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 21:104–114.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cremonesi M, Garibaldi C, Timmerman R,
Ferrari M, Ronchi S, Grana CM, Travaini L, Gilardi L, Starzynska A,
Ciardo D, et al: Interim 18F-FDG-PET/CT during
chemo-radiotherapy in the management of oesophageal cancer
patients. A systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 125:200–212. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Upadhyay M, Samal J, Kandpal M, Singh OV
and Vivekanandan P: The Warburg effect: Insights from the past
decade. Pharmacol Ther. 137:318–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thorens B and Mueckler M: Glucose
transporters in the 21st Century. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
298:E141–E145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu H, Forbes RA and Verma A:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis
implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem.
277:23111–23115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Qian Y and Wu S: The Warburg
effect: Evolving interpretations of an established concept. Free
Radic Biol Med. 79:253–263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dang CV: Links between metabolism and
cancer. Genes Dev. 26:877–890. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsieh AL, Walton ZE, Altman BJ, Stine ZE
and Dang CV: MYC and metabolism on the path to cancer. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 43:11–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Makinoshima H, Takita M, Saruwatari K,
Umemura S, Obata Y, Ishii G, Matsumoto S, Sugiyama E, Ochiai A, Abe
R, et al: Signaling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
(PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis is responsible for
aerobic glycolysis mediated by glucose transporter in epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J Biol
Chem. 290:17495–17504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toschi A, Lee E, Thompson S, Gadir N,
Yellen P, Drain CM, Ohh M and Foster DA: Phospholipase D-mTOR
requirement for the Warburg effect in human cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 299:72–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dang CV, Kim JW, Gao P and Yustein J: The
interplay between MYC and HIF in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:51–56.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Wang H, Qu A, Li J, Zhao Y and Wang
J: Combined effects of C225 and 125-iodine seed radiation on
colorectal cancer cells. Radiat Oncol. 8:2192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tian Y, Xie Q, Tian Y, Liu Y, Huang Z, Fan
C, Hou B, Sun D, Yao K and Chen T: Radioactive 125I seed
inhibits the cell growth, migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by triggering DNA damage and inactivating VEGF-A/ERK
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e740382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cron GO, Beghein N, Crokart N, Chavée E,
Bernard S, Vynckier S, Scalliet P and Gallez B: Changes in the
tumor microenvironment during low-dose-rate permanent seed
implantation iodine-125 brachytherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 63:1245–1251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hu L, Wang H, Huang L, Zhao Y and Wang J:
The protective roles of ROS-mediated mitophagy on 125I
seeds radiation induced cell death in HCT116 cells. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:94604622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brown RS, Leung JY, Kison PV, Zasadny KR,
Flint A and Wahl RL: Glucose transporters and FDG uptake in
untreated primary human non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med.
40:556–565. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
van Baardwijk A, Dooms C, van Suylen RJ,
Verbeken E, Hochstenbag M, Dehing-Oberije C, Rupa D, Pastorekova S,
Stroobants S, Buell U, et al: The maximum uptake of
(18)F-deoxyglucose on positron emission tomography scan correlates
with survival, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and GLUT-1 in
non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 43:1392–1398. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzawa N, Ito M, Qiao S, Uchida K, Takao
M, Yamada T, Takeda K and Murashima S: Assessment of factors
influencing FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer on PET/CT by
investigating histological differences in expression of glucose
transporters 1 and 3 and tumour size. Lung Cancer. 72:191–198.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung JK, Lee YJ, Kim SK, Jeong JM, Lee DS
and Lee MC: Comparison of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake with
glucose transporter-1 expression and proliferation rate in human
glioma and non-small-cell lung cancer. Nucl Med Commun. 25:11–17.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
de Geus-Oei LF, van Krieken JH, Aliredjo
RP, Krabbe PF, Frielink C, Verhagen AF, Boerman OC and Oyen WJ:
Biological correlates of FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 55:79–87. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dang CV: Rethinking the Warburg effect
with Myc micromanaging glutamine metabolism. Cancer Res.
70:859–862. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Morrish F, Isern N, Sadilek M, Jeffrey M
and Hockenbery DM: c-Myc activates multiple metabolic networks to
generate substrates for cell-cycle entry. Oncogene. 28:2485–2491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Collier JJ, Doan TT, Daniels MC, Schurr
JR, Kolls JK and Scott DK: c-Myc is required for the
glucose-mediated induction of metabolic enzyme genes. J Biol Chem.
278:6588–6595. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Broecker-Preuss M, Becher-Boveleth N,
Bockisch A, Dührsen U and Müller S: Regulation of glucose uptake in
lymphoma cell lines by c-MYC- and PI3K-dependent signaling pathways
and impact of glycolytic pathways on cell viability. J Transl Med.
15:1582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|