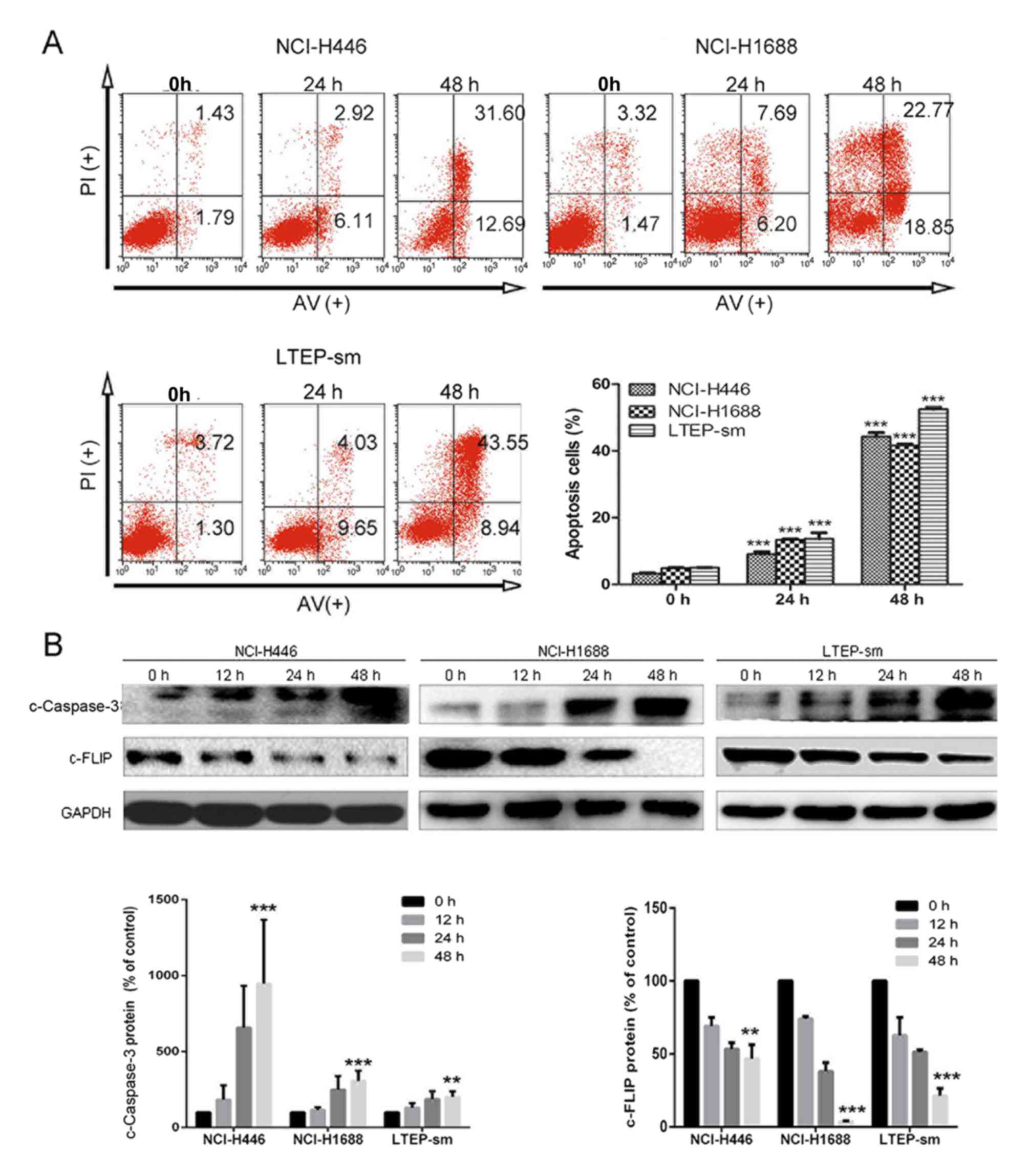
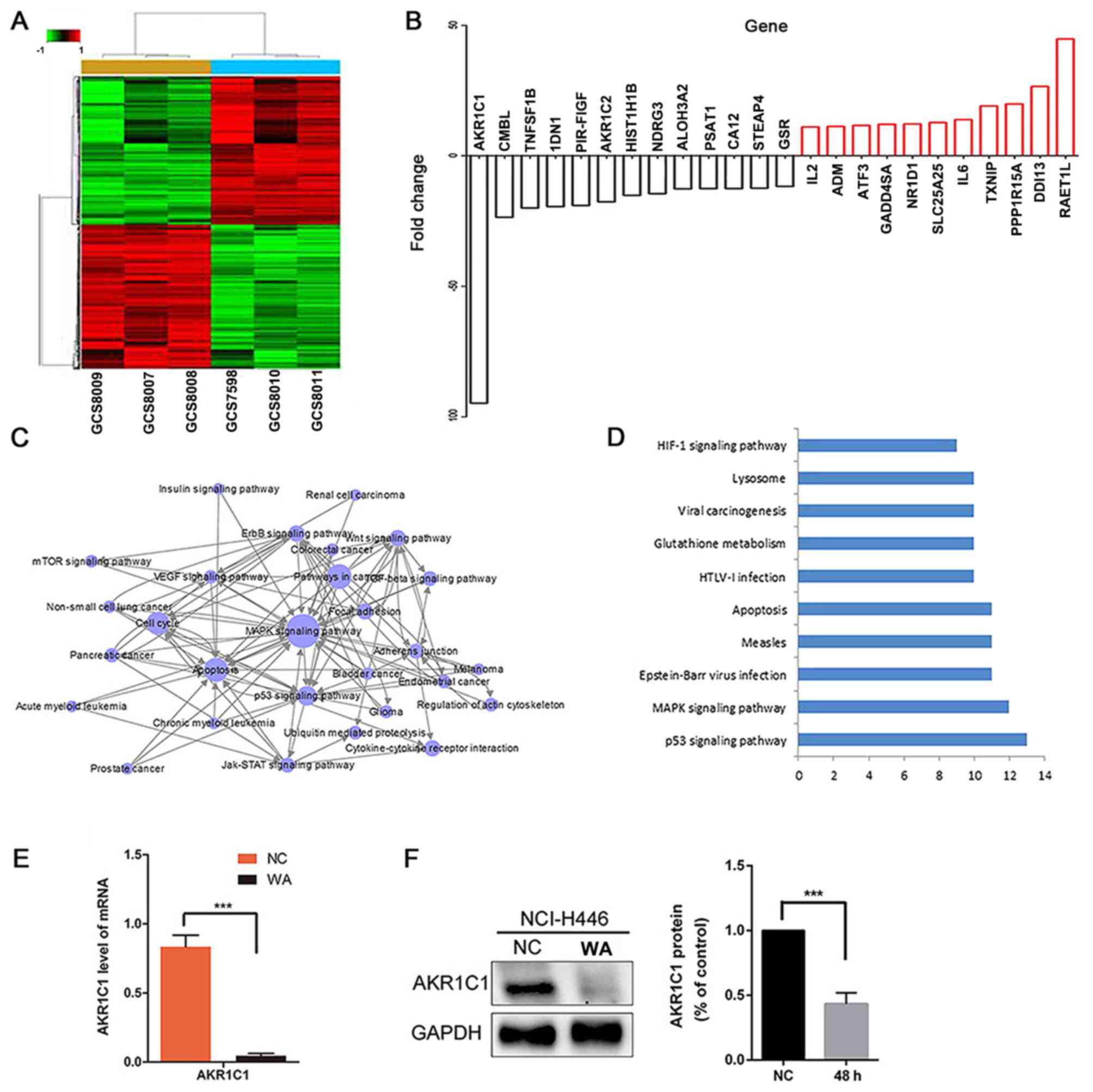
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stinchcombe TE: Current treatments for
surgically resectable, limited-stage, and extensive-stage small
cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 22:1510–1517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mamdani H, Induru R and Jalal SI: Novel
therapies in small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
4:533–544. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu B, Qin J and Zhou J: Advances in the
treatment of relapsed small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za
Zhi. 20:192–198. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
George J, Jing SL, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretić
L, Kong G, Leenders F, Lu X, Fernández-Cuesta L, Bosco G, et al:
Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature.
524:47–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calcabrini C, Catanzaro E, Bishayee A,
Turrini E and Fimognari C: Marine sponge natural products with
anticancer potential: An updated review. Mar Drugs. 15:pii:
E3102017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hussain H and Green IR: A patent review of
the therapeutic potential of isoflavones (2012–2016). Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 27:1135–1146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Russo P, Nastrucci C and Cesario A: From
the sea to anticancer therapy. Curr Med Chem. 18:3551–3562. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lv C, Hong Y, Miao L, Li C, Xu G, Wei S,
Wang B, Huang C and Jiao B: Wentilactone A as a novel potential
antitumor agent induces apoptosis and G2/M arrest of human lung
carcinoma cells, and is mediated by HRas-GTP accumulation to
excessively activate the Ras/Raf/ERK/p53-p21 pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e9522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sherlock G: Gene ontology: Tool for the
unification of biology. Can Instit Food Sci Technol J.
22:4152009.
|
|
11
|
Ge QM, Huang CM, Zhu XY, Bian F and Pan
SM: Differentially expressed miRNAs in sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury target oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
pathways. PLoS One. 12:e01732922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wright GW and Simon RM: A random variance
model for detection of differential gene expression in small
microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 19:2448–2455. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang H, Crawford N, Lukes L, Finney R,
Lancaster M and Hunter KW: Metastasis predictive signature profiles
pre-exist in normal tissues. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:593–603. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin J, Shackel N, Zekry A, McGuinness PH,
Richards C, Putten KV, McCaughan GW, Eris JM and Bishop GA:
Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
for measurement of cytokine and growth factor mRNA expression with
fluorogenic probes or SYBR Green I. Immunol Cell Biol. 79:213–221.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Palackal NT, Lee SH, Harvey RG, Blair IA
and Penning TM: Activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
trans-dihydrodiol proximate carcinogens by human aldo-keto
reductase (AKR1C) enzymes and their functional overexpression in
human lung carcinoma (A549) cells. J Biol Chem. 277:24799–24808.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Chen W, Zeng W, Bai L, Tesfaigzi
Y, Belinsky SA and Lin Y: Akt-mediated eminent expression of c-FLIP
and Mcl-1 confers acquired resistance to TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity
to lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1156–1163. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Safa AR and Pollok KE: Targeting the
anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP for cancer therapy.
|
|
19
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sankari SL, Masthan KM, Babu NA,
Bhattacharjee T and Elumalai M: Apoptosis in cancer-an update.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4873–4878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Savitskaya MA and Onishchenko GE:
Mechanisms of apoptosis. Biochemistry (Mosc). 80:1393–1405. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 27:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian H, Li X, Jiang W, Lv C, Sun W, Huang
C and Chen R: High expression of AKR1C1 is associated with
proliferation and migration of small-cell lung cancer cells. Lung
Cancer (Auckl). 7:53–61. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Penning TM: The aldo-keto reductases
(AKRs): Overview. Chem Biol Interact. 234:236–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M,
Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K and Yamamoto M: Oxidative stress
sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to
regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7130–7139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jaiswal AK: Nrf2 signaling in coordinated
activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med.
36:1199–1207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Homma S, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Yamadori T,
Matsuno Y, Haraguchi N, Kikuchi N, Satoh H, Sakamoto T, Hizawa N,
et al: Nrf2 enhances cell proliferation and resistance to
anticancer drugs in human lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:3423–3432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaspar JW, Niture SK and Jaiswal AK:
Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol
Med. 47:1304–1309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen T, Yang CS and Pickett CB: The
pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating Nrf2 activation in
response to chemical stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:433–441. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Vries HE, Witte M, Hondius D,
Rozemuller AJ, Drukarch B, Hoozemans J and van Horssen J:
Nrf2-induced antioxidant protection: A promising target to
counteract ROS-mediated damage in neurodegenerative disease? Free
Radic Biol Med. 45:1375–1383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zenkov NK, Menshchikova EB and Tkachev VO:
Keap1/Nrf2/ARE redox-sensitive signaling system as a
pharmacological target. Biochemistry (Mosc). 78:19–36. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu JB, Shi J, Zhang Y, Gong LR, Dong SA,
Cao XS, Wu LL and Wu LN: Electroacupuncture ameliorates acute renal
injury in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rabbits via induction of
HO-1 through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathways. PLoS One. 10:e01416222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tao Y, Pinzi V, Bourhis J and Deutsch E:
Mechanisms of disease: Signaling of the insulin-like growth factor
1 receptor pathway-therapeutic perspectives in cancer. Nat Clin
Pract Oncol. 4:591–602. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nurwidya F, Andarini S, Takahashi F,
Syahruddin E and Takahashi K: Implications of insulin-like growth
factor 1 receptor activation in lung cancer. Malays J Med Sci.
23:9–21. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tao Y1, Pinzi V, Bourhis J and Deutsch E:
Expression and distribution of insulin-like growth factor-1
receptor pathway-therapeutic perspectives in cancer. Nat Clin Pract
Oncol. 4:591–602. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yi CH and Yuan AJ: The Jekyll and Hyde
functions of caspases. Dev Cell. 16:21–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|