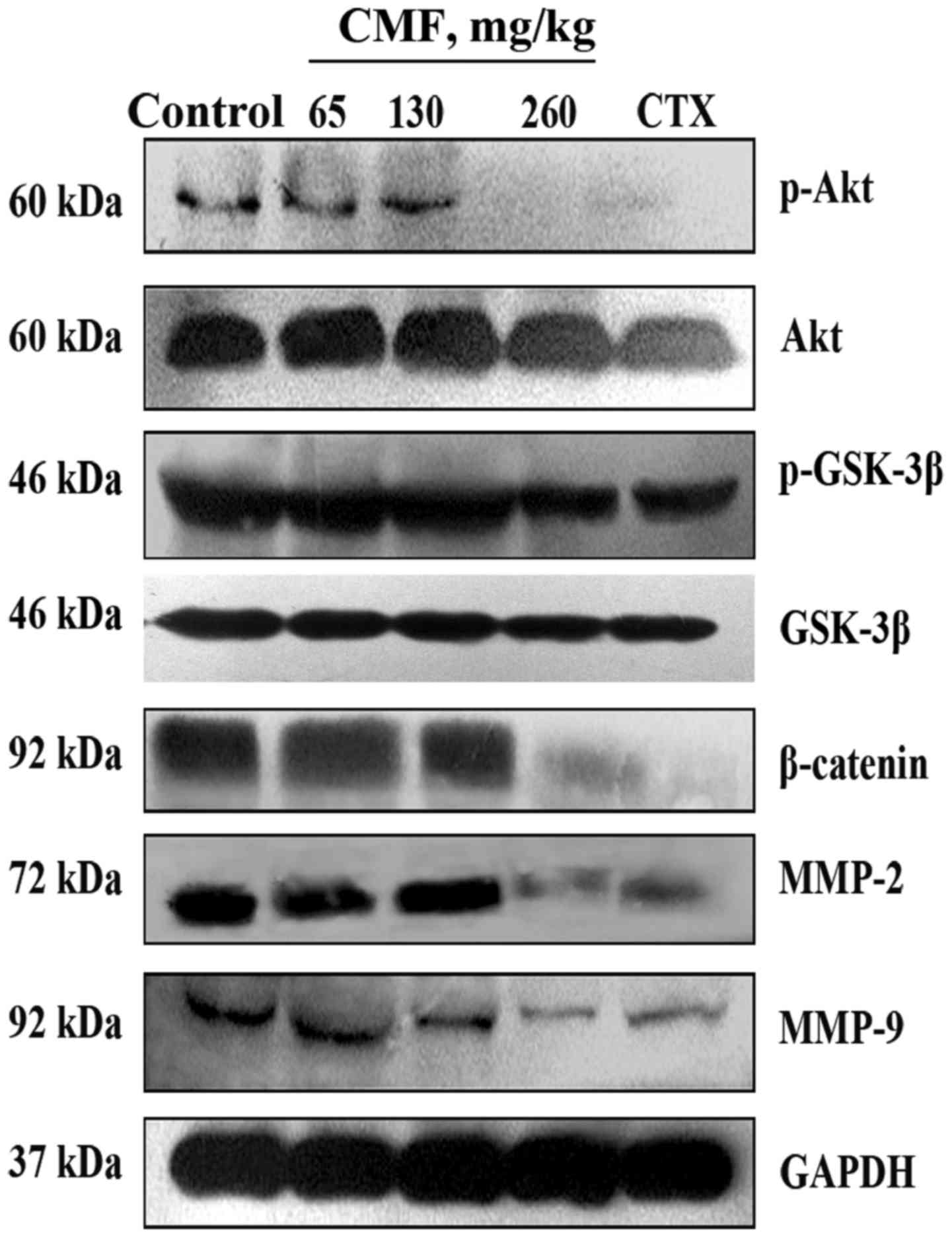
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Youlden DR, Cramb SM and Baade PD: The
international epidemiology of lung cancer: Geographical
distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol. 3:819–831. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Riihimaki M, Hemminki A, Fallah M, Thomsen
H, Sundquist K, Sundquist J and Hemminki K: Metastatic sites and
survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:78–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosell R and Karachaliou N: Relationship
between gene mutation and lung cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 34:243–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Yan L, Wu YQ, Hu HZ,
Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ, Xu LQ and Shi JG: Comprehensive gene and
microRNA expression profiling reveals miR-206 inhibits MET in lung
cancer metastasis. Mol Biosyst. 11:2290–2302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X and Adjei AA: Lung cancer and
metastasis: New opportunities and challenges. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 34:169–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Novaes FT, Cataneo DC, Junior Ruiz RL,
Defaveri J, Michelin OC and Cataneo AJ: Lung cancer: Histology,
staging, treatment and survival. J Bras Pneumol. 34:595–600.
2008.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van't Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wieczorek E, Jablonska E, Wasowicz W and
Reszka E: Matrix metalloproteinases and genetic mouse models in
cancer research: A mini-review. Tumour Biol. 36:163–175. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garbisa S, Scagliotti G, Masiero L, Di
Francesco C, Caenazzo C, Onisto M, Micela M, Stetler-Stevenson WG
and Liotta LA: Correlation of serum metalloproteinase levels with
lung cancer metastasis and response to therapy. Cancer Res.
52:4548–4549. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hrabec E, Strek M, Nowak D and Hrabec Z:
Elevated level of circulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 in
patients with lung cancer. Respir Med. 95:1–4. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vidal SJ, Rodriguez-Bravo V, Galsky M,
Cordon-Cardo C and Domingo-Domenech J: Targeting cancer stem cells
to suppress acquired chemotherapy resistance. Oncogene.
33:4451–4463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gai JQ, Sheng X, Qin JM, Sun K, Zhao W and
Ni L: The effect and mechanism of bufalin on regulating
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 48:338–348. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin J and Beer DG: Molecular predictors of
prognosis in lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:669–676. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uematsu K, He B, You L, Xu Z, McCormick F
and Jablons DM: Activation of the Wnt pathway in non small cell
lung cancer: Evidence of dishevelled overexpression. Oncogene.
22:7218–7221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui JD: Biotechnological production and
applications of Cordyceps militaris, a valued traditional Chinese
medicine. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 35:475–484. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang HJ, Baik HW, Kim SJ, Lee SG, Ahn HY,
Park JS, Park SJ, Jang EJ, Park SW, Choi JY, et al: Cordyceps
militaris enhances cell-mediated immunity in healthy korean men. J
Med Food. 18:1164–1172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yue K, Ye M, Zhou Z, Sun W and Lin X: The
genus Cordyceps: A chemical and pharmacological review. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 65:474–493. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu JY, Feng CP, Li X, Chang MC, Meng JL
and Xu LJ: Immunomodulatory and antioxidative activity of Cordyceps
militaris polysaccharides in mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 86:594–598.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiu CP, Liu SC, Tang CH, Chan Y,
El-Shazly M, Lee CL, Du YC, Wu TY, Chang FR and Wu YC:
Anti-inflammatory Cerebrosides from Cultivated Cordyceps militaris.
J Agric Food Chem. 64:1540–1548. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liao Y, Ling J, Zhang G, Liu F, Tao S, Han
Z, Chen S, Chen Z and Le H: Cordycepin induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis by inducing DNA damage and up-regulation of p53 in
Leukemia cells. Cell Cycle. 14:761–771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong JW, Jin CY, Park C, Han MH, Kim GY,
Moon SK, Kim CG, Jeong YK, Kim WJ, Lee JD and Choi YH: Inhibition
of migration and invasion of LNCaP human prostate carcinoma cells
by cordycepin through inactivation of Akt. Int J Oncol.
40:1697–1704. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian T, Song L, Zheng Q, Hu X and Yu R:
Induction of apoptosis by Cordyceps militaris fraction in human
chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells involved with mitochondrial
dysfunction. Pharmacogn Mag. 10:325–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo Q, Shen S, Liao M, Lian P and Wang X:
NGX6 inhibits cell invasion and adhesion through suppression of
Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in colon cancer. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:450–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J and Condeelis J:
Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:559–564. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gu S, Honisch S, Kounenidakis M, Alkahtani
S, Alarifi S, Alevizopoulos K, Stournaras C and Lang F: Membrane
androgen receptor down-regulates c-src-activity and beta-catenin
transcription and triggers GSK-3beta-phosphorylation in colon tumor
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1402–1412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei Q, Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, Dong QZ, Dong XJ,
Han Y, Zhao C and Wang EH: Dishevelled family proteins are
expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and function differentially
on tumor progression. Lung Cancer. 62:181–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shay G, Lynch CC and Fingleton B: Moving
targets: Emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and
metastasis. Matrix Biol. 44–46:1–206. 2015.
|
|
33
|
Leinonen T, Pirinen R, Böhm J, Johansson R
and Kosma VM: Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2
(MMP-2) predicts tumour recurrence and unfavourable outcome in
non-small cell lung cancer. Histol Histopathol. 23:693–700.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maru Y: The lung metastatic niche. J Mol
Med (Berl). 93:1185–1192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kruger A: Premetastatic niche formation in
the liver: Emerging mechanisms and mouse models. J Mol Med (Berl).
93:1193–1201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reck M, Popat S, Reinmuth N, De Ruysscher
D, Kerr KM and Peters S; and ESMO Guidelines Working Group, :
Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical
practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann
Oncol. 25 Suppl 3:iii27–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ye L, Jia Y, Ji KE, Sanders AJ, Xue K, Ji
J, Mason MD and Jiang WG: Traditional Chinese medicine in the
prevention and treatment of cancer and cancer metastasis. Oncol
Lett. 10:1240–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mehlen P and Puisieux A: Metastasis: A
question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:449–458. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM and Gallagher WM:
Cancer invasion and metastasis: Changing views. J Pathol.
214:283–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luu HH, Zhang R, Haydon RC, Rayburn E,
Kang Q, Si W, Park JK, Wang H, Peng Y, Jiang W and He TC:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway as novel cancer drug targets.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:653–671. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yuan H, Meng X, Guo W, Cai P, Li W, Li Q,
Wang W, Sun Y, Xu Q and Gu Y: Transmembrane-bound IL-15-promoted
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cancer cells requires
the Src-dependent Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Neoplasia.
17:410–420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song X, Wang S and Li L: New insights into
the regulation of Axin function in canonical Wnt signaling pathway.
Protein Cell. 5:186–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rayasam GV, Tulasi VK, Sodhi R, Davis JA
and Ray A: Glycogen synthase kinase 3: More than a namesake. Br J
Pharmacol. 156:885–898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|