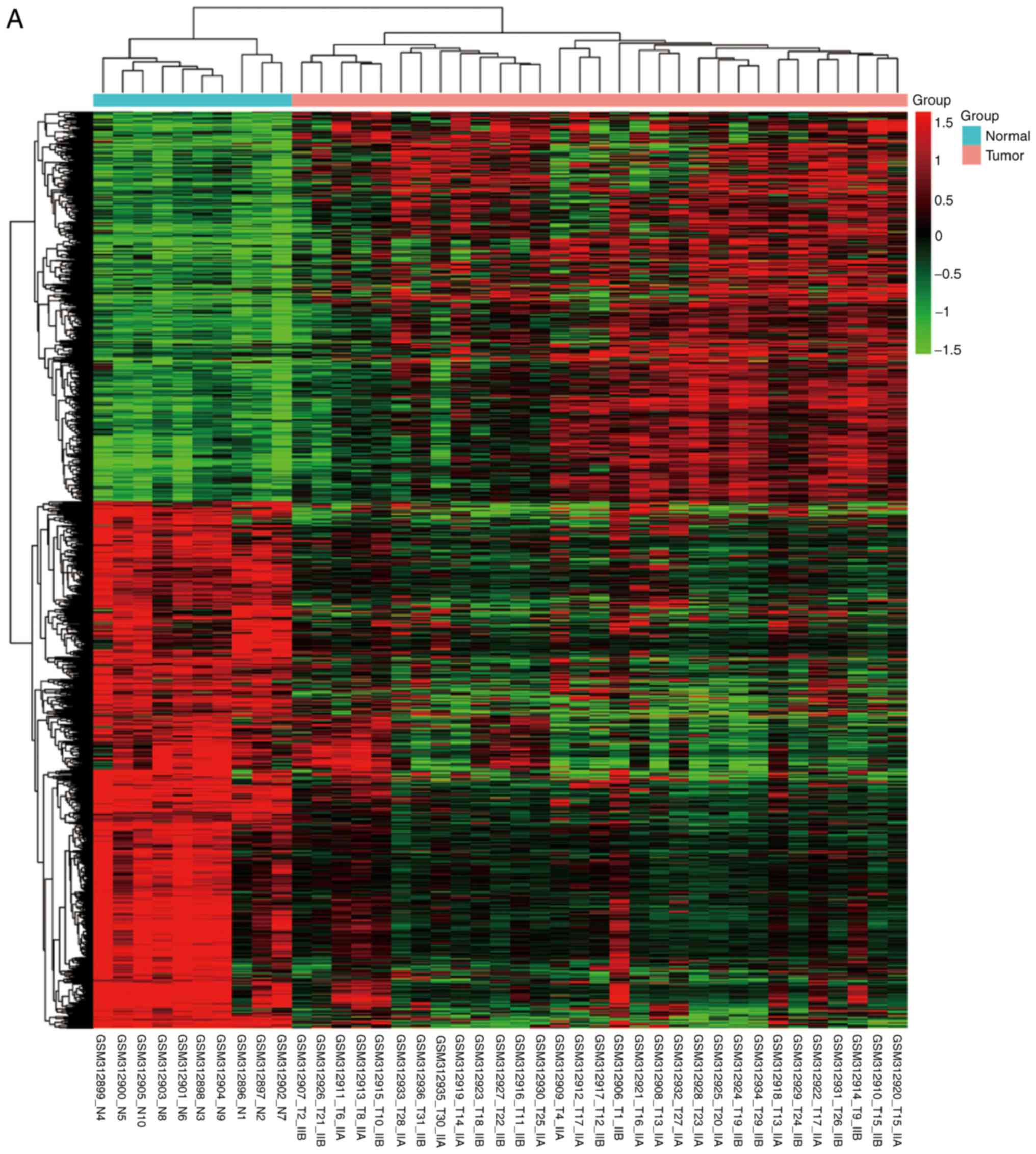
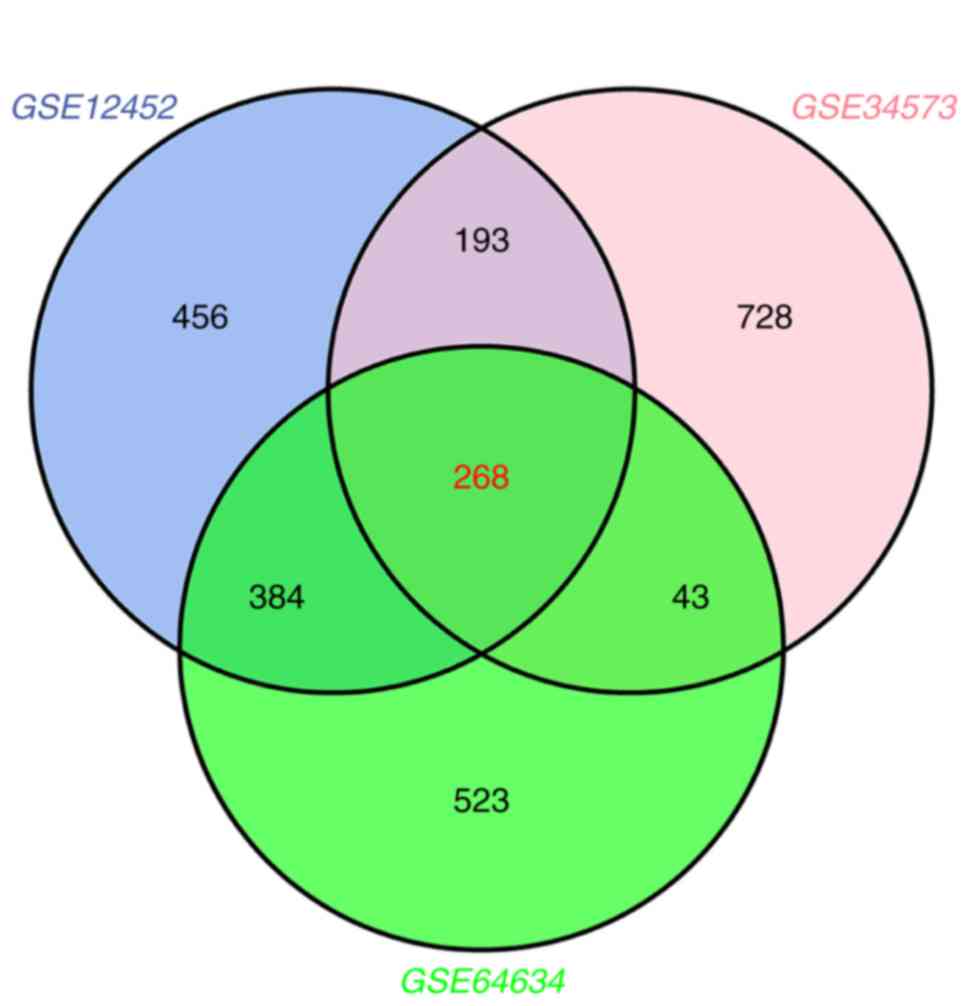
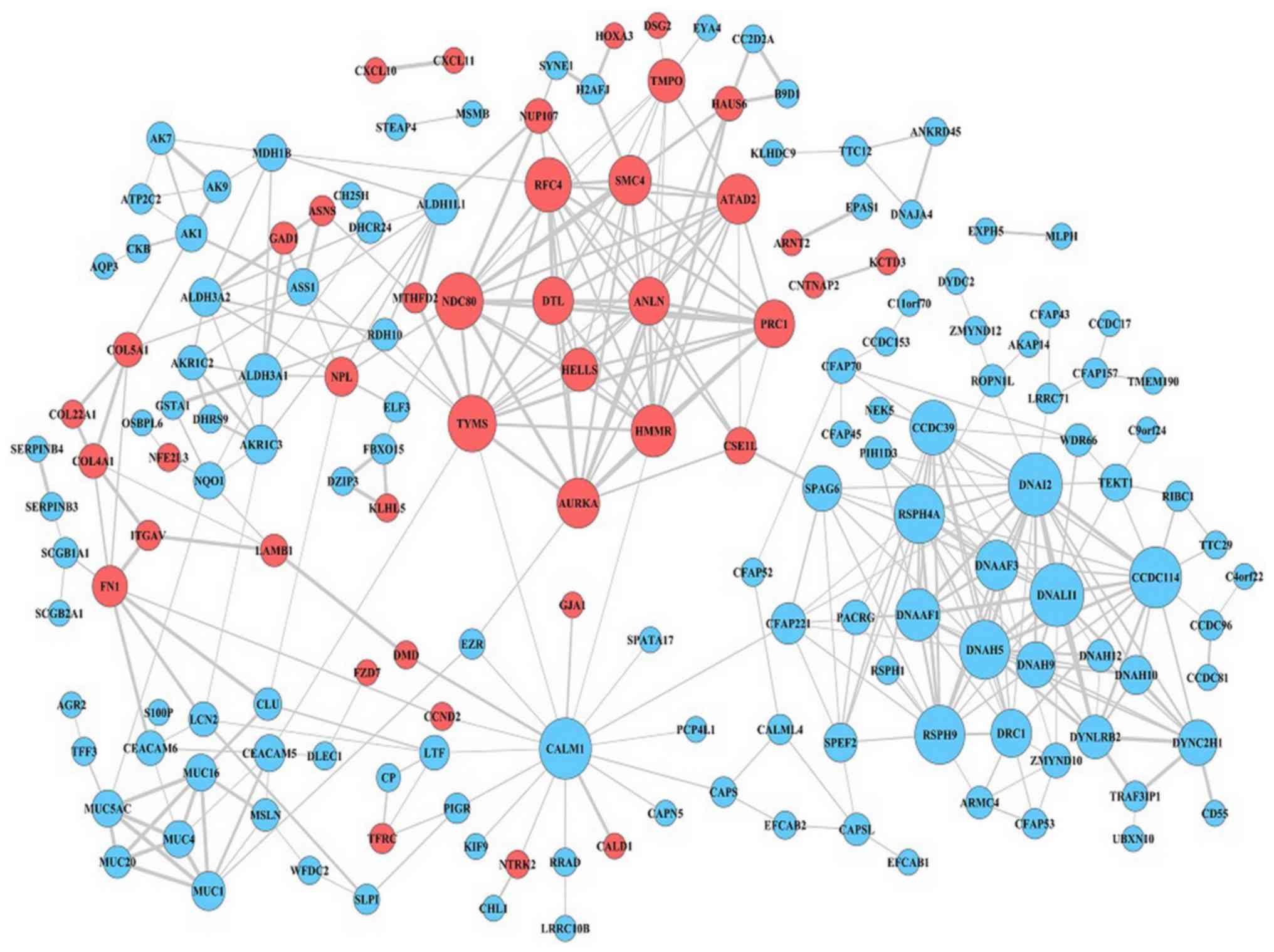
|
1
|
Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP and Chan ATC:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li K, Lin GZ, Shen JC and Zhou Q: Time
trends of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in urban Guangzhou over a
12-year period (2000–2011): Declines in both incidence and
mortality. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9899–9903. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee AW, Sze WM, Au JS, Leung SF, Leung TW,
Chua DT, Zee BC, Law SC, Teo PM, Tung SY, et al: Treatment results
for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the modern era: The Hong Kong
experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 61:1107–1116. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jing L, Zou X, Wu YL, Guo JC, Yun JP, Xu
M, Feng QS, Chen LZ, Bei JX, Zeng YX and Chen MY: A comparison
between the Sixth and seventh editions of the UICC/AJCC staging
system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese cohort. PLoS One.
9:e1162612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pan JJ, Ng WT, Zong JF, Lee SW, Choi HC,
Chan LL, Lin SJ, Guo QJ, Sze HC, Chen YB, et al: Prognostic
nomogram for refining the prognostication of the proposed 8th
edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system for nasopharyngeal cancer
in the era of intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Cancer.
122:3307–3315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan KCA, WOO JKS, King A, Zee BCY, Lam
WKJ, Chan SL, Chu SWI, Mak C, Tse IOL, Leung SYM, et al: Analysis
of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA to screen for nasopharyngeal
cancer. New Engl J Med. 377:513–522. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tulalamba W and Janvilisri T:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma signaling pathway: An update on molecular
biomarkers. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:5946812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang G, Du MY, Zhu H, Zhang N, Lu ZW,
Qian LX, Zhang W, Tian X, He X and Yin L: MiRNA-34a reversed
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of
SMAD4 in NPC cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:217–224. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu HM, Jiang XS, Li HZ, Qian LX, Du MY,
Lu ZW, Wu J, Tian XK, Fei Q, He X and Yin L: miR-184 inhibits tumor
invasion, migration and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
targeting Notch2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:1564–1576. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Coghill AE, Hsu WL, Pfeiffer RM, Juwana H,
Yu KJ, Lou PJ, Wang CP, Chen JY, Chen CJ, Middeldorp JM and
Hildesheim A: Epstein-Barr virus serology as a potential screening
marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma among high-risk individuals
from multiplex families in Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 23:1213–1219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ng WT, Yau TK, Yung RW, Sze WM, Tsang AH,
Law AL and Lee AW: Screening for family members of patients with
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 113:998–1001. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kulasingam V and Diamandis EP: Strategies
for discovering novel cancer biomarkers through utilization of
emerging technologies. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 5:588–599. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nannini M, Pantaleo MA, Maleddu A, Astolfi
A, Formica S and Biasco G: Gene expression profiling in colorectal
cancer using microarray technologies: Results and perspectives.
Cancer Treat Rev. 35:201–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bustin SA and Dorudi S: Gene expression
profiling for molecular staging and prognosis prediction in
colorectal cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 4:599–607. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Mei F, Gao X and Wang S:
Identification of genes involved in Epstein-Barr virus-associated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 12:2375–2380. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang X, Feng L, Dai B, Li L and Lu W:
Identification of key genes involved in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 83:670–676. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton
MA, Dahl DB, Chen M, Cheng YJ, Westra WH, Chen CJ, Hildesheim A, et
al: Genome-wide expression profiling reveals EBV-associated
inhibition of MHC Class I expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 66:7999–8006. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu C, Wei W, Chen X, Woodman CB, Yao Y,
Nicholls JM, Joab I, Sihota SK, Shao JY, Derkaoui KD, et al: A
global view of the oncogenic landscape in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
An integrated analysis at the genetic and expression levels. PLoS
One. 7:e410552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bo H, Gong Z, Zhang W, Li X, Zeng Y, Liao
Q, Chen P, Shi L, Lian Y, Jing Y, et al: Upregulated long
non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 expression is associated with progression
and poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:20404–20418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tweedie S, Ashburner M, Falls K, Leyland
P, McQuilton P, Marygold S, Millburn G, Osumi-Sutherland D,
Schroeder A, Seal R, et al: FlyBase: Enhancing Drosophila gene
ontology annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:(Database Issue).
D555–D559. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9. 1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Zou X, Wu YL, Guo JC, Yun JP, Xu M,
Feng QS, Chen LZ, Bei JX, Zeng YX and Chen MY: A Comparison between
the Sixth and Seventh Editions of the UICC/AJCC staging System for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese cohort. PLoS One.
9:e1162612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi XK, Han HQ, Zhang HJ, Xu M, Li L, Chen
L, Xiang T, Feng QS, Kang T, Qian CN, et al: OVOL2 links stemness
and metastasis via fine-tuning epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Theranostics. 8:2202–2216. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao Q, Tang L, Wu L, Li K, Wang H, Li W,
Wu J, Li M, Wang S and Zhao L: LASP1 promotes nasopharyngeal
carcinoma progression through negatively regulation of the tumor
suppressor PTEN. Cell Death Dis. 9:3932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ren X, Yang X, Cheng B, Chen X, Zhang T,
He Q, Li B, Li Y, Tang X, Wen X, et al: HOPX hypermethylation
promotes metastasis via activating SNAIL transcription in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Commun. 8:140532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vicente CM, Ricci R, Nader HB and Toma L:
Syndecan-2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells through
interactions with extracellular matrix produced by stromal
fibroblasts. BMC Cell Biol. 14:252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schvartzman JM, Thompson CB and Finley
LWS: Metabolic regulation of chromatin modifications and gene
expression. J Cell Biol. 217:2247–2259. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peng Y, Chen Z, Guan WJ, Zhu Z, Tan KS,
Hong H, Zi X, Zeng J, Li Y, Ong YK, et al: Downregulation and
aberrant localization of Forkhead Box J1 in allergic nasal mucosa.
Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 176:115–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Parris TZ, Danielsson A, Nemes S, Kovács
A, Delle U, Fallenius G, Möllerström E, Karlsson P and Helou K:
Clinical implications of gene dosage and gene expression patterns
in diploid breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3860–3874. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fedick AM, Jalas C, Treff NR, Knowles MR
and Zariwala MA: Carrier frequencies of eleven mutations in eight
genes associated with primary ciliary dyskinesia in the Ashkenazi
Jewish population. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 3:137–142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Milara J, Armengot M, Bañuls P, Tenor H,
Beume R, Artigues E and Cortijo J: Roflumilast N-oxide, a PDE4
inhibitor, improves cilia motility and ciliated human bronchial
epithelial cells compromised by cigarette smoke in vitro. Br J
Pharmacol. 166:2243–2262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weile J, Sun S, Cote AG, Knapp J, Verby M,
Mellor JC, Wu Y, Pons C, Wong C, van Lieshout N, et al: A framework
for exhaustively mapping functional missense variants. Mol Syst
Biol. 13:9572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim JY, Lee E, Park K, Park WY, Jung HH,
Ahn JS, Im YH and Park YH: Clinical implications of genomic
profiles in metastatic breast cancer with a focus on TP53 and
PIK3CA, the most frequently mutated genes. Oncotarget.
8:27997–28007. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ren Y, Yeoh KW, Hao P, Kon OL and Sze SK:
Irradiation of epithelial carcinoma cells upregulates
calcium-binding proteins that promote survival under hypoxic
conditions. J Proteome Res. 15:4258–4264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Onoufriadis A, Paff T, Antony D, Shoemark
A, Micha D, Kuyt B, Schmidts M, Petridi S, Dankert-Roelse JE,
Haarman EG, et al: Splice-site mutations in the axonemal outer
dynein arm docking complex gene CCDC114 cause primary ciliary
dyskinesia. Am J Hum Genet. 92:88–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiu Q, Peng Y, Zhu Z, Chen Z, Zhang C, Ong
HH, Tan KS, Hong H, Yan Y, Huang H, et al: Absence or
mislocalization of DNAH5 is a characteristic marker for motile
ciliary abnormality in nasal polyps. Laryngoscope. 128:E97–E104.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yoon HY, Kim YJ, Kim JS, Kim YW, Kang HW,
Kim WT, Yun SJ, Ryu KH, Lee SC and Kim WJ: RSPH9 methylation
pattern as a prognostic indicator in patients with non-muscle
invasive bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1195–1203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Castleman VH, Romio L, Chodhari R, Hirst
RA, de Castro SC, Parker KA, Ybot-Gonzalez P, Emes RD, Wilson SW,
Wallis C, et al: Mutations in radial spoke head protein genes RSPH9
and RSPH4A cause primary ciliary dyskinesia with
central-microtubular-pair abnormalities. Am J Hum Genet.
84:197–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang X, Guan Z, Dong Y, Zhu Z, Wang J and
Niu B: Inhibition of thymidylate synthase affects neural tube
development in mice. Reprod Toxicol. 76:17–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lin H, Zhang Z, Guo S, Chen F, Kessler JM,
Wang YM and Dutcher SK: A NIMA-related kinase suppresses the
flagellar instability associated with the loss of multiple axonemal
structures. PLoS Genet. 11:e10055082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|