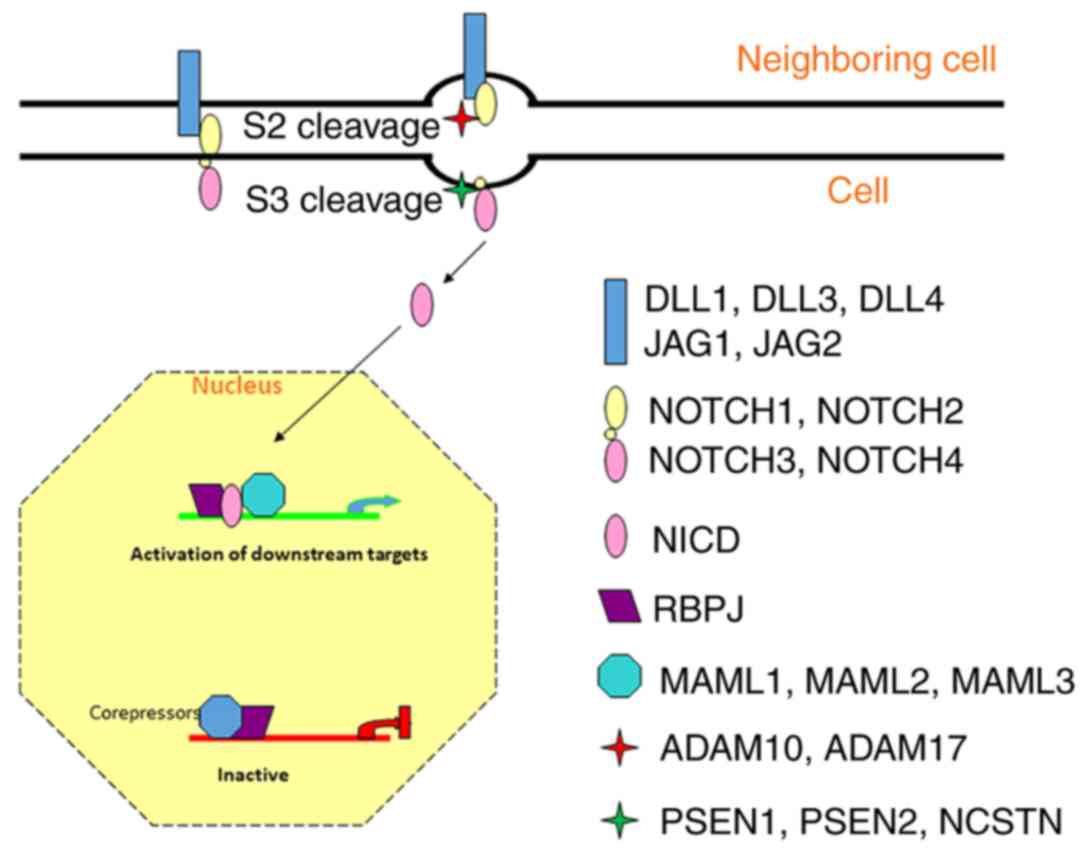
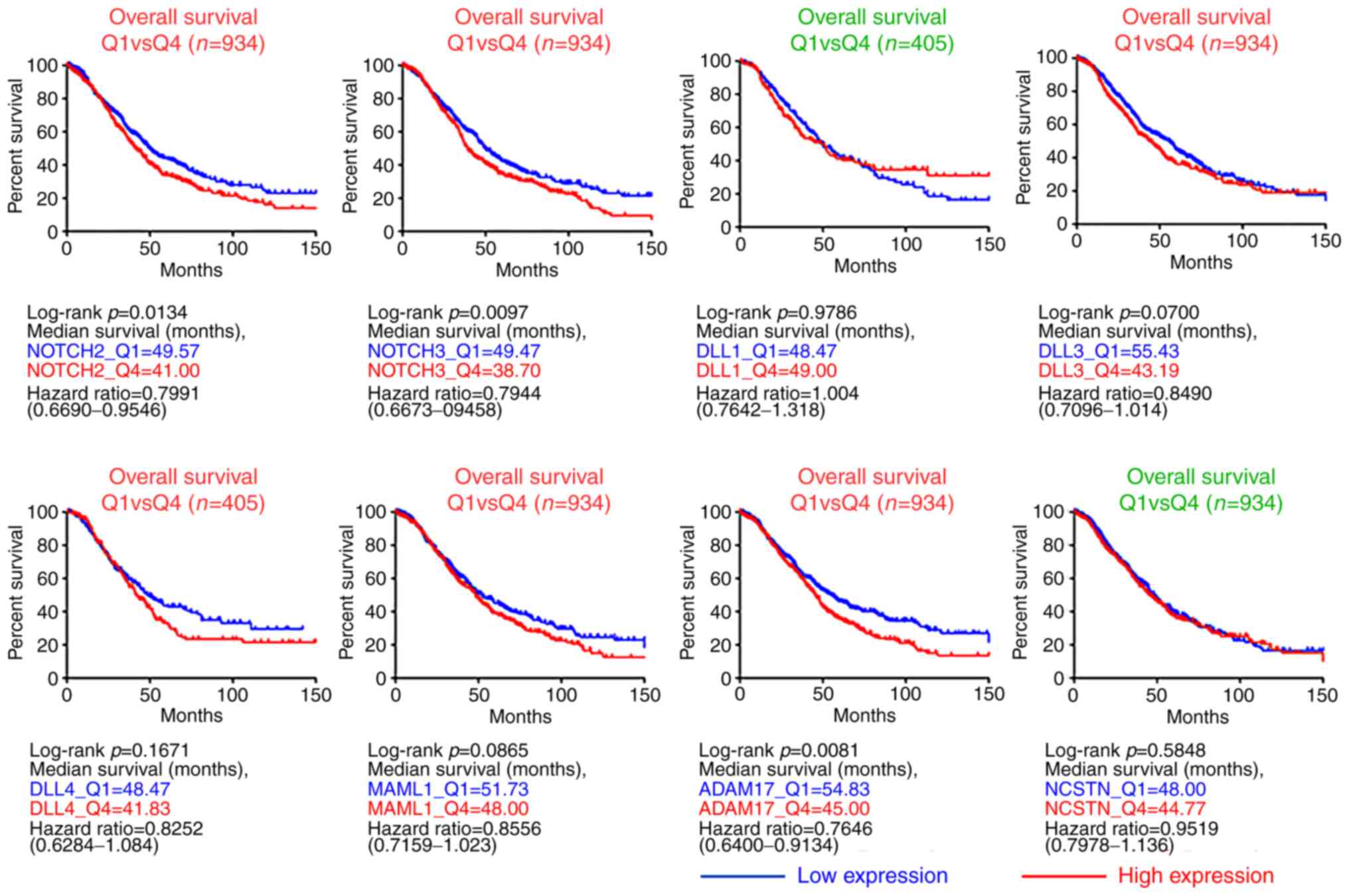
|
1
|
Siebel C and Lendahl U: Notch signaling in
development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. Physiol Rev.
97:1235–1294. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schwanbeck R, Martini S, Bernoth K and
Just U: The Notch signaling pathway: molecular basis of cell
context dependency. Eur J Cell Biol. 90:572–581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jia D, Tamori Y, Pyrowolakis G and Deng
WM: Regulation of broad by the Notch pathway affects timing of
follicle cell development. Dev Biol. 392:52–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zacharioudaki E and Bray SJ: Tools and
methods for studying Notch signaling in Drosophila melanogaster.
Methods. 68:173–182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jaleco AC, Neves H, Hooijberg E, Gameiro
P, Clode N, Haury M, Henrique D and Parreira L: Differential
effects of Notch ligands Delta-1 and Jagged-1 in human lymphoid
differentiation. J Exp Med. 194:991–1002. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lobry C, Oh P, Mansour MR, Look AT and
Aifantis I: Notch signaling: Switching an oncogene to a tumor
suppressor. Blood. 123:2451–2459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Radtke F and Raj K: The role of Notch in
tumorigenesis: oncogene or tumour suppressor? Nature reviews.
Cancer. 3:756–767. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Xiong H, Chu Q, Yu S,
Wu GS and Wu K: Notch signaling: An emerging therapeutic target for
cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 369:20–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu S, Liu C, Li L, Tian T, Wang M, Hu Y,
Yuan C, Zhang L, Ji C and Ma D: Inactivation of Notch signaling
reverses the Th17/Treg imbalance in cells from patients with immune
thrombocytopenia. Lab Invest. 95:157–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagase H and Nakayama K:
γ-Secretase-regulated signaling typified by Notch signaling in the
immune system. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:341–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang T, Zhu L, Gao W, Gong M, Ren J, Yao
H, Wang K and Shi D: Coculture of endothelial progenitor cells and
mesenchymal stem cells enhanced their proliferation and
angiogenesis through PDGF and Notch signaling. FEBS Open Bio.
7:1722–1736. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang M, Wang J, Wang L, Wu L and Xin X:
Notch1 expression correlates with tumor differentiation status in
ovarian carcinoma. Med Oncol. 27:1329–1335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Galic V, Shawber CJ, Reeves C, Shah M,
Murtomaki A, Wright J, Herzog T, Tong GX and Kitajewski J: NOTCH2
expression is decreased in epithelial ovarian cancer and is related
to the tumor histological subtype. Pathol Discov. 1:42013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu W, Liu T, Ivan C, Sun Y, Huang J,
Mangala LS, Miyake T, Dalton HJ, Pradeep S, Rupaimoole R, et al:
Notch3 pathway alterations in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
74:3282–3293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jung SG, Kwon YD, Song JA, Back MJ, Lee
SY, Lee C, Hwang YY and An HJ: Prognostic significance of Notch 3
gene expression in ovarian serous carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
101:1977–1983. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu W, Lu C, Dong HH, Huang J, Shen DY,
Stone RL, Nick AM, Shahzad MM, Mora E, Jennings NB, et al:
Biological roles of the Delta family Notch ligand Dll4 in tumor and
endothelial cells in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 71:6030–6039.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Riedle S, Kiefel H, Gast D, Bondong S,
Wolterink S, Gutwein P and Altevogt P: Nuclear translocation and
signalling of L1-CAM in human carcinoma cells requires ADAM10 and
presenilin/gamma-secretase activity. Biochem J. 420:391–402. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, Bratman SV,
Feng W, Kim D, Nair VS, Xu Y, Khuong A, Hoang CD, et al: The
prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across
human cancers. Nat Med. 21:938–945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin G, Kang TW, Yang S, Baek SJ, Jeong YS
and Kim SY: GENT: Gene expression database of normal and tumor
tissues. Cancer Inform. 10:149–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan TZ, Yang H, Ye J, Low J, Choolani M,
Tan DS, Thiery JP and Huang RY: CSIOVDB: A microarray gene
expression database of epithelial ovarian cancer subtype.
Oncotarget. 6:43843–43852. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N: Integrated
genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature. 474:609–615. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N,
Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV,
Sonkin D, et al: The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables
predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature.
483:603–607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taylor AB and MacKinnon DP: Four
applications of permutation methods to testing a single-mediator
model. Behavi Res Methods. 44:806–844. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Simes RJ: An improved bonferroni procedure
for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika. 73:751–754. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ismail E and Kornovski Y: Surgical staging
of ovarian cancer (I FIGO STAGE): IGCS-0018 ovarian cancer. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 25 Suppl 1:S522015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ismail E and Kornovski Y: Advanced stage
of epithelial ovarian cancer (ii-iv figo stage). The role of lymph
node dissection: IGCS-0019 ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 25
Suppl 1:S532015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Javadi S, Ganeshan DM, Qayyum A, Iyer RB
and Bhosale P: Ovarian cancer, the revised FIGO staging system, and
the role of imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 206:1351–1360. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gil-Garcia B and Baladron V: The complex
role of NOTCH receptors and their ligands in the development of
hepatoblastoma, cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biol Cell. 108:29–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borggrefe T, Lauth M, Zwijsen A,
Huylebroeck D, Oswald F and Giaimo BD: The Notch intracellular
domain integrates signals from Wnt, Hedgehog, TGFbeta/BMP and
hypoxia pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:303–313. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu L and Griffin JD: Modulation of Notch
signaling by mastermind-like (MAML) transcriptional co-activators
and their involvement in tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:348–356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao MQ, Choi YP, Kang S, Youn JH and Cho
NH: CD24+ cells from hierarchically organized ovarian
cancer are enriched in cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 29:2672–2680.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yen WC, Fischer MM, Axelrod F, Bond C,
Cain J, Cancilla B, Henner WR, Meisner R, Sato A, Shah J, et al:
Targeting Notch signaling with a Notch2/Notch3 antagonist
(tarextumab) inhibits tumor growth and decreases tumor-initiating
cell frequency. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2084–2095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu PC, Aliabadi HM, Uludag H and Han J:
Identification of potential drug targets in cancer signaling
pathways using stochastic logical models. Sci Rep Uk. 6:230782016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|