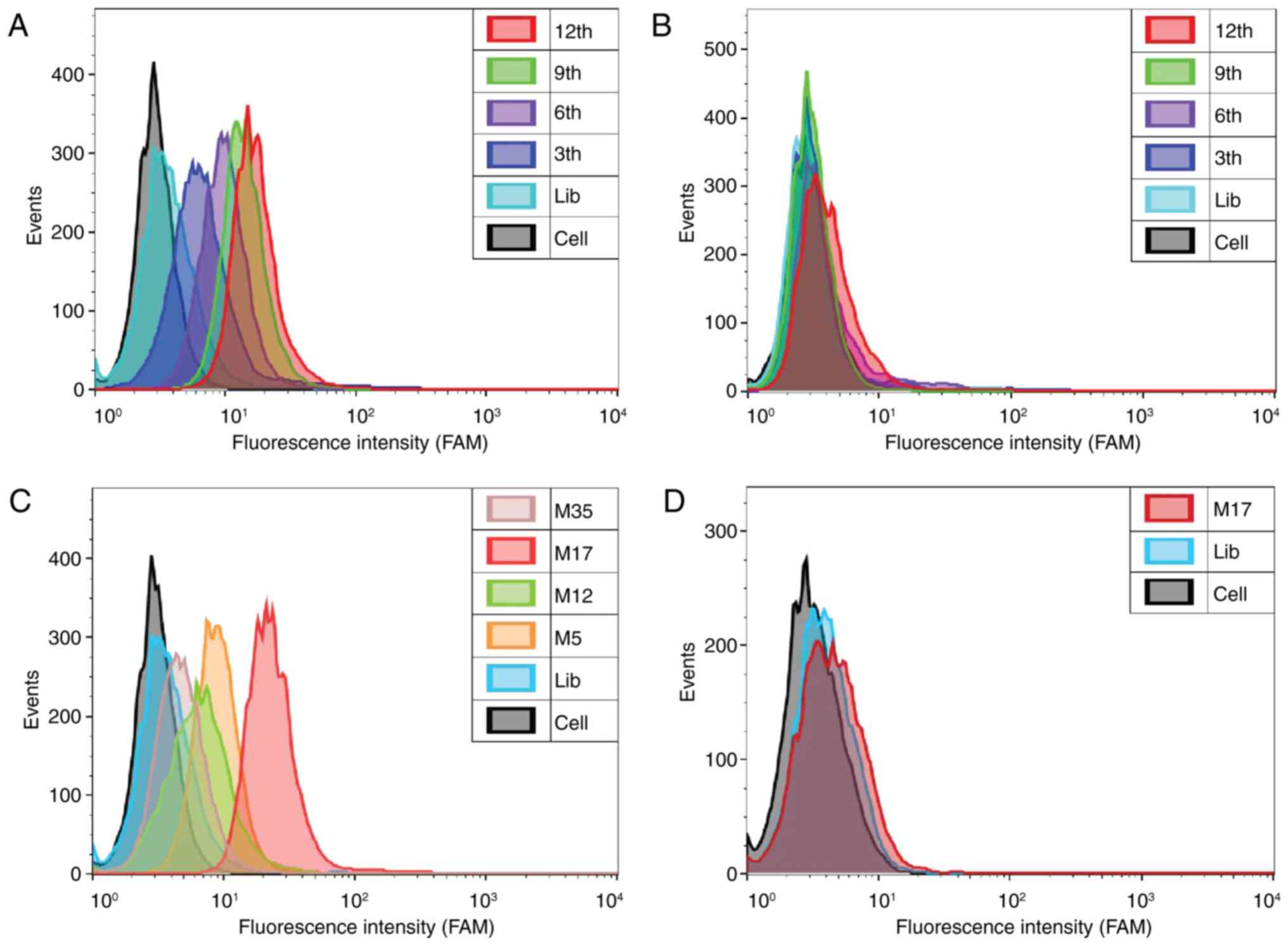
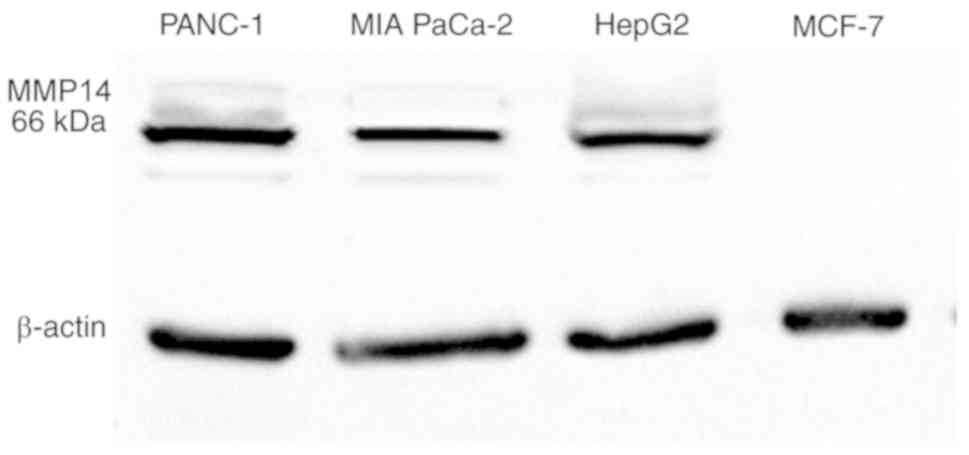
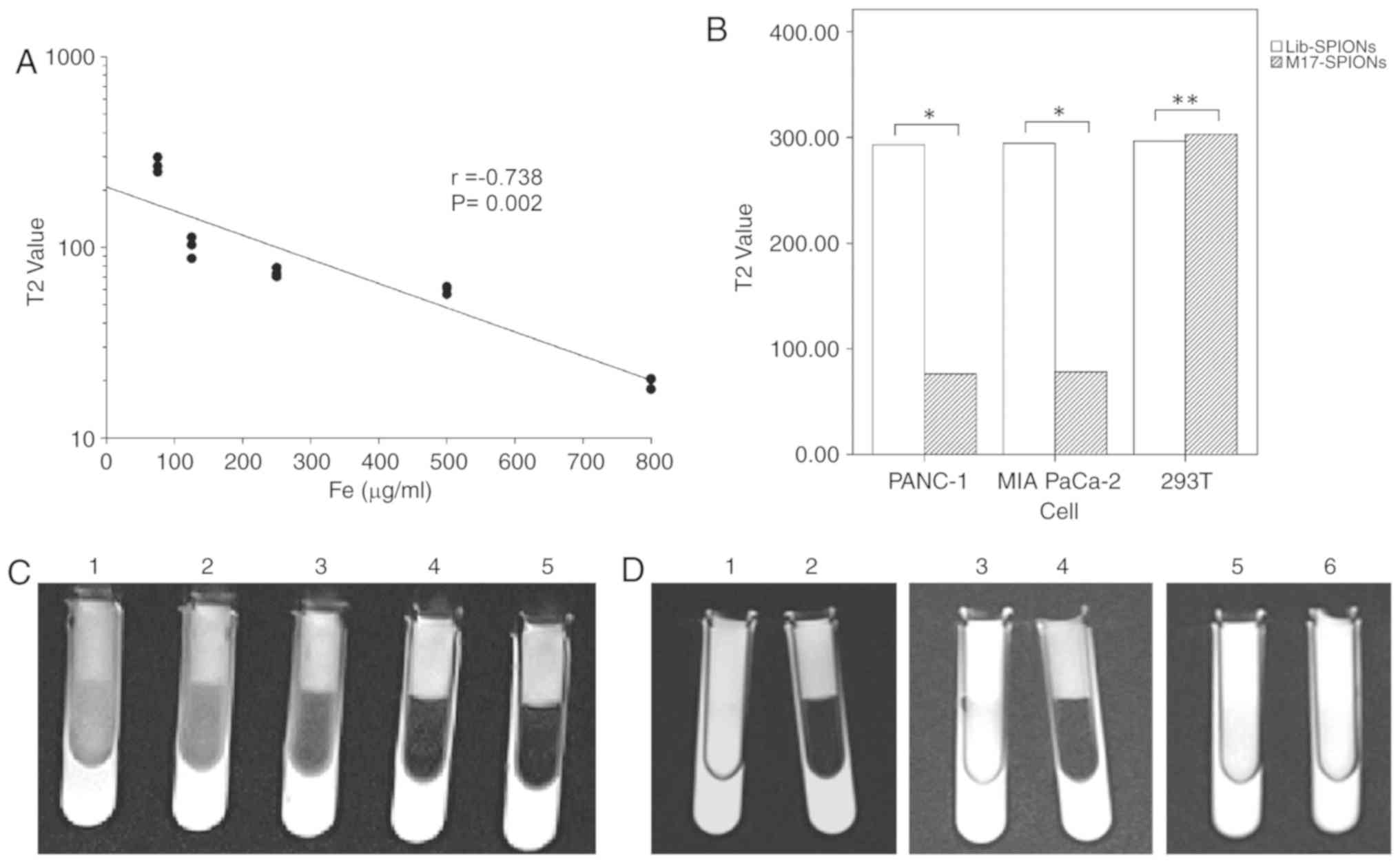
|
1
|
Brinckerhoff CE and Matrisian LM: Matrix
metalloproteinases: A tail of a frog that became a prince. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 3:207–214. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki A, Lu J, Kusakai G, Kishimoto A,
Ogura T and Esumi H: ARK5 is a tumor invasion-associated factor
downstream of Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3526–3535. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seiki M: Membrane-type 1 matrix
metalloproteinase: A key enzyme for tumor invasion. Cancer Lett.
194:1–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galvez BG, Matias-Roman S, Albar JP,
Sanchez-Madrid F and Arroyo AG: Membrane type 1-matrix
metalloproteinase is activated during migration of human
endothelial cells and modulates endothelial motility and matrix
remodeling. J Biol Chem. 276:37491–37500. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arroyo AG, Genis L, Gonzalo P,
Matias-Roman S, Pollan A and Galvez BG: Matrix metalloproteinases:
New routes to the use of MT1-MMP as a therapeutic target in
angiogenesis-related disease. Curr Pharm Des. 13:1787–1802. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wickramasinghe RD, Ko Ferrigno P and Roghi
C: Peptide aptamers as new tools to modulate clathrin-mediated
internalisation-inhibition of MT1-MMP internalisation. BMC Cell
Biol. 11:582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ottaviano AJ, Sun L, Ananthanarayanan V
and Munshi HG: Extracellular matrix-mediated membrane-type 1 matrix
metalloproteinase expression in pancreatic ductal cells is
regulated by transforming growth factor-beta1. Cancer Res.
66:7032–7040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Imamura T, Ohshio G, Mise M, Harada T,
Suwa H, Okada N, Wang Z, Yoshitomi S, Tanaka T, Sato H, et al:
Expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human
pancreatic adenocarcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 124:65–72.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen TY, Li YC, Liu YF, Tsai CM, Hsieh YH,
Lin CW, Yang SF and Weng CJ: Role of MMP14 gene polymorphisms in
susceptibility and pathological development to hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2348–2356. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, Cao J,
Shinagawa A, Yamamoto E and Seiki M: A matrix metalloproteinase
expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature.
370:61–65. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tokuraku M, Sato H, Murakami S, Okada Y,
Watanabe Y and Seiki M: Activation of the precursor of gelatinase
A/72 kDa type IV collagenase/MMP-2 in lung carcinomas correlates
with the expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase
(MT-MMP) and with lymph node metastasis. Int J Cancer. 64:355–359.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Polette M, Nawrocki B, Gilles C, Sato H,
Seiki M, Tournier JM and Birembaut P: MT-MMP expression and
localisation in human lung and breast cancers. Virchows Arch.
428:29–35. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nawrocki B, Polette M, Marchand V, Monteau
M, Gillery P, Tournier JM and Birembaut P: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human bronchopulmonary
carcinomas: Quantificative and morphological analyses. Int J
Cancer. 72:556–564. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mori M, Mimori K, Shiraishi T, Fujie T,
Baba K, Kusumoto H, Haraguchi M, Ueo H and Akiyoshi T: Analysis of
MT1-MMP and MMP2 expression in human gastric cancers. Int J Cancer.
74:316–321. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nomura H, Sato H, Seiki M, Mai M and Okada
Y: Expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase in human
gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 55:3263–3266. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bando E, Yonemura Y, Endou Y, Sasaki T,
Taniguchi K, Fujita H, Fushida S, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Miwa K
and Seiki M: Immunohistochemical study of MT-MMP tissue status in
gastric carcinoma and correlation with survival analyzed by
univariate and multivariate analysis. Oncol Rep. 5:1483–1488.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohtani H, Motohashi H, Sato H, Seiki M and
Nagura H: Dual over-expression pattern of membrane-type
metalloproteinase-1 in cancer and stromal cells in human
gastrointestinal carcinoma revealed by in situ hybridization and
immunoelectron microscopy. Int J Cancer. 68:565–570. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ueno H, Nakamura H, Inoue M, Imai K,
Noguchi M, Sato H, Seiki M and Okada Y: Expression and tissue
localization of membrane-types 1, 2, and 3 matrix
metalloproteinases in human invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res.
57:2055–2060. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jones JL, Glynn P and Walker RA:
Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, their inhibitors, and the activator
MT1-MMP in primary breast carcinomas. J Pathol. 189:161–168. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Yuan J, Tu Y, Mao X, He S, Fu G,
Zong J and Zhang Y: Co-expression of MMP-14 and MMP-19 predicts
poor survival in human glioma. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:139–145. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gilles C, Polette M, Piette J, Munaut C,
Thompson EW, Birembaut P and Foidart JM: High level of MT-MMP
expression is associated with invasiveness of cervical cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 65:209–213. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang ZH, Wen DD, Fu X, Zhong JM, Lu JT,
Huang XF, Ren J, Yang Y and Huan Y: Study on the expression and
clinical significance of survivin and MMP14 in pancreatic cancer.
Progress in Modern Biomed. 15:3022–3027. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Shimizu Y, Temma T, Sano K, Ono M and Saji
H: Development of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase-specific
activatable fluorescent probe for malignant tumor detection. Cancer
Sci. 102:1897–1903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Devy L, Huang L, Naa L, Yanamandra N,
Pieters H, Frans N, Chang E, Tao Q, Vanhove M, Lejeune A, et al:
Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-14 blocks tumor
growth, invasion, and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 69:1517–1526. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ingvarsen S, Porse A, Erpicum C, Maertens
L, Jurgensen HJ, Madsen DH, Melander MC, Gardsvoll H, Hoyer-Hansen
G, Noel A, et al: Targeting a single function of the
multifunctional matrix metalloprotease MT1-MMP: Impact on
lymphangiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 288:10195–10204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haage A, Nam DH, Ge X and Schneider IC:
Matrix metalloproteinase-14 is a mechanically regulated activator
of secreted MMPs and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
450:213–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Udi Y, Grossman M, Solomonov I, Dym O,
Rozenberg H, Moreno V, Cuniasse P, Dive V, Arroyo AG and Sagi I:
Inhibition mechanism of membrane metalloprotease by an
exosite-swiveling conformational antibody. Structure. 23:104–115.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chung E, Ochs CJ, Wang Y, Lei L, Qin Q,
Smith AM, Alex S, Kamm RD, Qi YX, Lu S and Wang YP: Activatable and
Cell-Penetrable Multiplex FRET Nanosensor for Profiling MT1-MMP
Activity in Single Cancer Cells. Nano Lett. 15:5025–5032. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sefah K, Shangguan D, Xiong X, O'Donoghue
MB and Tan W: Development of DNA aptamers using Cell-SELEX. Nat
Protoc. 5:1169–1185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ellington AD and Szostak JW: In
vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands.
Nature. 346:818–822. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tuerk C and Gold L: Systematic evolution
of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage
T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 249:505–510. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shangguan D, Li Y, Tang Z, Cao ZC, Chen
HW, Mallikaratchy P, Sefah K, Yang CJ and Tan W: Aptamers evolved
from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:11838–11843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, You M, Pu Y, Liu H, Ye M and Tan W:
Recent developments in protein and cell-targeted aptamer selection
and applications. Curr Med Chem. 18:4117–4125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xing H, Wong NY, Xiang Y and Lu Y: DNA
aptamer functionalized nanomaterials for intracellular analysis,
cancer cell imaging and drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol.
16:429–435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hwang DW, Ko HY, Lee JH, Kang H, Ryu SH,
Song IC, Lee DS and Kim S: A nucleolin-targeted multimodal
nanoparticle imaging probe for tracking cancer cells using an
aptamer. J Nucl Med. 51:98–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mosafer J, Abnous K, Tafaghodi M,
Mokhtarzadeh A and Ramezani M: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of
anti-nucleolin-targeted magnetic PLGA nanoparticles loaded with
doxorubicin as a theranostic agent for enhanced targeted cancer
imaging and therapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 113:60–74. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
You XG, Tu R, Peng ML, Bai YJ, Tan M, Li
HJ, Guan J and Wen LJ: Molecular magnetic resonance probe targeting
VEGF165: Preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Contrast
Media Mol Imaging. 9:349–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pu Y, Liu Z, Lu Y, Yuan P, Liu J, Yu B,
Wang G, Yang CJ, Liu H and Tan W: Using DNA aptamer probe for
immunostaining of cancer frozen tissues. Anal Chem. 87:1919–1924.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pilapong C, Sitthichai S, Thongtem S and
Thongtem T: Smart magnetic nanoparticle-aptamer probe for targeted
imaging and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Pharm.
473:469–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li CH, Kuo TR, Su HJ, Lai WY, Yang PC,
Chen JS, Wang DY, Wu YC and Chen CC: Fluorescence-guided probes of
aptamer-targeted gold nanoparticles with computed tomography
imaging accesses for in vivo tumor resection. Sci Rep.
5:156752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|