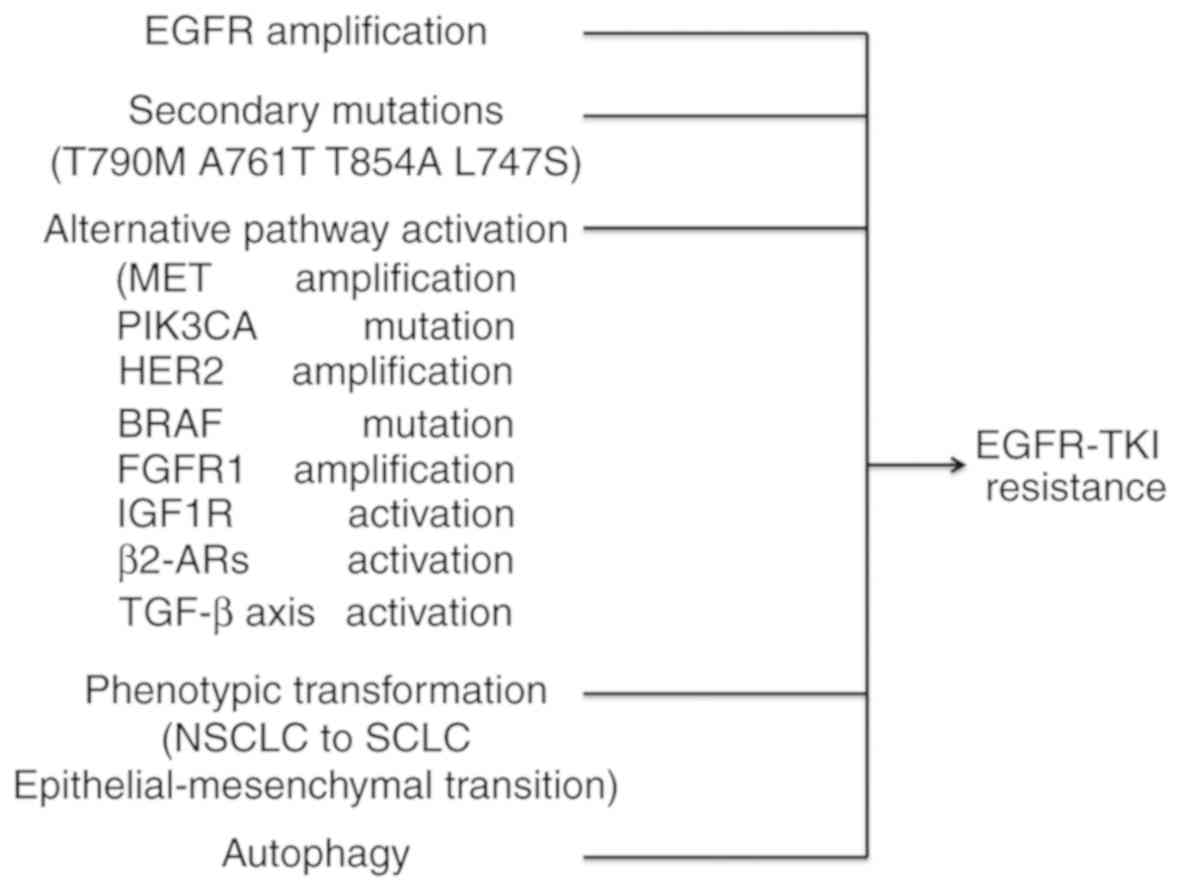
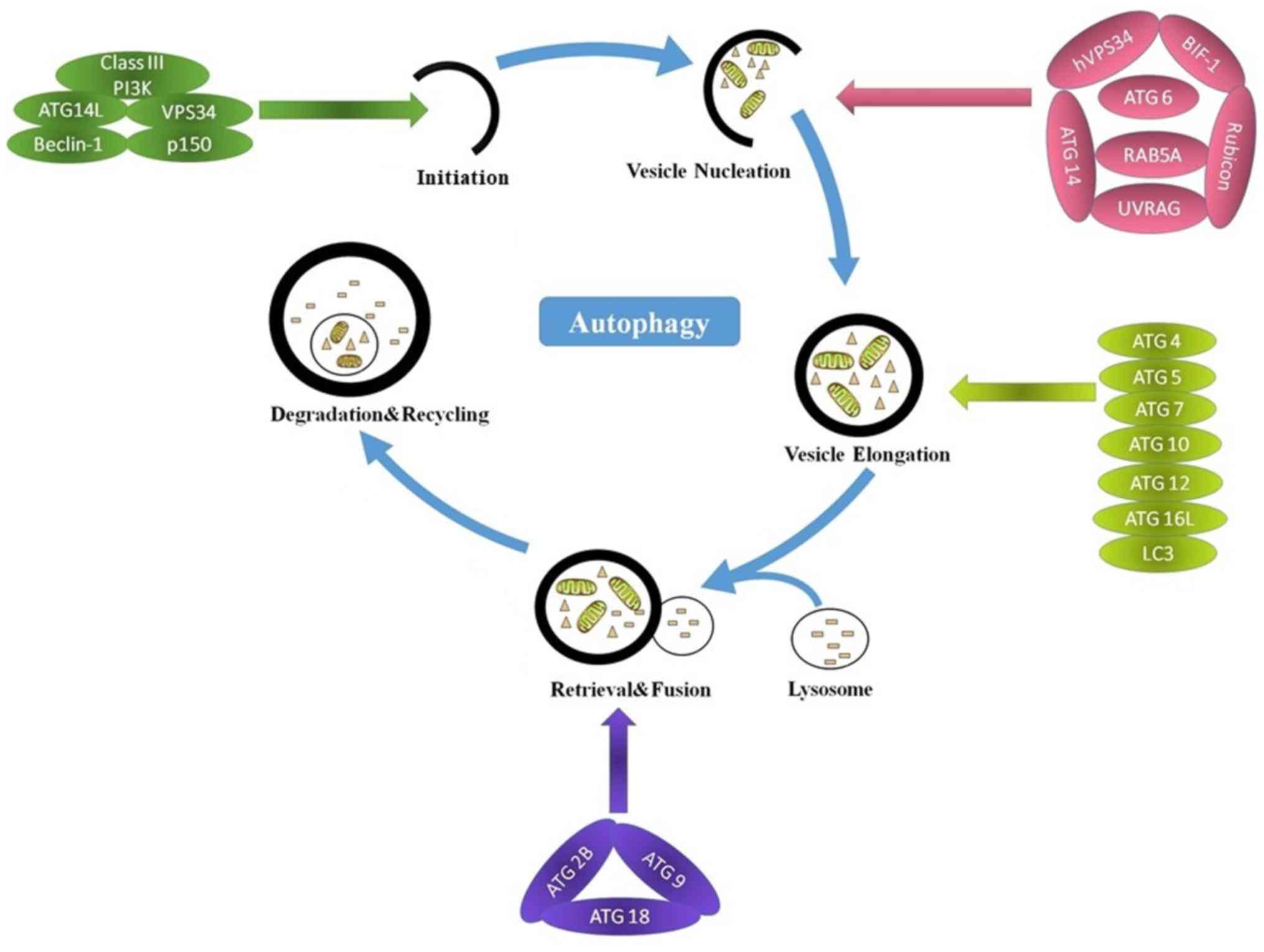
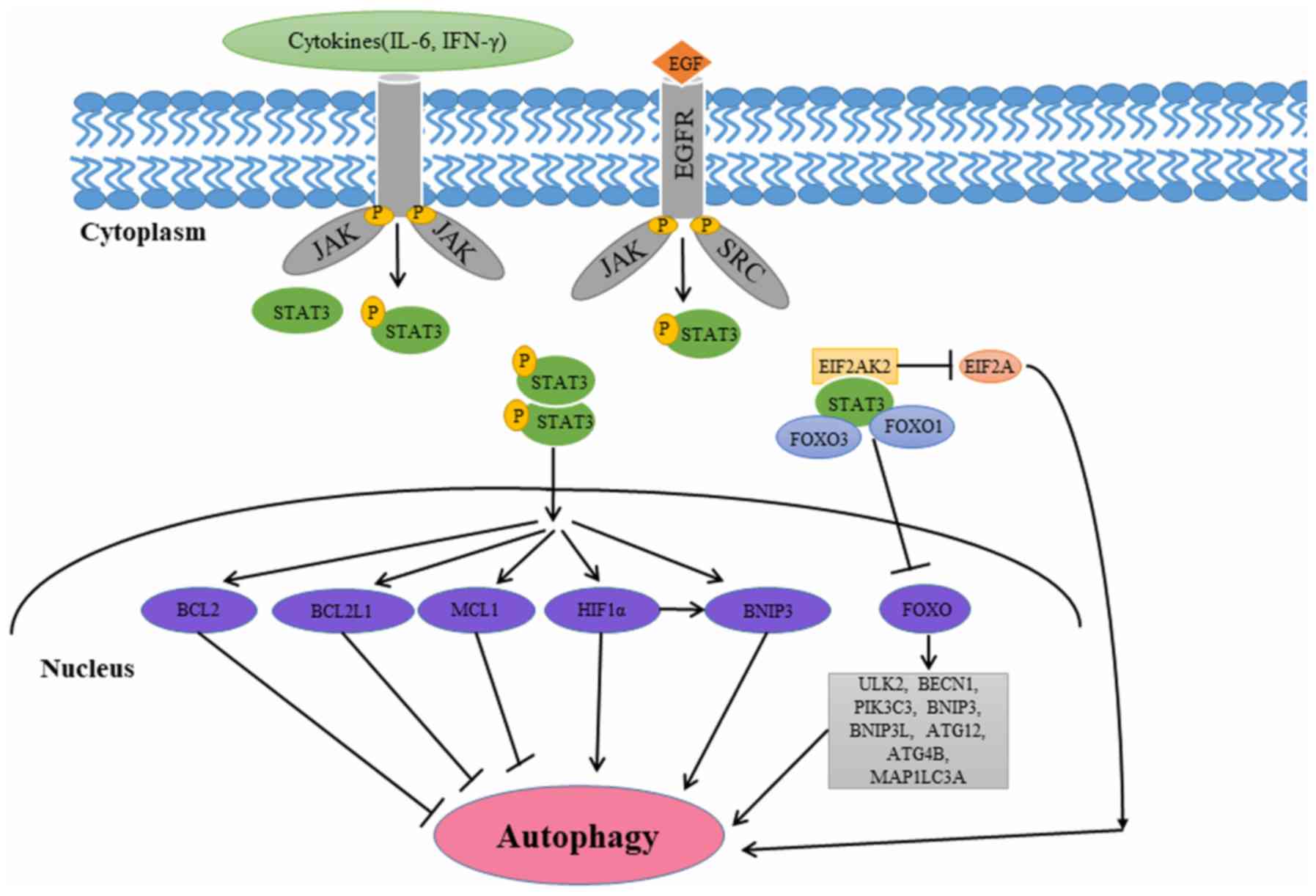
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mao Y, Yang D, He J and Krasna MJ:
Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 25:439–445.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Farsi A and Ellis PM: Treatment
paradigms for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer,
squamous lung cancer: First, second, and third-line. Front Oncol.
4:1572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Inal C, Yilmaz E, Piperdi B, Perez-Soler R
and Cheng H: Emerging treatment for advanced lung cancer with egfr
mutation. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 20:597–612. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pao W and Chmielecki J: Rational,
biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:760–774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carrera S, Buque A, Azkona E, Aresti U,
Calvo B, Sancho A, Arruti M, Nuño M, Rubio I, de Lobera AR, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
treatment resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: Biological
basis and therapeutic strategies. Clin Transl Oncol. 16:339–350.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu D, Yang Y and Zhao S: Autophagy
facilitates the EGFR-TKI acquired resistance of non-small-cell lung
cancer cells. J Formos Med Assoc. 113:141–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sakuma Y, Matsukuma S, Nakamura Y,
Yoshihara M, Koizume S, Sekiguchi H, Saito H, Nakayama H, Kameda Y,
Yokose T, et al: Enhanced autophagy is required for survival in
EGFR-independent EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells. Lab Invest.
93:1137–1146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J and Ferguson KM:
The egfr family: Not so prototypical receptor tyrosine kinases.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:a0207682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Zhu J, Li Y, Lin T, Siclari VA,
Chandra A, Candela EM, Koyama E, Enomoto-Iwamoto M and Qin L:
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling regulates
epiphyseal cartilage development through β-catenin-dependent and
-independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 288:32229–32240. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brisken C and O'Malley B: Hormone action
in the mammary gland. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
2:a0031782010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee HC, Su MY, Lo HC, Wu CC, Hu JR, Lo DM,
Chao TY, Tsai HJ and Dai MS: Cancer metastasis and EGFR signaling
is suppressed by amiodarone-induced versican V2. Oncotarget.
6:42976–42987. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clapéron A, Mergey M, Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires
TH, Vignjevic D, Wendum D, Chrétien Y, Merabtene F, Frazao A,
Paradis V, Housset C, et al: EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the
progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Hepatol. 61:325–332. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Masuda H, Zhang D, Bartholomeusz C,
Doihara H, Hortobagyi GN and Ueno NT: Role of epidermal growth
factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
136:331–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi YK, Wang L, Han BH, Li W, Yu P, Liu
YP, Ding CM, Song X, Ma ZY, Ren XL, et al: First-line icotinib
versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for
patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma
(CONVINCE): A phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Ann Oncol.
28:2443–2450. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou C, Zhang L,
Zhang S, Wang D, Li Q, Qin S, Hu C, et al: Icotinib versus
gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
(ICOGEN): A randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial.
Lancet Oncol. 14:953–961. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Antonelli A, Fallahi P, Ulisse S, Ferrari
SM, Minuto M, Saraceno G, Santini F, Mazzi V, D'Armiento M and
Miccoli P: New targeted therapies for anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 12:87–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koustas E, Karamouzis MV, Mihailidou C,
Schizas D and Papavassiliou AG: Co-targeting of EGFR and autophagy
signaling is an emerging treatment strategy in metastatic
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 396:94–102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Costa DB, Nguyen KS, Cho BC, Sequist LV,
Jackman DM, Riely GJ, Yeap BY, Halmos B, Kim JH, Jänne PA, et al:
Effects of erlotinib in EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancers
with resistance to gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7060–7067. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu HA and Pao W: Targeted therapies:
Afatinib-new therapy option for EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 10:551–552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa
K, Niho S, Tsuji F, Linke R, Rosell R, Corral J, et al: Dacomitinib
versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with
EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1454–1466.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang S, Cang S and Liu D: Third-generation
inhibitors targeting EGFR T790M mutation in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 9:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Russo A, Franchina T, Ricciardi GRR,
Smiroldo V, Picciotto M, Zanghi M, Rolfo C and Adamo V: Third
generation EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutated NSCLC: Where are we now and
where are we going. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 117:38–47. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J,
Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura
F, Nogami N, Kurata T, et al: Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:113–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Santarpia M, Liguori A, Karachaliou N,
Gonzalez-Cao M, Daffinà MG, D'Aveni A, Marabello G, Altavilla G and
Rosell R: Osimertinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer: Design, development and place in therapy. Lung Cancer
(Auckl). 8:109–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Piotrowska Z and Sequist LV: Epidermal
growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer: New drugs, new
resistance mechanisms, and future treatment options. Cancer J.
21:371–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu HA, Riely GJ and Lovly CM: Therapeutic
strategies utilized in the setting of acquired resistance to EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5898–5907. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rotow J and Bivona TG: Understanding and
targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:637–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yao Z, Fenoglio S, Gao DC, Camiolo M,
Stiles B, Lindsted T, Schlederer M, Johns C, Altorki N, Mittal V,
et al: TGF-beta IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive
mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:15535–15540. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nilsson MB, Sun H, Diao L, Tong P, Liu D,
Li L, Fan Y, Poteete A, Lim SO, Howells K, et al: Stress hormones
promote EGFR inhibitor resistance in NSCLC: Implications for
combinations with β-blockers. Sci Transl Med. 9(pii): eaao43072017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in
aging, disease and death: The true identity of a cell death
impostor. Cell Death Differ. 16:1–2. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: A
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cuervo AM and Wong E: Chaperone-mediated
autophagy: Roles in disease and aging. Cell Res. 24:92–104. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Z, Guo M, Zhao S, Xu W, Shao J,
Zhang F, Wu L, Lu Y and Zheng S: The update on transcriptional
regulation of autophagy in normal and pathologic cells: A novel
therapeutic target. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:17–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jing Z, Han W, Sui X, Xie J and Pan H:
Interaction of autophagy with microRNAs and their potential
therapeutic implications in human cancers. Cancer Lett.
356:332–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li L, Chen H, Gao Y, Wang YW, Zhang GQ,
Pan SH, Ji L, Kong R, Wang G, Jia YH, et al: Long noncoding RNA
MALAT1 promotes aggressive pancreatic cancer proliferation and
metastasis via the stimulation of autophagy. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:2232–2243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget.
6:8474–8490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fu Z, Luo W, Wang J, Peng T, Sun G, Shi J,
Li Z and Zhang B: Malat1 activates autophagy and promotes cell
proliferation by sponging miR-101 and upregulating STMN1, RAB5A and
ATG4D expression in glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
492:480–486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang K, Liu CY, Zhou LY, Wang JX, Wang M,
Zhao B, Zhao WK, Xu SJ, Fan LH, Zhang XJ, et al: APF lncRNA
regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting
miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 6:67792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen ZH, Wang WT, Huang W, Fang K, Sun YM,
Liu SR, Luo XQ and Chen YQ: The lncRNA HOTAIRM1 regulates the
degradation of PML-RARA oncoprotein and myeloid cell
differentiation by enhancing the autophagy pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 24:212–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Henson E, Chen Y and Gibson S: EGFR family
members' regulation of autophagy is at a crossroads of cell
survival and death in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9(pii): E272017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nyfeler B and Eng CH: Revisiting autophagy
addiction of tumor cells. Autophagy. 12:1206–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alexandrova AY, Kopnin PB, Vasiliev JM and
Kopnin BP: ROS up-regulation mediates Ras-induced changes of cell
morphology and motility. Exp Cell Res. 312:2066–2073. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou YY, Li Y, Jiang WQ and Zhou LF:
MAPK/JNK signalling: A potential autophagy regulation pathway.
Biosci Rep. 35(pii): e001992015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yip PY: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-Akt-mTOR)
signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 4:165–176. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jung CH, Seo M, Otto NM and Kim DH: ULK1
inhibits the kinase activity of mTORC1 and cell proliferation.
Autophagy. 7:1212–1221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ernst M and Putoczki TL: Stat3: Linking
inflammation to (gastrointestinal) tumourigenesis. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 39:711–718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Demaria M, Camporeale A and Poli V: Stat3
and metabolism: How many ways to use a single molecule? Int J
Cancer. 135:1997–2003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Niso-Santano M, Shen S, Adjemian S, Malik
SA, Mariño G, Lachkar S, Senovilla L, Kepp O, Galluzzi L, Maiuri MC
and Kroemer G: Direct interaction between STAT3 and EIF2AK2
controls fatty acid-induced autophagy. Autophagy. 9:415–417. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo B, Lin Y, Jiang S, Huang L, Yao H,
Zhuang Q, Zhao R, Liu H, He C and Lin Z: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress eIF2α-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction
regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Oh HM, Yu CR, Golestaneh N, Amadi-Obi A,
Lee YS, Eseonu A, Mahdi RM and Egwuagu CE: STAT3 protein promotes
T-cell survival and inhibits interleukin-2 production through
up-regulation of Class O Forkhead transcription factors. J Biol
Chem. 286:30888–30897. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Oh HM, Yu CR, Dambuza I, Marrero B and
Egwuagu CE: STAT3 protein interacts with Class O Forkhead
transcription factors in the cytoplasm and regulates
nuclear/cytoplasmic localization of FoxO1 and FoxO3a proteins in
CD4(+) T cells. J Biol Chem. 287:30436–30443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ray S, Zhao Y, Jamaluddin M, Edeh CB, Lee
C and Brasier AR: Inducible STAT3 NH2 terminal mono-ubiquitination
promotes BRD4 complex formation to regulate apoptosis. Cell Signal.
26:1445–1455. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kiprianova I, Remy J, Milosch N, Mohrenz
IV, Seifert V, Aigner A and Kögel D: Sorafenib sensitizes glioma
cells to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 by targeting MCL1 in a
STAT3-dependent manner. Neoplasia. 17:564–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sun L, Hu L, Cogdell D, Lu L, Gao C, Tian
W, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Fleming JB and Zhang W: MIR506 induces
autophagy-related cell death in pancreatic cancer cells by
targeting the STAT3 pathway. Autophagy. 13:703–714. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tai WT, Shiau CW, Chen HL, Liu CY, Lin CS,
Cheng AL, Chen PJ and Chen KF: Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin
1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e4852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yamada E, Bastie CC, Koga H, Wang Y,
Cuervo AM and Pessin JE: Mouse skeletal muscle fiber-type-specific
macroautophagy and muscle wasting are regulated by a
Fyn/STAT3/Vps34 signaling pathway. Cell Rep. 1:557–569. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nechemia-Arbely Y, Khamaisi M, Rosenberger
C, Koesters R, Shina A, Geva C, Shriki A, Klaus S, Rosen S,
Rose-John S, et al: In vivo evidence suggesting reciprocal renal
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 upregulation and signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 activation in response to hypoxic and
non-hypoxic stimuli. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 40:262–272. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li M, Tan J, Miao Y, Lei P and Zhang Q:
The dual role of autophagy under hypoxia-involvement of interaction
between autophagy and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 20:769–777. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Abdul Rahim SA, Dirkse A, Oudin A,
Schuster A, Bohler J, Barthelemy V, Muller A, Vallar L, Janji B,
Golebiewska A and Niclou SP: Regulation of hypoxia-induced
autophagy in glioblastoma involves ATG9A. Br J Cancer. 117:813–825.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hsieh DJ, Kuo WW, Lai YP, Shibu MA, Shen
CY, Pai P, Yeh YL, Lin JY, Viswanadha VP and Huang CY:
17β-estradiol and/or estrogen receptor β attenuate the autophagic
and apoptotic effects induced by prolonged hypoxia through
HIF-1α-mediated BNIP3 and IGFBP-3 signaling blockage. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 36:274–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wilkinson S and Ryan KM: Growth factor
signaling permits hypoxia-induced autophagy by a
HIF1alpha-dependent, BNIP3/3L-independent transcriptional program
in human cancer cells. Autophagy. 5:1068–1069. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Karpathiou G, Sivridis E, Koukourakis M,
Mikroulis D, Bouros D, Froudarakis M, Bougioukas G, Maltezos E and
Giatromanolaki A: Autophagy and Bcl-2/BNIP3 death regulatory
pathway in non-small cell lung carcinomas. APMIS. 121:592–604.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lai YC, Chuang YC, Chang CP and Yeh TM:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor has a permissive role in
concanavalin A-induced cell death of human hepatoma cells through
autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 6:e20082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li S, Xia Y, Chen K, Li J, Liu T, Wang F,
Lu J, Zhou Y and Guo C: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates
apoptosis and autophagy in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by
inhibiting BNIP3. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:631–647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Huang Z, Zhou L, Chen Z, Nice EC and Huang
C: Stress management by autophagy: Implications for
chemoresistance. Int J Cancer. 139:23–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Han W, Pan H, Chen Y, Sun J, Wang Y, Li J,
Ge W, Feng L, Lin X, Wang X, et al: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human lung
cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e186912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li YY, Lam SK, Mak JC, Zheng CY and Ho JC:
Erlotinib-induced autophagy in epidermal growth factor receptor
mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:354–361. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang Z, Du T, Dong X, Li Z, Wu G and Zhang
R: Autophagy inhibition facilitates erlotinib cytotoxicity in lung
cancer cells through modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Int J Oncol. 48:2558–2566. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zou Y, Ling YH, Sironi J, Schwartz EL,
Perez-Soler R and Piperdi B: The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine
overcomes the innate resistance of wild-type EGFR non-small-cell
lung cancer cells to erlotinib. J Thorac Oncol. 8:693–702. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Goldberg SB, Supko JG, Neal JW, Muzikansky
A, Digumarthy S, Fidias P, Temel JS, Heist RS, Shaw AT, McCarthy
PO, et al: A phase I study of erlotinib and hydroxychloroquine in
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1602–1608.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sotelo J, Briceño E and López-González MA:
Adding chloroquine to conventional treatment for glioblastoma
multiforme: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Ann Intern Med. 144:337–343. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Boone BA, Bahary N, Zureikat AH, Moser AJ,
Normolle DP, Wu WC, Singhi AD, Bao P, Bartlett DL, Liotta LA, et
al: Safety and biologic response of pre-operative autophagy
inhibition in combination with gemcitabine in patients with
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:4402–4410. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Rangwala R, Leone R, Chang YC, Fecher LA,
Schuchter LM, Kramer A, Tan KS, Heitjan DF, Rodgers G, Gallagher M,
et al: Phase I trial of hydroxychloroquine with dose-intense
temozolomide in patients with advanced solid tumors and melanoma.
Autophagy. 10:1369–1379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rosenfeld MR, Ye X, Supko JG, Desideri S,
Grossman SA, Brem S, Mikkelson T, Wang D, Chang YC, Hu J, et al: A
phase I/II trial of hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with
radiation therapy and concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in
patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Autophagy.
10:1359–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
La Monica S, Galetti M, Alfieri RR,
Cavazzoni A, Ardizzoni A, Tiseo M, Capelletti M, Goldoni M,
Tagliaferri S, Mutti A, et al: Everolimus restores gefitinib
sensitivity in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
Biochem Pharmacol. 78:460–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
So KS, Kim CH, Rho JK, Kim SY, Choi YJ,
Song JS, Kim WS, Choi CM, Chun YJ and Lee JC:
Autophagosome-mediated EGFR down-regulation induced by the CK2
inhibitor enhances the efficacy of EGFR-TKI on EGFR-mutant lung
cancer cells with resistance by T790M. PLoS One. 9:e1140002014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sano T, Takeuchi S, Nakagawa T, Ishikawa
D, Nanjo S, Yamada T, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K and Yano S: The novel
phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor,
BEZ235, circumvents erlotinib resistance of epidermal growth factor
receptor mutant lung cancer cells triggered by hepatocyte growth
factor. Int J Cancer. 133:505–513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Rao S, Yang H, Penninger JM and Kroemer G:
Autophagy in non-small cell lung carcinogenesis: A positive
regulator of antitumor immunosurveillance. Autophagy. 10:529–531.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Katheder NS, Khezri R, O'Farrell F,
Schultz SW, Jain A, Rahman MM, Schink KO, Theodossiou TA, Johansen
T, Juhász G, et al: Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour
growth. Nature. 541:417–420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|