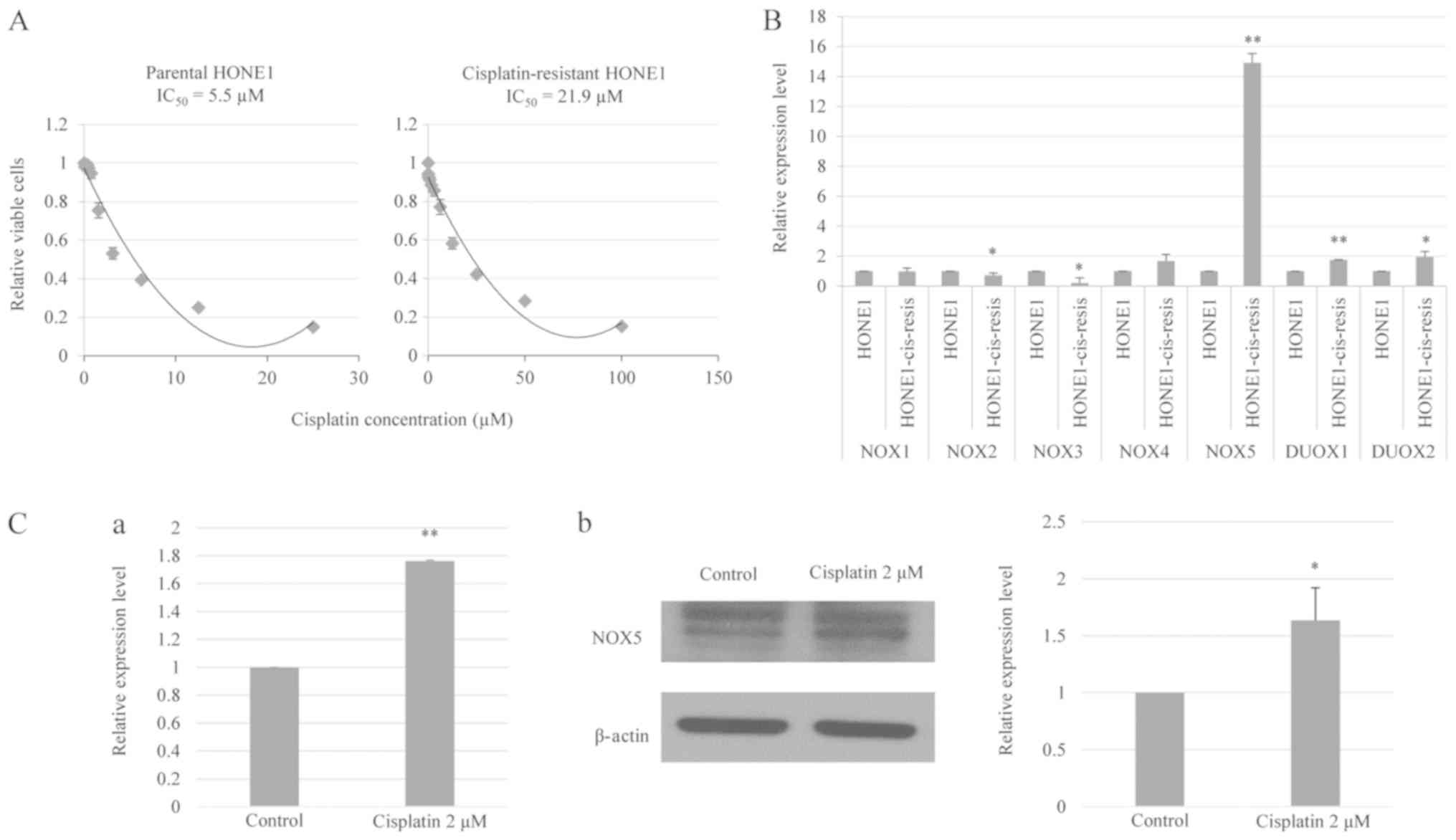
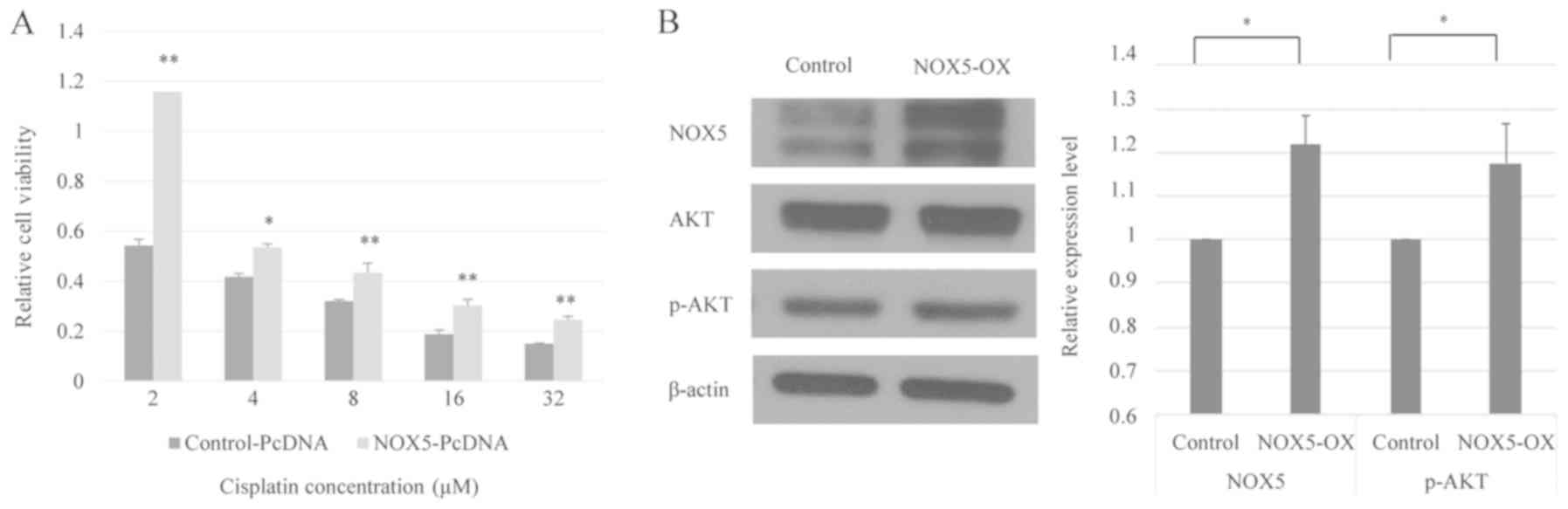
|
1
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin JC, Jan JS, Hsu CY, Liang WM, Jiang RS
and Wang WY: Phase III study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus
radiotherapy alone for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Positive
effect on overall and progression-free survival. J Clin Oncol.
21:631–637. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trimbos JB, Vergote I, Bolis G, Vermorken
JB, Mangioni C, Madronal C, Franchi M, Tateo S, Zanetta G, Scarfone
G, et al: Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy and surgical staging in
early-stage ovarian carcinoma: European Organisation for Research
and Treatment of Cancer-Adjuvant ChemoTherapy in Ovarian Neoplasm
trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:113–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK,
Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE and
Ensley JF: Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with
advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Phase III randomized Intergroup
study 0099. J Clin Oncol. 16:1310–1317. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu RY, Dong Z, Liu J, Yin JY, Zhou L, Wu
X, Yang Y, Mo W, Huang W, Khoo SK, et al: Role of eIF3a in
regulating cisplatin sensitivity and in translational control of
nucleotide excision repair of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene.
30:4814–4823. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Z, Liu J, Li L, Nie D, Tao Q, Wu J,
Fan J, Lin C, Zhao S and Ju D: Inhibition of autophagy potentiated
the antitumor effect of nedaplatin in cisplatin-resistant
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 10:e01352362015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stewart DJ: Mechanisms of resistance to
cisplatin and carboplatin. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 63:12–31. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Sá Junior PL, Câmara DAD, Porcacchia
AS, Fonseca PMM, Jorge SD, Araldi RP and Ferreira AK: The roles of
ROS in cancer heterogeneity and therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:24679402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bedard K and Krause KH: The NOX family of
ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology.
Physiol Rev. 87:245–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takac I, Schröder K and Brandes RP: The
Nox family of NADPH oxidases: Friend or foe of the vascular system?
Curr Hypertens Rep. 14:70–78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Oh GS, Moon HD,
Kwon KB, Park C, Park BH, Lee HK, Chung SY, et al: Roles of NADPH
oxidases in cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species generation
and ototoxicity. J Neurosci. 30:3933–3946. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S and
Ramkumar V: Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: Clinical and
experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med. 219:177–186. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ammon HP and Wahl MA: Pharmacology of
Curcuma longa. Planta Med. 57:1–7. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Chen F, Braun C, Zhou YQ, Rittner
H, Tian YK, Cai XY and Ye DW: Role of curcumin in the management of
pathological pain. Phytomedicine. 48:129–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sreekanth CN, Bava SV, Sreekumar E and
Anto RJ: Molecular evidences for the chemosensitizing efficacy of
liposomal curcumin in paclitaxel chemotherapy in mouse models of
cervical cancer. Oncogene. 30:3139–3152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vinod BS, Antony J, Nair HH,
Puliyappadamba VT, Saikia M, Narayanan SS, Bevin A and Anto RJ:
Mechanistic evaluation of the signaling events regulating
curcumin-mediated chemosensitization of breast cancer cells to
5-fluorouracil. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duarte VM, Han E, Veena MS, Salvado A, Suh
JD, Liang LJ, Faull KF, Srivatsan ES and Wang MB: Curcumin enhances
the effect of cisplatin in suppression of head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma via inhibition of IKKβ protein of the NFκB pathway.
Mol Cancer Ther. 9:2665–2675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glaser R, Zhang HY, Yao KT, Zhu HC, Wang
FX, Li GY, Wen DS and Li YP: Two epithelial tumor cell lines (HNE-1
and HONE-1) latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus that were
derived from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:9524–9528. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Strong MJ, Baddoo M, Nanbo A, Xu M,
Puetter A and Lin Z: Comprehensive high-throughput RNA sequencing
analysis reveals contamination of multiple nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell lines with HeLa cell genomes. J Virol. 88:10696–10704. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Veena MS, Stevenson K, Tang C, Ho
B, Suh JD, Duarte VM, Faull KF, Mehta K, Srivatsan ES and Wang MB:
Liposome-encapsulated curcumin suppresses growth of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in xenografts through the
inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB by an Akt-independent pathway.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:6228–6236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spitkovsky D, Schulze A, Boye B and
Jansen-Dürr P: Down-regulation of cyclin A gene expression upon
genotoxic stress correlates with reduced binding of free E2F to the
promoter. Cell Growth Differ. 8:699–710. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsumoto Y, Takano H and Fojo T: Cellular
adaptation to drug exposure: Evolution of the drug-resistant
phenotype. Cancer Res. 57:5086–5092. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chua BT, Gallego-Ortega D, Ramirez de
Molina A, Ullrich A, Lacal JC and Downward J: Regulation of
Akt(ser473) phosphorylation by choline kinase in breast carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer. 8:1312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Basu A and Krishnamurthy S: Cellular
responses to Cisplatin-induced DNA damage. J Nucleic Acids.
2010:2013672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Florea AM and Büsselberg D: Cisplatin as
an anti-tumor drug: Cellular mechanisms of activity, drug
resistance and induced side effects. Cancers (Basel). 3:1351–1371.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hall MD, Okabe M, Shen DW, Liang XJ and
Gottesman MM: The role of cellular accumulation in determining
sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 48:495–535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kartalou M and Essigmann JM: Mechanisms of
resistance to cisplatin. Mutat Res. 478:23–43. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Godwin AK, Meister A, O'Dwyer PJ, Huang
CS, Hamilton TC and Anderson ME: High resistance to cisplatin in
human ovarian cancer cell lines is associated with marked increase
of glutathione synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:3070–3074.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang SF, Chen MS, Chou YC, Ueng YF, Yin
PH, Yeh TS and Lee HC: Mitochondrial dysfunction enhances cisplatin
resistance in human gastric cancer cells via the ROS-activated
GCN2-eIF2α-ATF4-xCT pathway. Oncotarget. 7:74132–74151.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng Y, Chen CW, Yung MMH, Sun W, Sun J,
Li Z, Li J, Li Z, Zhou W, Liu SS, et al: DUOXA1-mediated ROS
production promotes cisplatin resistance by activating ATR-Chk1
pathway in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 428:104–116. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tong L, Chuang CC, Wu S and Zuo L:
Reactive oxygen species in redox cancer therapy. Cancer Lett.
367:18–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Skonieczna M, Hejmo T, Poterala-Hejmo A,
Cieslar-Pobuda A and Buldak RJ: NADPH oxidases: Insights into
selected functions and mechanisms of action in cancer and stem
cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:94205392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nogueira V and Hay N: Molecular pathways:
Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and
implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4309–4314.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu M, Qi B, Xiaoxiang W, Xu J and Liu X:
Baicalein increases cisplatin sensitivity of A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 90:677–685. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Altenhöfer S, Radermacher KA, Kleikers PW,
Wingler K and Schmidt HH: Evolution of NADPH oxidase inhibitors:
Selectivity and mechanisms for target engagement. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 23:406–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fulton DJR: Nox5 and the regulation of
cellular function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2443–2452. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Blasius R, Reuter S, Henry E, Dicato M and
Diederich M: Curcumin regulates signal transducer and activator of
transcription (STAT) expression in K562 cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1547–1554. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Prasad S, Tyagi AK and Aggarwal BB: Recent
developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and
metabolism of curcumin: The golden pigment from golden spice.
Cancer Res Treat. 46:2–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baharuddin P, Satar N, Fakiruddin KS,
Zakaria N, Lim MN, Yusoff NM, Zakaria Z and Yahaya BH: Curcumin
improves the efficacy of cisplatin by targeting cancer stem-like
cells through p21 and cyclin D1-mediated tumour cell inhibition in
non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 35:13–25. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zou J, Zhu L, Jiang X, Wang Y, Wang Y,
Wang X and Chen B: Curcumin increases breast cancer cell
sensitivity to cisplatin by decreasing FEN1 expression. Oncotarget.
9:11268–11278. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|