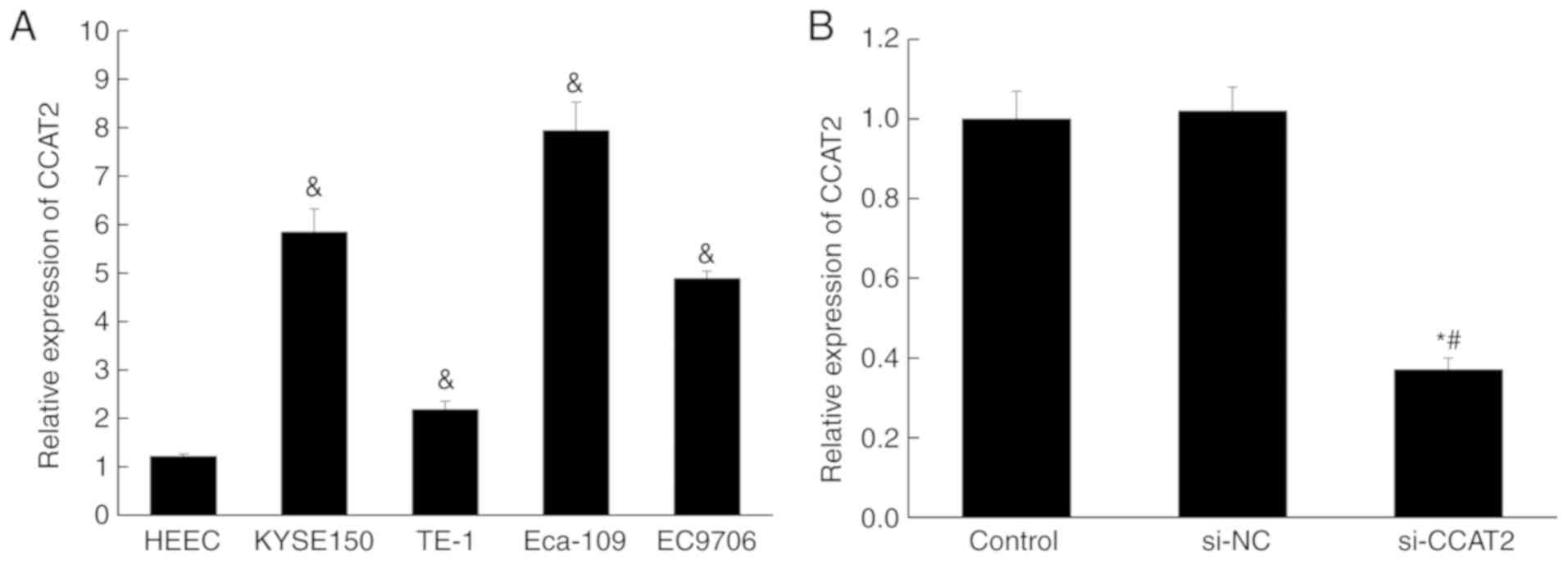
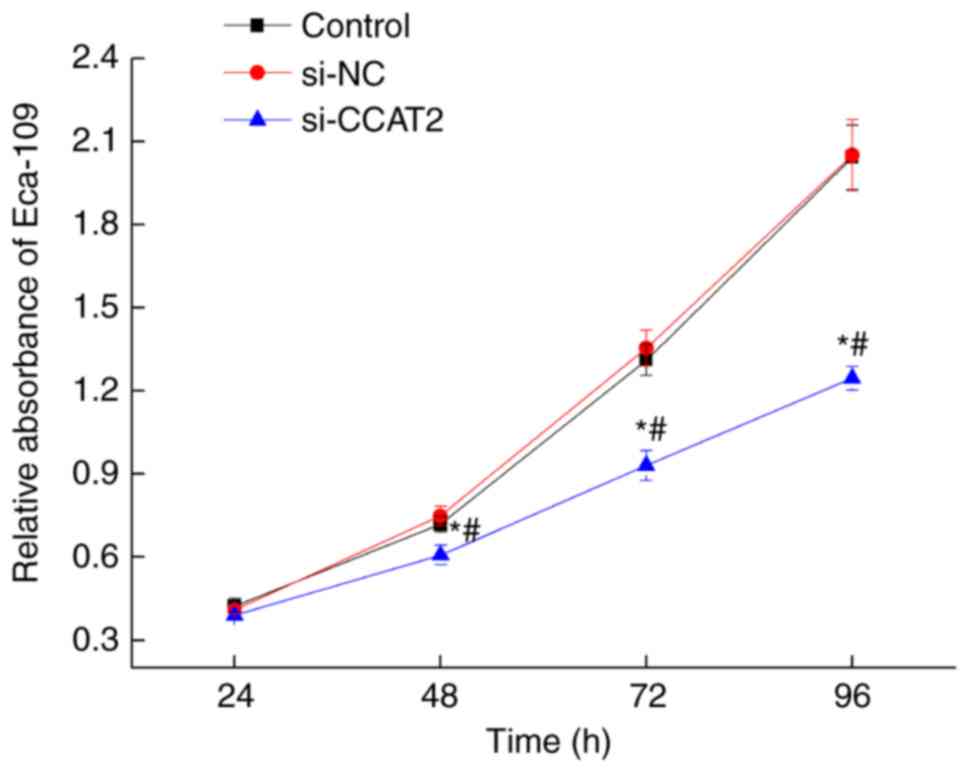
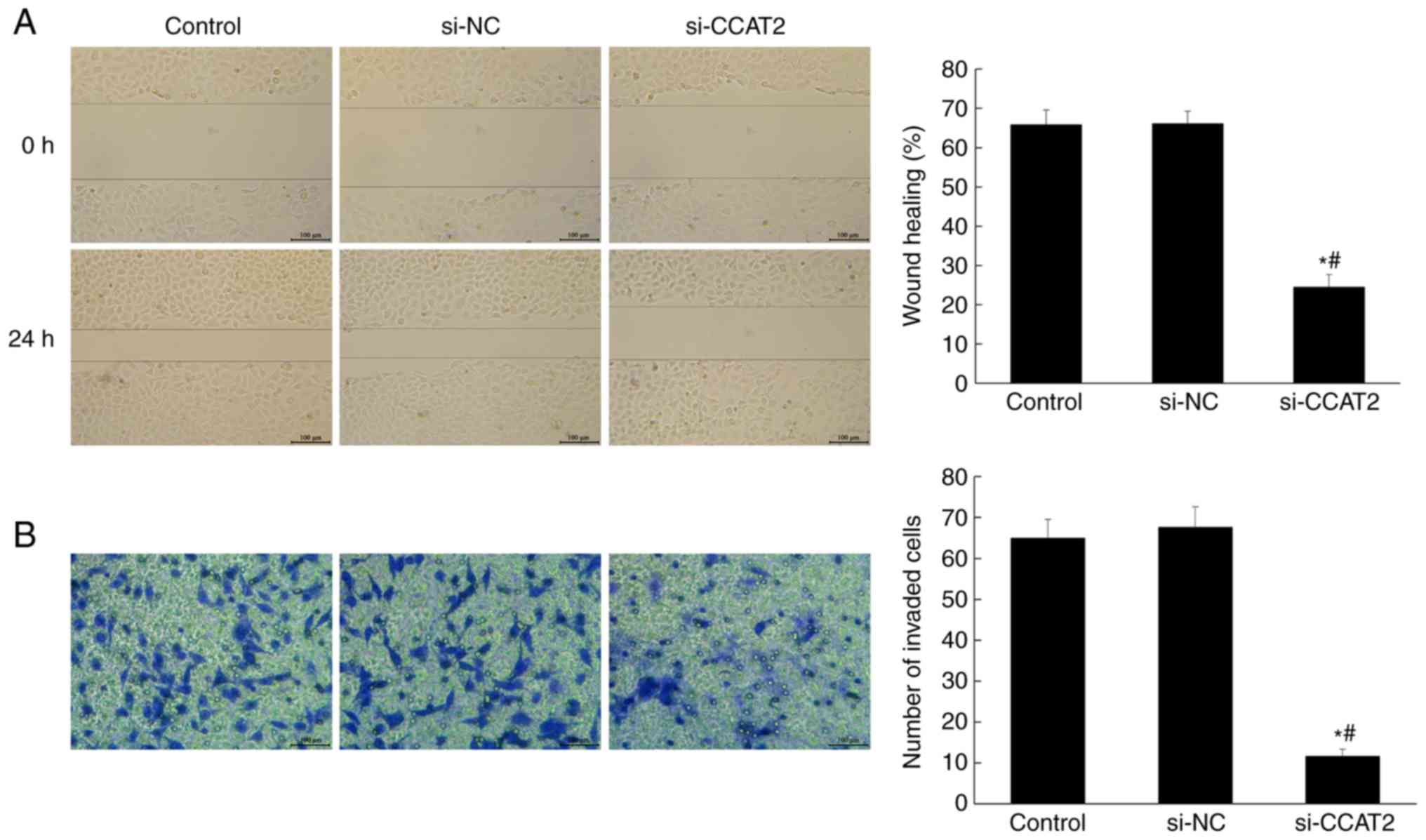
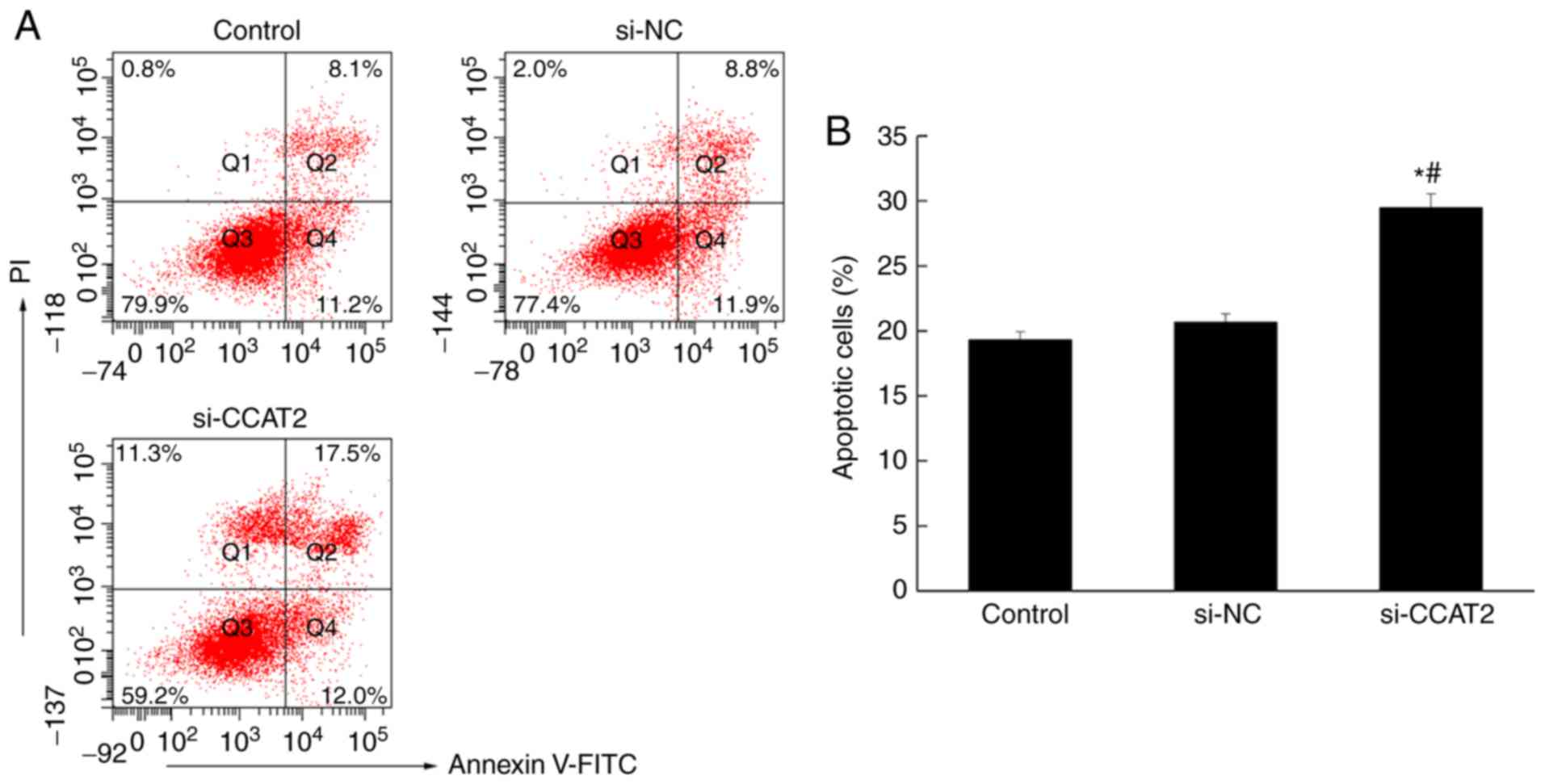
|
1
|
Bajpai M, Das KM, Lefferts J, Lisovsky M,
Mashimo H, Phillips WA, Srivastava A and To H: Molecular
epidemiology of and genetic susceptibility to esophageal cancer.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1325:40–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Napier KJ, Scheerer M and Misra S:
Esophageal cancer: A Review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging
workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
6:112–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, He Y, Kikuchi S, Qiao Y,
Ueda J, Wei W, Inoue M and Tanaka H: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer in Japan and China. J Epidemiol. 23:233–242. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Qiu M, Xu Y, Li M, Dong G, Mao Q,
Yin R and Xu L: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 correlates with smoking in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:5523–5528.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Łaźniak S, Lutkowska A, Wareńczak-Florczak
Ż, Sowińska A, Tsibulski A, Roszak A, Sajdak S and Jagodziński PP:
The association of CCAT2 rs6983267 SNP with MYC expression and
progression of uterine cervical cancer in the Polish population.
Arch Gynecol Obstet. 297:1285–1292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jing X, Liang H, Cui X, Han C, Hao C and
Huo K: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 can predict metastasis and a poor
prognosis: A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 468:159–165. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kasagi Y, Oki E, Ando K, Ito S, Iguchi T,
Sugiyama M, Nakashima Y, Ohgaki K, Saeki H, Mimori K and Maehara Y:
The expression of CCAT2, a novel long noncoding RNA transcript, and
rs6983267 single-nucleotide polymorphism genotypes in colorectal
cancers. Oncology. 92:48–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lang HL, Hu GW, Zhang B, Kuang W, Chen Y,
Wu L and Xu GH: Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit
endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that
contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2. Oncol Rep. 38:785–798. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ozawa T, Matsuyama T, Toiyama Y, Takahashi
N, Ishikawa T, Uetake H, Yamada Y, Kusunoki M, Calin G and Goel A:
CCAT1 and CCAT2 long noncoding RNAs, located within the 8q.24.21
‘gene desert’, serve as important prognostic biomarkers in
colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 28:1882–1888. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Redis RS, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Tudoran
O, Ivan C, Spizzo R, Zhang X, de Weerd V, Shimizu M, Ling H, et al:
CCAT2, a novel long non-coding RNA in breast cancer: Expression
study and clinical correlations. Oncotarget. 4:1748–1762. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang YJ, Liu JZ, Lv P, Dang Y, Gao JY and
Wang Y: Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes gastric cancer
proliferation and invasion by regulating the E-cadherin and LATS2.
Am J Cancer Res. 6:2651–2660. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng J, Zhao S, He X, Zheng Z, Bai W,
Duan Y, Cheng S, Wang J, Liu X and Zhang G: The up-regulation of
long non-coding RNA CCAT2 indicates a poor prognosis for prostate
cancer and promotes metastasis by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 480:508–514. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Hu X, Shang C, Zhong M and Guo Y:
Silencing of long non-coding RNA CCAT2 depressed malignancy of oral
squamous cell carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177176702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu M, Xu Y, Yang X, Wang J, Hu J, Xu L
and Yin R: CCAT2 is a lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding
RNA and promotes invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour
Biol. 35:5375–5380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Y, He J and Zhang D: Suppression of
long non-coding RNA CCAT2 improves tamoxifen-resistant breast
cancer cells' response to tamoxifen. Mol Biol (Mosk). 50:821–827.
2016.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng X, Zhao Y, Wu X and Song G:
Upregulation of CCAT2 promotes cell proliferation by repressing the
P15 in breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:1160–1166. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fan YH, Fang H, Ji CX, Xie H, Xiao B and
Zhu XG: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 can predict metastasis and poor
prognosis: A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 466:120–126. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Redis RS, Vela LE, Lu W, Ferreira de
Oliveira J, Ivan C, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Adamoski D, Pasculli B,
Taguchi A, Chen Y, et al: Allele-specific reprogramming of cancer
metabolism by the long non-coding RNA CCAT2. Mol Cell. 61:520–534.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Xu Y, He C, Guo X, Zhang J, He C,
Zhang L, Kong M, Chen B and Zhu C: Elevated expression of CCAT2 is
associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 111:834–839. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Kamberov YG,
Wilder EL, Klein PS and Rustgi AK: Wnt-1 but not epidermal growth
factor induces beta-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent transcription
in esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:277–282. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ge C, Wu S, Wang W, Liu Z, Zhang J, Wang
Z, Li R, Zhang Z, Li Z, Dong S, et al: miR-942 promotes cancer stem
cell-like traits in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through
activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Oncotarget.
6:10964–10977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia Y, Yang Y, Zhan Q, Brock MV, Zheng X,
Yu Y, Herman JG and Guo M: Inhibition of SOX17 by microRNA 141 and
methylation activates the WNT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. J Mol Diagn. 14:577–585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi M, Cheng J, He Y, Jiang Z, Bodinga BM,
Liu B, Chen H and Li Q: Effect of FH535 on in vitro maturation of
porcine oocytes by inhibiting WNT signaling pathway. Anim Sci J.
89:631–639. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pang Y, Liu J, Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang B,
Zhang J, Du N, Xu C, Liang R, Ren H, et al: Nano Let7b
sensitization of eliminating esophageal cancer stemlike cells is
dependent on blockade of Wnt activation of symmetric division. Int
J Oncol. 51:1077–1088. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao B, Yang W, Jin Y, Zhang M, He T, Zhan
Q, Herman JG, Zhong G and Guo M: Silencing NKD2 by promoter region
hypermethylation promotes esophageal cancer progression by
activating Wnt signaling. J Thorac Oncol. 11:1912–1926. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zang B, Huang G, Wang X and Zheng S:
HPV-16 E6 promotes cell growth of esophageal cancer via
downregulation of miR-125b and activation of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13687–13694.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang M, Linghu E, Zhan Q, He T, Cao B,
Brock MV, Herman JG, Xiang R and Guo M: Methylation of DACT2
accelerates esophageal cancer development by activating Wnt
signaling. Oncotarget. 7:17957–17969. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gustafson CT, Mamo T, Shogren KL, Maran A
and Yaszemski MJ: FH535 suppresses osteosarcoma growth in vitro and
inhibits Wnt signaling through tankyrases. Front Pharmacol.
8:2852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suknuntha K, Thita T, Togarrati PP,
Ratanachamnong P, Wongtrakoongate P, Srihirun S, Slukvin I and
Hongeng S: Wnt signaling inhibitor FH535 selectively inhibits cell
proliferation and potentiates imatinib-induced apoptosis in myeloid
leukemia cell lines. Int J Hematol. 105:196–205. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wen D, Liao T, Ma B, Qu N, Shi RL, Lu ZW,
Wang YL, Wei WJ and Ji QH: Downregulation of CSN6 attenuates
papillary thyroid carcinoma progression by reducing Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and sensitizes cancer cells to FH535 therapy. Cancer Med.
7:285–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Li G, Liu D and Liu J: FH535
inhibits the proliferation of HepG2 cells via downregulation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 9:1289–1292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gedaly R, Galuppo R, Daily MF, Shah M,
Maynard E, Chen C, Zhang X, Esser KA, Cohen DA, Evers BM, et al:
Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in liver cancer stem
cells and hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with FH535. PLoS One.
9:e992722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen Y, Rao X, Huang K, Jiang X, Wang H
and Teng L: FH535 inhibits proliferation and motility of colon
cancer cells by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J
Cancer. 8:3142–3153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo H, Hu G, Yang Q, Zhang P, Kuang W, Zhu
X and Wu L: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA CCAT2 suppressed
proliferation and migration of glioma cells. Oncotarget.
7:81806–81814. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang JL, Liao Y, Qiu MX, Li J and An Y:
Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes cell proliferation and invasion
through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177113142017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sarrafzadeh S, Geranpayeh L, Tasharrofi B,
Soudyab M, Nikpayam E, Iranpour M, Mirfakhraie R, Gharesouran J and
Ghafouri-Fard S and Ghafouri-Fard S: Expression study and clinical
correlations of MYC and CCAT2 in breast cancer patients. Iran
Biomed J. 21:303–311. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang B, Liu M, Zhuang R, Jiang J, Gao J,
Wang H, Chen H, Zhang Z, Kuang Y and Li P: Long non-coding RNA
CCAT2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition involving
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncol
Lett. 15:3369–3375. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cai Y, He J and Zhang D: Long noncoding
RNA CCAT2 promotes breast tumor growth by regulating the Wnt
signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2657–2664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|