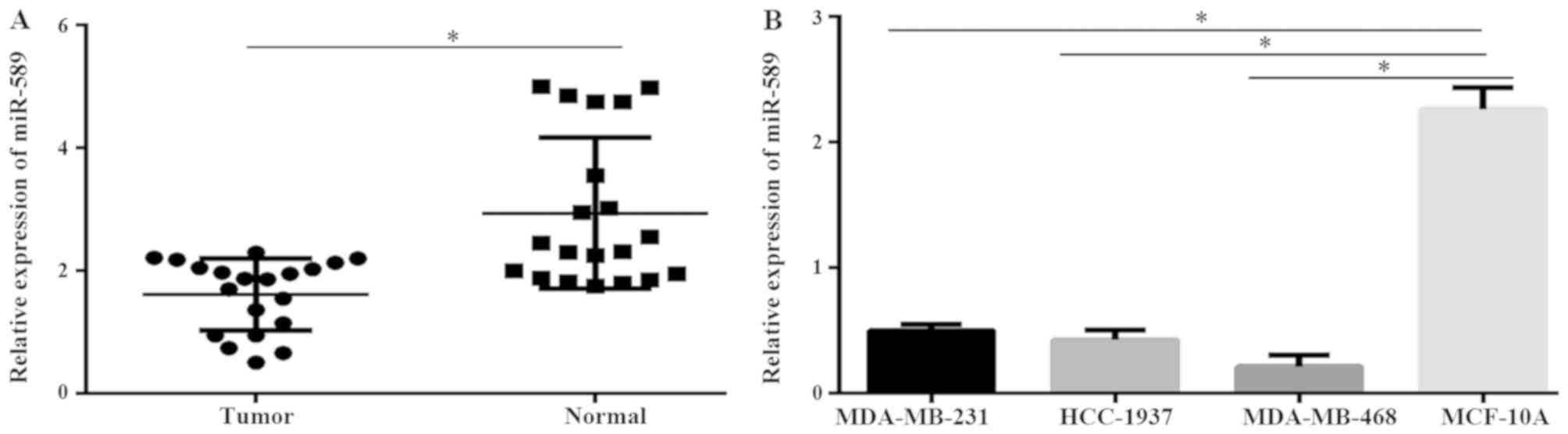
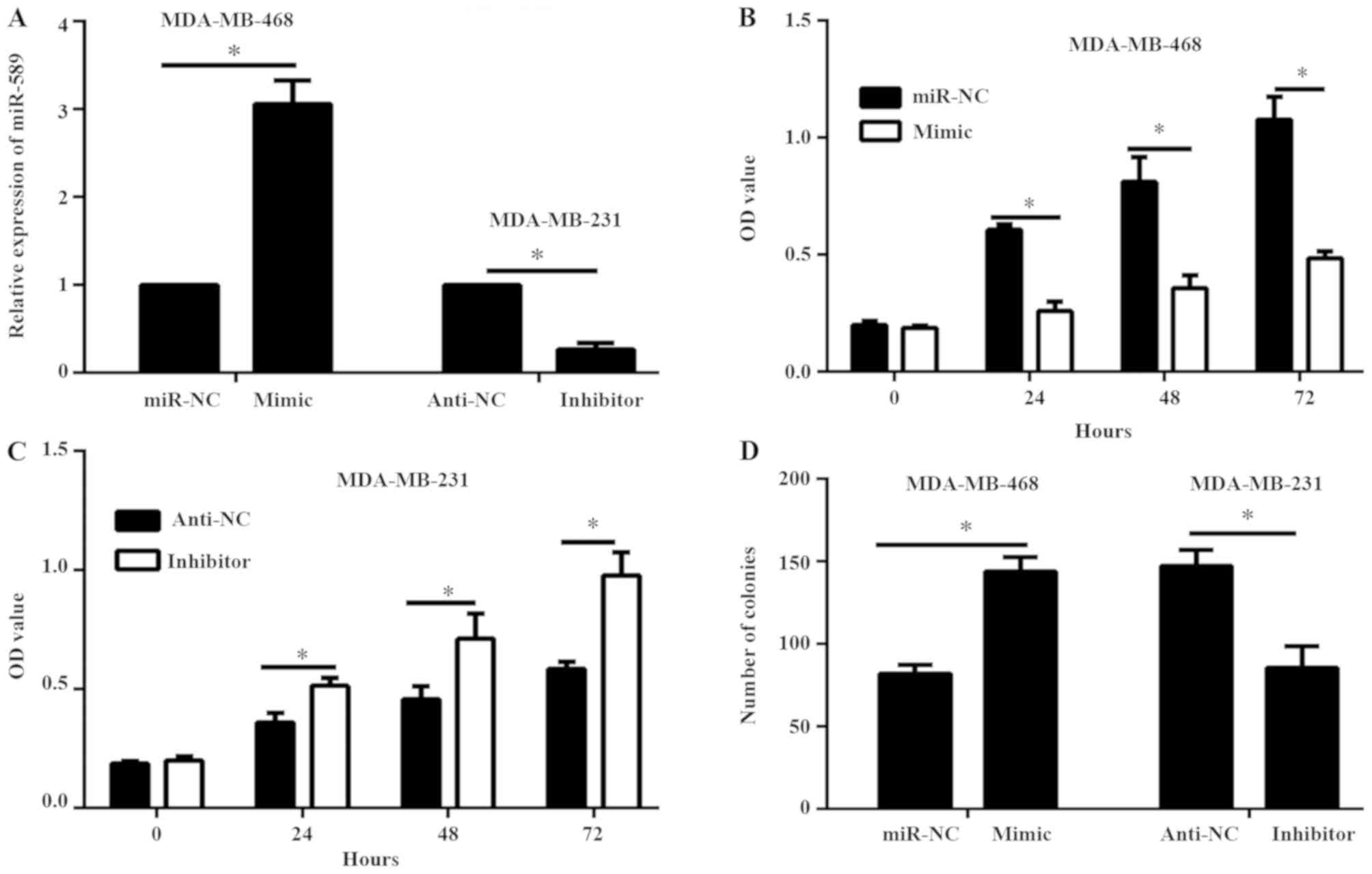
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Goding Sauer A, Newman
LA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in
mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:439–448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA and
Caggiano V: Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor
(ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and
HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative
phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer
Registry. Cancer. 109:1721–1728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wahba HA and El-Hadaad HA: Current
approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Biol Med. 12:106–116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 9:8522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Christodoulatos GS and Dalamaga M:
Micro-RNAs as clinical biomarkers and therapeutic targets in breast
cancer: Quo vadis? World J Clin Oncol. 5:71–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lü L, Mao X, Shi P, He B, Xu K, Zhang S
and Wang J: MicroRNAs in the prognosis of triple-negative breast
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e70852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Piasecka D, Braun M, Kordek R, Sadej R and
Romanska H: MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast
cancer progression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:1401–1411. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu M, Wang Y, He HT and Yang Q: MiR-589-5p
is a potential prognostic marker of hepatocellular carcinoma and
regulates tumor cell growth by targeting MIG-6. Neoplasma.
65:753–761. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cesarini V, Silvestris DA, Tassinari V,
Tomaselli S, Alon S, Eisenberg E, Locatelli F and Gallo A:
ADAR2/miR-589-3p axis controls glioblastoma cell
migration/invasion. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:2045–2059. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu C, Lv D, Li M, Zhang X, Sun G, Bai Y
and Chang D: Hypermethylation of miRNA-589 promoter leads to
upregulation of HDAC5 which promotes malignancy in non-small cell
lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 50:2079–2090. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, Jiang P, Shuai L, Chen K, Li Z,
Zhang Y, Jiang Y and Li X: miR-589-5p inhibits MAP3K8 and
suppresses CD90+ cancer stem cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang F, Li K, Pan M, Li W, Wu J, Li M,
Zhao L and Wang H: miR-589 promotes gastric cancer aggressiveness
by a LIFR-PI3K/AKT-c-Jun regulatory feedback loop. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37:1522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patil Okaly GV, Panwar D, Lingappa KB,
Kumari P, Anand A, Kumar P, Chikkalingaiah MH and Kumar RV: FISH
and HER2/neu equivocal immunohistochemistry in breast carcinoma.
Indian J Cancer. 56:119–123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fu J, Qin L, He T, Qin J, Hong J, Wong J,
Liao L and Xu J: The TWIST/Mi2/NuRD protein complex and its
essential role in cancer metastasis. Cell Res. 21:275–289. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Long J, Jiang C, Liu B, Dai Q, Hua R, Chen
C, Zhang B and Li H: Maintenance of stemness by miR-589-5p in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells promotes chemoresistance via STAT3
signaling. Cancer Lett. 423:113–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar R, Wang RA and Bagheri-Yarmand R:
Emerging roles of MTA family members in human cancers. Semin Oncol
30 (5 Suppl). S30–S37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Covington KR and Fuqua SA: Role of MTA2 in
human cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33:921–928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Covington KR, Brusco L, Barone I,
Tsimelzon A, Selever J, Corona-Rodriguez A, Brown P, Kumar R,
Hilsenbeck SG and Fuqua SA: Metastasis tumor-associated protein 2
enhances metastatic behavior and is associated with poor outcomes
in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 141:375–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|